Part 2: Pick up at Back Pain
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
- trauma
- improper alignment/mechanisms causing injury
- malignancy
Most common etiologies of back pain...
Herniated discs
less than 2% of back pain cases. Diagnosed by MRI. Causes back pain and sciatica (radicular pain, paresthesia) as sx's. Positive SLR test
L4-L5
most common disc herniation
Posterolateral
____ herniation of a disc is the most common
MRI
CT is less sensitive. It is okay to do screening with X-rays especially in outpatient settings.
Imaging used for diagnosis of herniated disc
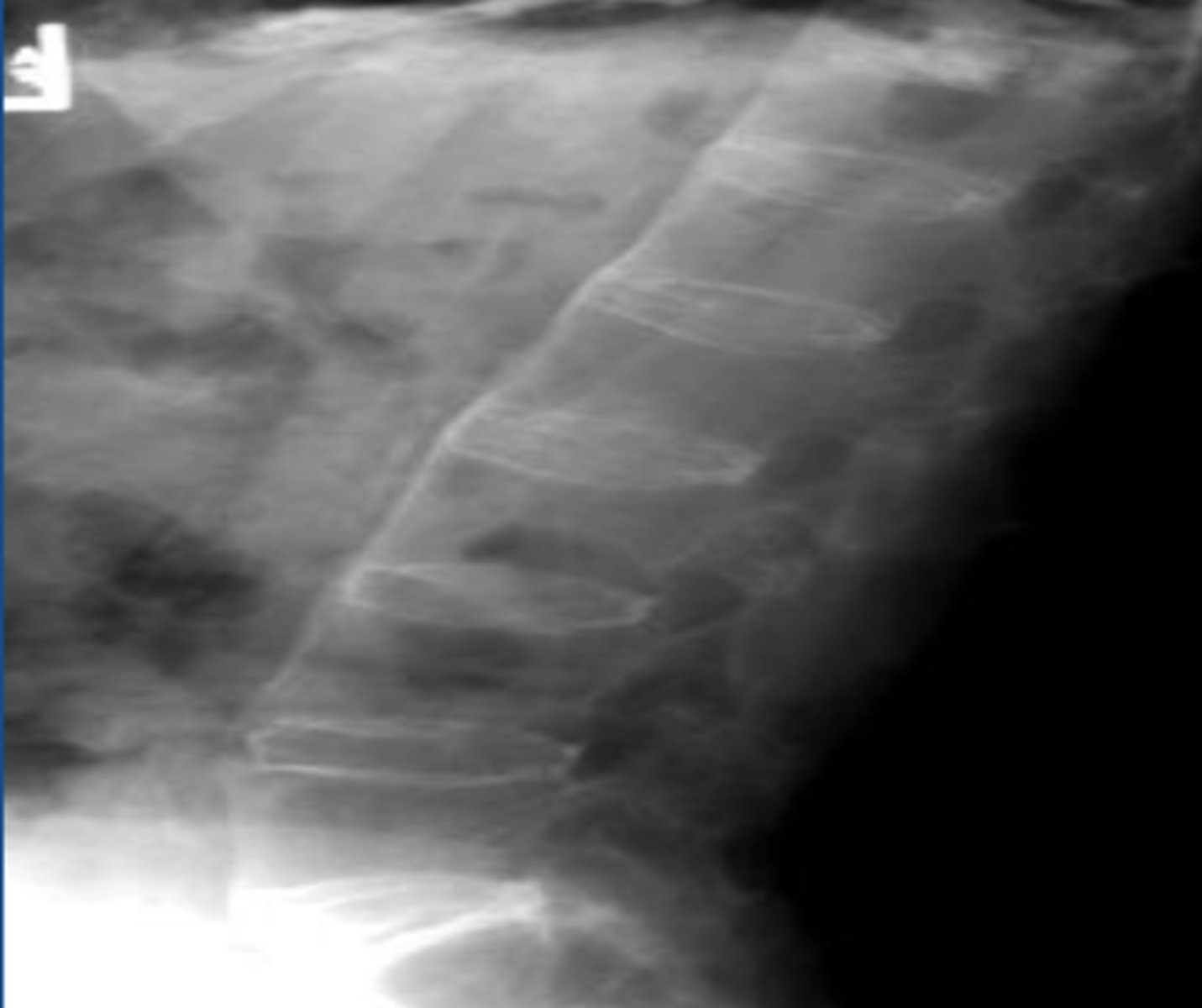
Degenerative disc disease (DDD)
dehydration of the nucleus pulposus causing compression of the disc space. End plates become sclerotic with osteophyte production at endplates.
X-rays
initial study for DDD
MRI
study of choice for DDD
Degenerative disc disease (DDD)
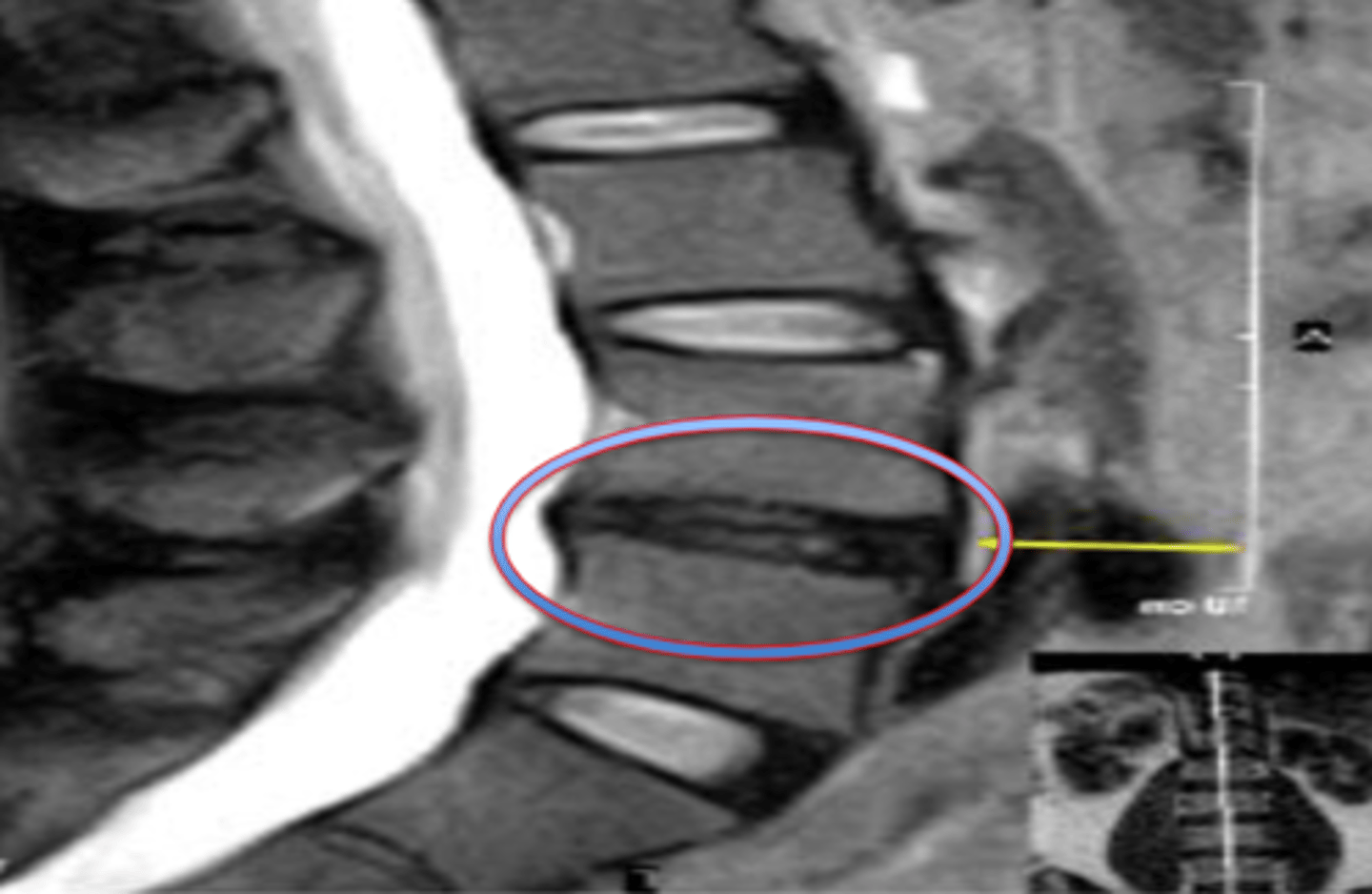
Osteoarthritis of facet joints
cause of back pain that involves osteophyte formation at the neural foramina. Causes radicular pain due to nerve root compression. High association with later stage DDD.
CT scan
the best imaging for the visualization of facet joints.
MRI
imaging that is best to visualize nerve roots and discs
Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH)
thick, bridging calcifications between 4 consecutive VBs. Usually lower thoracic or cervical spine. Usually anterior, occasionally posterior. Disc spaces/spaces joints PRESERVED. Back stiffness, but usually NO pain.
SI joints are not affected by DISH
How do you differentiate DISH from Ankylosing Spondylitis?
X-rays
appropriate fist diagnostic study for DISH
DISH
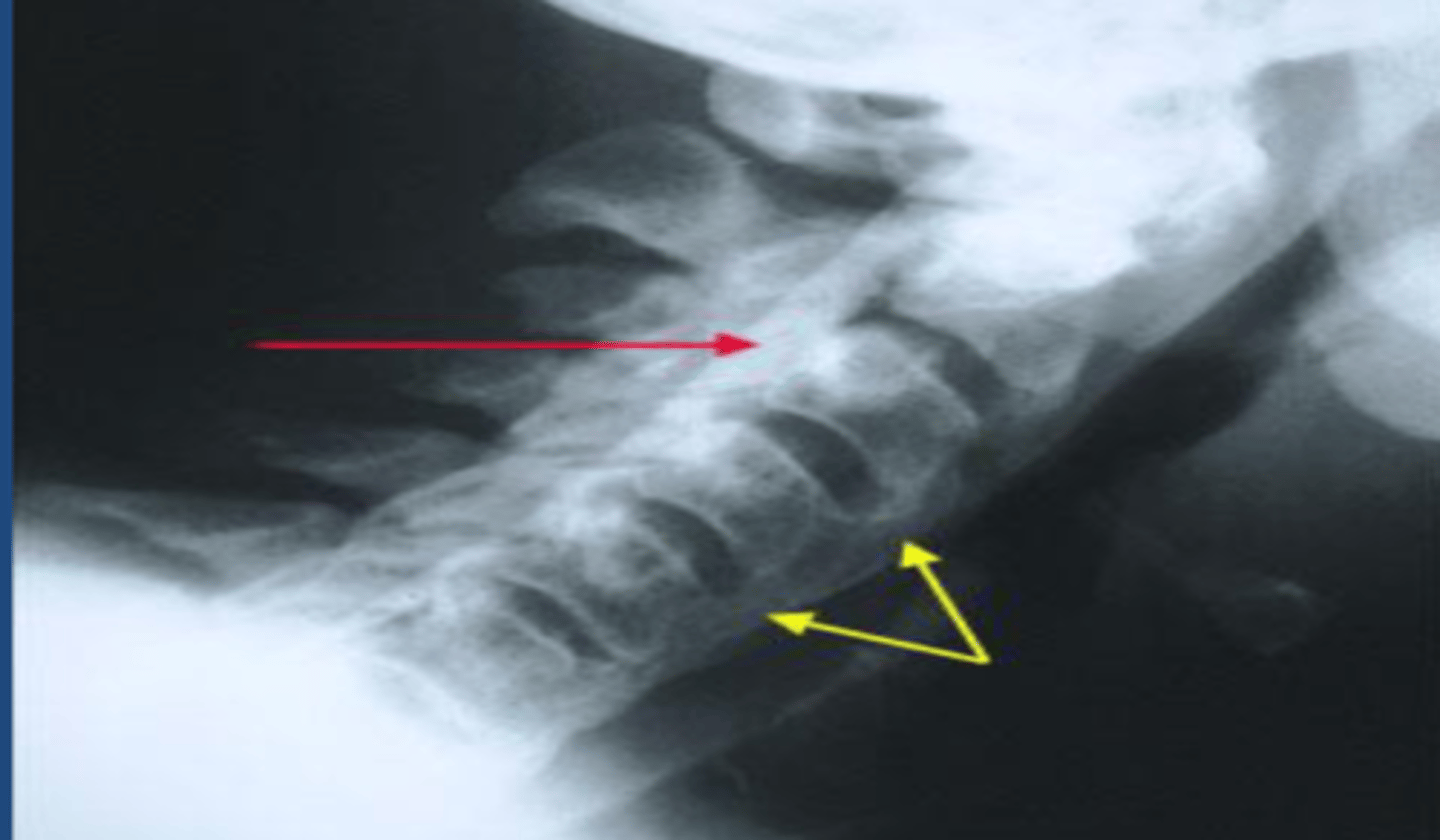
DISH
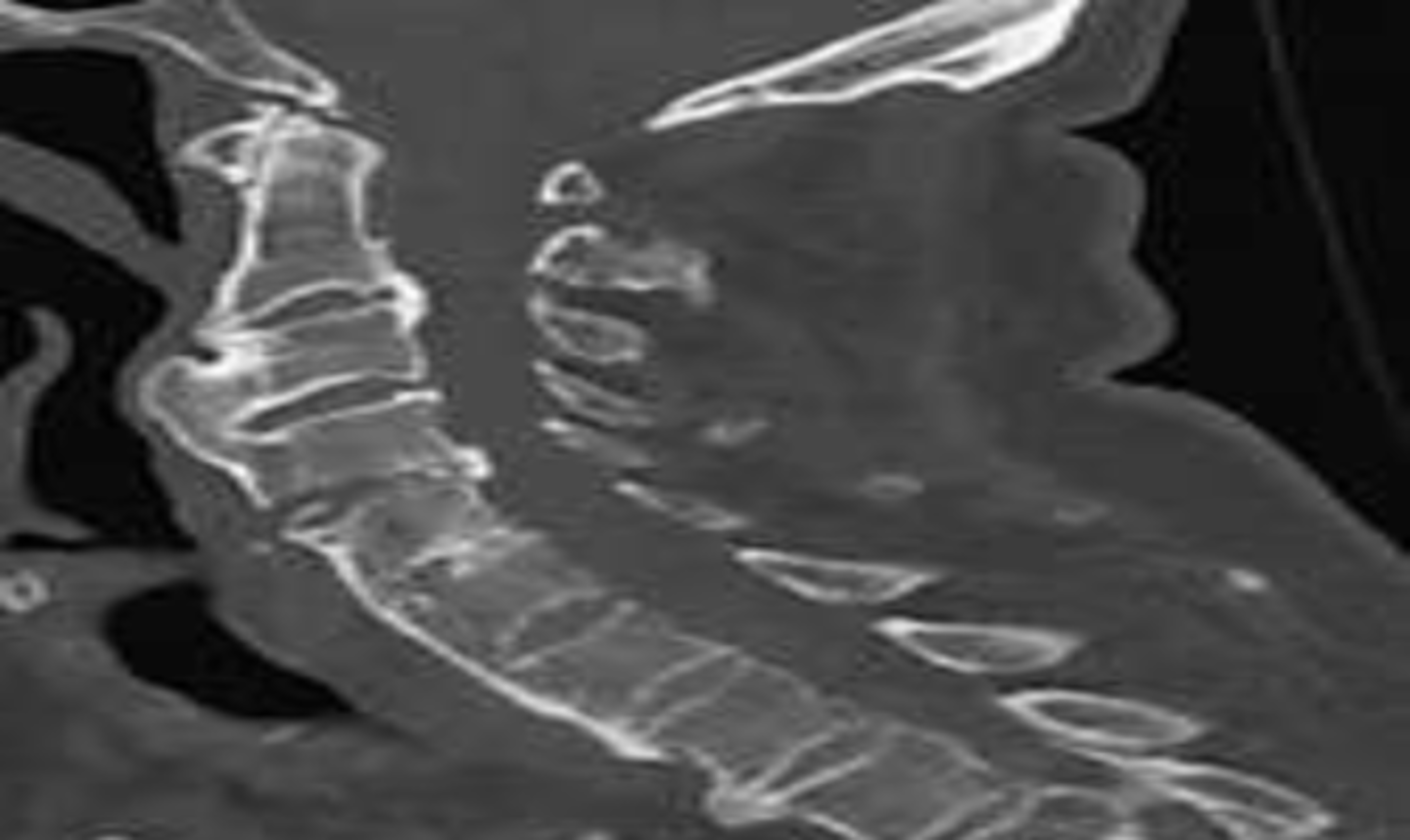
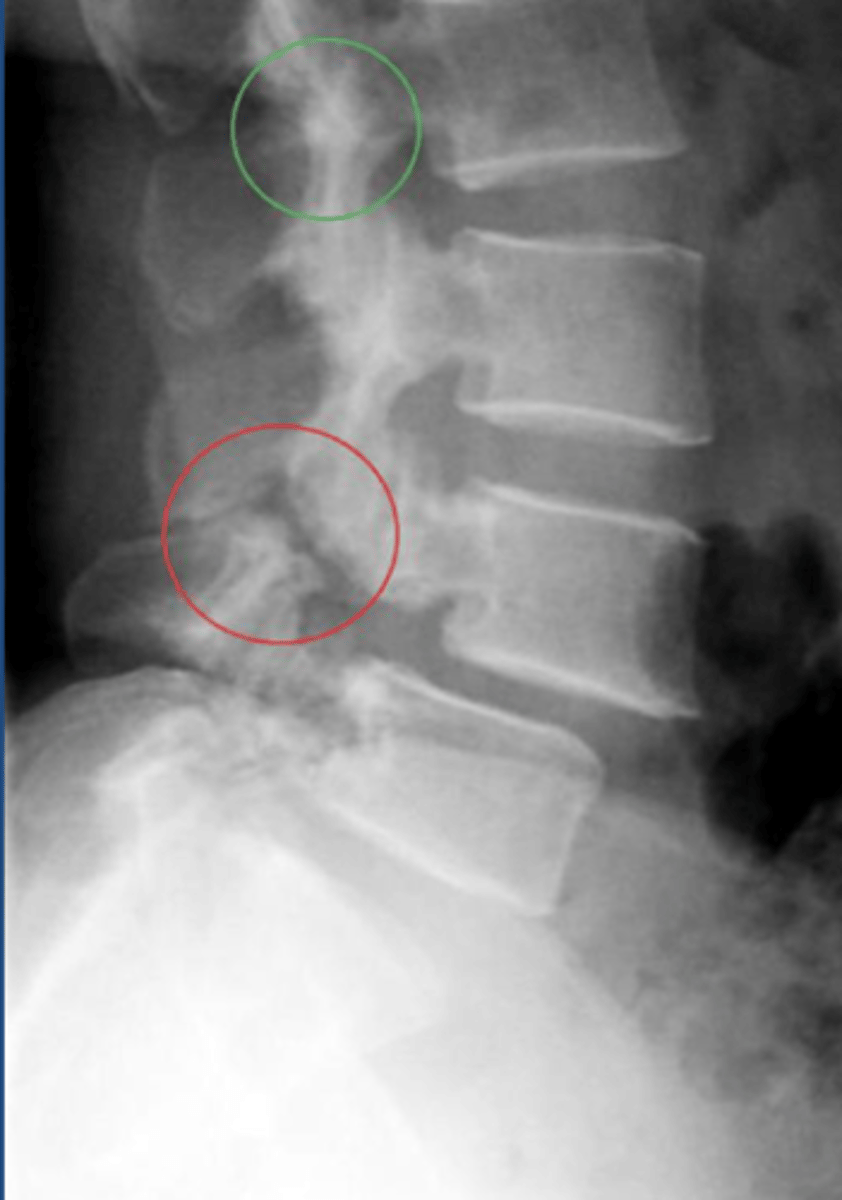
Vertebral body compression fracture
cause of back pain more common in females, usually secondary to osteoporotic lesions. Anterior and superior VB more common location. Wedge shaped deformity. Radiologically note a 20% compression vs VB increase or decrease the compressed VB. Greater than or equal to 3 mm different between anterior vs posterior VB height.
NO
Are there typically neuro deficits with vertebral body compression fracture?
X-ray
initial screening for vertebral body compression fracture
CT (trauma related)
MRI (malignancy vs. osteo)
Bone scan (age of fracture)
imaging that may be used after X-ray in vertebral body compression fracture
VB compression fracture
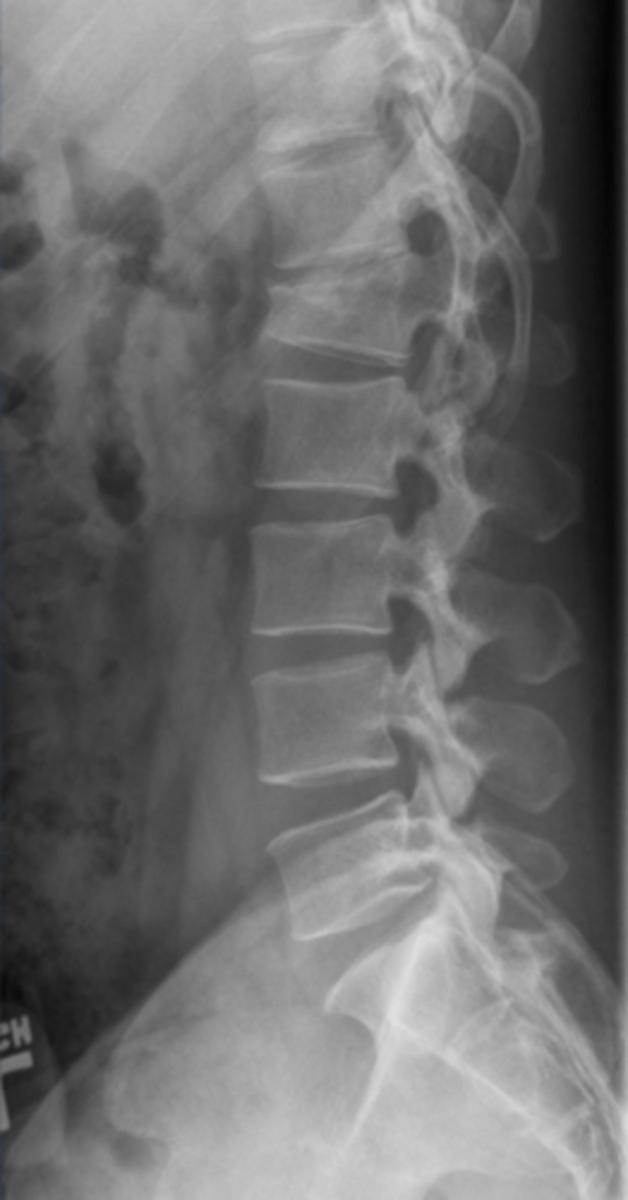
VB body fracture (MRI)
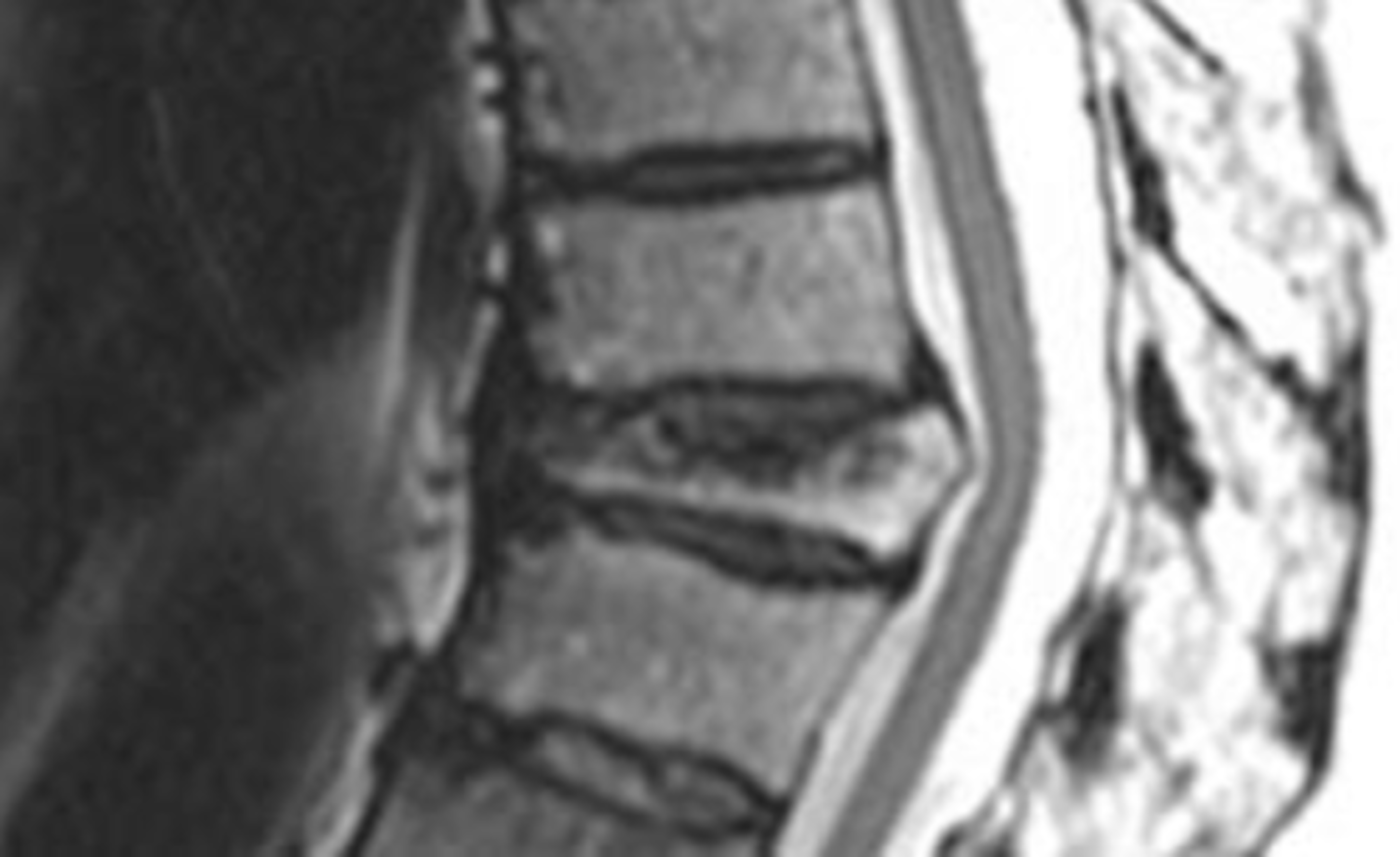
VB compression fracture (CT scan)
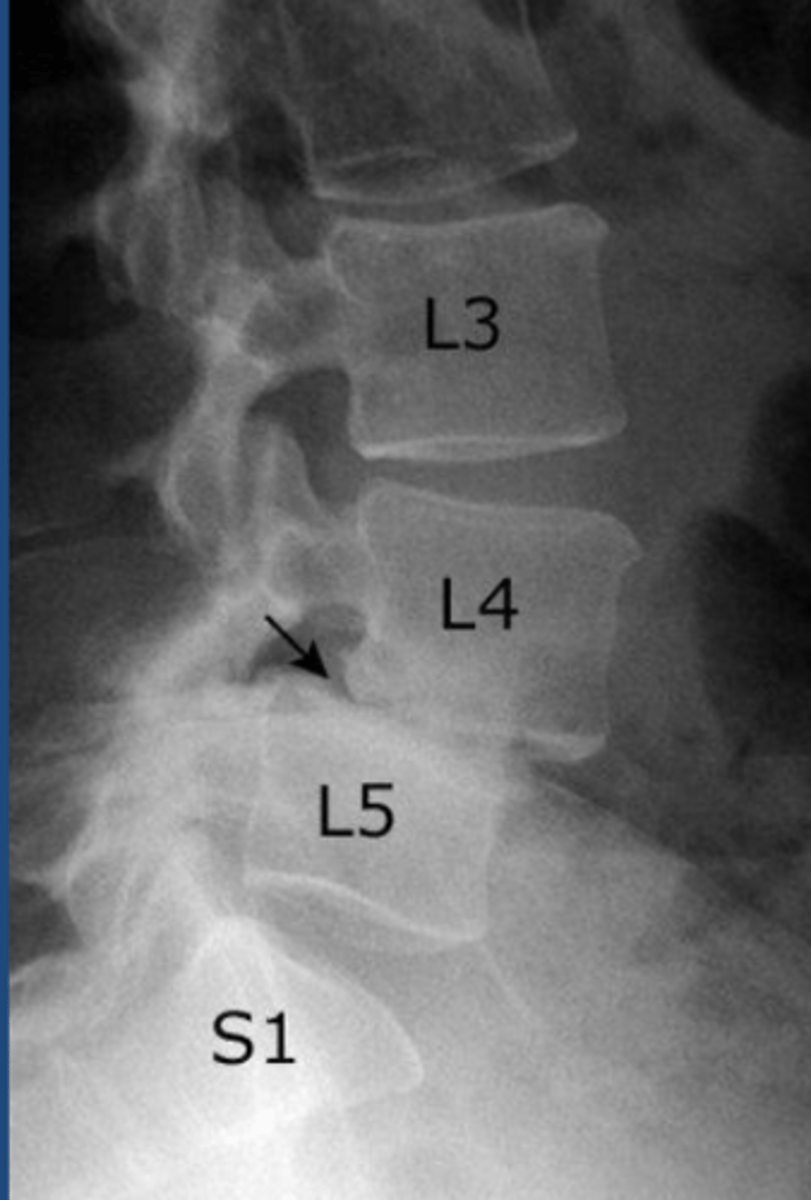
Spondylolisthesis
slippage of 1 vertebral body, upon another. Caused by degenerative changes, trauma, malignancy, congenital anormalies.
Anterolisthesis and Retrolisthesis
two directions of spondylolisthesis
L4-L5
most common location of spondylolisthesis
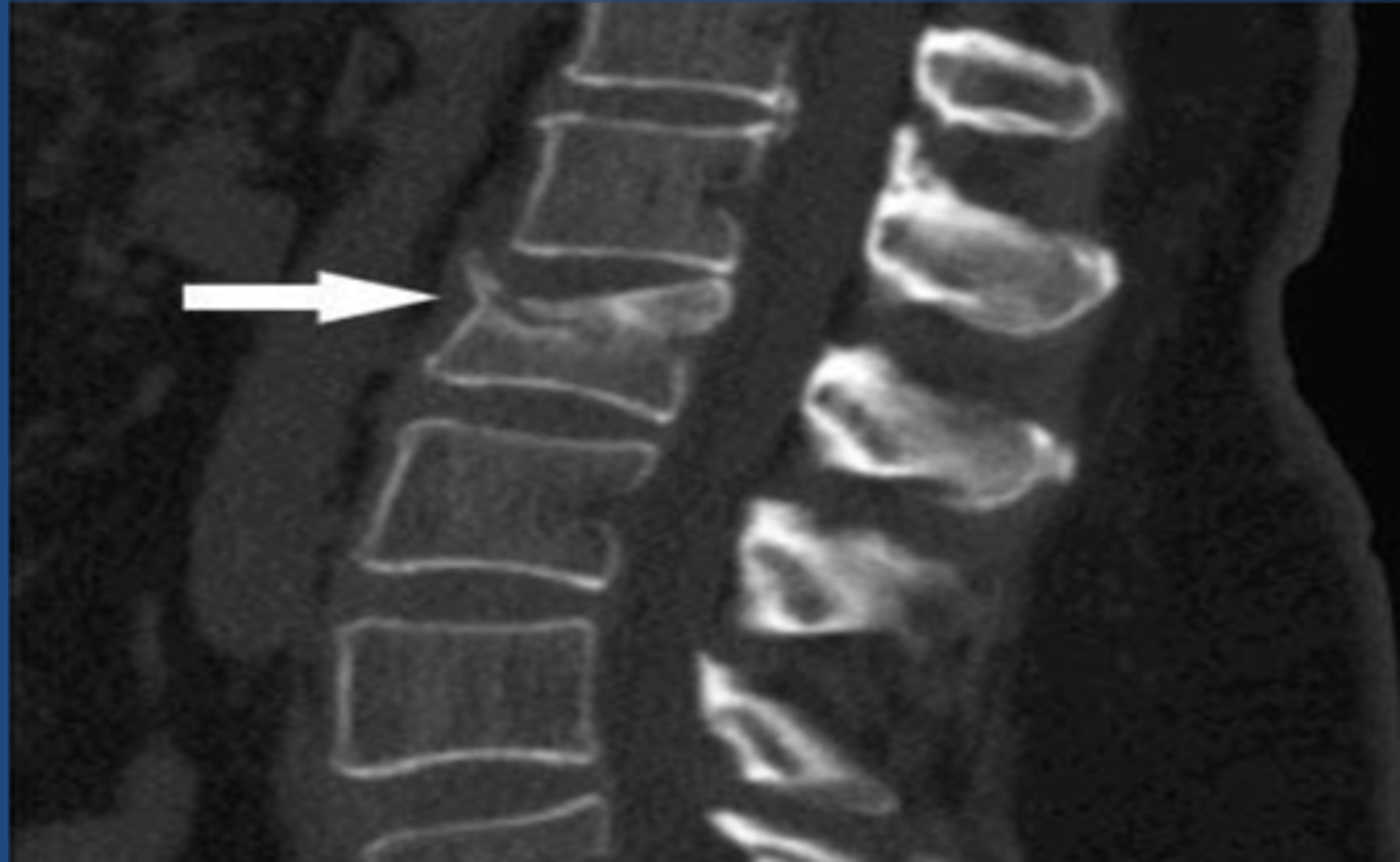
spondylolysis
bilateral pars interarticularis fractures
X-rays
primary imaging for spondylolisthesis
slippage of vertebral bodies
What would be seen on lateral view of spondylolisthesis
Scottie dog collar
Oblique view X-ray or CT for spondylolysis would display __________ disruption in the case of a pars fracture.
CT scan
if spondylolisthesis is seen on X-ray, ____ is performed to identify spondylolysis which is often difficult to see on X-ray
Spondylolysis
scotty dog collar
Spondylolisthesis
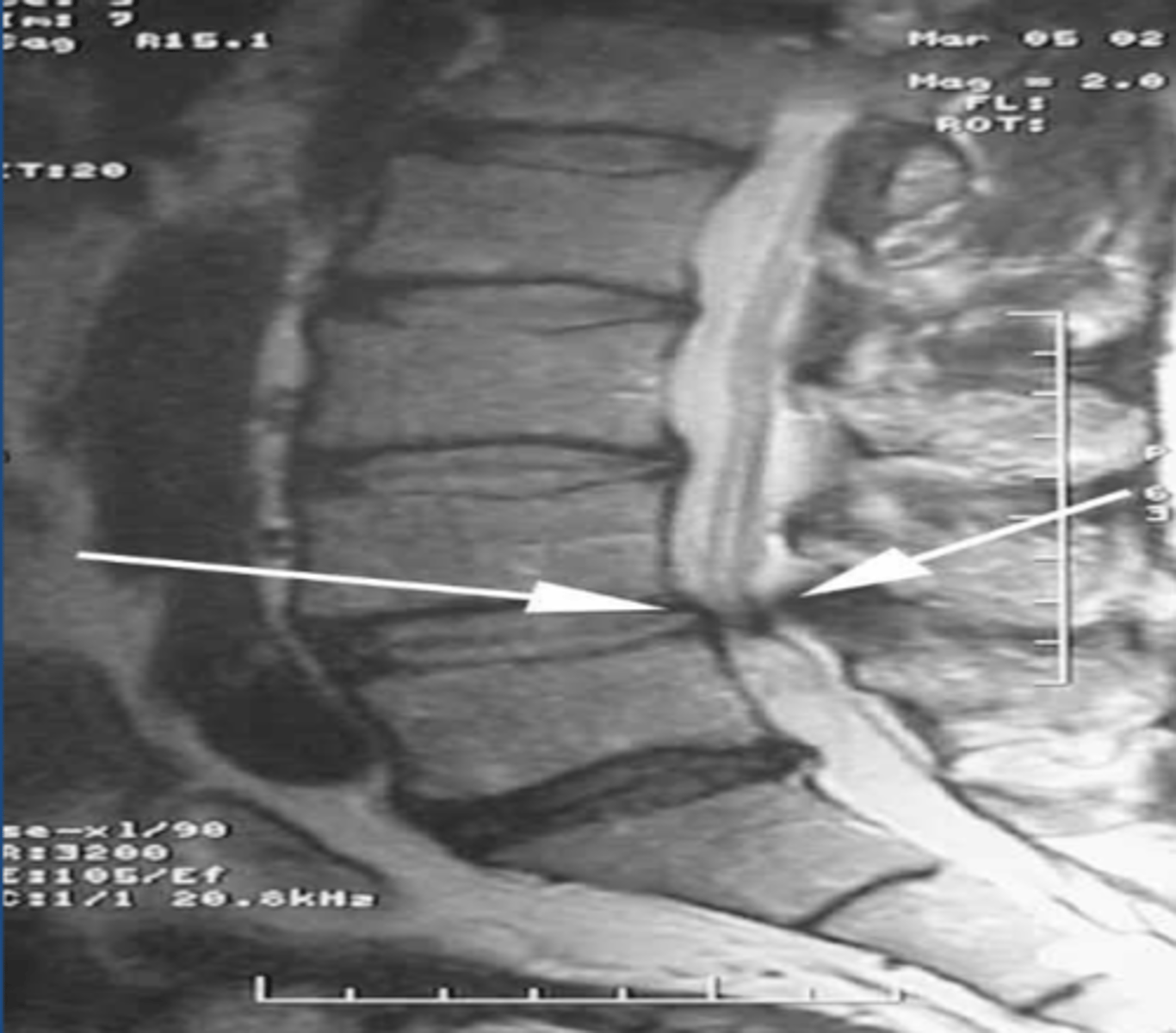
Spinal stenosis
canal or foraminal narrowing. May be related to soft tissue pathologies (hypertrophy of ligamentum flavum, building discs, ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament), bony pathologies (osteophytes, facet osteoarthritis, spondylolisthesis), acquired. Cuases radiculopathy and neurogenic claudication.
Cervical and lumbar
spinal stenosis most commonly occurs at which reginos?
X-ray
screening study for spinal stenosis
MRI
study of choice for spinal stenosis
spinal stenosis
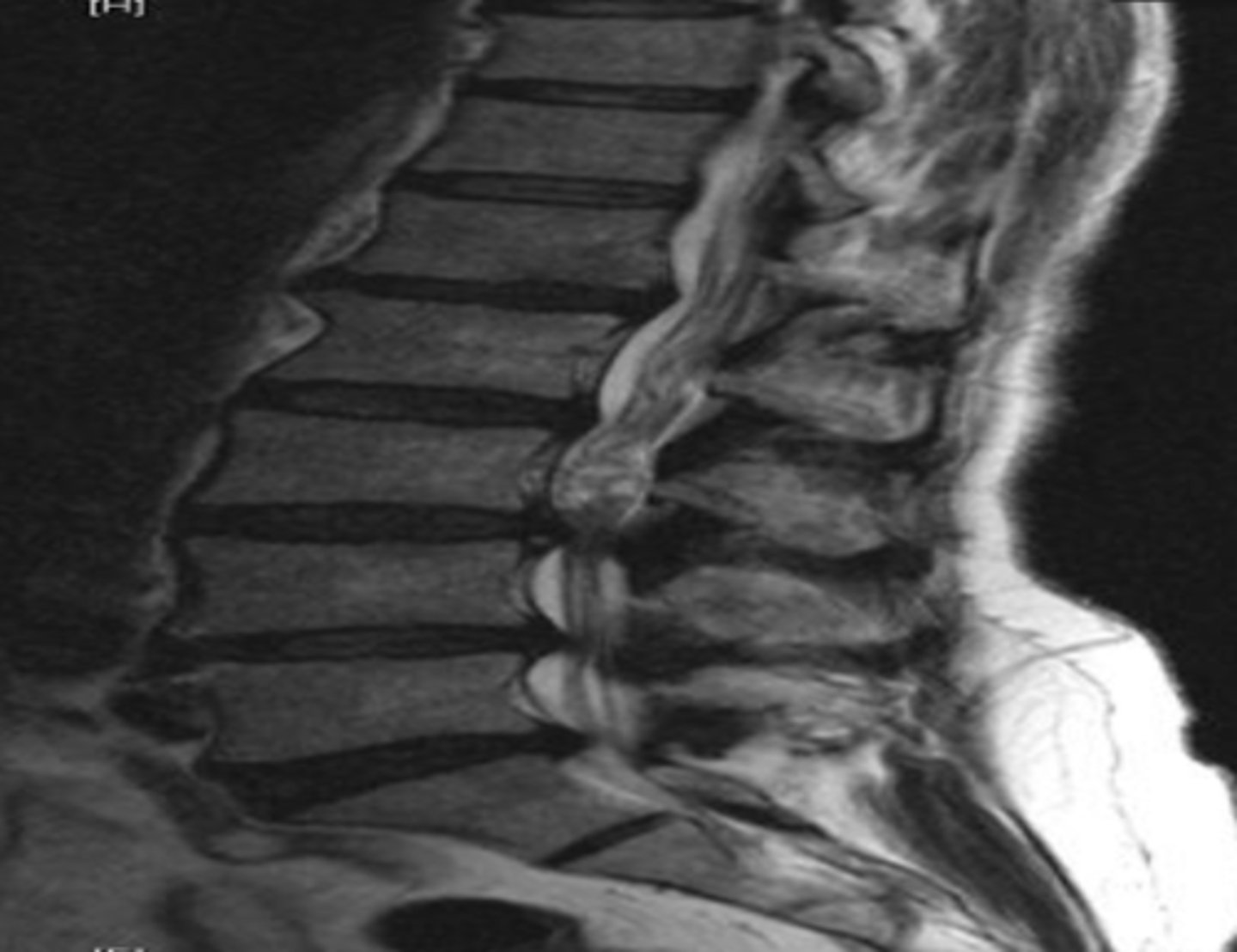
spinal stenosis
Ankylosing Spondylitis
condition that involves inflammation, calcification, ossification around entheses (insertion sites of tendons, ligaments, joint capsule). Chronic, progressive arthritic condition associated with HLA-B27 antigen, commonly seen in young males. Involves inflammation/fusion of the SI joints and spinal facet joints.
Sacroiliitis
hallmark sign of Ankylosing spondylitis
Bamboo spine
In Ankylosing Spondylitis, ossification of outer fibers of annulus fibrosis leads to bony bridges between VBs called syndesmophytes which leads to ___________
X-ray
screening study for Ankylosing Spondylitis
Syndesmophytes
bamboo spine appearance in Ankylosing Spondylitis
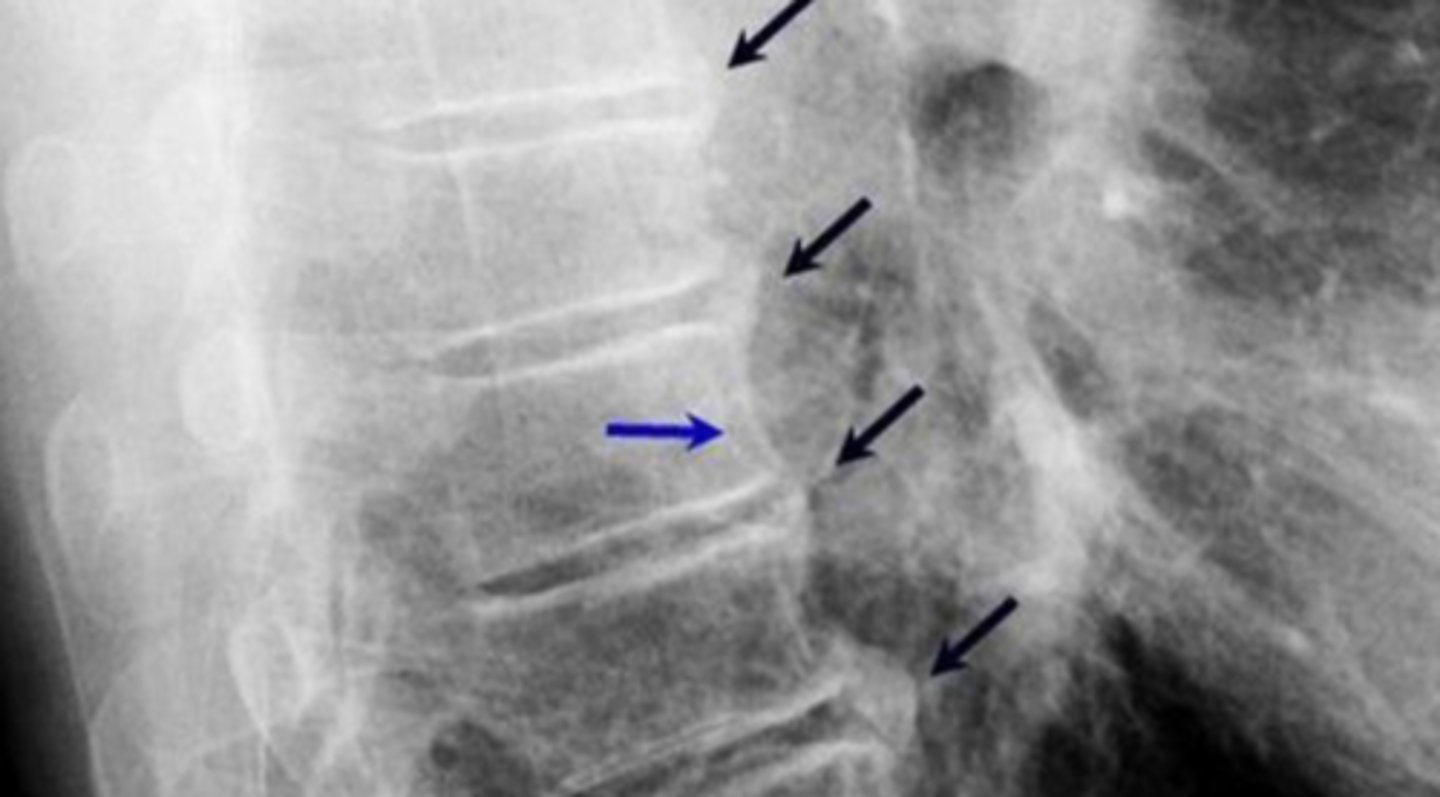
Bamboo spine indicated of Ankylosing Spondylitis
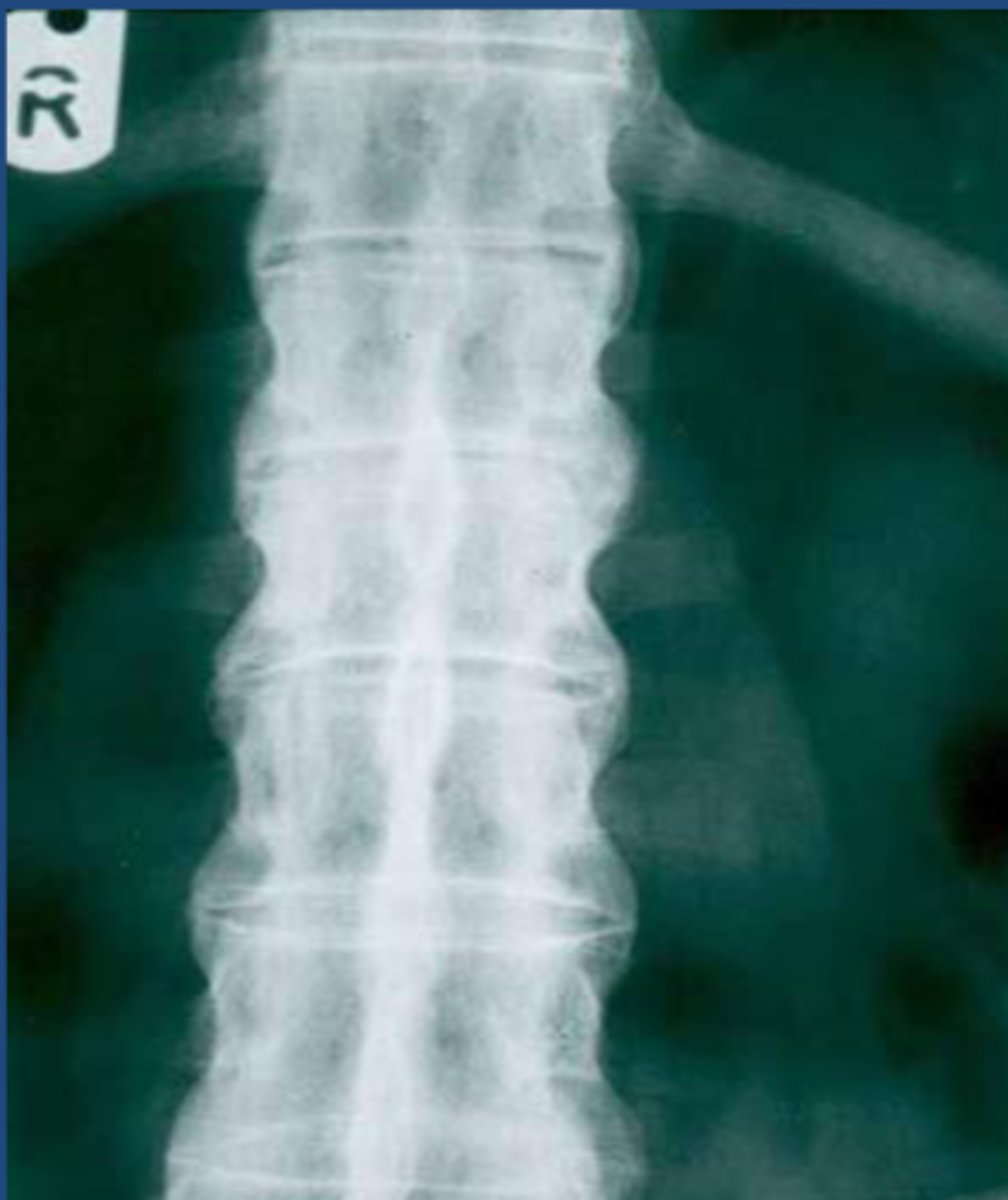
Bamboo spine indicative of AS