forces + motion EOT
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What is the difference between a scalar and a vector quantity?
A scalar quantity has only magnitude (e.g., speed, distance, mass),
A vector quantity has both magnitude and direction (e.g., velocity, force, displacement)
How can a vector quantity be represented (in a diagram)?
Using an arrow , where the length represents magnitude and the direction of the arrow shows direction.
What is the difference between a contact and a non-contact force?
Contact forces require objects to be touching (e.g., friction, tension),
Non-contact forces act at a distance (e.g., gravity, magnetism).
What forces are exerted when two objects interact?
They exert equal and opposite forces on each other (Newton’s Third Law).
What is a resultant force?
The overall force acting on an object when multiple forces are combined
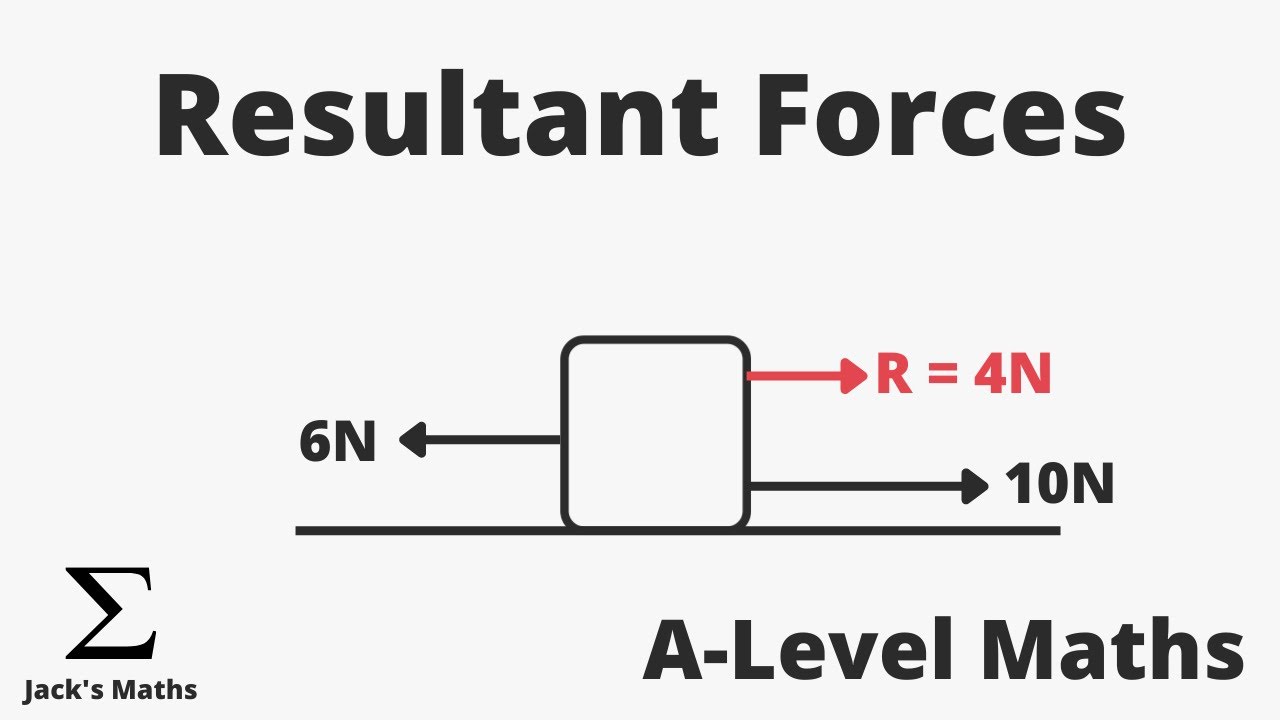
What happens if the resultant force on an object is zero?
The object stays at rest or continues moving at a constant velocity.
What happens if the resultant force is greater than zero?
The object will accelerate in the direction of the force.
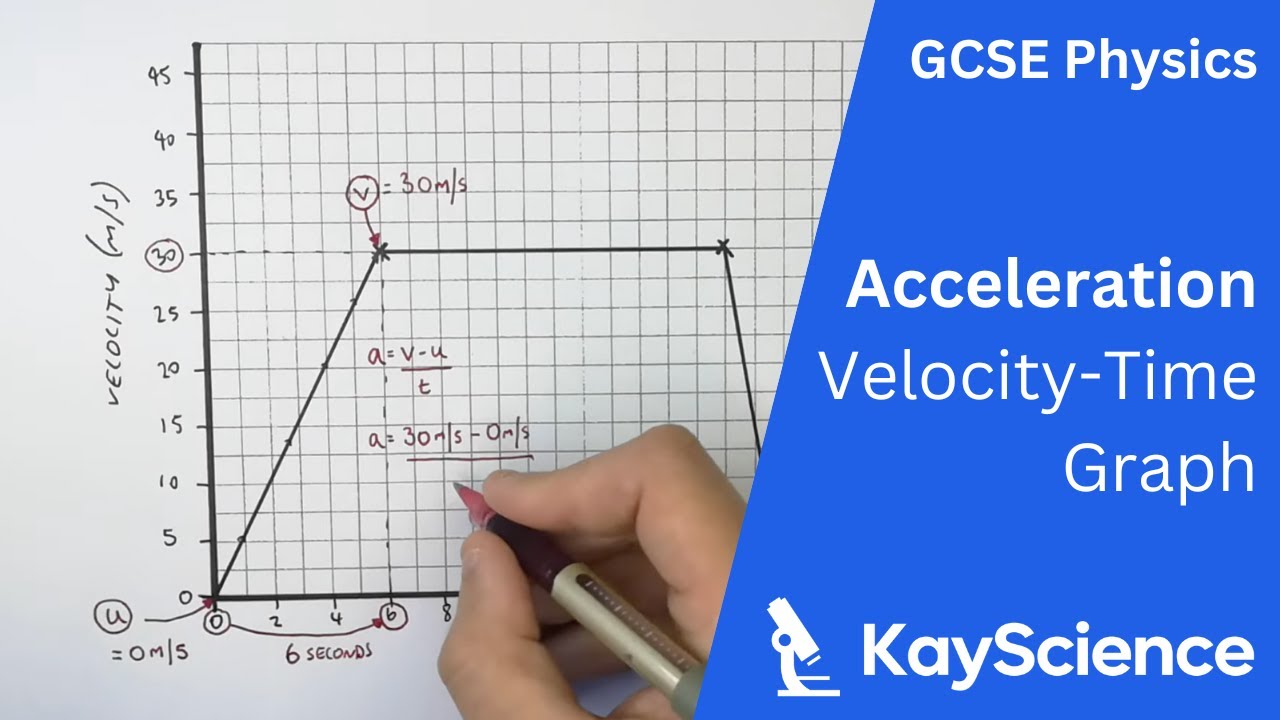
What is the equation for acceleration?
acceleration = change of velocity ÷ time taken
How can you tell if an object is accelerating or decelerating on a velocity-time graph? (If the line is..)
If the line is sloping upwards, it's accelerating; if it's sloping downwards, it's decelerating.
How do you calculate acceleration from a velocity-time graph?
Find the gradient of the graph.
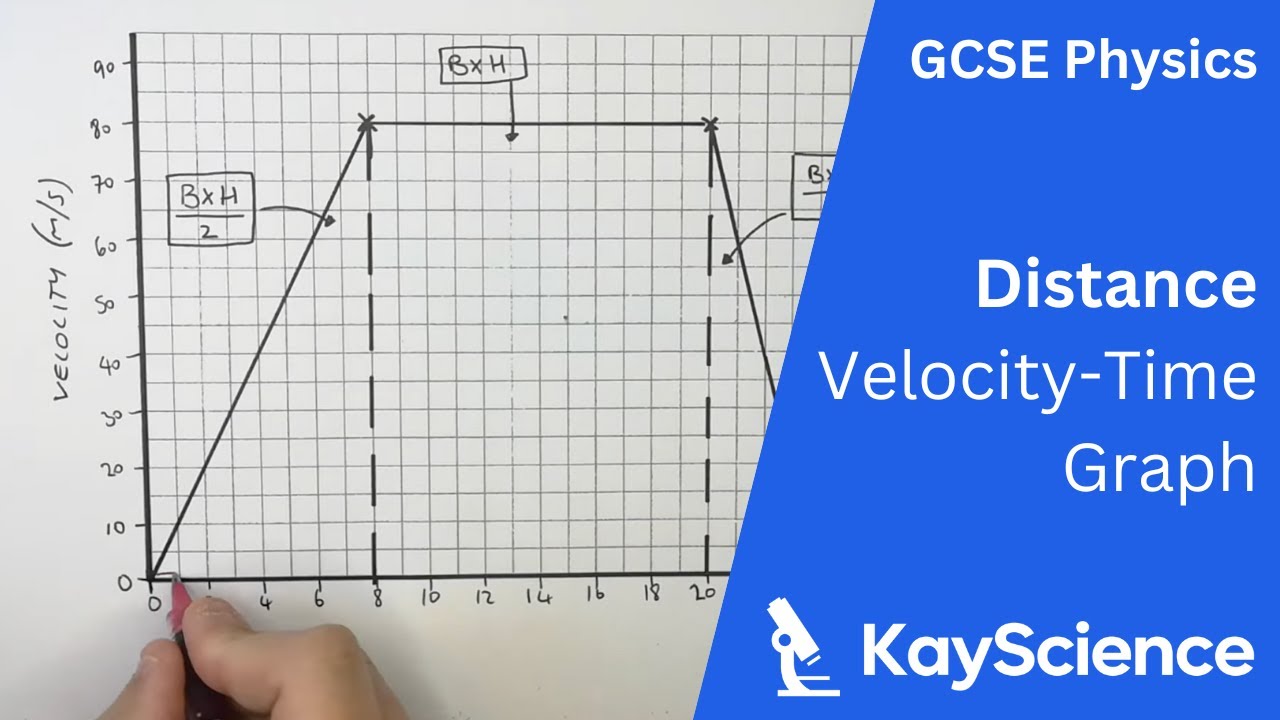
How do you calculate distance from a velocity-time graph?
Find the area under the graph.
How does the acceleration of an object depend on the resultant force acting on it?
Greater force = greater acceleration (Newton’s 2nd Law: F=mxa)
How does the mass of an object affect its acceleration?
Larger mass = smaller acceleration, if the same force is applied.
What is the formula for resultant force?
force = mass x acceleration
What is the difference between mass and weight?
Mass is the amount of matter in an object (kg)
Weight is the force due to gravity acting on mass (N)
How do you calculate weight?
weight = mass × gravitational field strength
Describe the motion of a falling object acted on only by gravity. ( force of gravity )
It accelerates at 9.8 m/s² until air resistance balances gravity.
What is terminal velocity?
The constant speed an object reaches when the forces of gravity and air resistance are balanced.
What can be said about the resultant force acting on an object falling at terminal velocity?
The resultant force is zero, so the object moves at a constant velocity.