GI E2- Pancreas
1/55
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
What does the pancreatic duct join the common bile duct to form?
Hepatopancreatic ampulla (of vater)
Where does the hepatopancreatic ampulla of vater empty?
Into duodenum at major duodenal papilla (controlled by sphincter of Oddi)
What cells secrete pancreatic juice?
Acinar cells
What do pancreatic secretions consist of?
Amylase, lipase, deoxyribonuclease & ribonuclease, sodium bicarbonate, & proteases (trypsin, elastase, etc)
What are endocrine functions of the pancreas?
Islets of langerhans which secrete insulin, glucagon, & somatostatin
What are exocrine functions of the pancreas?
Digestive / pro-enzymes (Trypsinogen, chymotrypsinogen) controlled by gastrin, secretin, & CCK
What condition is an acute, reversible pancreatic inflammation with enzymatic release into the parenchyma, which activates enzymes that lead to autodigestion of the pancreas?
Acute pancreatitis
What contributes to injury in acute pancreatitis?
Edema → vascular insufficiency → ischemia
What is the pathogenesis of hereditary pancreatitis?
Genetic mutations create imbalance of proteases & inhibitors → inappropriate activation of pancreatic zymogens → autodigestion & inflammation
What is the “I get smashed” mnemonic for causes of acute pancreatitis?
Idiopathic
Gallstones
Ethanol
Trauma
Steroids
Mumps
Autoimmune
Scorpion sting
Hypercalcemia or Hypertriglyceridemia (serum TG > 1000 mg/dl)
ERCP
Drugs
At what serum TG levels would hypertriglyceridemia associated pancreatitis occur?
≥ 1000 mg/dL
What is the pathogenesis of alcohol induced pancreatitis?
First attack occurs after 8-10 yrs of heavy usage & episodes will continue to occur with continued alcohol abuse
What is the pathogenesis of gallstone induced pancreatitis?
Related to transient or complete obstruction of pancreatic ductal flow or reflux of bile into pancreatic duct (occurs with choledolcolithiasis)
What drugs can cause drug induced pancreatitis?
Cannabis, codeine, enalapril, furosemide, mesalamine, metronidazole, simvastatin, etc
What occurs in 5-7% patients undergoing ERCP?
ERCP induced pancreatitis
The following ssx are associated with what condition?
Epigastric / LUQ pain that radiates through to the back
steady, boring pain, increases in intensity
often bends forward or pulls knees to chest
N, V, abd distension, restless
very tender to palpation
dec bowel sounds
+/- fever
Acute pancreatitis
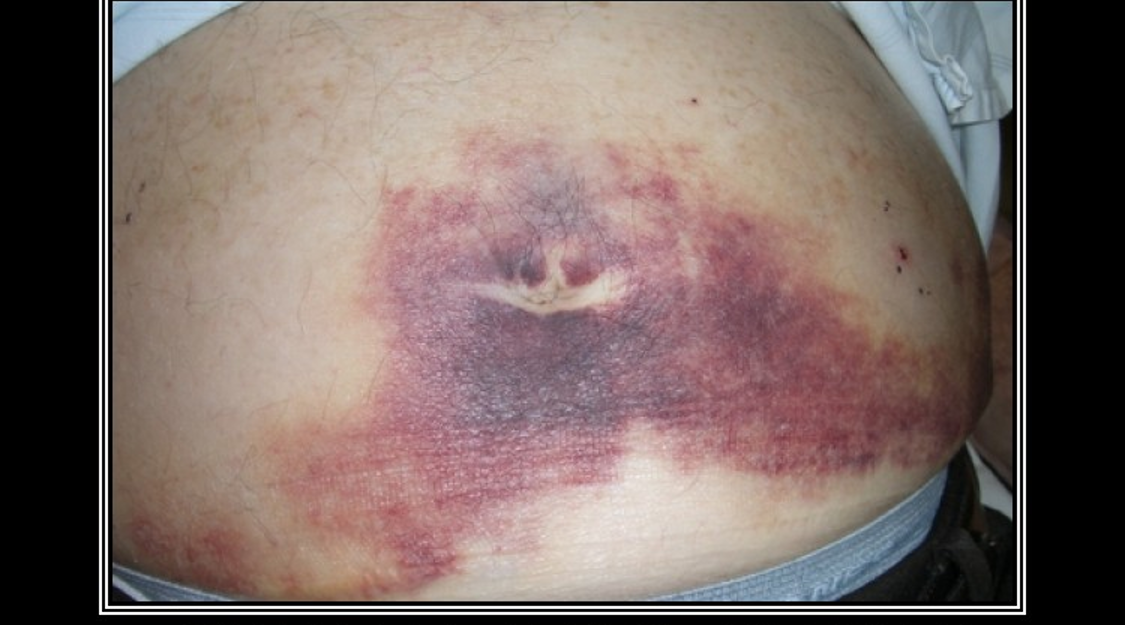
What is Cullen’s sign?
Blue discoloration to umbilicus form retroperitoneal bleeding in pancreatic necrosis
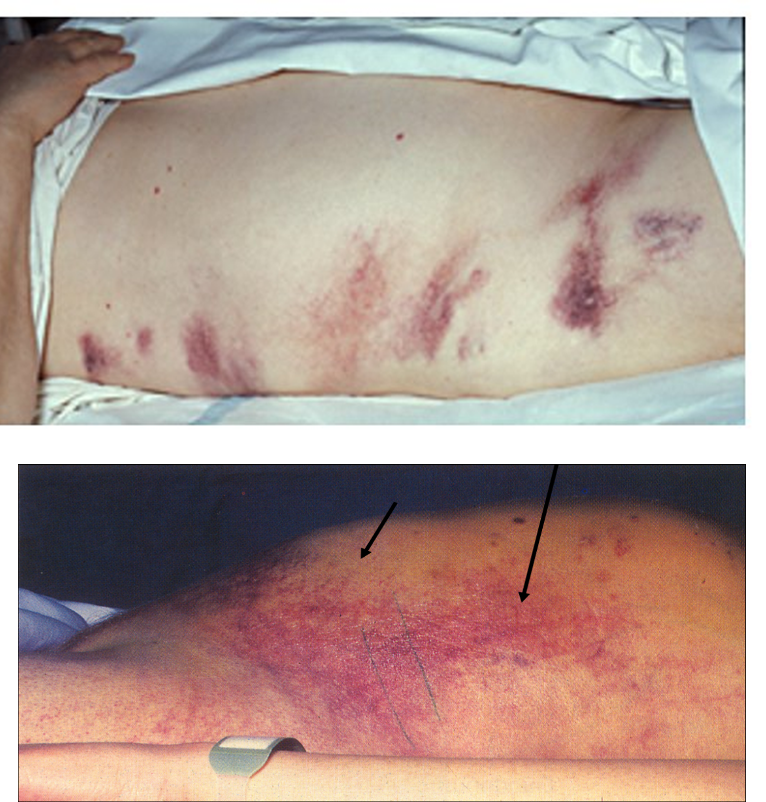
What is Grey Turner’s sign?
Green brown discoloration to flanks seen with severe, necrotizing pancreatitis
The following PE findings can be seen in a patient with what condition?
anxious, “shocky”, rarely jaundice
erythematous nodules form fat necrosis
rales, atelectasis, effusions, diminished/absent bowel sounds
Cullens sign or grey turners sign (if severe)
Acute pancreatitis
The following labs are likely to be seen in what condition?
Amylase & lipase elevated >3x upper limit w/in 12 hrs for several days
lipase more specific, sensitive, & elevated longer
hypocalcemia bc necrotic fat binds calcium
LFTs- ALT > 150 (highly specific for stones)
possible protein casts in UA
etc
Acute pancreatitis
What is the preferred lab test for acute pancreatitis because it is most specific, sensitive, & remains elevated the longest?
Lipase
What should you think of with increased ALP & bilirubin?
Biliary disease
What is the gold standard for acute pancreatitis imaging?
CT abd
What is seen on abd flat plate imaging of acute pancreatitis?
Sentinel loop → dilatation of segment of large or small intestine
What criteria aids in predicting the mortality of acute pancreatitis & the severity of pancreatic necrosis, based upon labs at admission and at 48 hrs?
Ranson’s criteria
What is Ranson’s criteria?
Glucose > 200
AST > 250
LDH > 350
Age > 55
WBCs > 16,000
+other factors after 48 hrs; 1 point for each

What is the APACHE II score?
Acute physiology and chronic health evaluation → provides estimate of ICU mortality based on lab values & patient signs beginning w/in first 24 hours of ICU admission
What is replacing Ranson’s & apache score in the evaluation of acute pancreatitis?
Bedside Index of Severity in Acute Pancreatitis (BISAP) → 5 factor scoring system useful w/in first 24 hrs of hospitalization
What is the criteria for BISAP?
Bun > 25 mg/dL
Impaired mental status
SIRS
Age > 60
Pleural effusion
*1 point for each; score of ≥ 3 associated w/ inc mortality & complications
What is the treatment for acute pancreatitis?
NPO, IVF, rest pancreas for 3-7 days, NG tube, analgesics, enteral feeding, pancreatic secretion suppression/enzyme blockage, IV acid blockers, possible ICU admission
What should be started in patients with mild acute pancreatitis once they are off analgesics, has normal bowel sounds, and is hungry?
Clear or full liquid diet
What should patients with gallstone induced pancreatitis undergo during admission to decrease the risk of recurrence?
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy
What causes death in acute pancreatitis?
Resp failure, ARF, intraabdominal abscess, hemorrhage
What complications can be seen with acute pancreatitis?
Pseudocyst, pancreatic ascites, SC fat necrosis
What condition?'
collection of fluid, tissue & debris within or adjacent to the pancreas (complication of acute pancreatitis)
frequently opens directly into pancreatic duct
sx: fever, tachycardia, abd mass, tenderness, infx, rupture, hemorrhage
Pseudocyst
What is the treatment for a pseudocyst caused by acute pancreatitis?
Observation or endoscopic/surgical drainage if sx, rapidly enlarging, or infected
What condition?
episodes of acute inflammation in already damaged pancreas OR pancreatic damage w/ malabsorption & persistent pain
destruction of parenchyma leads to fibrosis & calcifications
Chronic pancreatitis
What is the pathogenesis of chronic pancreatitis?
Pancreatic ducts become dilated, irregular or strictured → glandular tissue has irregular areas of patchy replacement of normal acing tissue fibrosis → neuritis & hypertrophy may create associated pain
What are causes of chronic pancreatitis?
Alcohol, idiopathic, genetic, autoimmune (PSC, PBC, T1DM), obstructive / tumors, recurrent (postnecrotic, vascular disorders)
The following sx are seen with what condition?
Hallmark: abd pain & pancreatic insufficiency
RUQ, LUQ, epigastric, episodic unrelenting pain that is persistent, deep, & boring to the back
worsens w/ alcohol & postprandial
steatorrhea - indicates fat malabsorption
metabolic bone disease (low trauma fx)
DM - late occurence
wt loss from malabsorption
Chronic pancreatitis
The following diagnostic workup is for what condition?
plain XRs- calcifications
abd U/S - low sensitivity
abd CT & MRI - mainstays
endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)
MRCP - chain of lakes (reserved when therapeutic intervention is necessary)
Chronic pancreatitis
What would show on MRCP in a patient with chronic pancreatitis?
Chain of lakes sign - dilatation & tortuosity of the main pancreatic duct
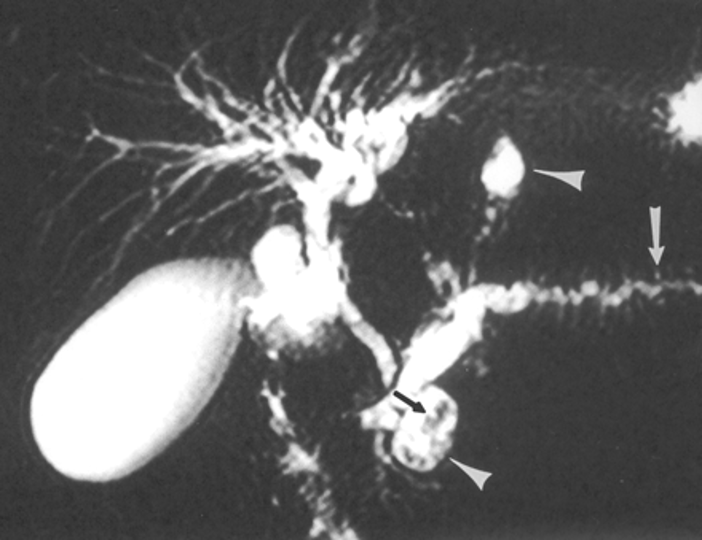
What is the treatment for chronic pancreatitis?
Analgesics, EUS guided celiac plexus block, replace pancreatic enzymes, H2RAs or PPIs (for acid suppression), octreotide, low fat diet, PO hypoglycemics or insulin, cyanocobalamin administration
What complications can occur with chronic pancreatitis?
Pseudocyst, inc risk of pancreatic cancer, obstruction (biliary, ductal, or duodenal), pancreatic ascites, pleural effusion, pancreatic fistulae, narcotic addiction
What is the median age of diagnosis for pancreatic cancer?
60-65 (rare before 45)
Who is pancreatic cancer MC in?
African American males
Pancreatic cancer is linked to a high association with what?
Smoking
What RF are associated with pancreatic cancer?
Smoking, fhx in first degree relative (can be autosomal dominant), long hx of DM & insulin resistance, obesity, high intake of fat and smoked/processed meat, hx of chronic pancreatitis
What are most pancreatic cancers?
ductal adenocarcinomas
What do nearly all pancreatic malignancies develop from?
Exocrine portion of the pancreas
The following sx are seen with what condition?
insidious vague low intensity & poorly localized epigastric or back pain
radiates from epigastrium to back
improves w/ bending forward
present for several mos prior to dx
jaundice if tumor is in head of pancreas
painless jaundice- obstruction of extra hepatic bile duct
wt loss, anorexia, weakness
bloating, constipation, diarrhea
courvoiseir sign
Pancreatic cancer
What is Courvoisier sign?
Obstructed bile duct is accompanied by a palpable, nontender gallbladder
How would labs appear in pancreatic cancer?
ALP inc 4-5x UNL, mild elevation of LFT, bilirubin inc in late disease, CA19-9 tumor marker
What are diagnostic imaging options for pancreatic cancer?
Transabdominal US, helical CT w/ contrast, endoscopic US, ERCP / MRCP
What is the prognosis of pancreatic cancer?
Poor - most present late in the disease
What is the treatment for pancreatic cancer?
Whipple procedure, chemo & XRT, palliative care