Project management week 7
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 6:54 AM on 4/11/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
1
New cards
Pre-design – Typical services
• Legal survey \n • Environmental site assessments \n • Geotechnical reports \n • Cost estimating \n • Archeological surveys \n • Financing and accounting \n • Assess permitting and code requirements
2
New cards
Pre-design - Budgeting
• An estimate of the cost of the project will be prepared either by the \n design team or by a separate cost consultant. \n • There are no building plans at this time so the assessment is very high \n level. \n • This is a “Class D” cost estimate and it can vary from -50% to +100% \n of the actual cost. \n • Class D cost estimates are typically based upon a metric specific to \n that occupancy. \n • I.e. Schools use ft2/student, hospitals use $/bed, etc.
3
New cards
Pre-design - programming
• At this stage, approximate floor plans can be prepared by the \n architect. \n • Gives a rough idea of the room layouts, room areas, and occupant flow. \n • Identifies any critical equipment required. I.e. Wood shops, lab \n exhaust systems, elevators, escalators, security systems, etc. \n • Identifies the required environmental conditions – if critical \n • If a room has very specific temperature and humidity requirements they \n would identify this here. If it is a standard office, the engineer will use best \n practices.
4
New cards
Pre-design – Moving forward
• Client has confidence moving forward. They know: \n • Site conditions \n • Permitting path \n • Rough building layout – not floor plans necessarily but at least bubble \n diagram \n • Requirements of the spaces \n • Services \n • Basic cost estimates \n • Code requirements
5
New cards
Schematic design - general
• Fine-tuning of architectural floor plans \n • Functional block plans. \n • Vertical sections showing height \n • CGI sketches/renderings of interior finishes and exterior \n • Massing models \n • Site plans developed to identify incoming services and general site \n impacts \n • Basic description of building systems \n • Mechanical \n • Electrical
6
New cards
Schematic design report - General
• Project understanding – reiterates the predesign decisions \n • Programming \n • Budget \n • Permitting/codes \n • Design process \n • All disciplines \n • Typically identify the relevant codes they must follow (i.e. ASHRAE 62 – 2001, \n ASHRAE 90.1 -2016, etc.)
7
New cards
Schematic design report - Architectural
• Present “parti”s \n • General architectural scheme of the building \n • Provide a “narrative” on the proposed design \n • Basic description of the architectural understanding of the building -how \n many rooms, what type of functionality, site description, etc. \n • Description of architectural systems – walls, roofs, windows, finishes, \n casework, etc. \n • Describes how occupants should feel in the various spaces. \n • Massing \n • Code analysis \n • Phasing (if required)
\
\
8
New cards
Schematic design report - Civil
• Description of site works \n • Paving \n • Parking areas \n • Ditches \n • Grading \n • Description of site services \n • Potable water \n • Sanitary drainage \n • Storm drainage \n • Electrical power \n • Communications
9
New cards
Schematic design report - Structural
• Design loads \n • Snow loads \n • Wind loads \n • Seismic loads \n • Foundation \n • Roofing framing \n • Floor framing \n • Wall framing
10
New cards
Schematic design report - Electrical
• Incoming services \n • Voltage and phase \n • Lighting \n • Telecommunications \n • Security \n • Fire alarm \n • Specialty systems \n • Emergency power
11
New cards
Schematic design report – Mechanical - \n General
• Design conditions \n • Winter and summer design temps \n • Indoor design temps (and humidity if important) \n • Climate zone \n • Elevation \n • Internal load assumptions (lighting, occupant heat production, etc.)
12
New cards
Schematic design report – Mechanical - HVAC
• Ventilation strategy and estimated load (cfm) \n • Heating strategy and estimated load (mbh) \n • Cooling strategy and estimated load (tons) \n • Plant equipment (or 2-3 options) \n • Description (including capacity) – typically no selection \n • Operating temperatures \n • Terminal equipment (or 2-3 options) \n • Description (including capacity) – typically no selection
13
New cards
Schematic design report – Mechanical - \n Plumbing
• Fixture types (commercial vs residential) \n • Piping materials \n • ABS, PVC, or cast iron for drainage and venting \n • Copper or PEX for potable \n • Schedule 40 steel for gas \n • Fixture flowrates \n • Water heater type
14
New cards
Schematic design report - others
• Landscape architects \n • Geotechnical (typically separate)
15
New cards
Schematic design –Mechanical work - general
• Provide estimated loads to civil (STW, SAN, DCW \[combined service\]). \n • Provide estimated electrical loads to electrical. \n • Big equipment i.e. AHUs, pumps, chillers, etc. \n • Emergency power requirements (if any) \n • Complete preliminary heating, cooling, and ventilation load \n calculations. \n • For renovation projects, complete a site survey. \n • Verify record drawings
• Provide estimated size of mechanical room to architectural and \n identify major pieces of equipment \n • Plant equipment \n • Repeated layouts (i.e. typical suite layout)
• Provide estimated size of mechanical room to architectural and \n identify major pieces of equipment \n • Plant equipment \n • Repeated layouts (i.e. typical suite layout)
16
New cards
Design development – Mechanical - General
• Confirm your space requirements have been allowed for. \n • If you see a space is too small, advise the architect ASAP. \n • If you don’t already have it, request the code report.
17
New cards
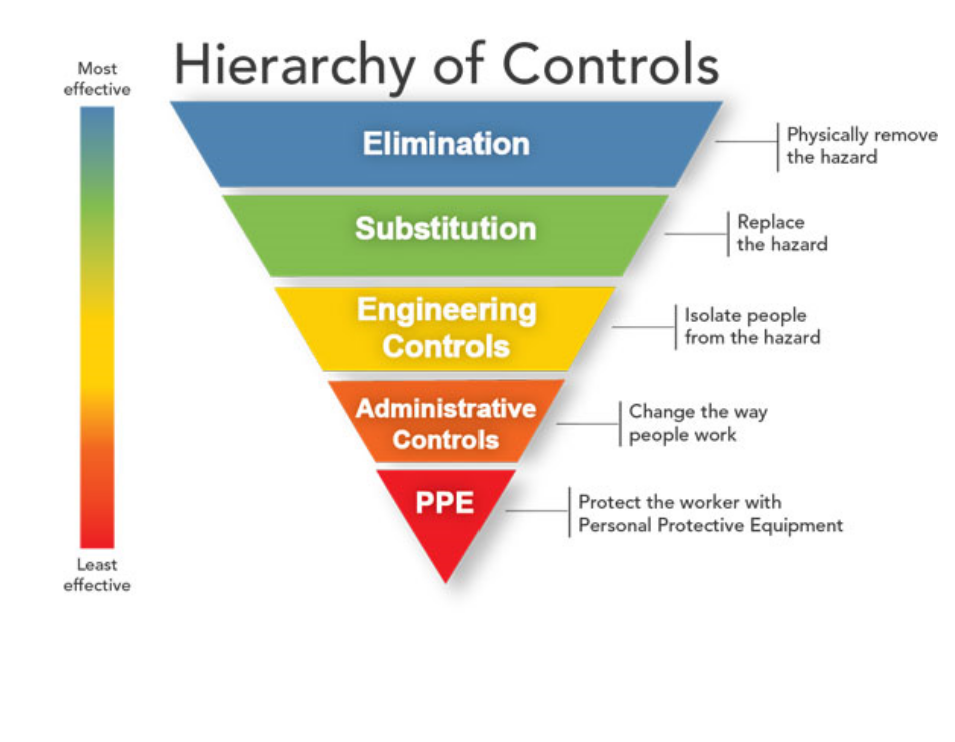
Elimination
• Remove the hazard
• Remove workers/occupants from the hazardous area.
• Most effective of the safety control mechanisms as the hazard is \n completely removed.
• Not always possible given the design constraints/owner’s \n requirements.
• Elimination may be codified in technical standards.
• Remove workers/occupants from the hazardous area.
• Most effective of the safety control mechanisms as the hazard is \n completely removed.
• Not always possible given the design constraints/owner’s \n requirements.
• Elimination may be codified in technical standards.
18
New cards
Substitution
• Substitute a hazardous system component for a more benign version. \n • Particularly prevalent today with refrigerants (steam vs hot water and glycol water)
19
New cards
Engineering controls and administrative \n controls
• Engineering controls \n Locate equipment/hazard away from occupants/workers. \n Provide safety guards/anchors for access. \n • Administrative controls \n • Put policies in place to ensure people do not come into direct contact with \n the hazard.
20
New cards
Managing project safety – hierarchy of design
21
New cards
PPE
• Least effective means of control. \n • Reliant on the user to use \n correctly.
22
New cards
CSA B52 - 2013
Standard used to assess the \n safety of a refrigerant containing \n system.
23
New cards
CSA B52 – 2013
System classification
System classification
\
Direct
Indirect
Refrigerant classification is based \n on flammability (1, 2, or 3) and \n toxicity (A or B).
Direct
Indirect
Refrigerant classification is based \n on flammability (1, 2, or 3) and \n toxicity (A or B).
24
New cards
BCBC 2018 - Parkades
\
Provide 5.74 cfm/ft2
Provide 5.74 cfm/ft2
25
New cards