Forensic Science CJ110 Quiz #4 (Tread, Fingerprints, Drugs, Toxicology)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/119
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:58 PM on 3/27/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
1
New cards
What are the tree types of shoe prints found at a crime scene?
Visible 2D, Visible 3D, Latent 2D
2
New cards
What is a Visible 2D Print?
dirt or other material picked up by shoe and deposited onto a flat surface
3
New cards
Which is an example of a Visible 2D print?
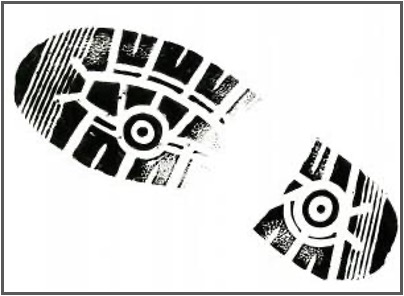
4
New cards
What is a Visible 3D print?
sheoeprint made in soft material (dirt or snow)
5
New cards
Which is an example of a Visible 3D Print?

6
New cards
What is a Latent 2D print?
barely visible dust/residue print; wet print or faint impression
7
New cards
Why should all shoe prints be documented even if the prints are suspected from coming from the same shoe?
To prevent destruction of evidence and to maintain integrity of the evidence
8
New cards
How is a barely visible sheoeprint located?
can be visualized by darkening a room and using a bright light at a low angle
9
New cards
How should a Visible 2D sheoeprint be documented and collected?
Taking an examination quality photo
10
New cards
How is a sheoeprint collected using electrostatic lift?
a charge is used to lift light dry materials from surface top lack film; provides more contrast and can be photographed
11
New cards
How is a 3D shoeprint documented and collected?
a dental stone cast picks up detail; photograph impression before casting
12
New cards
How is a Latent 2D print collected and documented?
dusting with a powder can visualize print; lift with adhesive or gelatin and transfer to a solid background
13
New cards
How is a 3D shoeprint documented and collected in snow?
spraying with colored wax highlights print for photo and prevents snow from melting during casting
14
New cards
What are the class characteristics of shoes?
pattern & size
15
New cards
What are the individual characteristics of shoes?
cuts, rocks, wear marks that are unique to one specific shoe
16
New cards
How can the individual characteristics of shoes change over time?
a show may become more worn or damaged, but they do not repair themselves
17
New cards
Why does a car with replacement tires be easier to identify than a car with OE tires?
thousands of cars have the same brand and size of tires, so replacement tires are usually different from original equipment tires
18
New cards
How can a tread indicator be used as a class characteristic of tires?
it shows the after wear; a raised bar under the tire pattern
19
New cards
What is the wheelbase?
from the front center to the back center of the tires
20
New cards
What is the track width?
the width of the right center to the left center; track width of front tires and rear tires are not always the same
21
New cards
What is the turning diameter?
diameter of a circle made when the wheels are fully turned
22
New cards
How should a 2D tire impression be documented and collected?
photos and log of location; entire track should be photographed with overlapping photos with a ruler
23
New cards
How should a 3D tire impressions documented and collected?
long sections (3 feet) should be casted using dental stone
24
New cards
What are the class characteristics of tire impressions?
size, tread design, some wear marks
25
New cards
What are the individual characteristics of tire impressions?
cuts, rocks, wear marks that are unique to one specific tire; can change over time
26
New cards
What are the raised areas of a fingerprint?
Ridges (Hills) ; black
27
New cards
What are the lowered areas of a fingerprint?
Furrows (Valleys) ; white
28
New cards
What part of the finger makes contact with a surface?
Ridges make contact
29
New cards
Do identical twins have identical fingerprints?
No
30
New cards
What are the three different patterns of prints?
arch, loop, whorl
31
New cards
Which is an arch print?
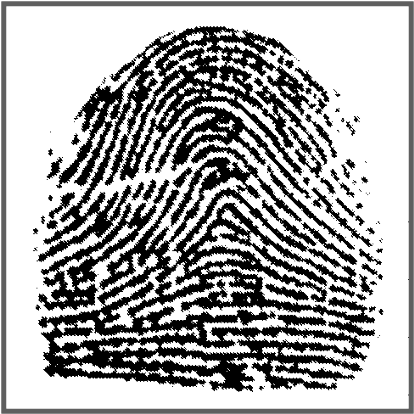

32
New cards
What is a loop print?
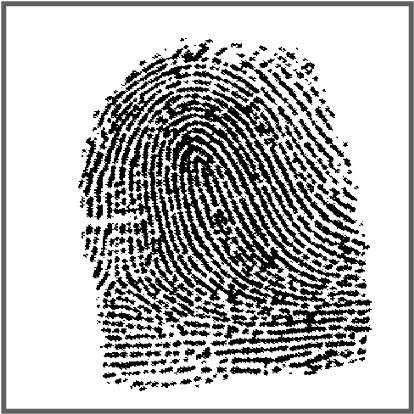

33
New cards
What is a whorl print?
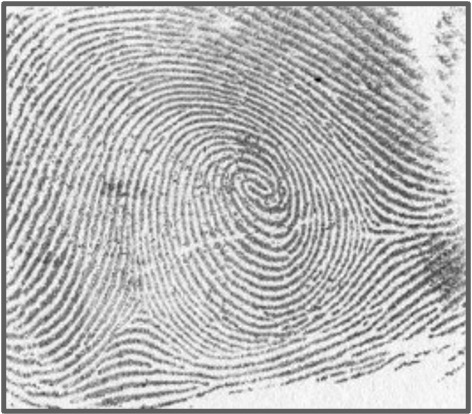

34
New cards
What are the four different minutia of prints?
bifurcation, ridge ending, island, dot
35
New cards
What is a bifurcation?

36
New cards
What is a ridge ending?

37
New cards
What is an island?

38
New cards
What is a dot?

39
New cards
How does computer software compare fingerprints?
it compares the locations of the minutia
40
New cards
What is the Bertillon system of identifying individuals?
used 11 body measurements to identify an individual
41
New cards
What is the Henry system for identifying individuals?
using a print card that identifies all 10 prints at once
42
New cards
What is the US fingerprint database?
AFIS (Automated Fingerprint Identification System)
43
New cards
What are the limitations to how a database compares fingerprints?
there must be a known print in the database that can be compared to the unknown sample; with nothing to compare the database can’t compare
44
New cards
What are the three types of fingerprints?
Visible, Impression, Latent
45
New cards
What is a visible fingerprint?
left by dirt, grease, blood, etc; does not need processing
46
New cards
What is an Impression fingerprint?
indented in soft material (butter, putty, etc.); may not need processing
47
New cards
What is a Latent fingerprint?
requires processing to make visible; process depends on type of material
48
New cards
What are the five methods for developing fingerprints?
\-Dusting
\-Iodine Fuming
\-Silver Nitrate
\-Ninhydrin
\-Super Glue Fuming
\-Iodine Fuming
\-Silver Nitrate
\-Ninhydrin
\-Super Glue Fuming
49
New cards
How do you dust a fingerprint?
\-apply powder to latent print or area
\-adheres to oils in print
\-good for **non-porou**s/large items
\-adheres to oils in print
\-good for **non-porou**s/large items
50
New cards
What is Iodine Fuming?
\-Iodine crystals are heated to form a gas
\-becomes trapped in the lipid components of the print
\-turns a brown color
\-good for **porous & non-porous**; print fades; good for valuable
\-becomes trapped in the lipid components of the print
\-turns a brown color
\-good for **porous & non-porous**; print fades; good for valuable
51
New cards
What is Silver Nitrate?
\-Silver reacts with Cl- ions in print
\-good for **porous** materials
\-messy, not sensitive
\-good for **porous** materials
\-messy, not sensitive
52
New cards
What is Ninhydrin?
\-reacts with amino acids; purple color
\-used on **porous** materials
\-painted, sprayed, dipped; heated
\-used on **porous** materials
\-painted, sprayed, dipped; heated
53
New cards
What is Super Glue Fuming?
\-heated to produce an off white print
\-reaction somewhat unknown
\- **non-porous** material
\-reaction somewhat unknown
\- **non-porous** material
54
New cards
What methods can be shown when fluoresced?
Ninhydrin and Super Glue Fuming prints
55
New cards
What is a controlled substance?
a legal term referring specifically to substances controlled by federal or state lawsControlled Substances Act of 1970
56
New cards
What is the legal act that scheduled drugs?
Controlled Substances Act of 1970 (established legal definitions for drugs)
57
New cards
What is Schedule 1?
drugs carry the most severe penalties; considered to have a “high potential for abuse” and have “no accepted medical use”
58
New cards
What is Schedule 2?
drugs have a high potential for abuse but have an accepted medical use
59
New cards
What is Schedule 3 & 4?
have an accepted medical use and decrease in potential for abuse
60
New cards
What are natural controlled substances?
Marijuana, cocaine, morphine, codeine, psilocybin/psilocin
61
New cards
What are synthetic controlled substances?
Phencyclidine (PCP), Amphetamines, Barbiturates
62
New cards
What are semisynthetic controlled substances?
Heroin, LSD
63
New cards
What are Opiates?
\-opium derivatives, their salts, isomers, and salts of isomers
\-poppies originated in hot, dry Middle East
\-poppies originated in hot, dry Middle East
64
New cards
What is Heroin?
synthesized from morphine as passes blood-brain barrier
65
New cards
What are Amphetamines?
-synthetic stimulant covers amphetamine
\-legal precursors are regulated by limiting purchases
\-legal precursors are regulated by limiting purchases
66
New cards
What is Cocaine?
\-coca leaves and any salt, compound, derivative, etc.
\-originates in the Andes Mountains
\-medically used as a local anesthetic and stimulant
\-originates in the Andes Mountains
\-medically used as a local anesthetic and stimulant
67
New cards
What is the difference in cocaine?
Cocaine hydrochloride is powder form; Crack cocaine is base (can be smoked)
68
New cards
What is Marijuana?
\-originated in Asia, but now grows worldwide
\-remains Schedule 1, but states can decriminalize
\-remains Schedule 1, but states can decriminalize
69
New cards
What are cannabinoids?
\-psychoactive compounds primarily (delta 9-THC)
\-synthetic cannabinoids (spice) are synthetic and interact with cannabinoid receptors
\-synthetic cannabinoids (spice) are synthetic and interact with cannabinoid receptors
70
New cards
What are Cathinones?
derived from Khat leaves
71
New cards
What is a Kratom?
herbal extract of Mitragyna speciosa
72
New cards
What are Barbiturates?
Scheduled 2-4 depressants
73
New cards
What is LSD & Ecstasy?
a Schedule 1 hallucinogen
74
New cards
What is Psilocybin?
a Schedule 1 hallucinogen from mushrooms
75
New cards
What are the four different screening tests for pills and powders?
\-Color Test
\-Microcrystal Test
\-Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC)
\-Gas Chromatography
\-Microcrystal Test
\-Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC)
\-Gas Chromatography
76
New cards
What is a Color Test?
\-small amount of chemical in spot plate;
\-color changing reagent added
\-color change noted
\-color changing reagent added
\-color change noted
77
New cards
What is a Microcrystal Test?
\-small amount of sample dissolved in solution
\-reagent added contains another chemical that reacts w/ drug
\-crystal formed; crystal suggests type of drug
\-reagent added contains another chemical that reacts w/ drug
\-crystal formed; crystal suggests type of drug
78
New cards
What is a Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC) test?
\-dot of drug placed at bottom of paper or thin silica place
\-dipped in solvent; different solvents result in different distances/some include color change componenets
\-dipped in solvent; different solvents result in different distances/some include color change componenets
79
New cards
What is a Gas Chromatography test?
\-similar to TLC; different chemicals will moved at different rates through a capillary
\-the time it takes to pass through gives an indication of what drug it is
\-the time it takes to pass through gives an indication of what drug it is
80
New cards
What is the screening processes for Marijuana?
Microscopic & Macroscopic Exams
81
New cards
What does a Macroscopic Exam for marijuana identify?
Leaf and stem structure
82
New cards
What does a Microscopic Exam for marijuana identify?
Tiny hairs on leaf surface
83
New cards
What is alternate method to identify Marijuana (Resin ID)?
Color test & TLC (tests for chemical THC)
84
New cards
What is the screening process for Peyote?
Macroscopic Exam & Test for alkaloids, confirming mescaline is not necessary
85
New cards
What does a Macroscopic Exam for peyote identify?
looks for cotton-like tufts
86
New cards
What does the test for alkaloids for peyote use?
TLC & Gas chromatography
87
New cards
What is the screening process for mushrooms?
Macroscopic Exam, a screening, requires confirmation
88
New cards
What does a Macroscopic Exam for mushrooms identify?
identifies that mushrooms contain psilocybin
89
New cards
What does a screening for mushrooms consist of?
color test, TLC, and UV spectroscopy
90
New cards
What are the different methods for preparing drug samples for confirmation tests?
1) Physical Separation
2) Dry Wash
3) Dry Extraction
4) Liquid/Liquid Extraction
2) Dry Wash
3) Dry Extraction
4) Liquid/Liquid Extraction
91
New cards
What is Physical Separation?
particles are operated based on microscope appearance
92
New cards
What is Dry Wash?
liquid dissolves adulterants; solid drug left behind
93
New cards
What is Dry Extraction?
liquid dissolves drug; solid adulterants left behind
94
New cards
What is Liquid/Liquid Extraction?
\-entire sample dissolved in aqueous (water) liquid
\-organic liquid (oil-like) mixed with solution
\-organic liquid removes adulterants
\-sample remains in aqueous layer
\-organic liquid (oil-like) mixed with solution
\-organic liquid removes adulterants
\-sample remains in aqueous layer
95
New cards
What are the two drug confirmation methods?
Mass Spectroscopy & Infrared Spectroscopy
96
New cards
What is Mass Spectroscopy?
will smash a molecule into pieces and measure the mass of the pieces; every drug will break in a unique way
97
New cards
What is Infrared Spectroscopy?
\-a range of infrared light wavelengths are passed through a sample
\-some light passes through; some is absorbed
\-different drugs have different patterns
\-some light passes through; some is absorbed
\-different drugs have different patterns
98
New cards
What is toxicology?
the study of poisons
99
New cards
What is forensic toxicology?
all aspects of toxicity that have legal implications
100
New cards
What are the three categories of forensic toxicology?
\-Postmortem Drug Testing
\-Workplace Drug Testing
\-Criminal Drug Testing
\-Workplace Drug Testing
\-Criminal Drug Testing