Anatomy - Bones/Muscles/TMJ
1/193
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
194 Terms
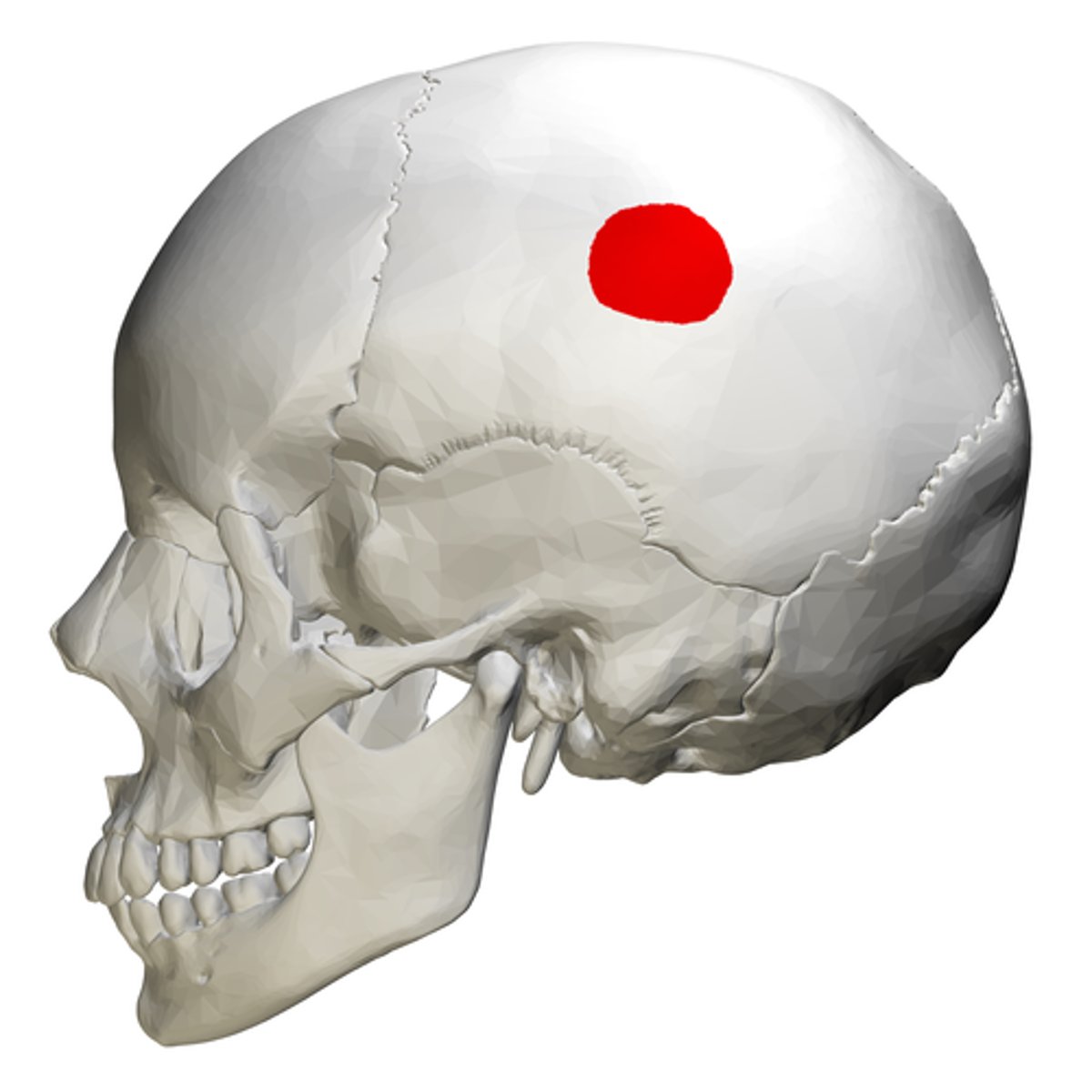
parietal bone
What is shown on the image?
Frontal bone
What is shown on the image?

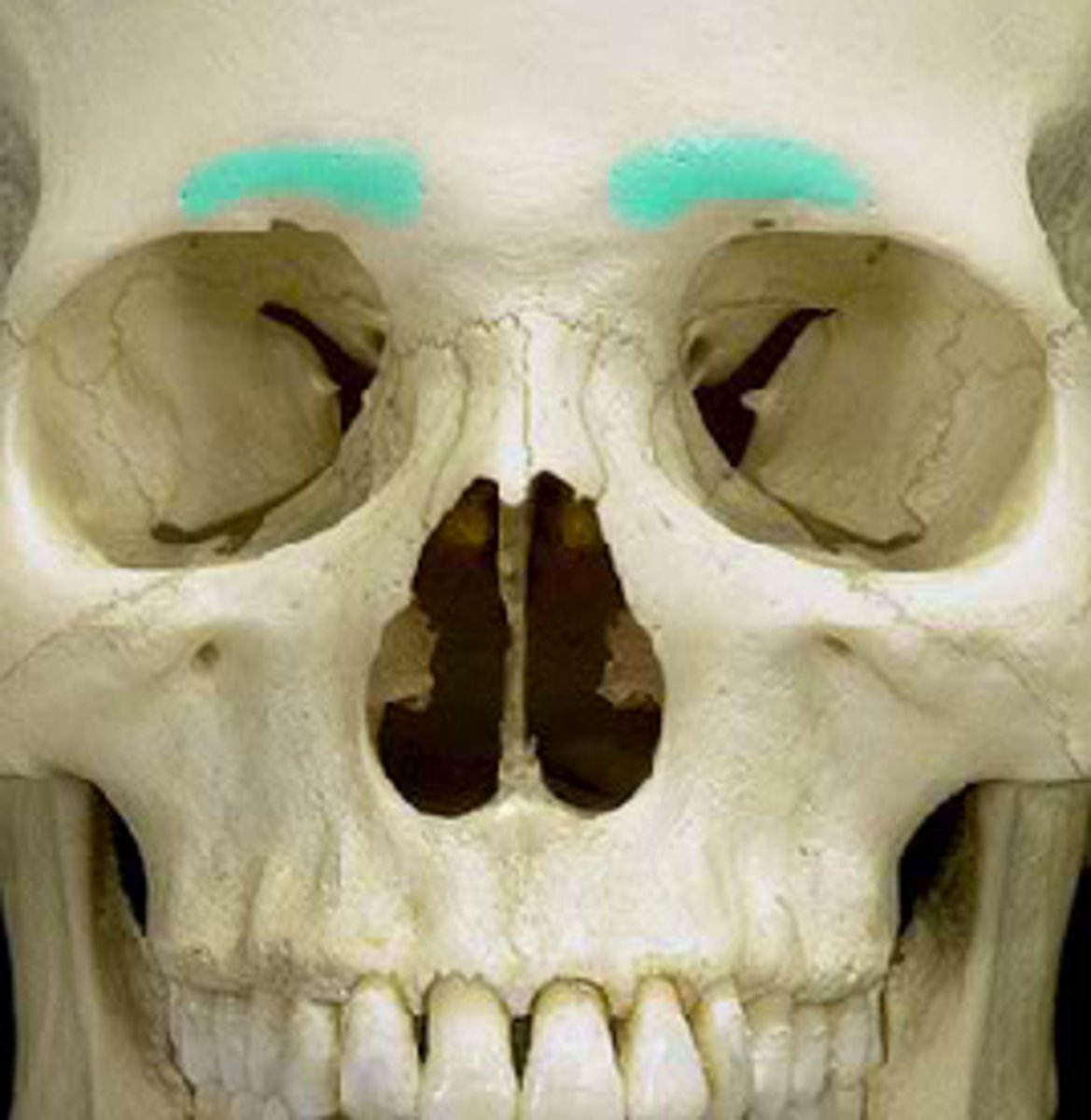
Supraorbital ridge
What is shown on the image?
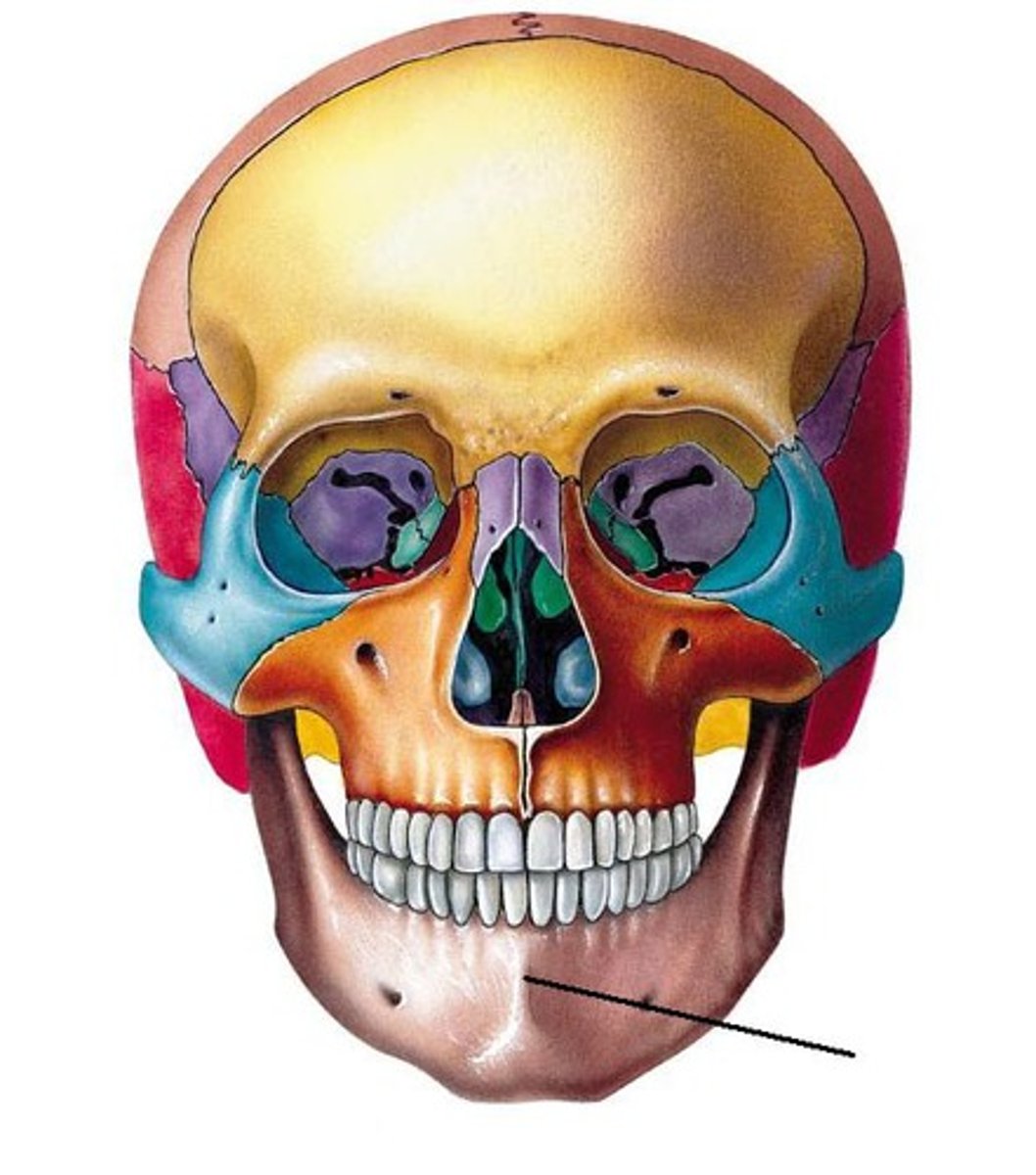
Nasal region
What is shown on the image?
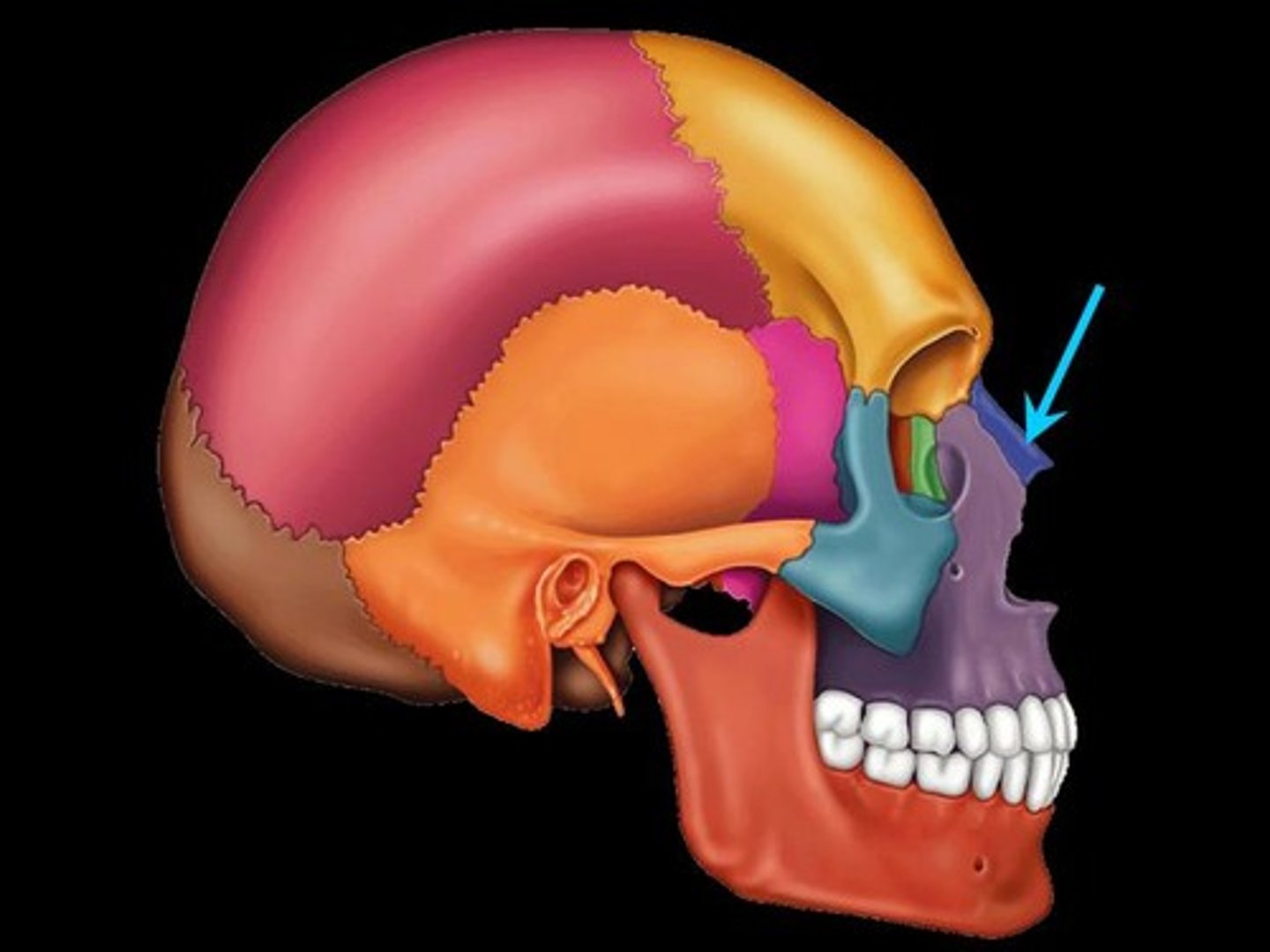
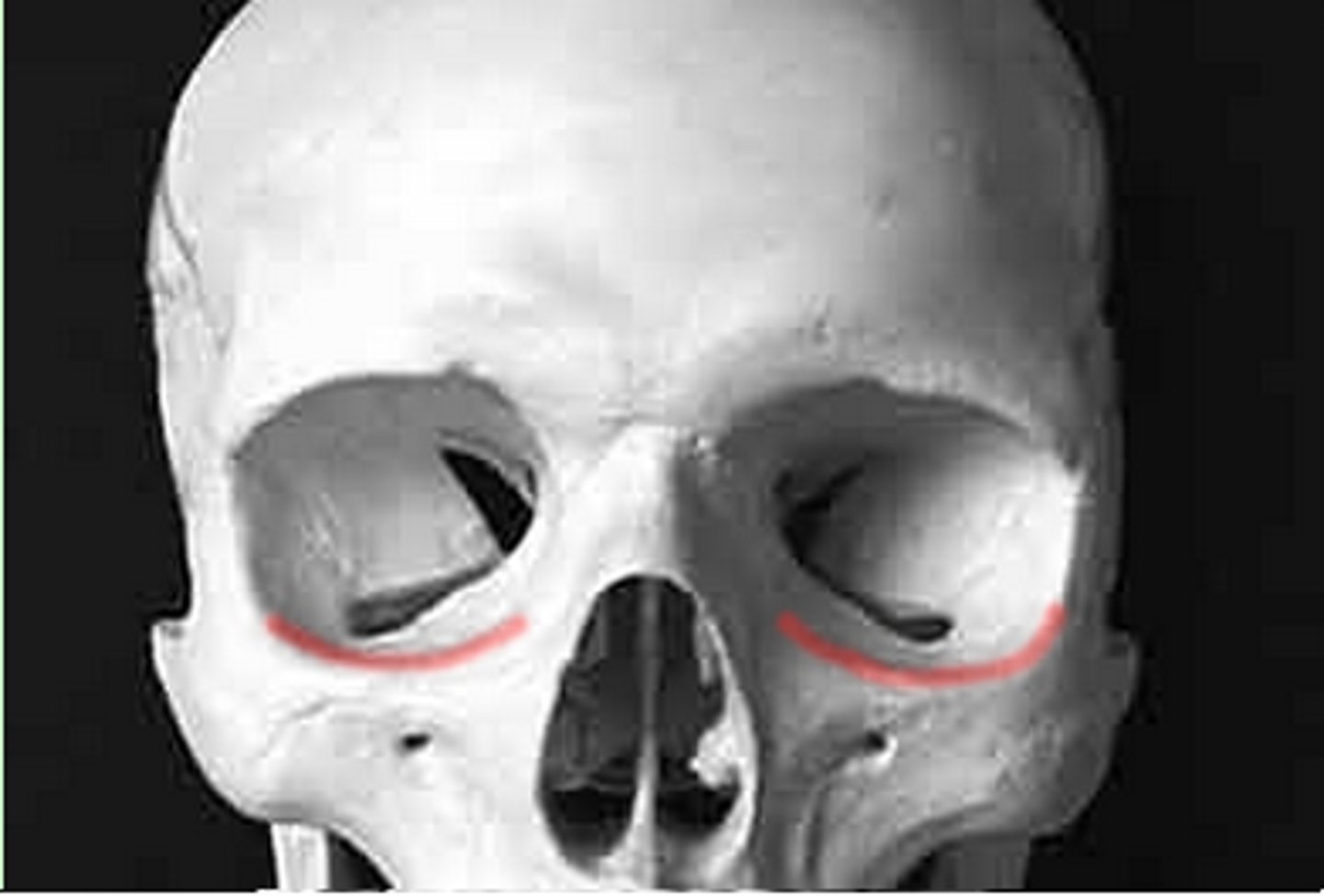
Infraorbital region
What is shown on the image?
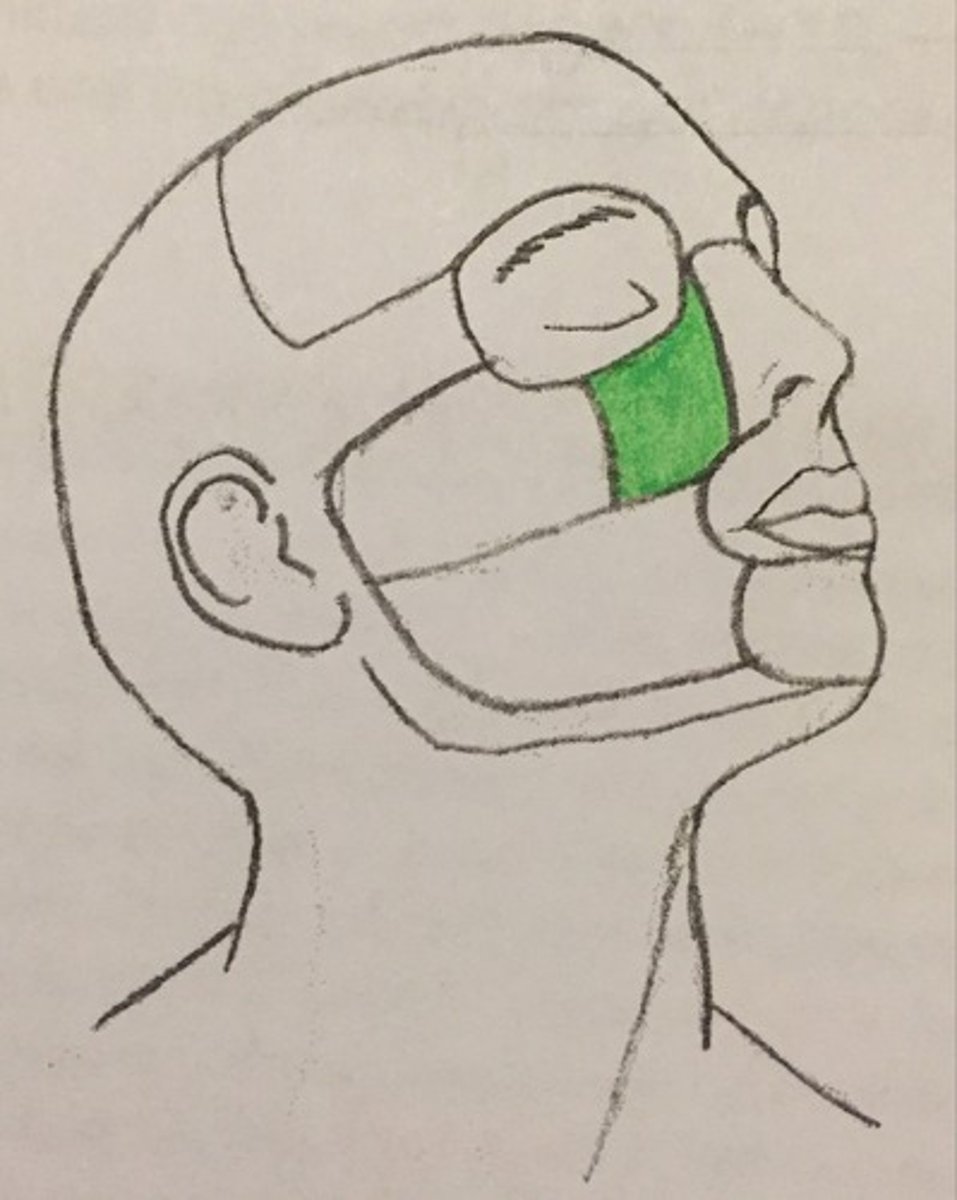
Mental region
What is shown on the image?
Buccal region
What is shown on the image?
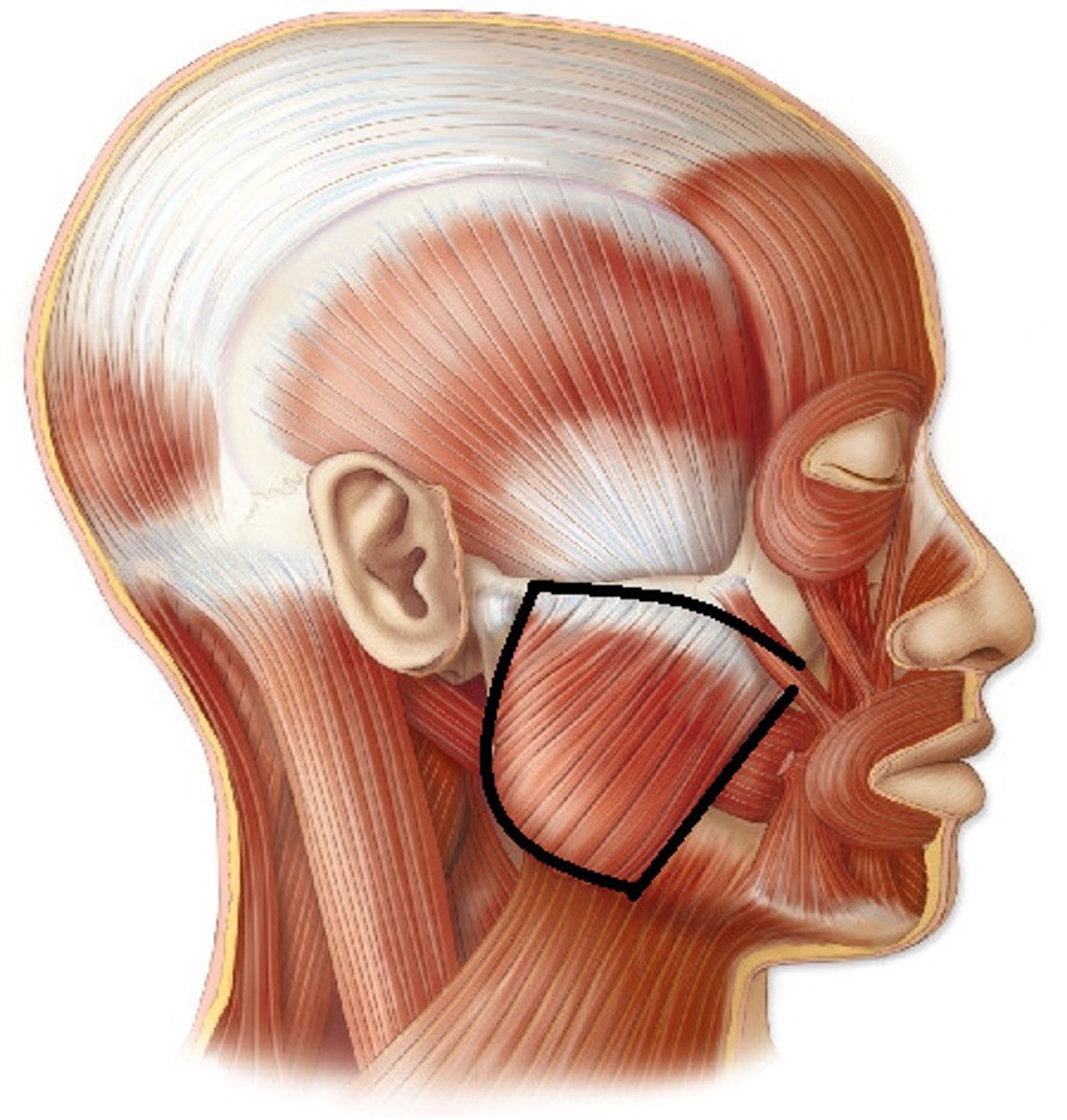
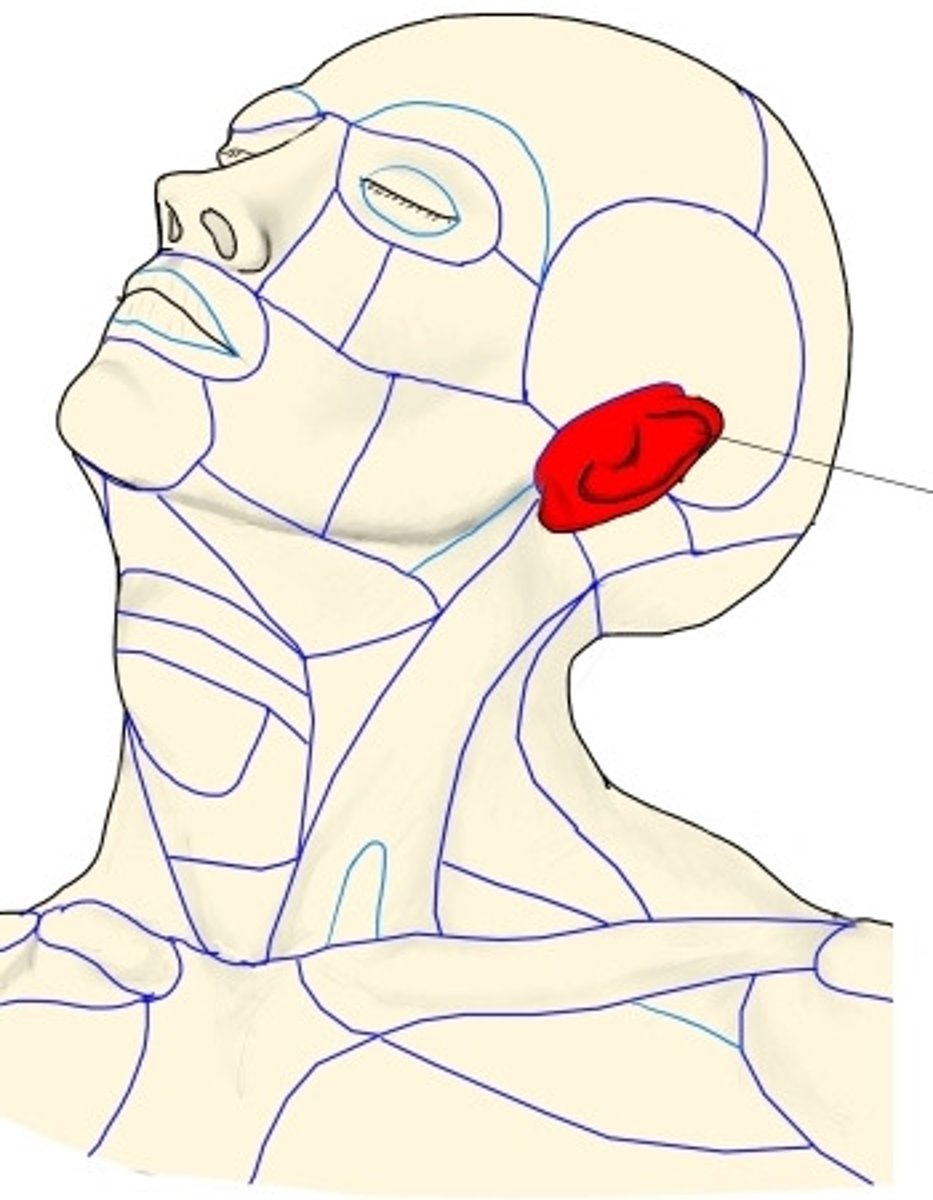
Parotid region
What is shown on the image?
Zygomatic region
What is shown on the image?
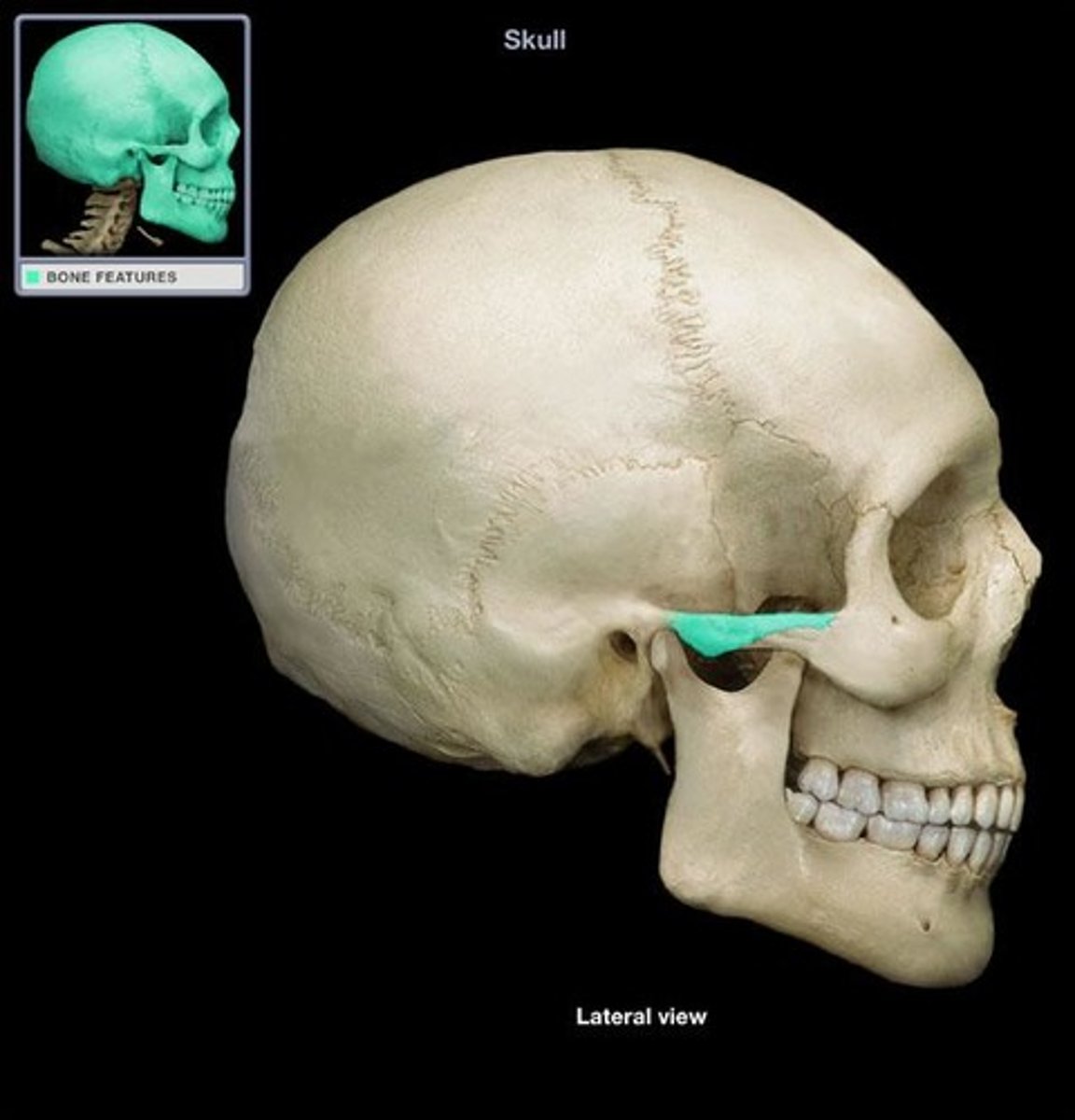
Auricular region
What is shown on the image?
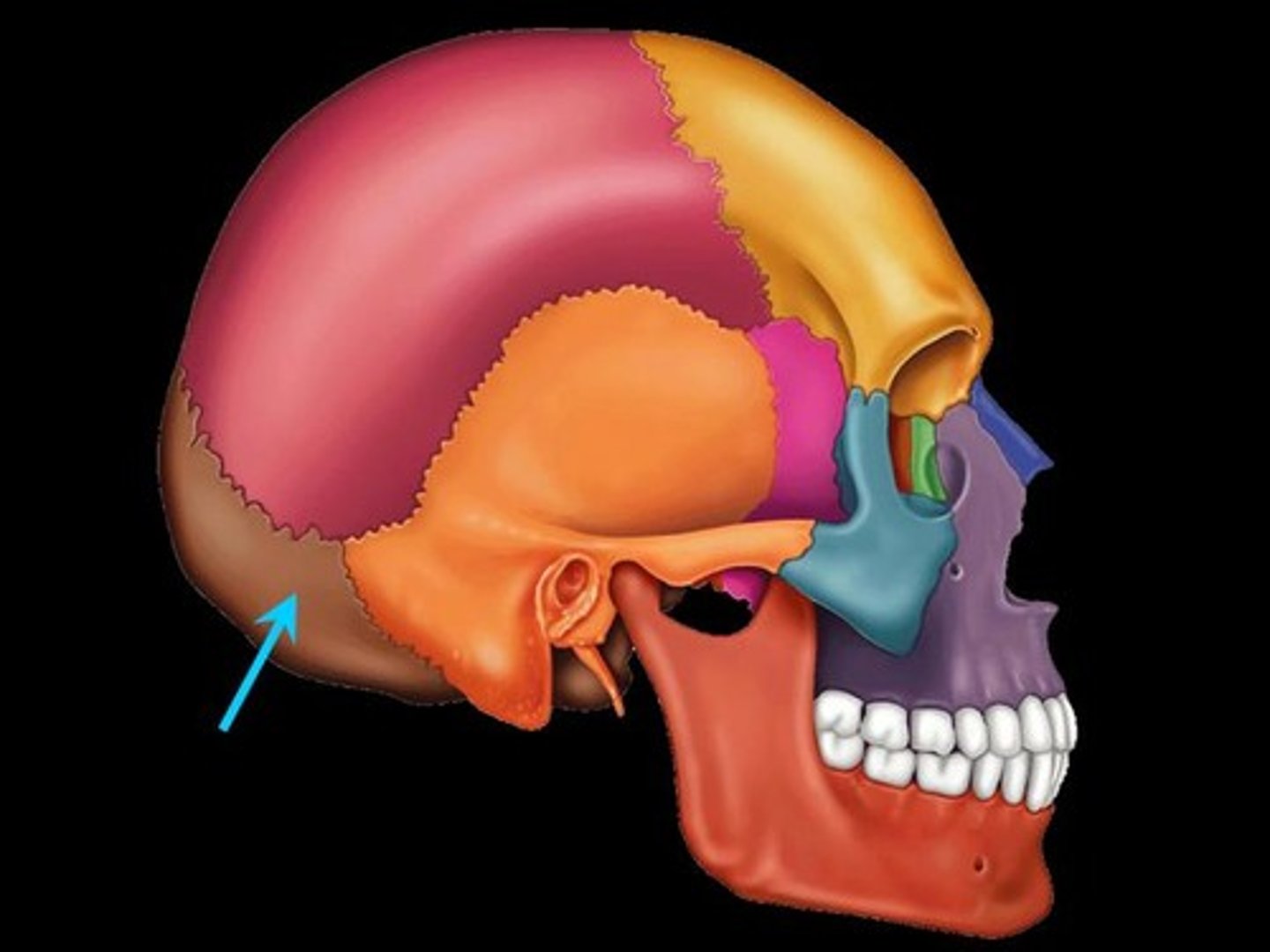
Occipital region
What is shown on the image?
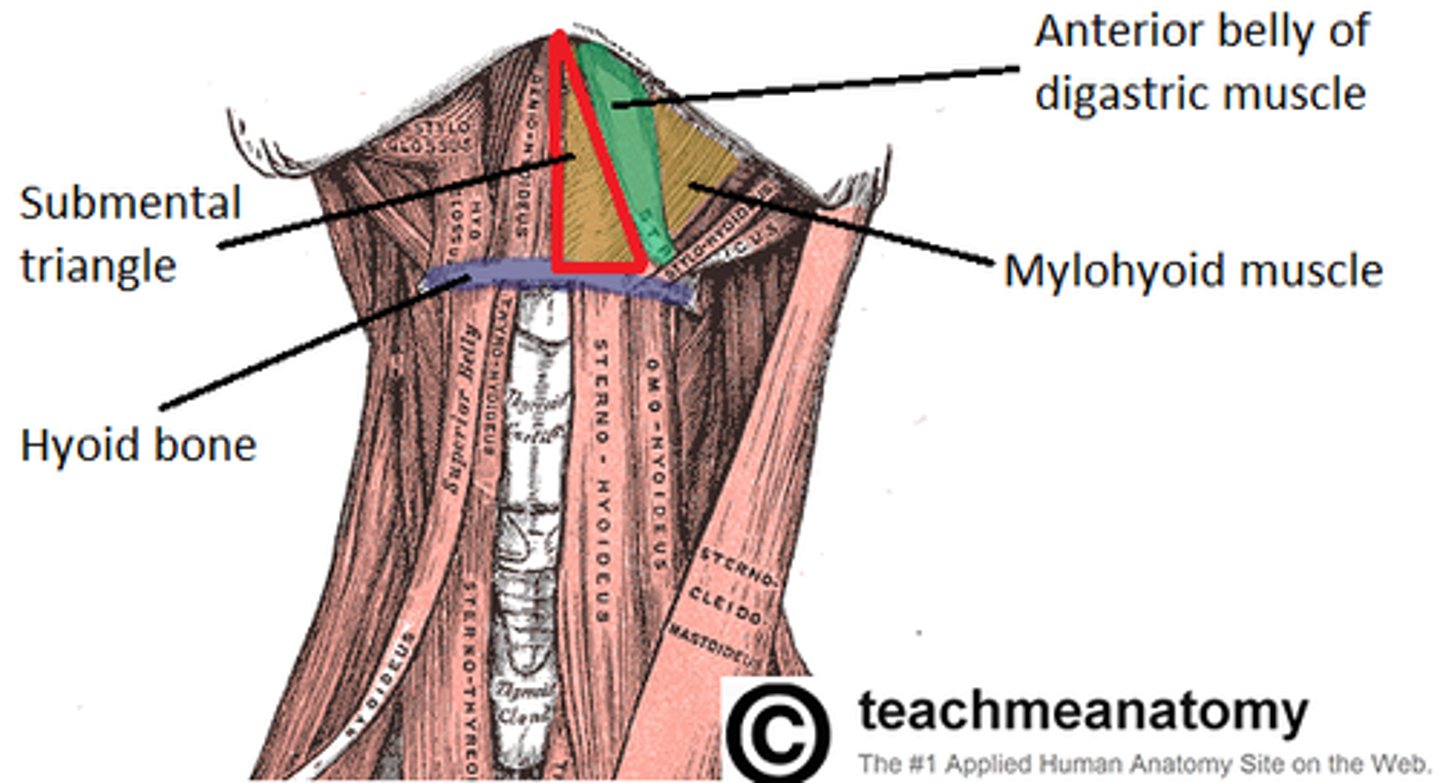
Submental triangle
What is shown on the image?
Submandibular triangle
What is shown on the image?

Carotid traingle
What is shown on the image?
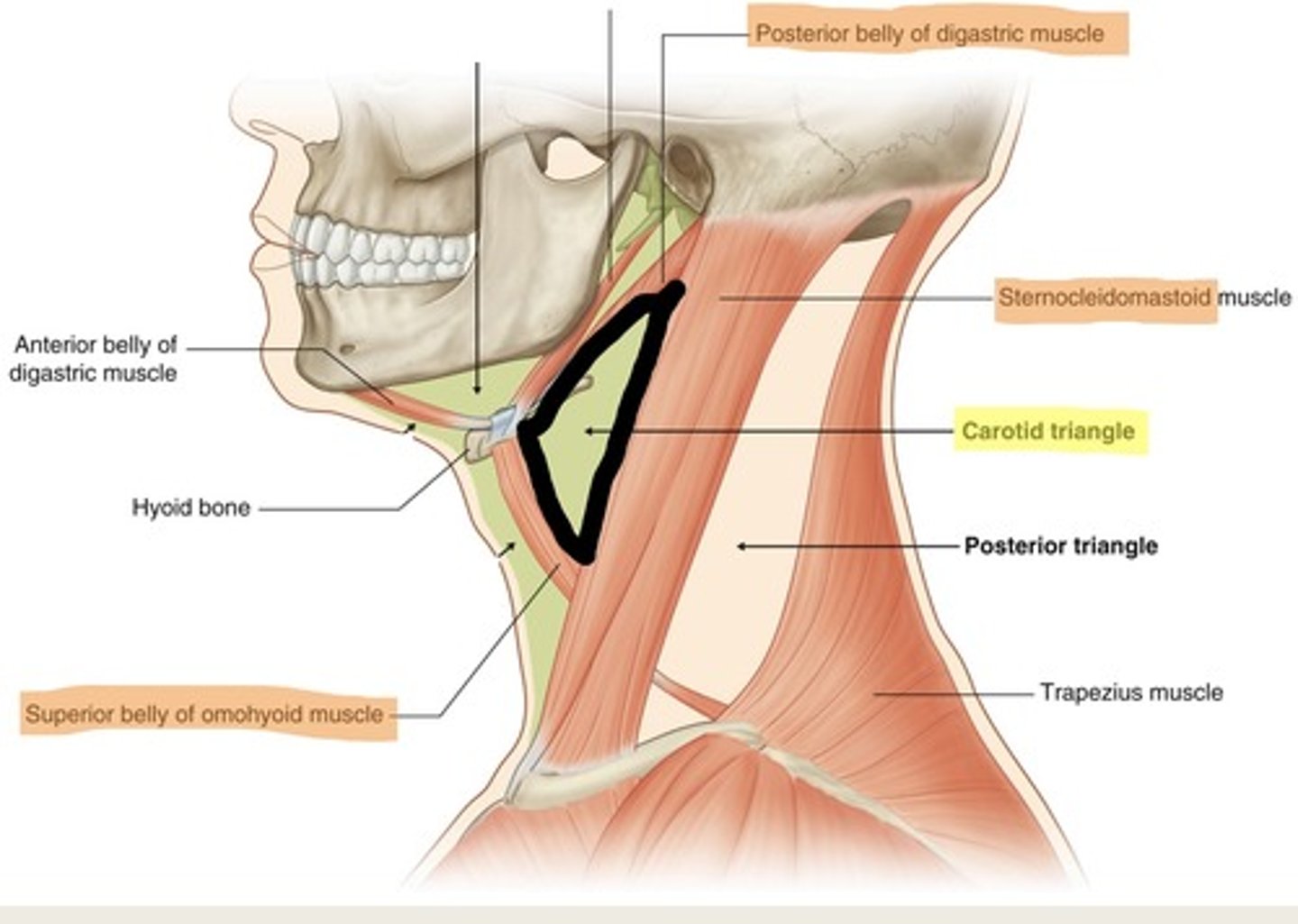
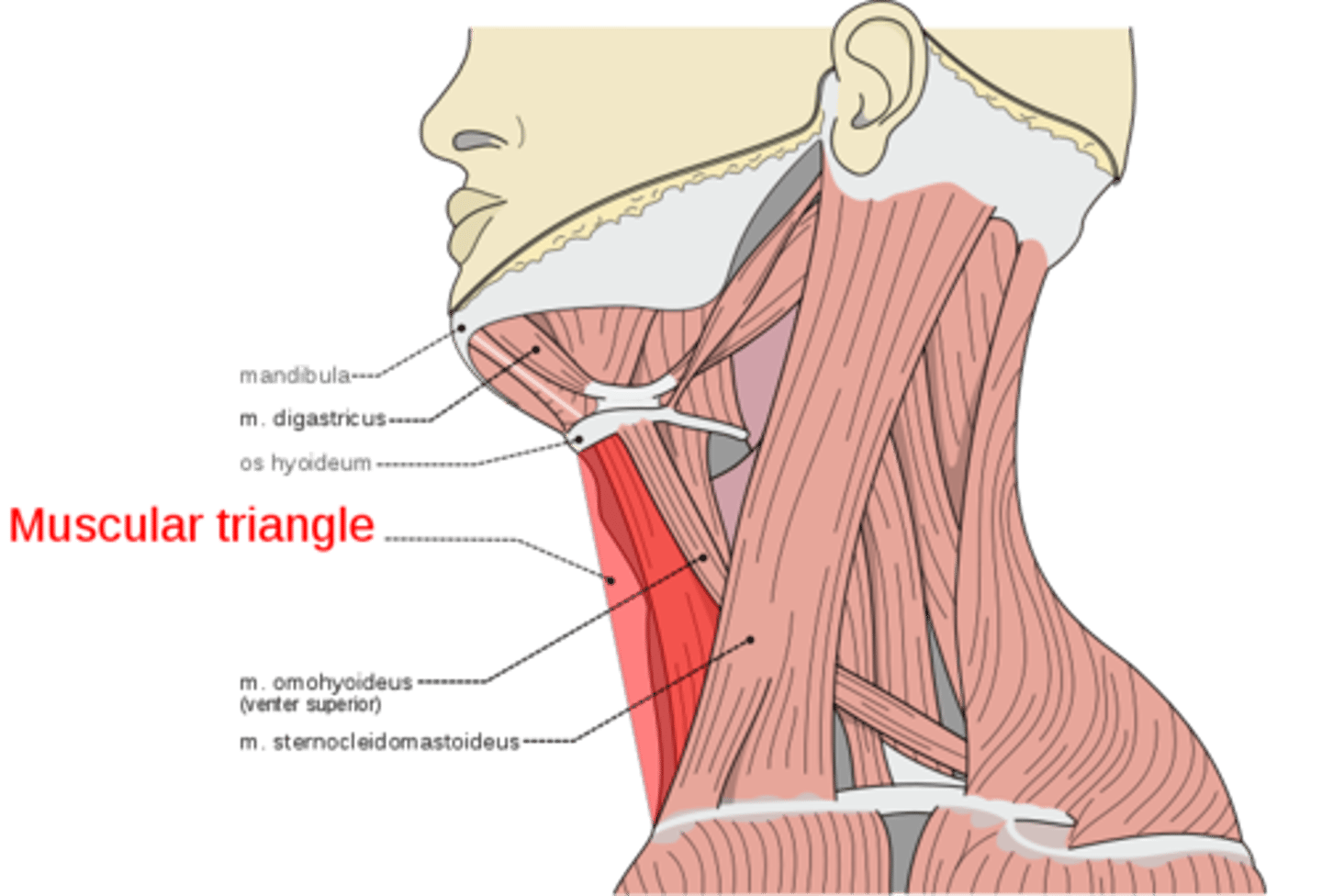
Muscular triangle
What is shown on the image?
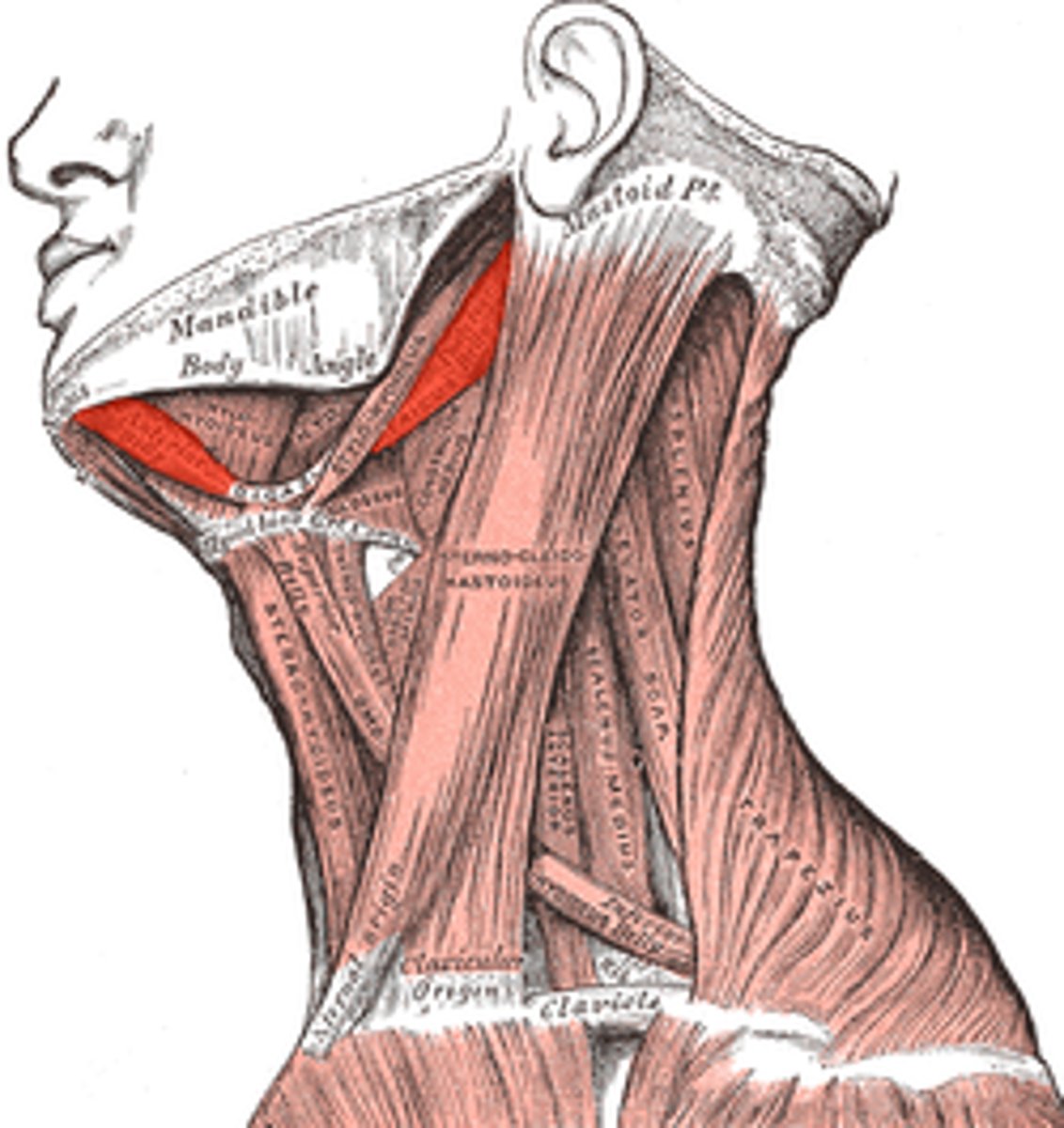
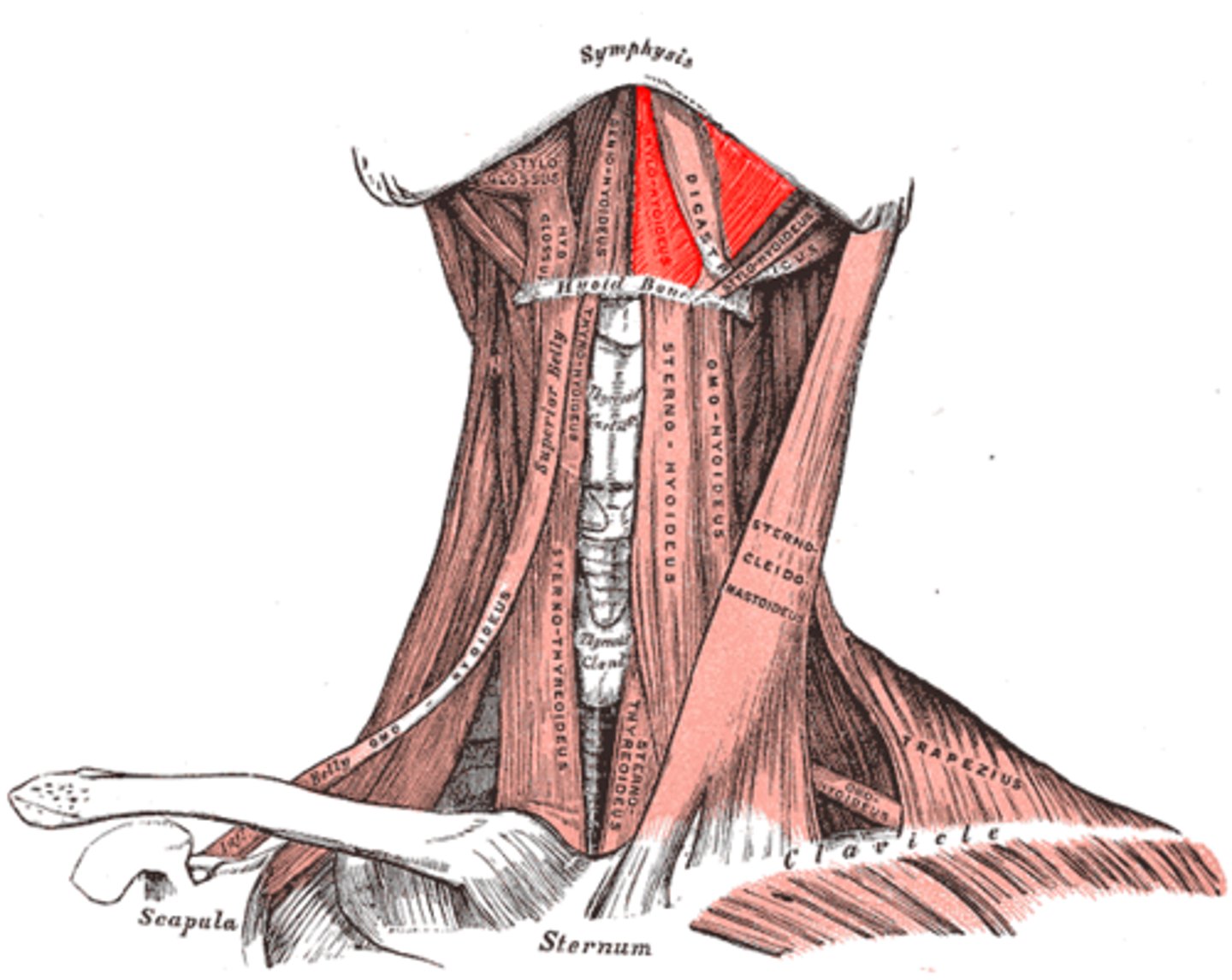
Digastric muscle
What is shown on the image?
Mylohyoid muscle
What is shown on the image?
Omohyoid muscle
What is shown on the image?
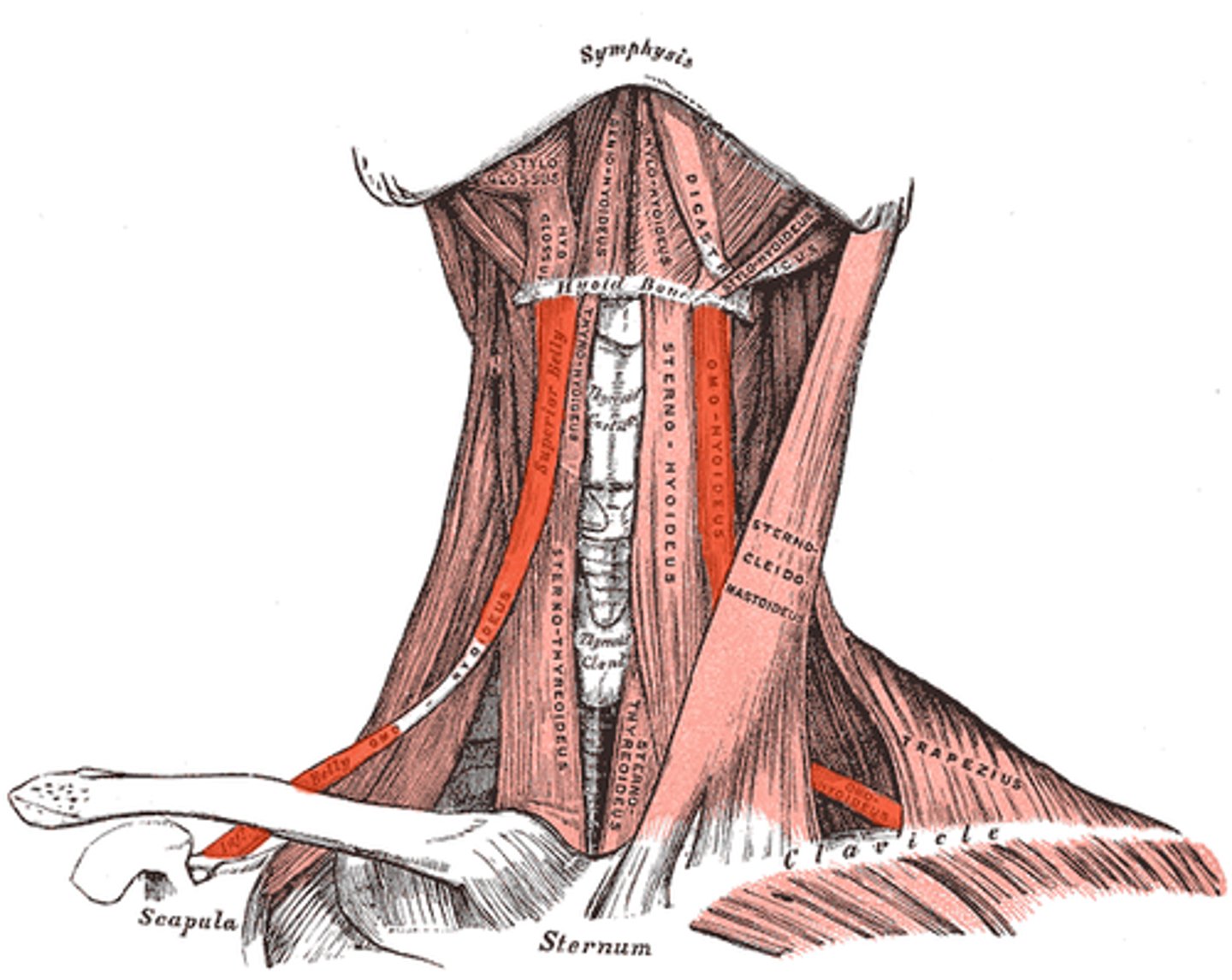
Sternocleidomastoid muscle
What is shown on the image?
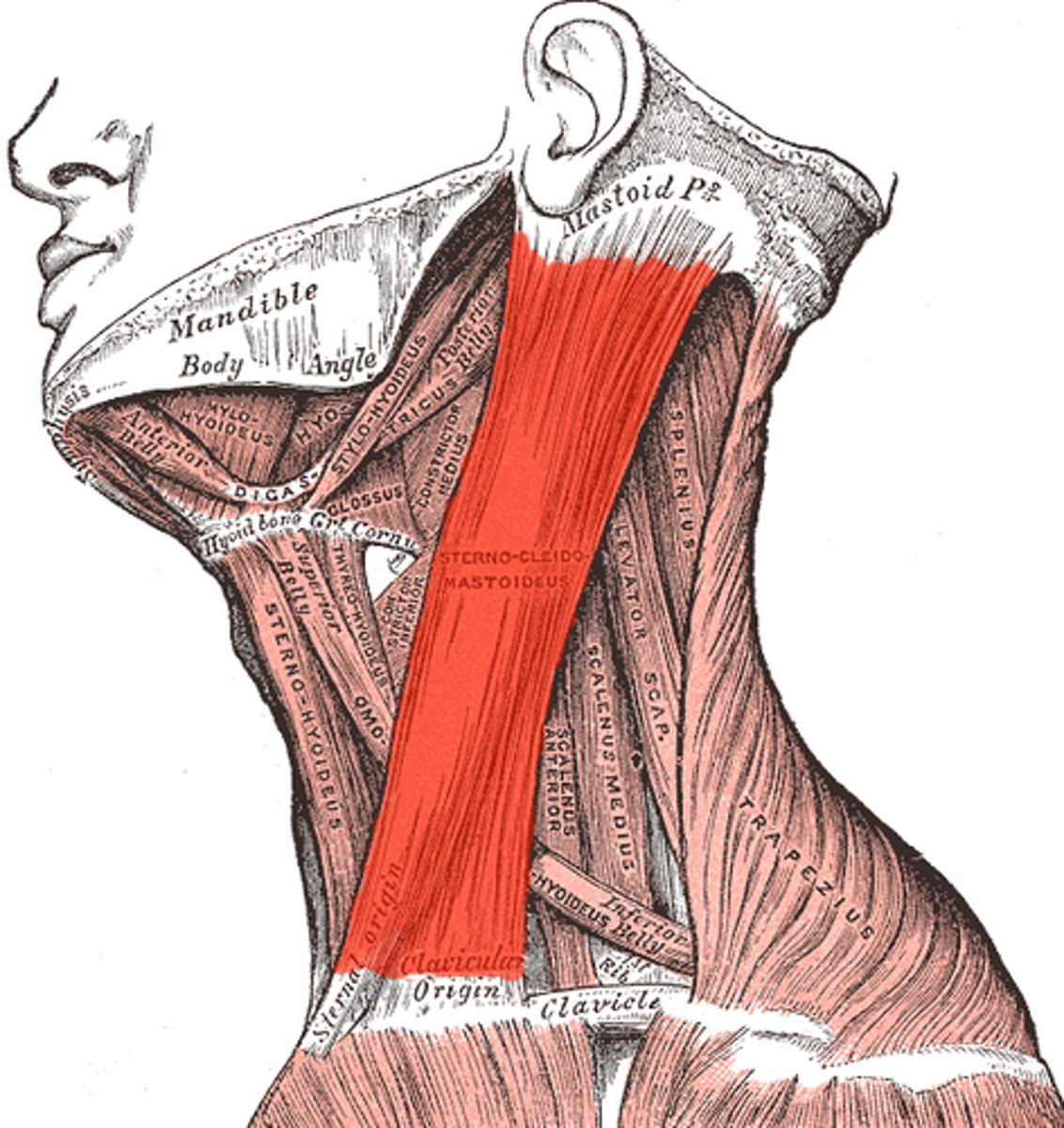
Occipital triangle
What is shown on the image?
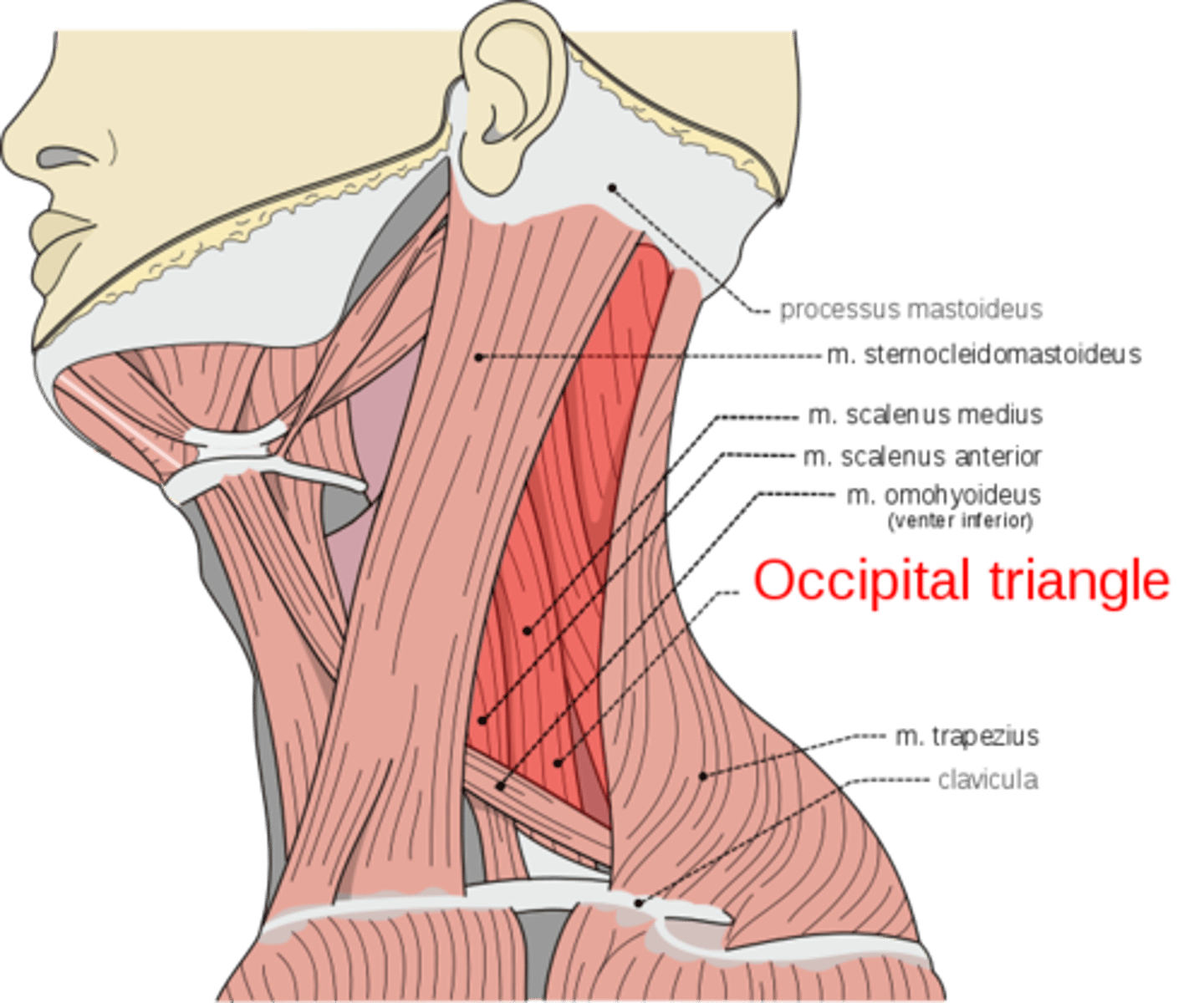
Subclavian triangle
What is shown on the image?
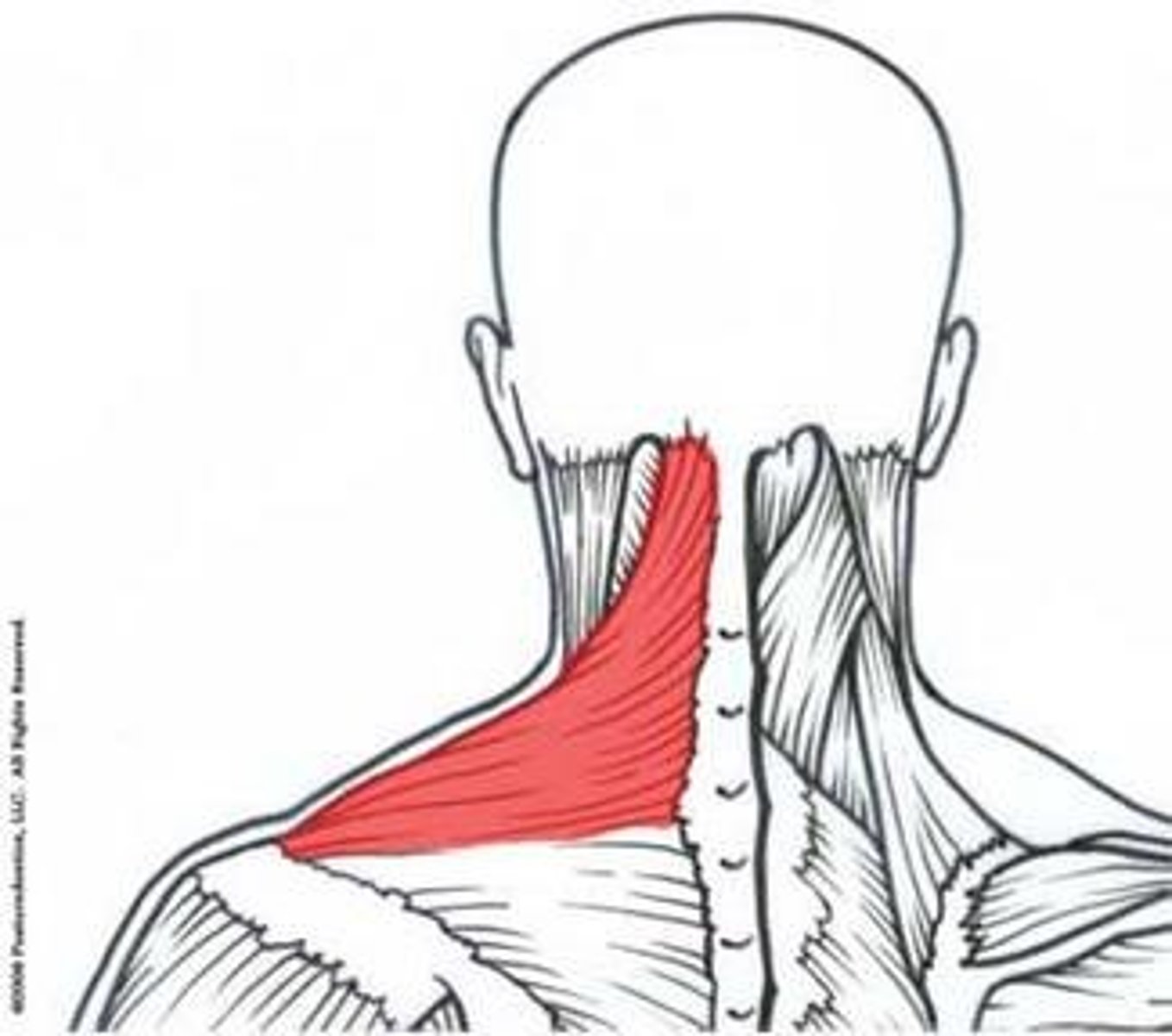
Trapezius muscle
What is shown on the image?
Clavicula
What is shown on the image?

Scalenus anterior, medius, posterior
What is shown on the image?

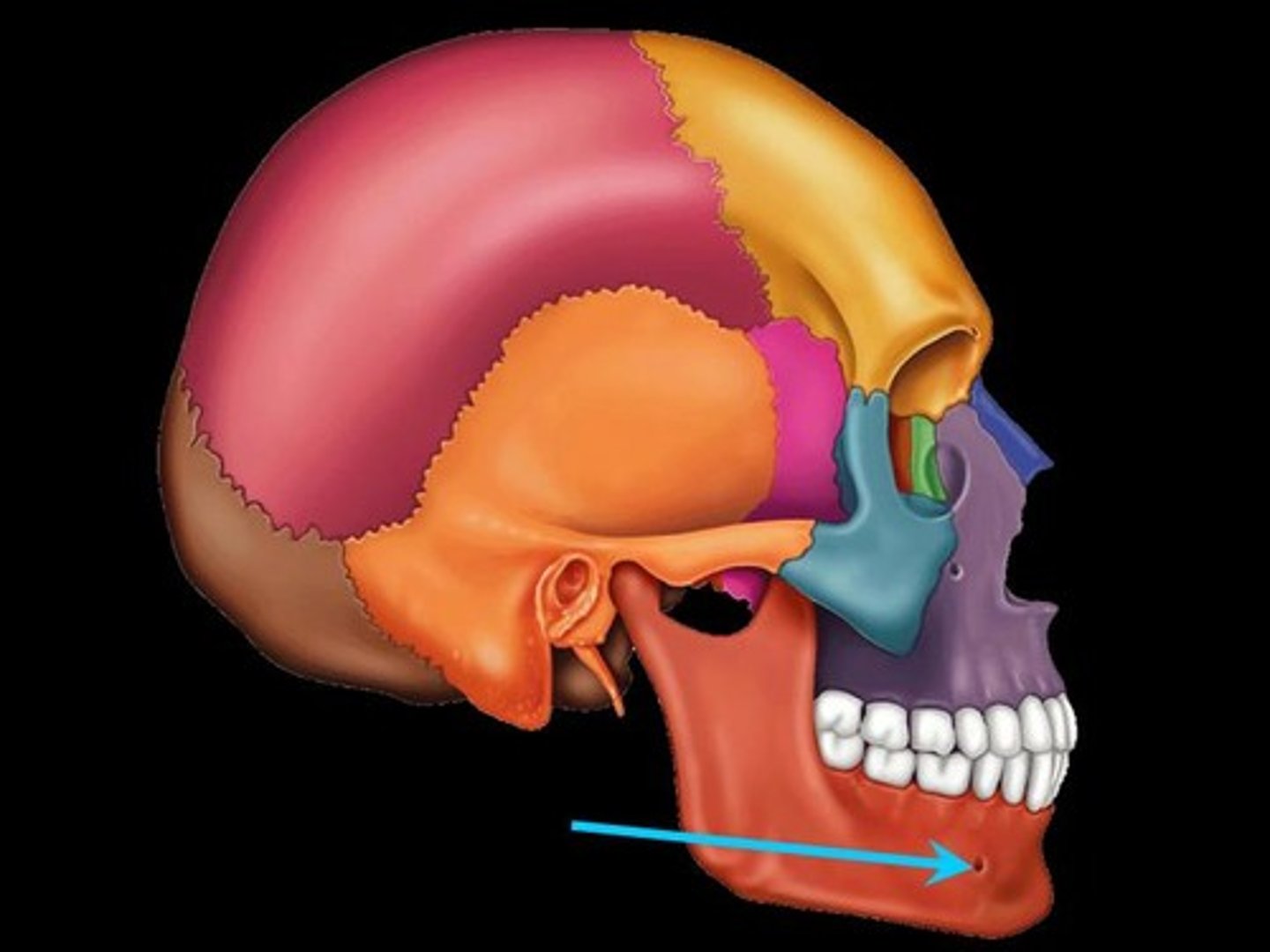
22 - paired and single
There are how many bones of the head?
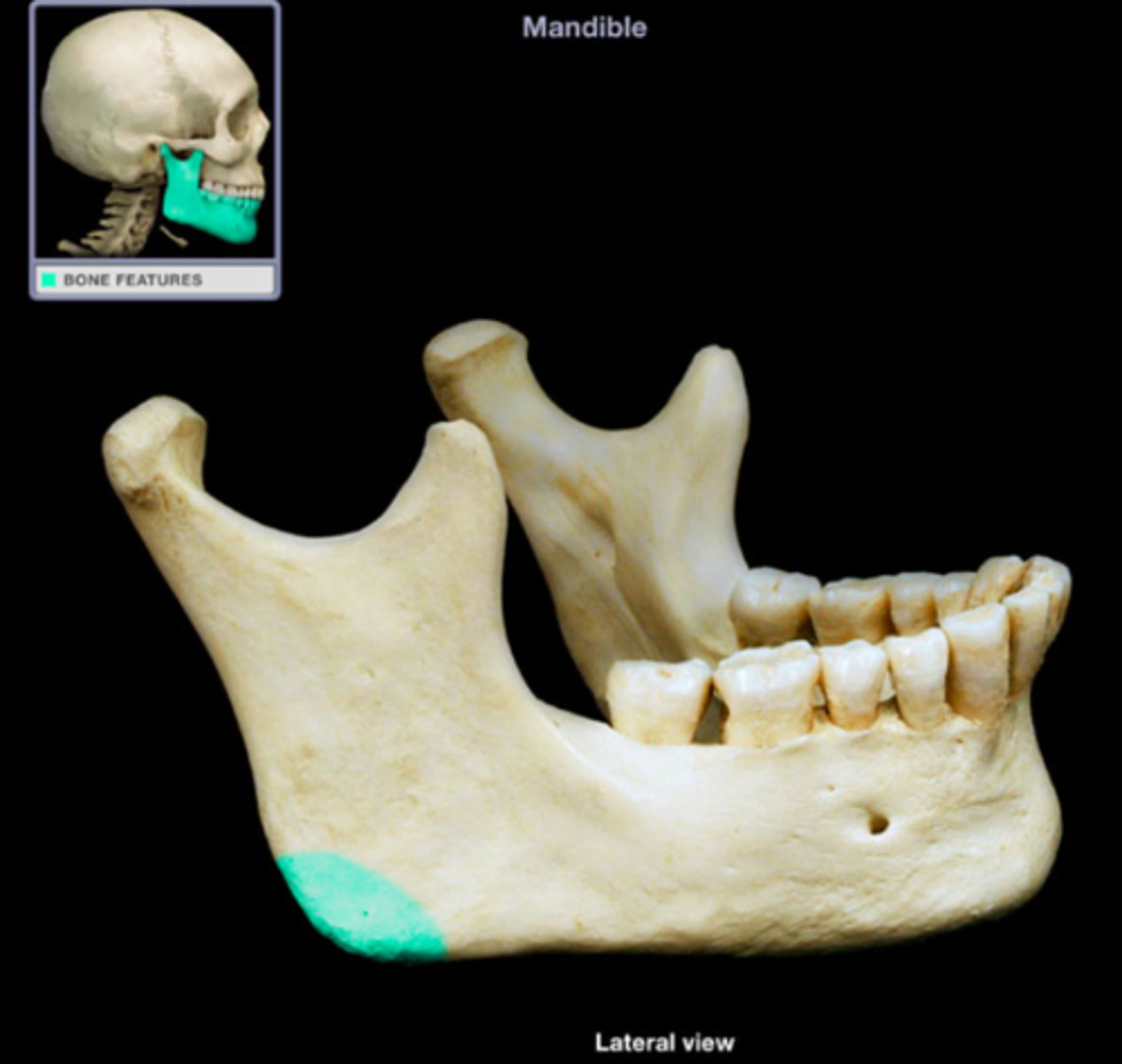
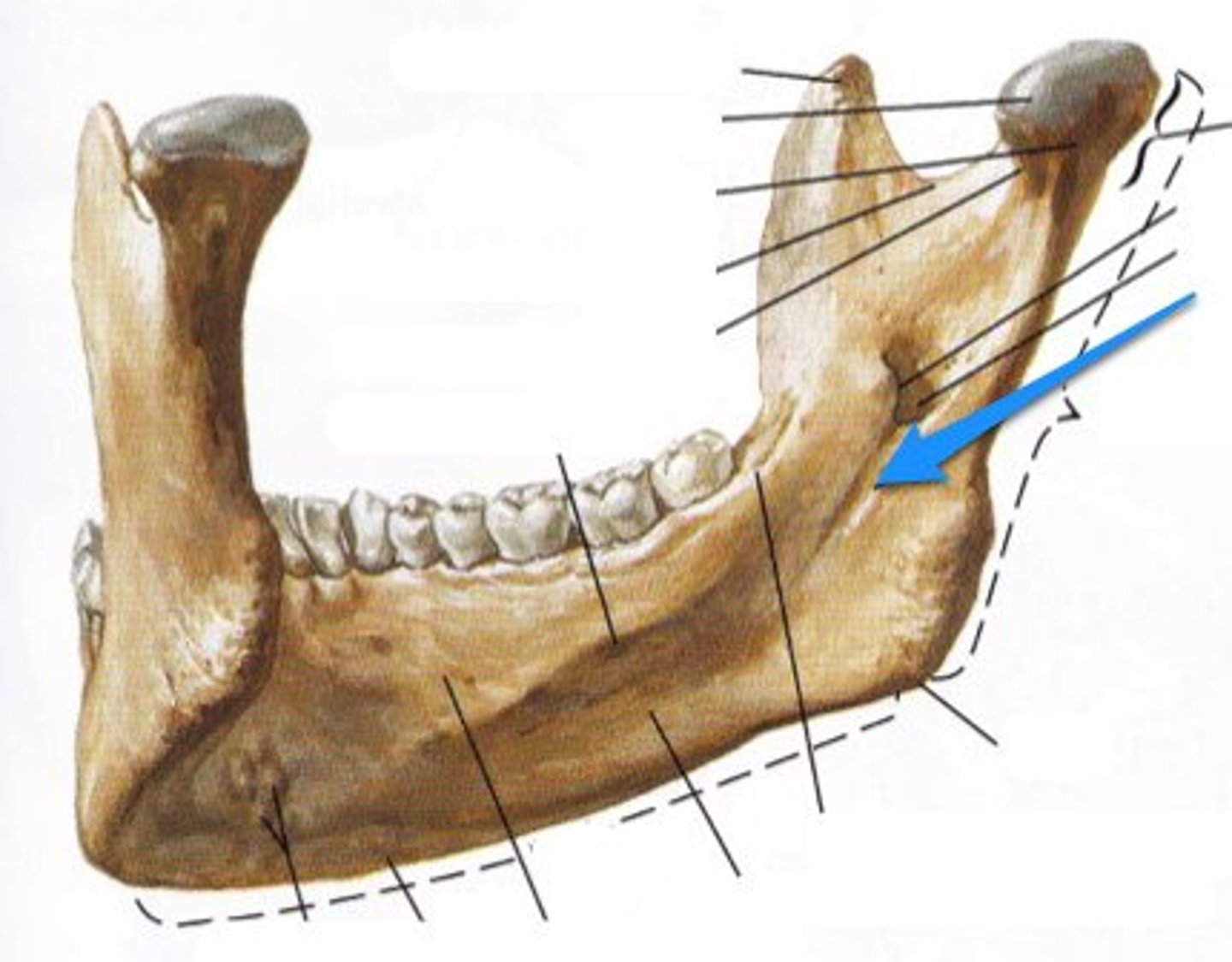
Ramus
What is shown on the image?
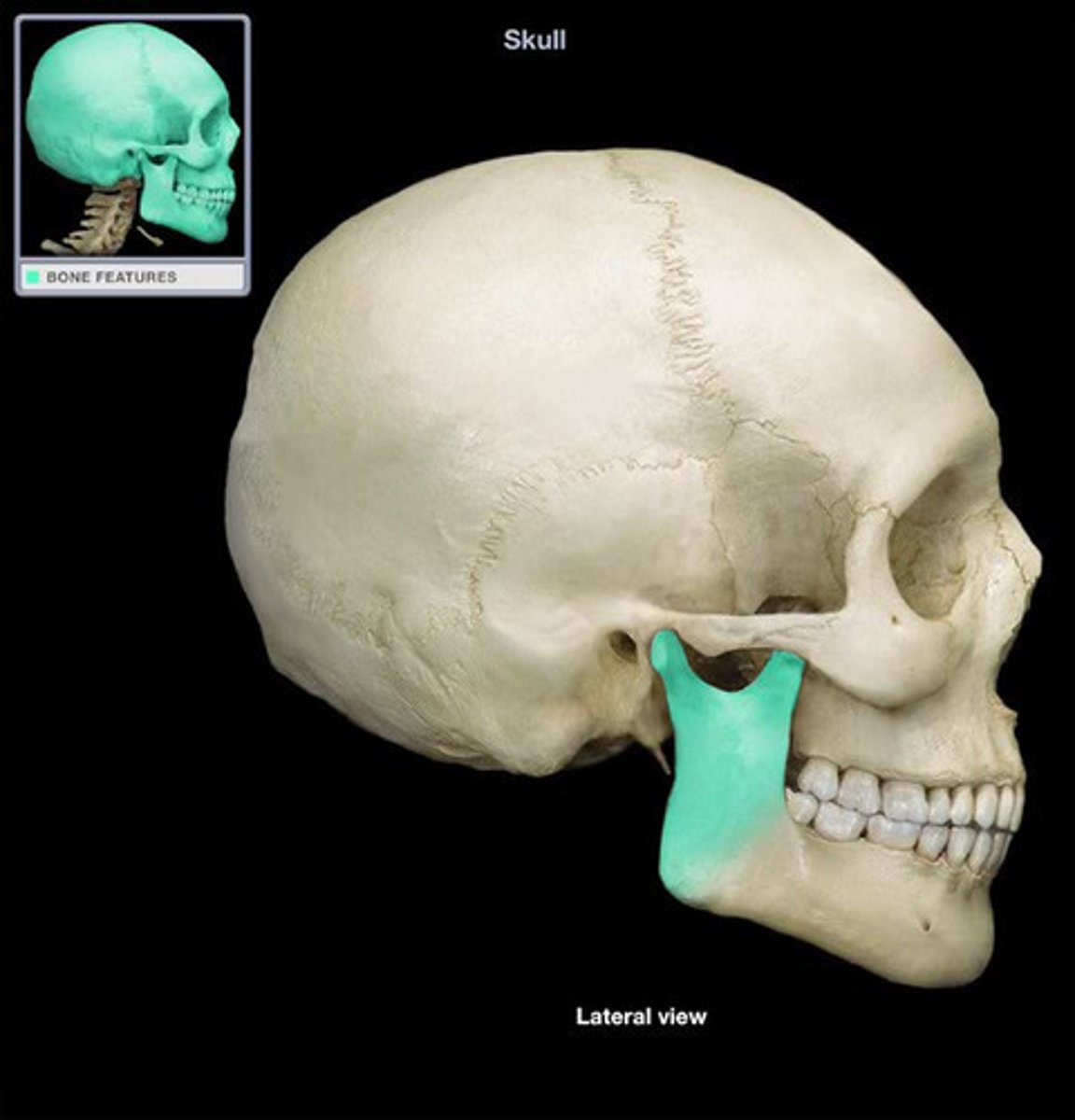
Angle of jaw
What is shown on the image?
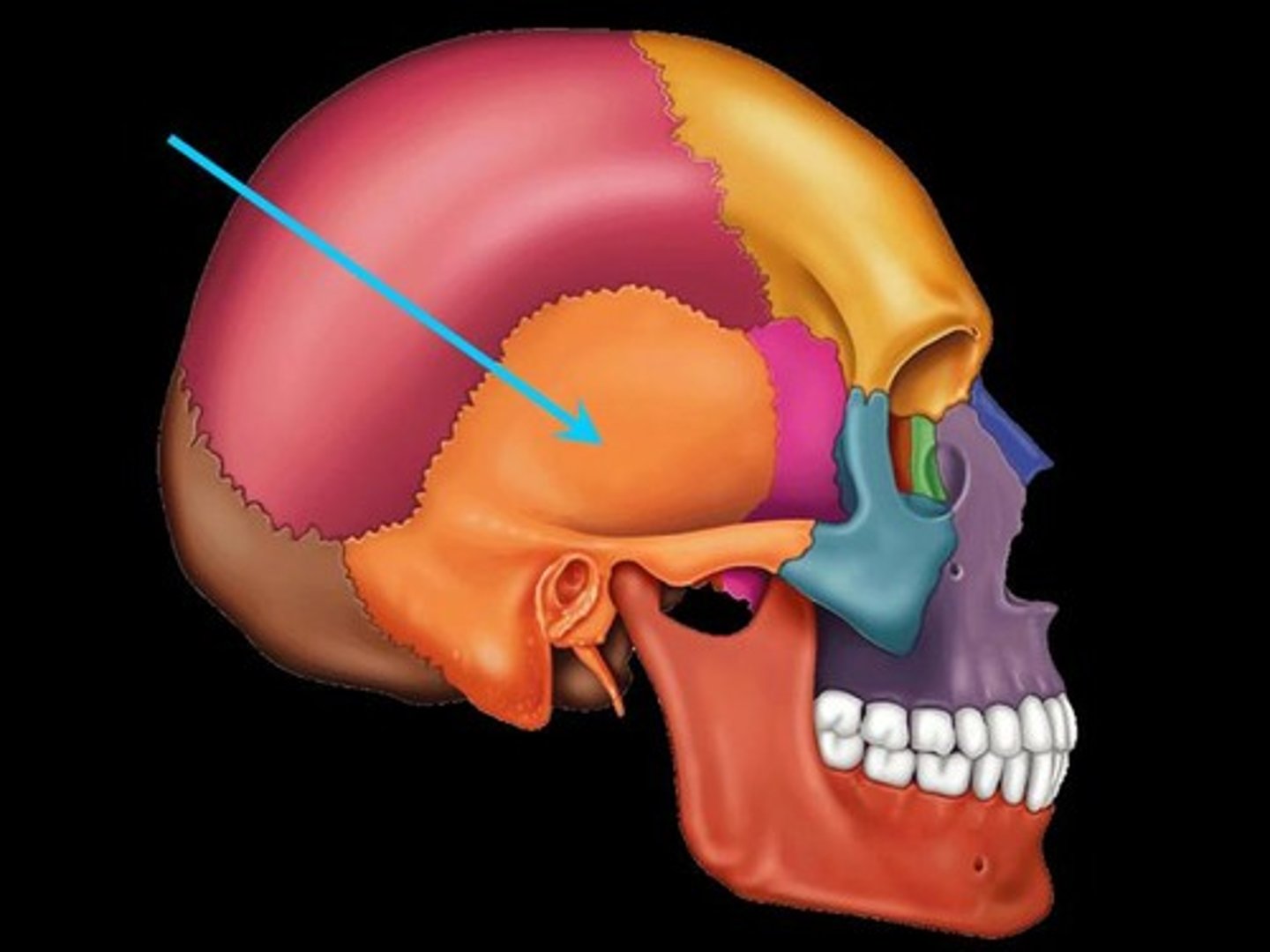
Temporal bone
What is shown on the image?
Nasal concha
What is shown on the image?
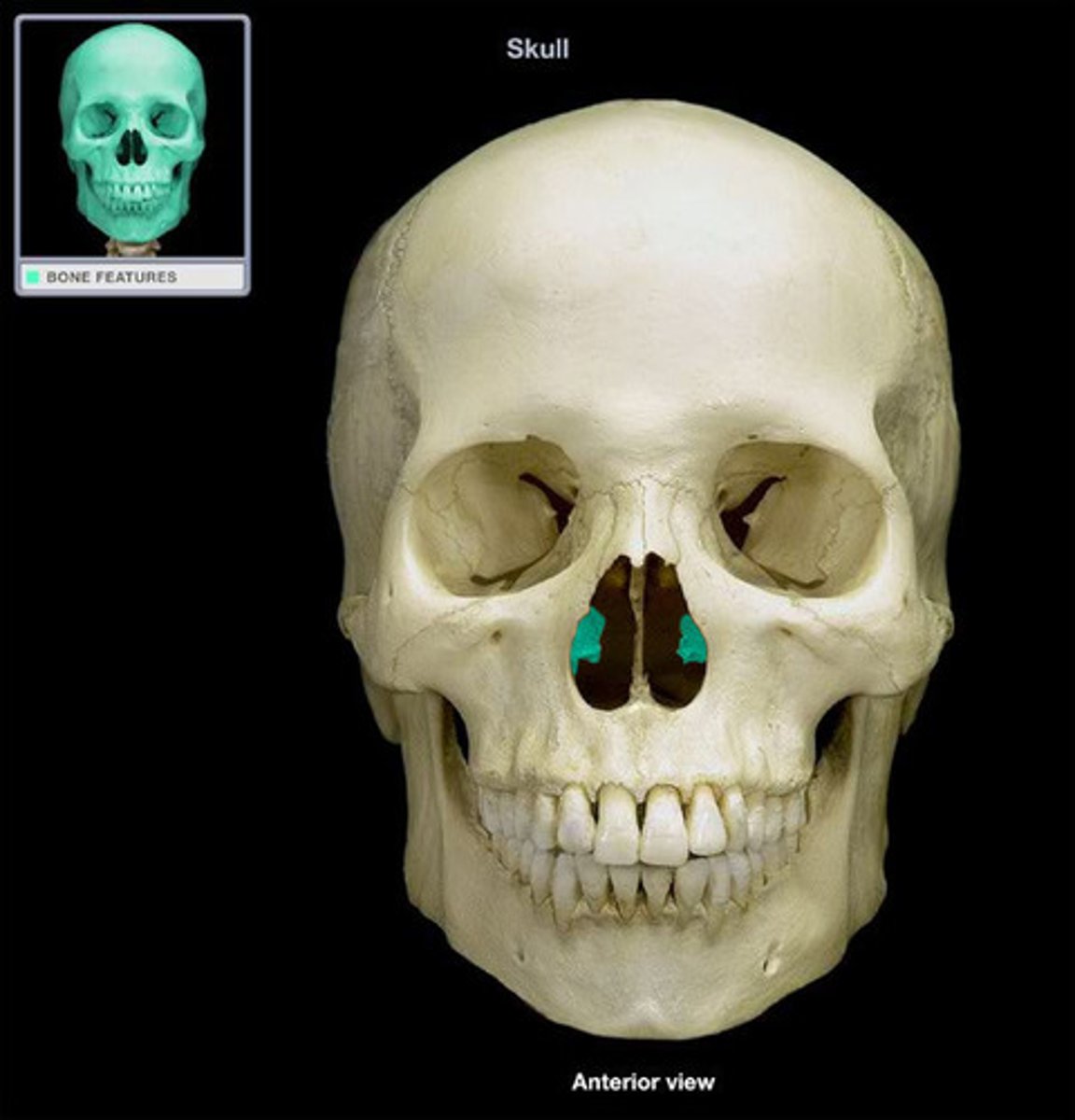
Mental tuberosity
What is shown on the image?
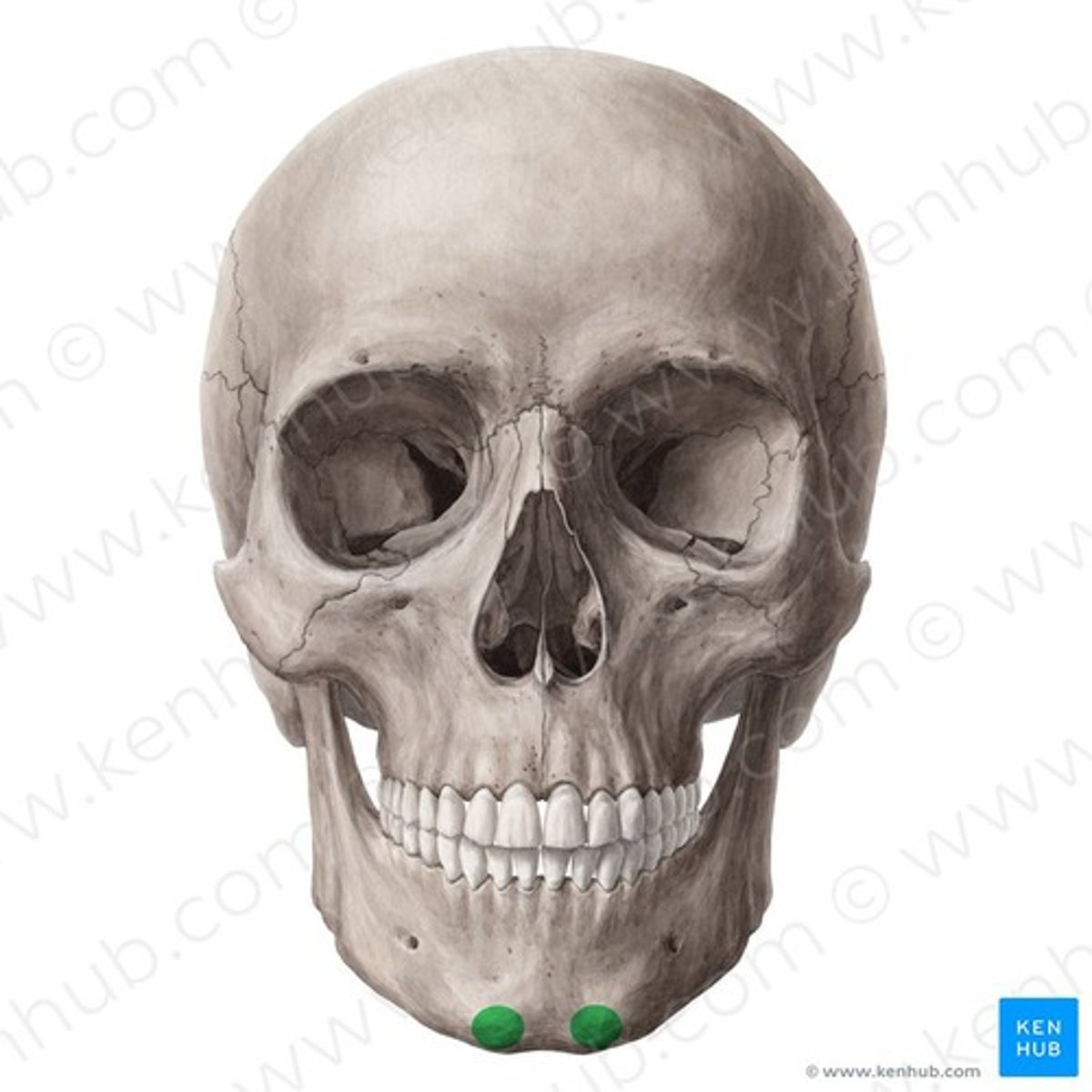
Mental protuberance
What is shown on the image?
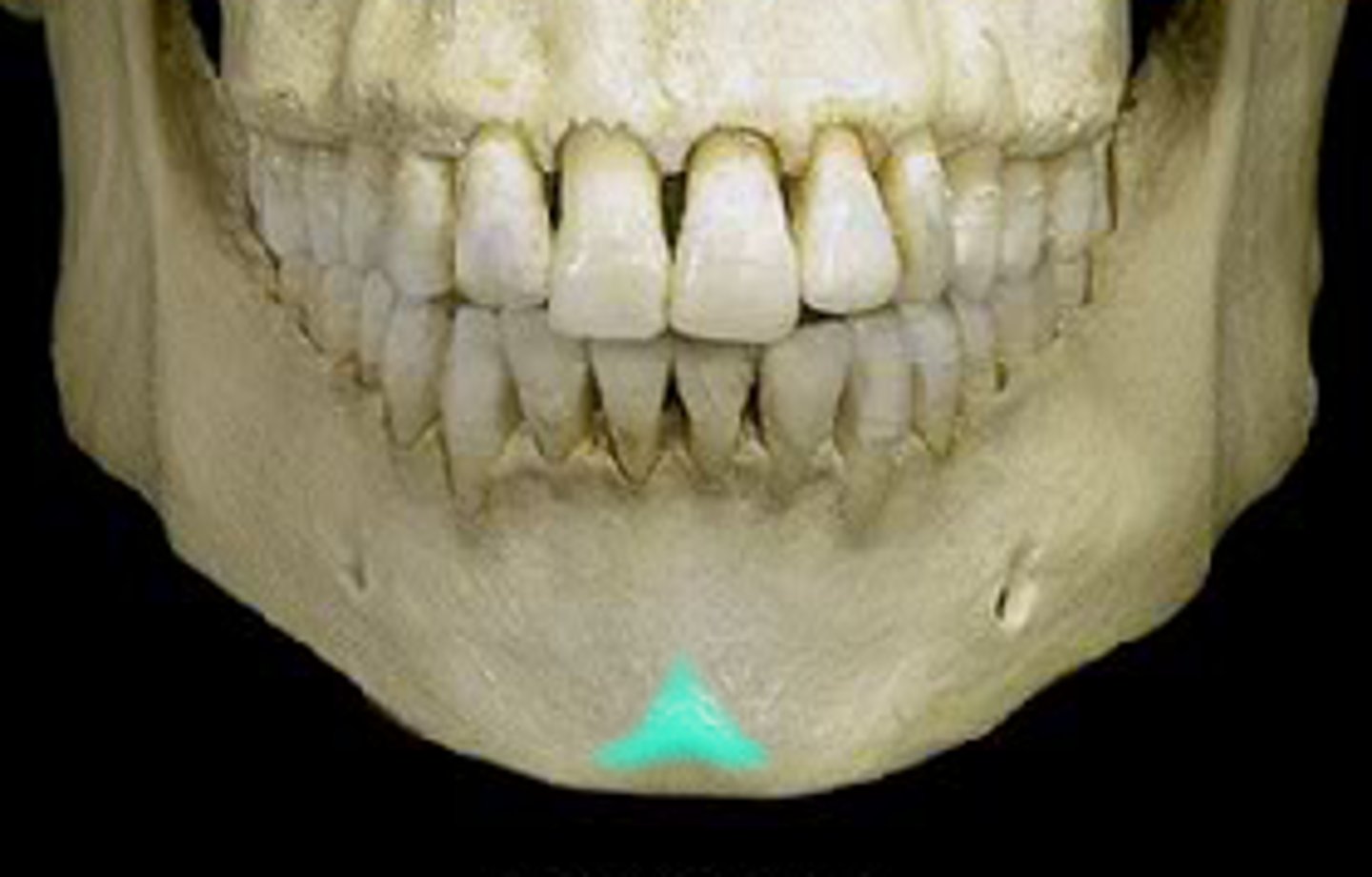
Coronal suture
What is shown on the image?

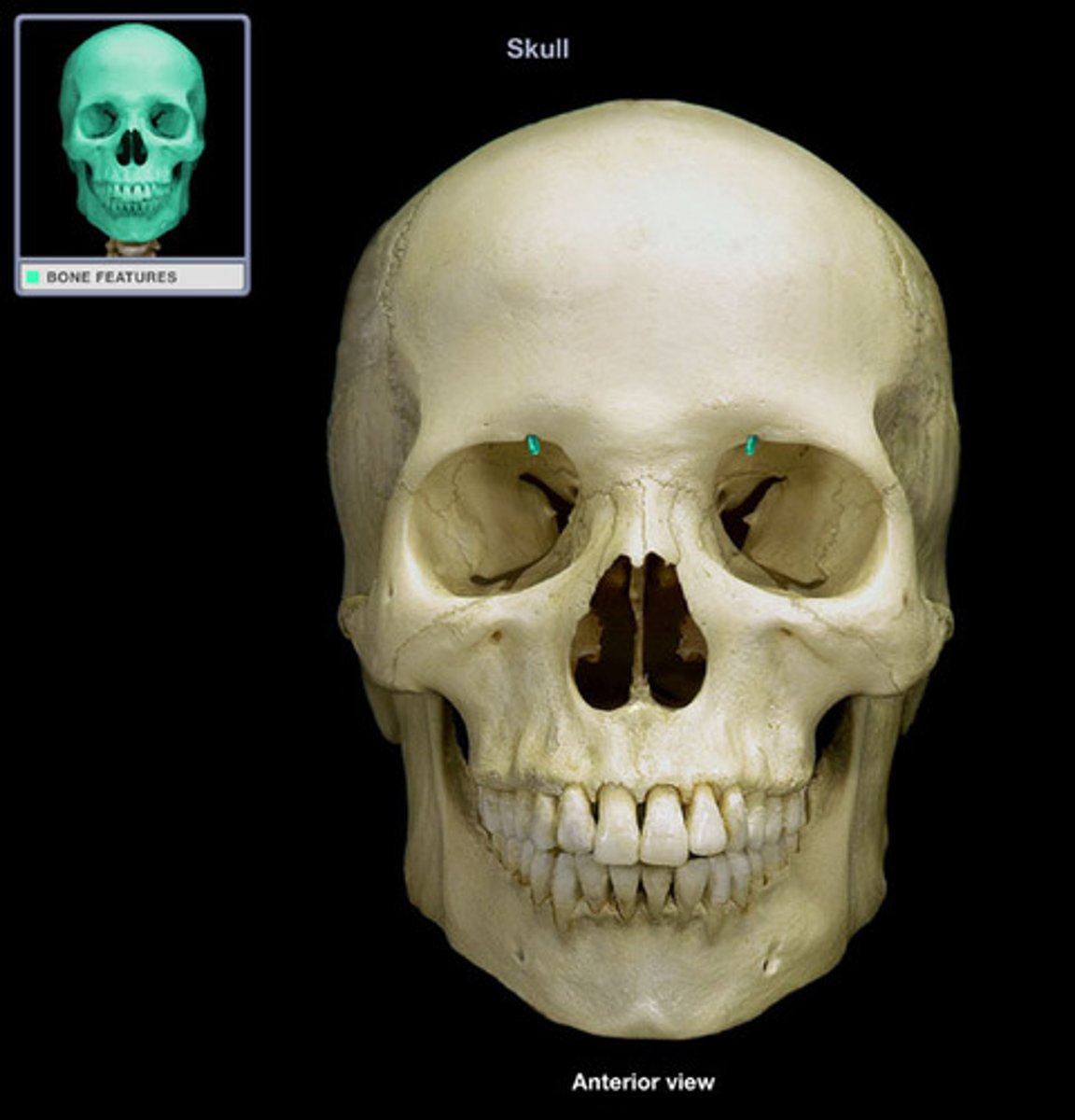
Glabella
What is shown on the image?
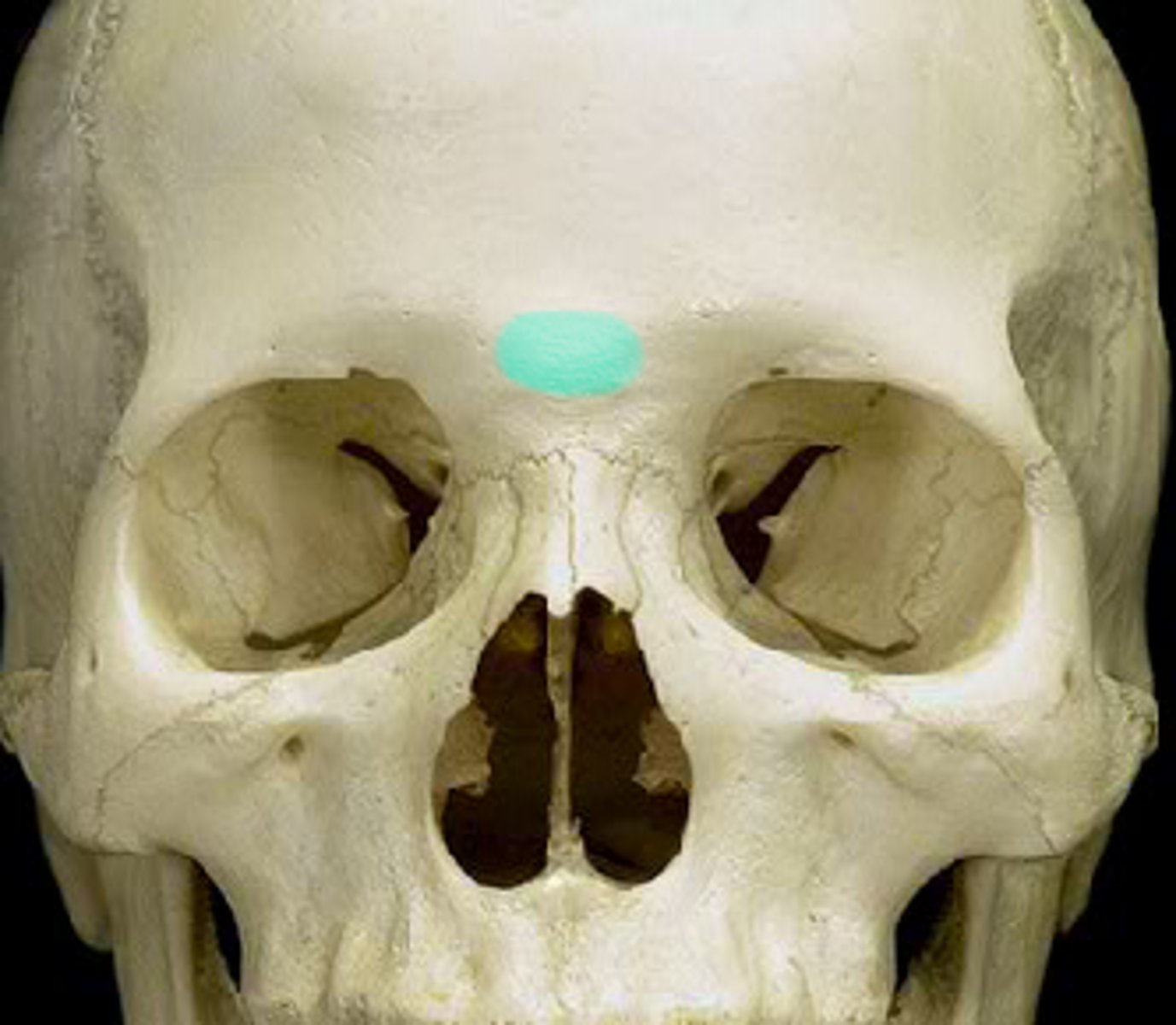
Supraorbital foramen
What is shown on the image?
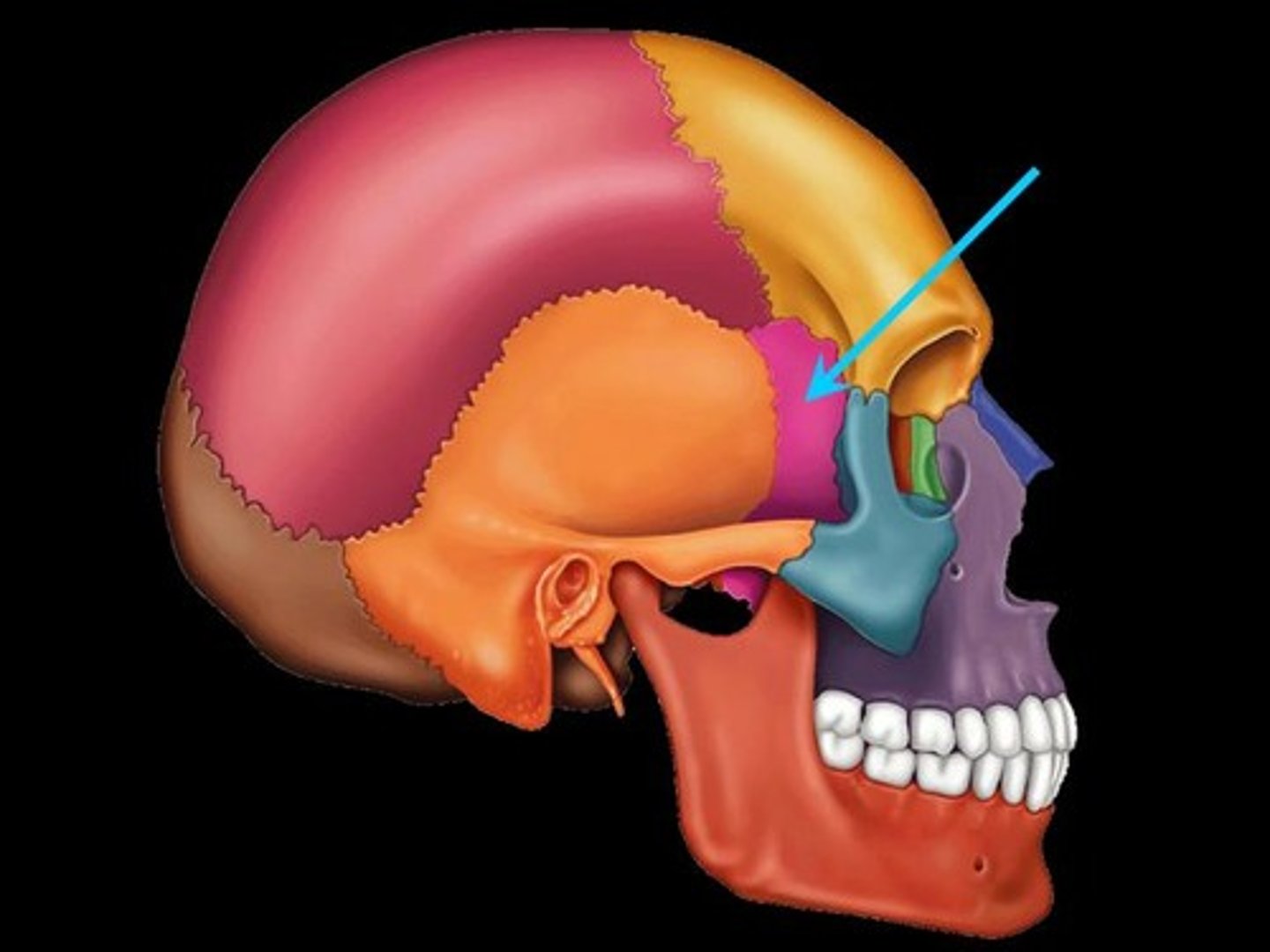
Sphenoid bone
What is shown on the image?
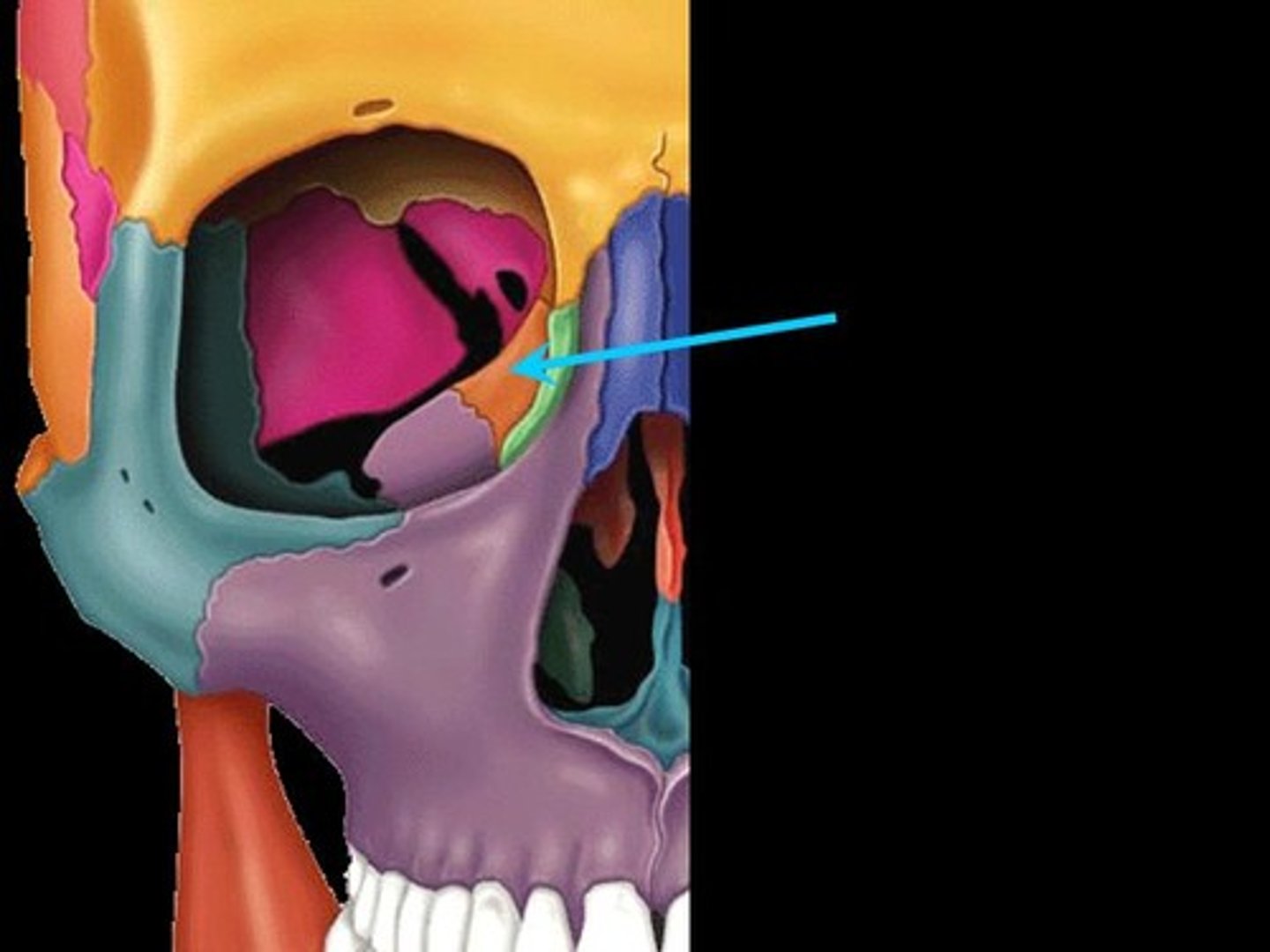
Ethmoid bone
What is shown on the image?
Volmer
What is shown on the image?
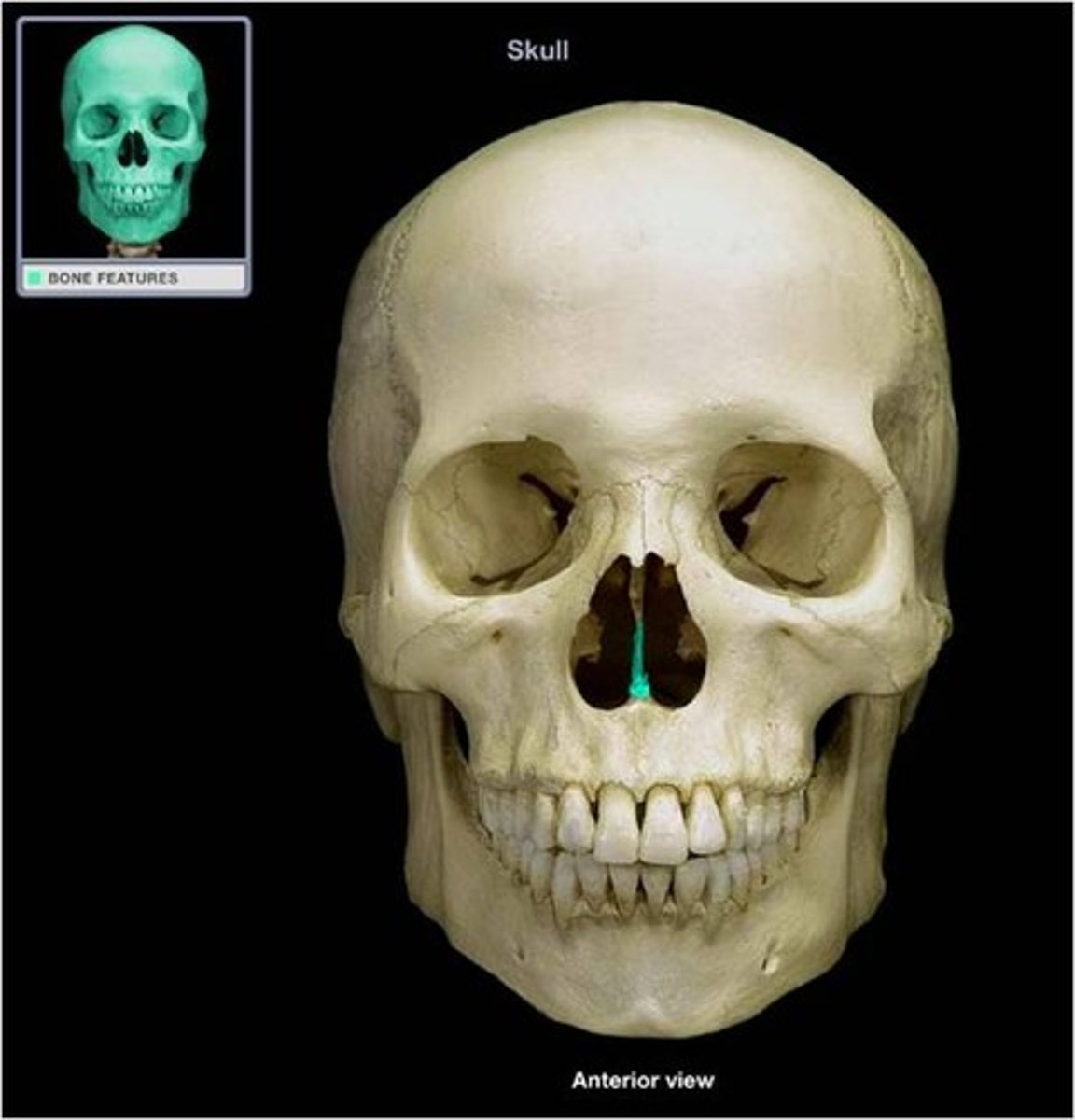
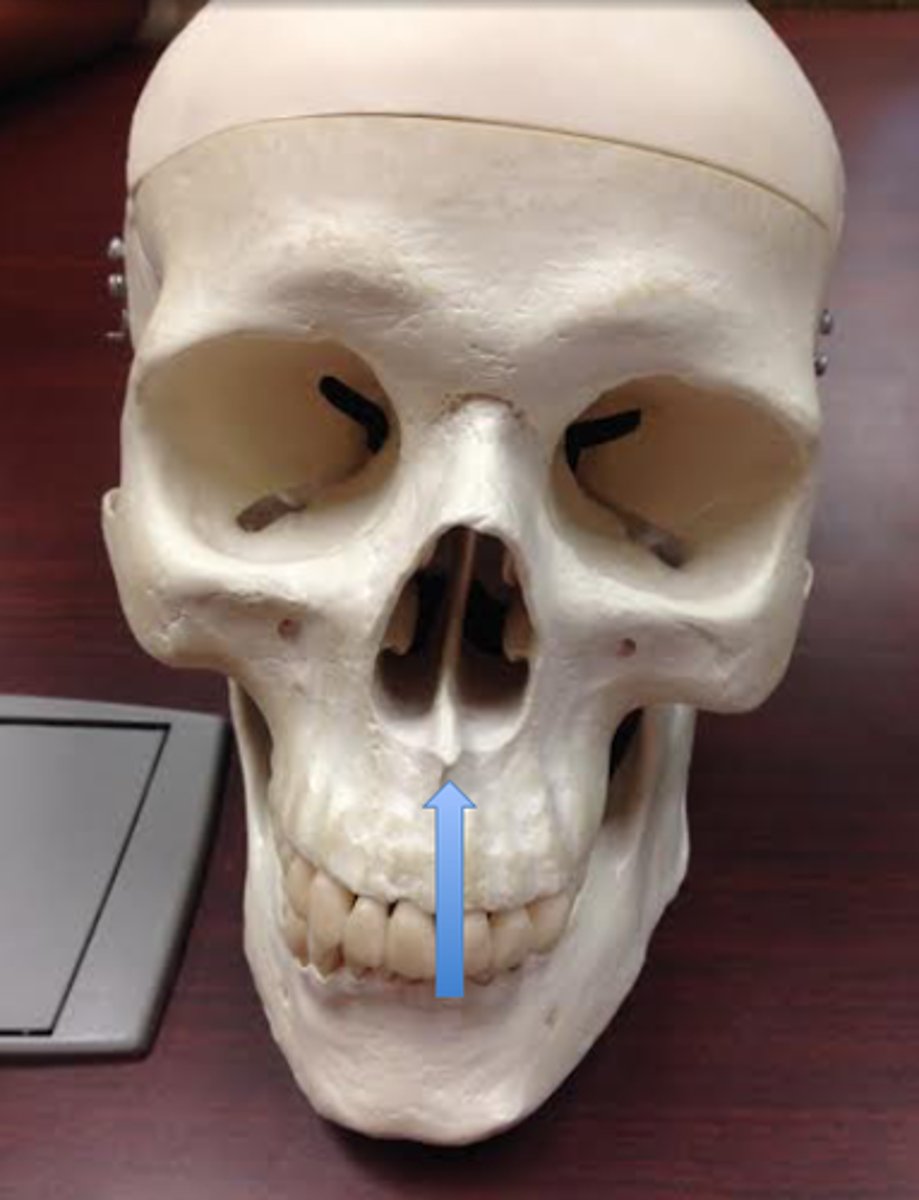
Nasal spine
What is shown on the image?
8 (frontal, parietal (2), occipital, temporal (2), sphenoid, ethmoid,
How many cranial bones are there?
14
How many facial bones are there?
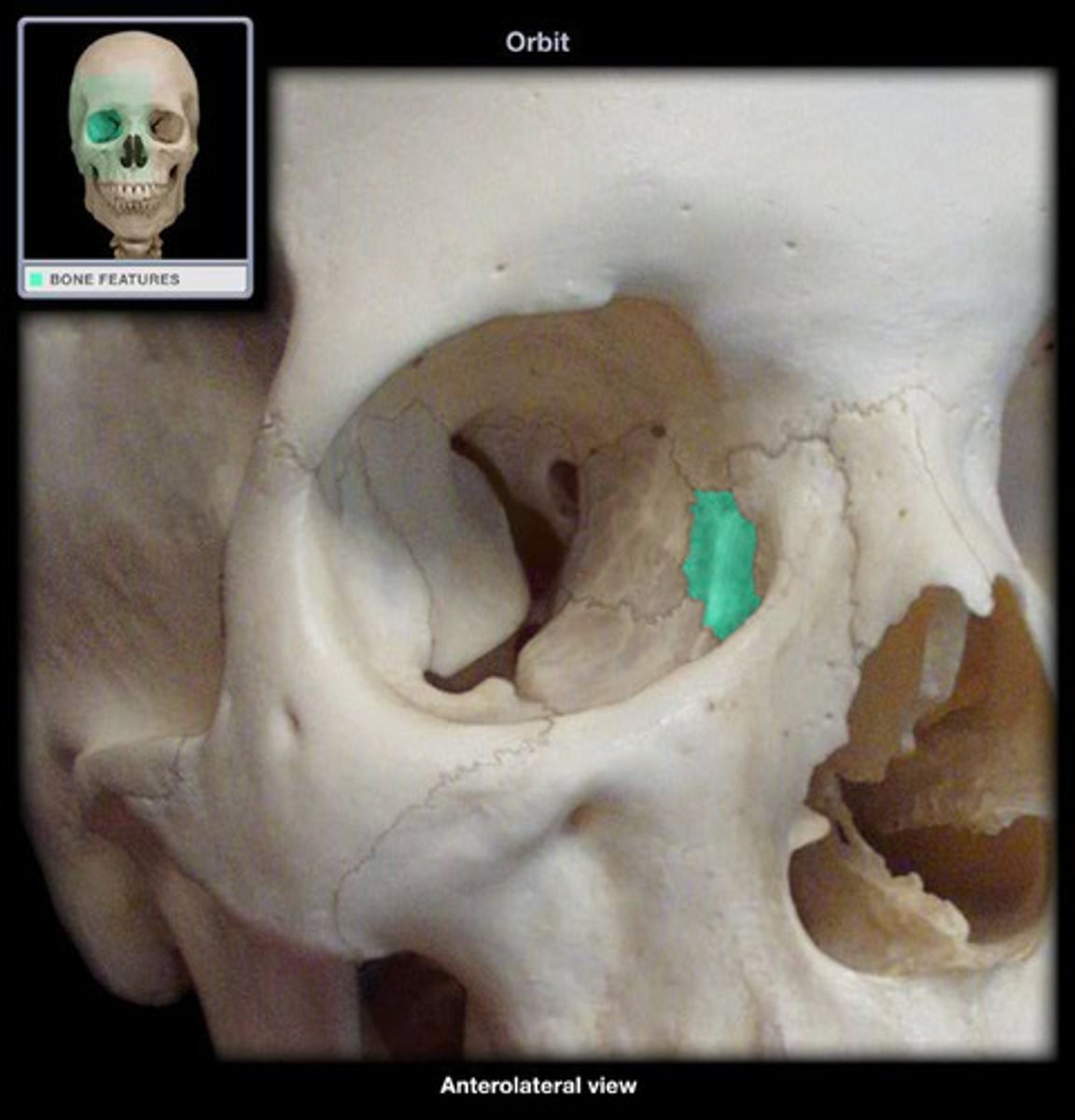
Lacrimal bone
What is shown on the image?
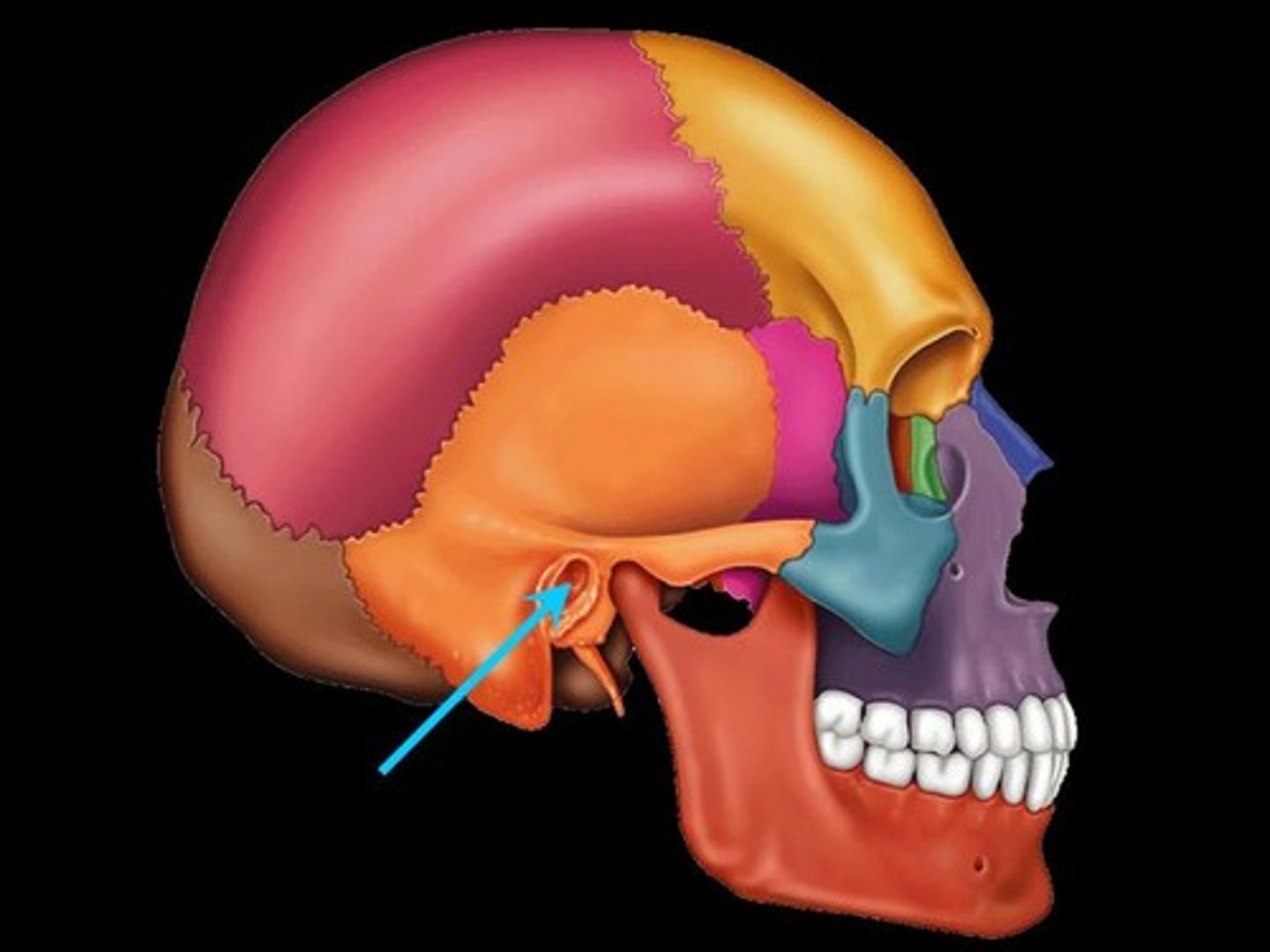
External acoustic meatus
What is shown on the image?
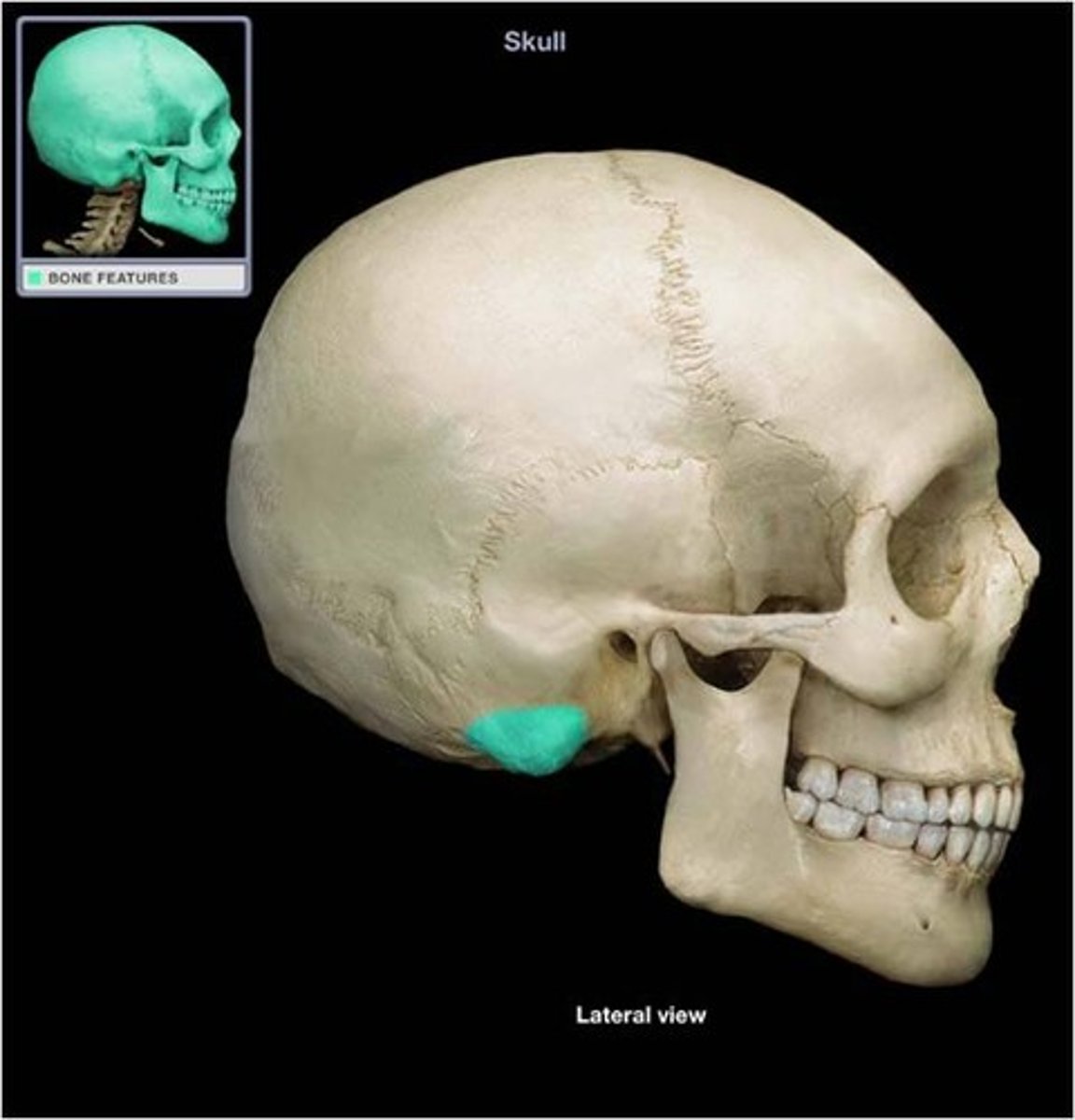
Mastoid process
What is shown on the image?
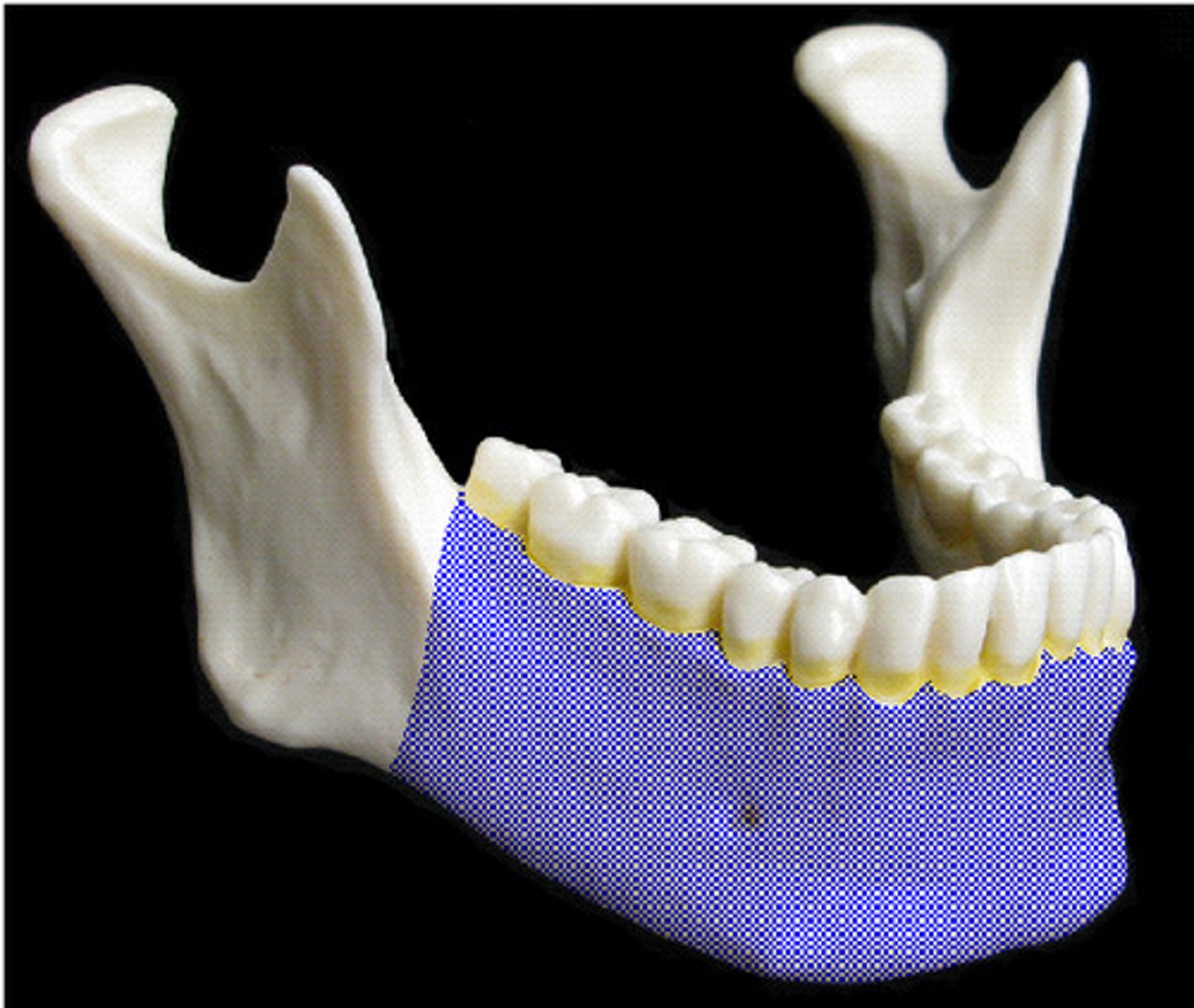
Body of mandible
What is shown on the image?
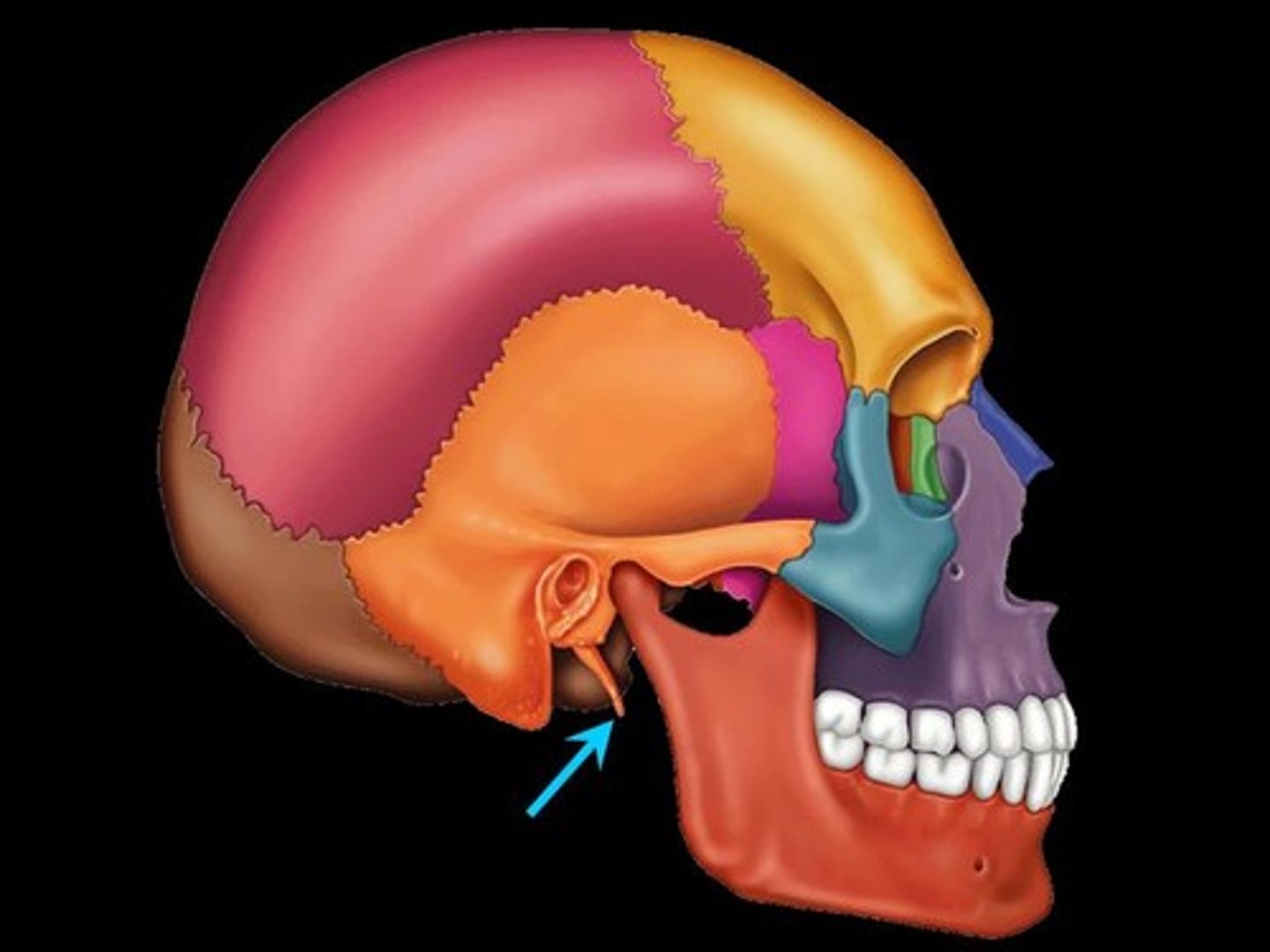
Styloid process
What is shown on the image?
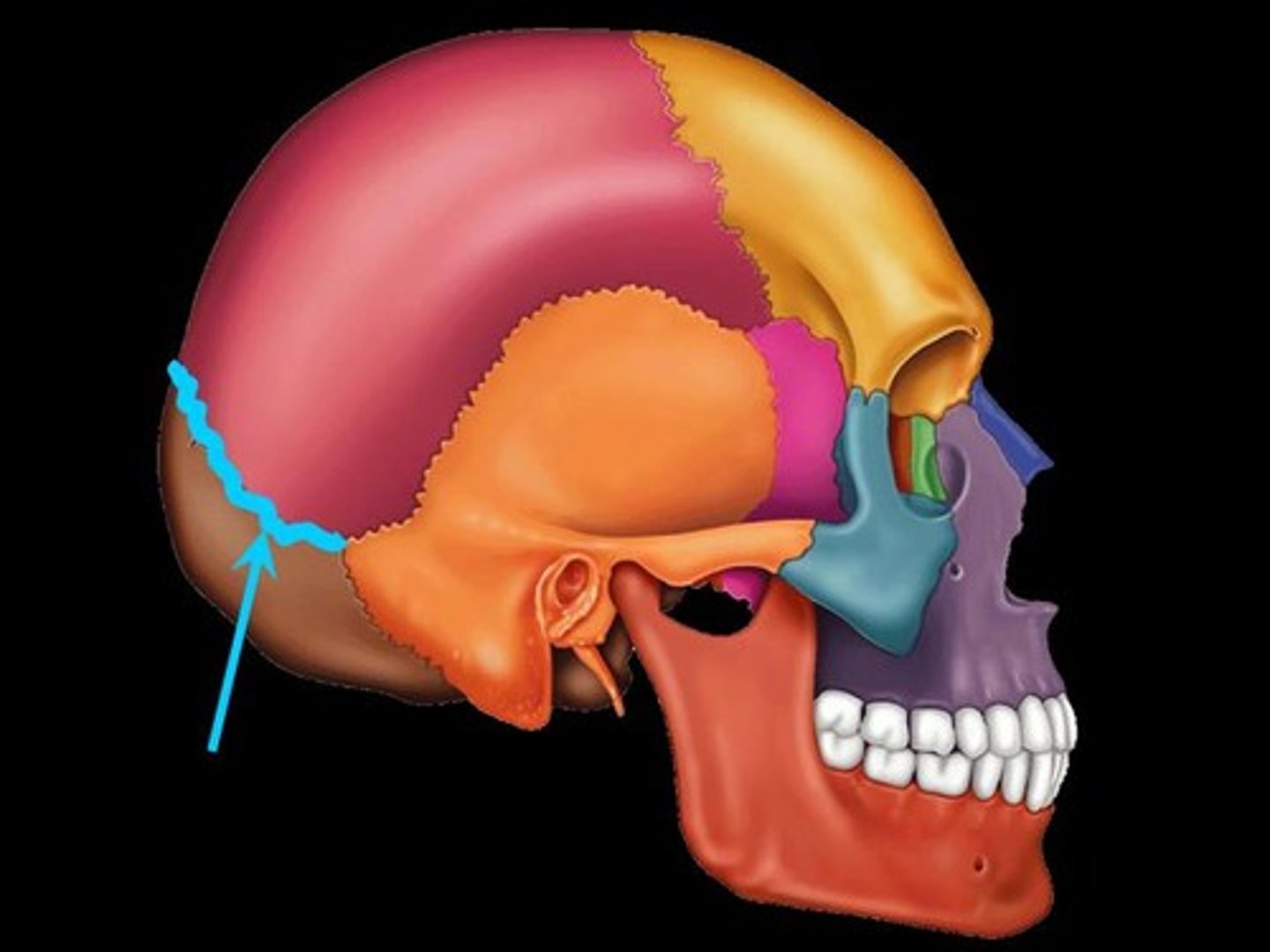
Lambdoid suture
What is shown on the image?
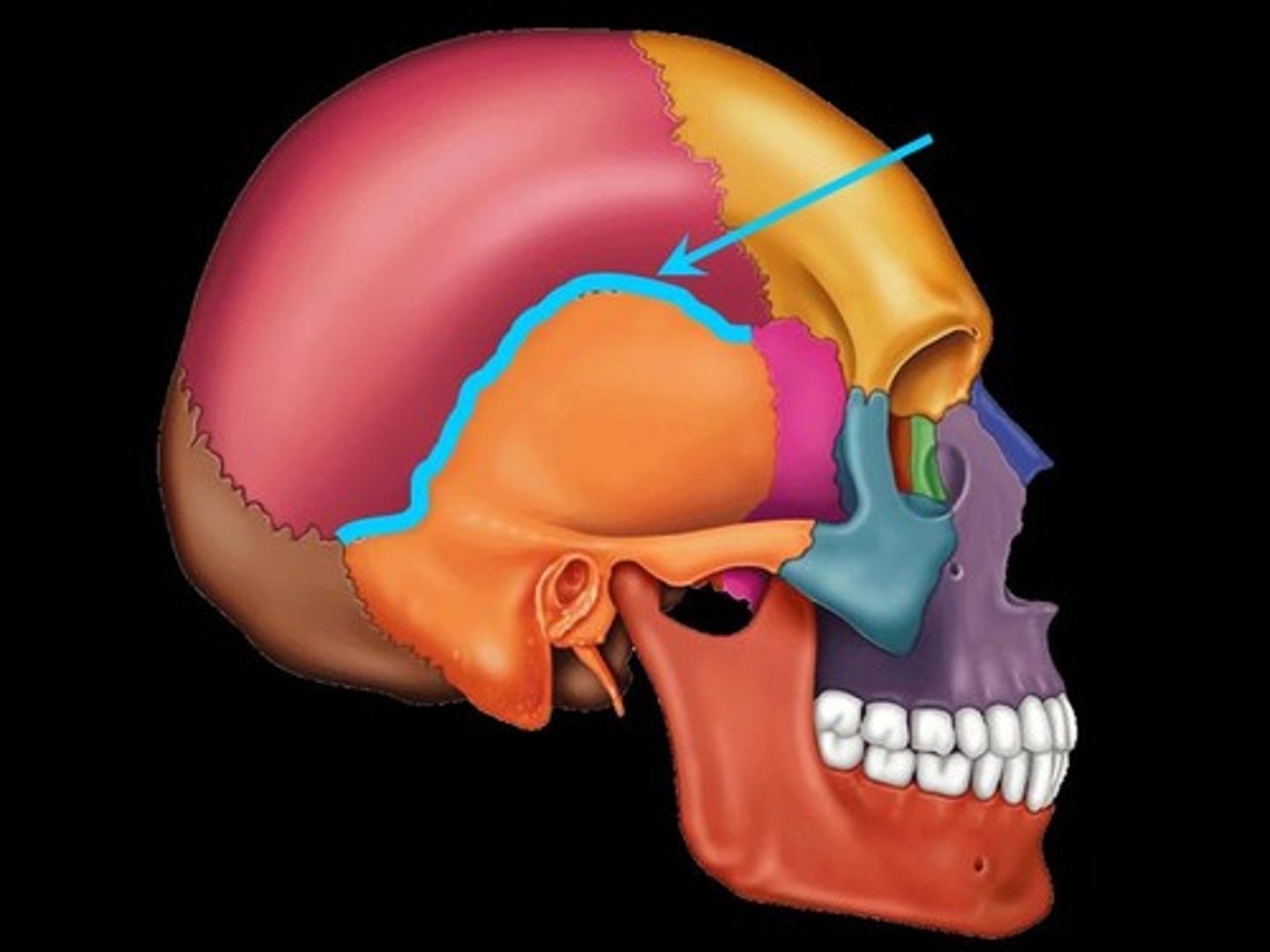
Squamous suture
What is shown on the image?
area where bones are joined to each other
Articulation:
general terms for any prominence on bony surface; usually attachment sites for muscles, ligaments, or tendons or articulation site
Process:
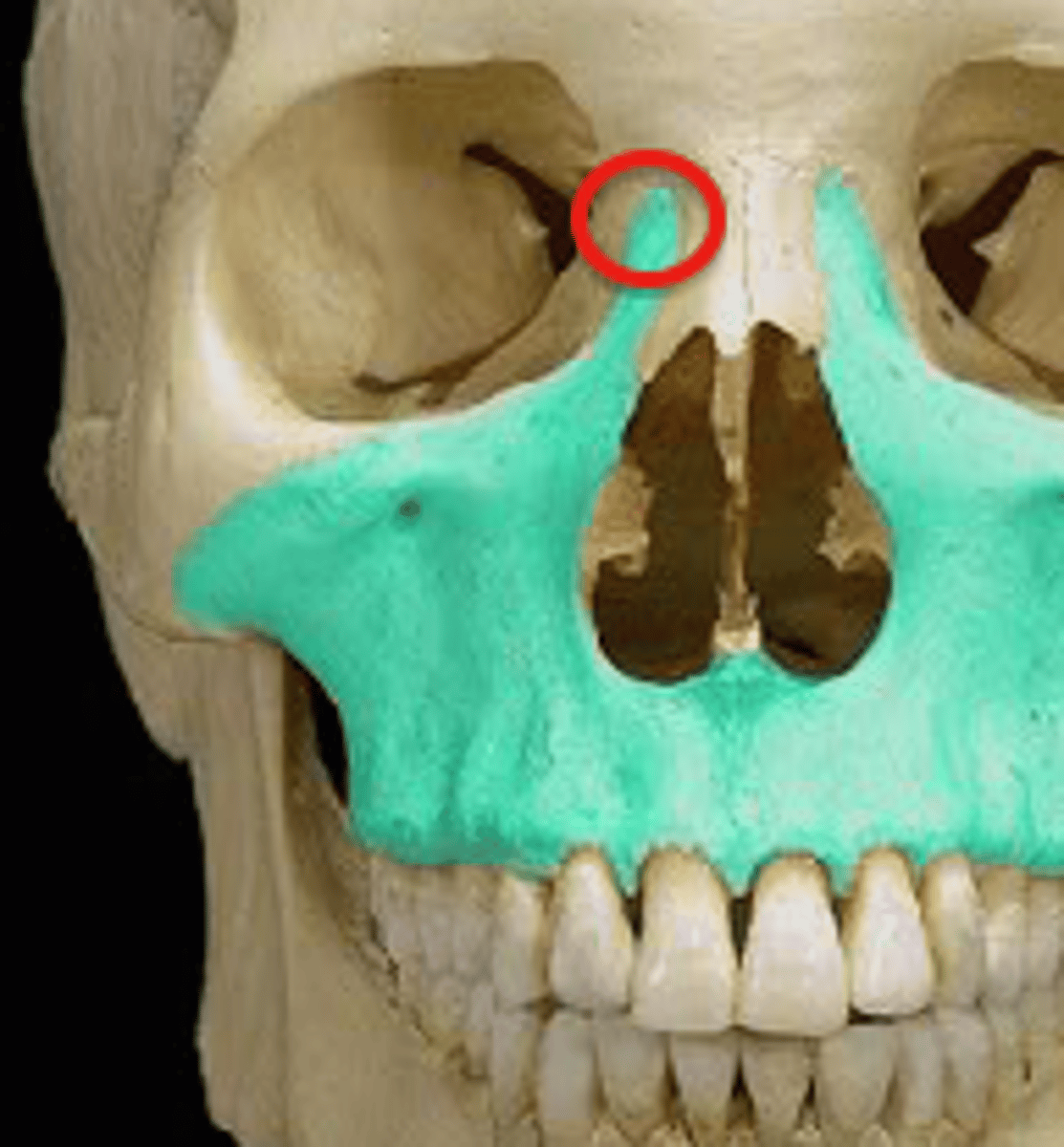
Frontal process
What is shown on the image?
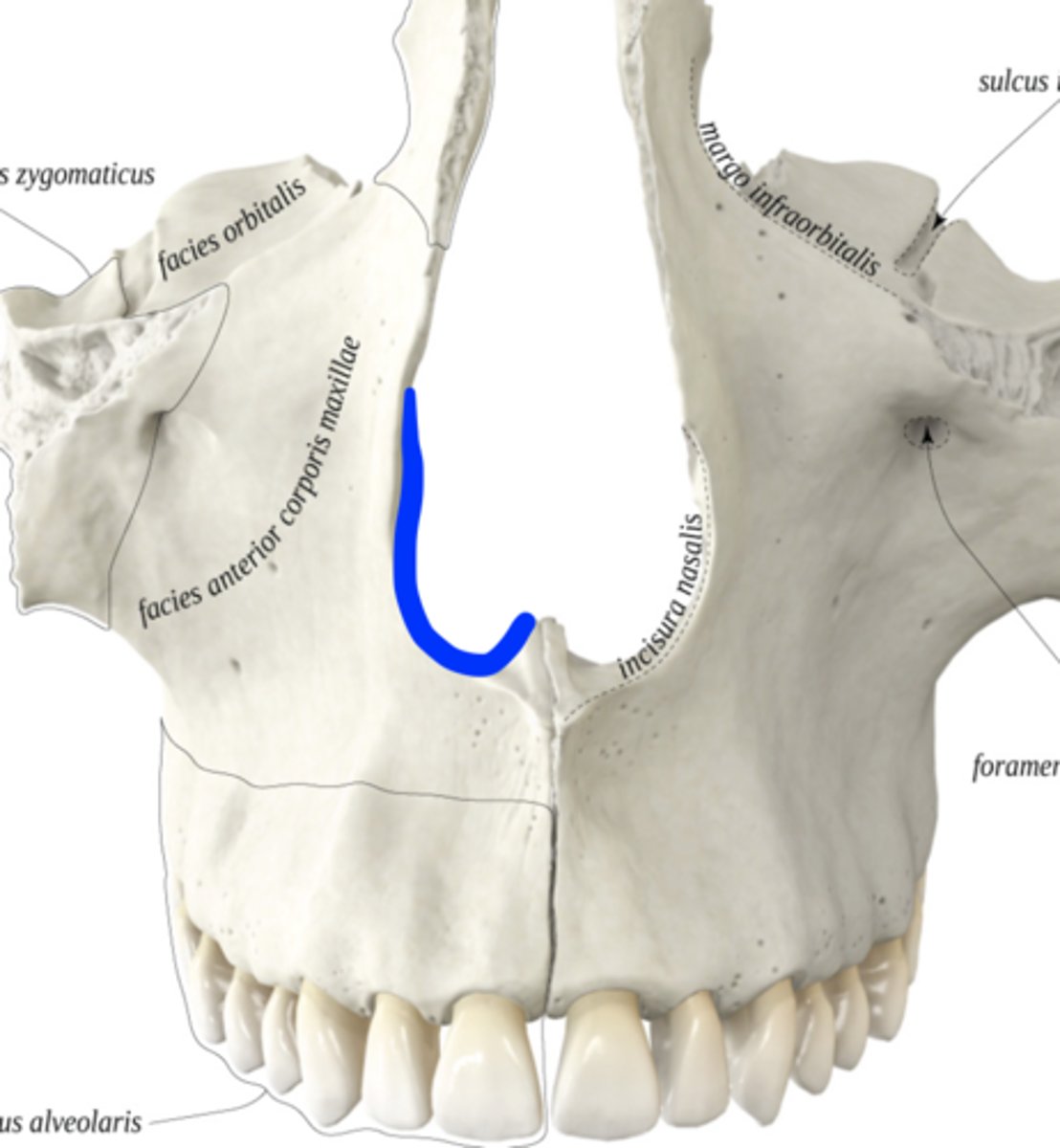
Infraorbital margin
What is shown on the image?
Nasal notch
What is shown on the image?
Nasal crest (6)
What is shown on the image?
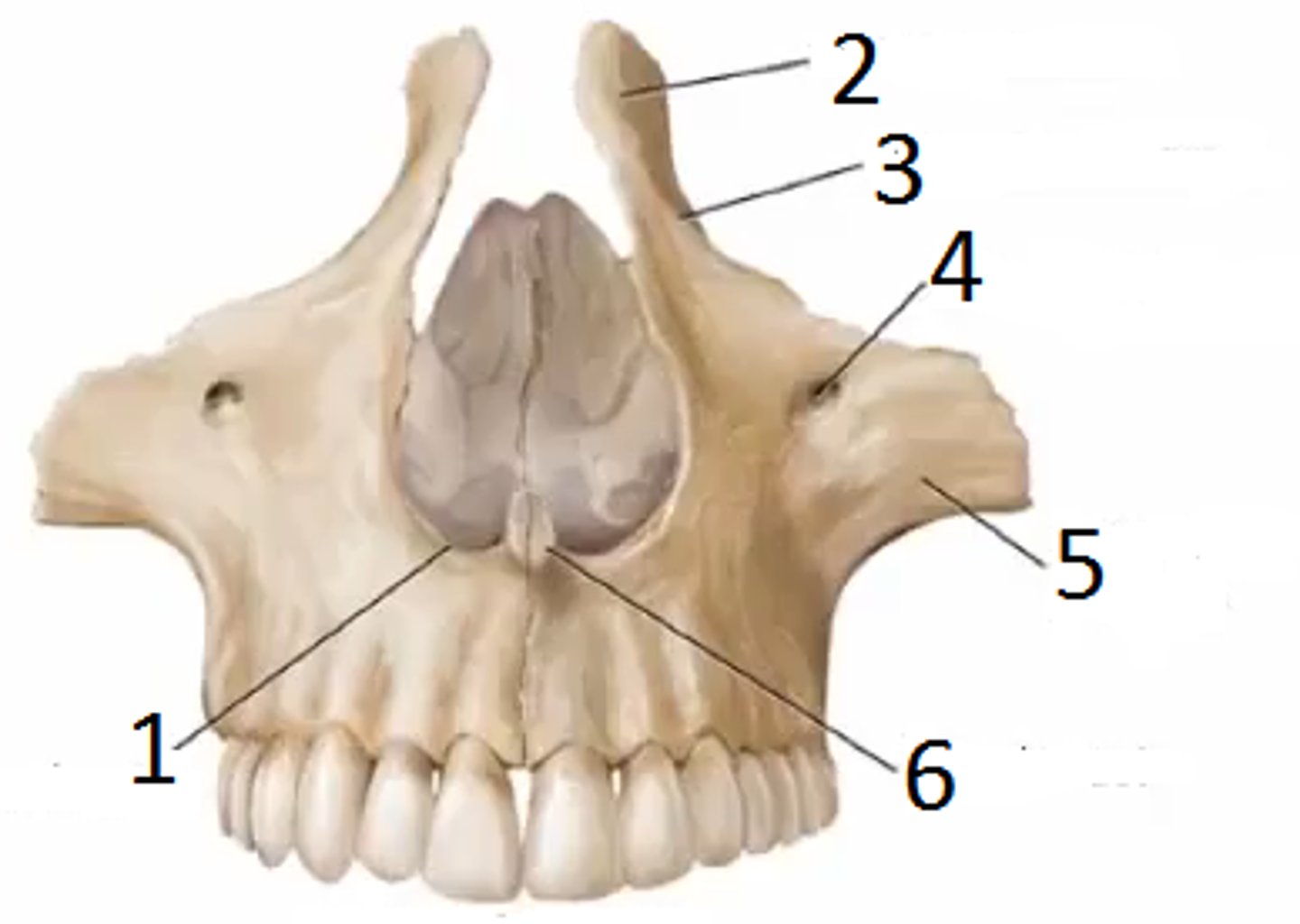
Maxillary sinus
What is shown on the image?
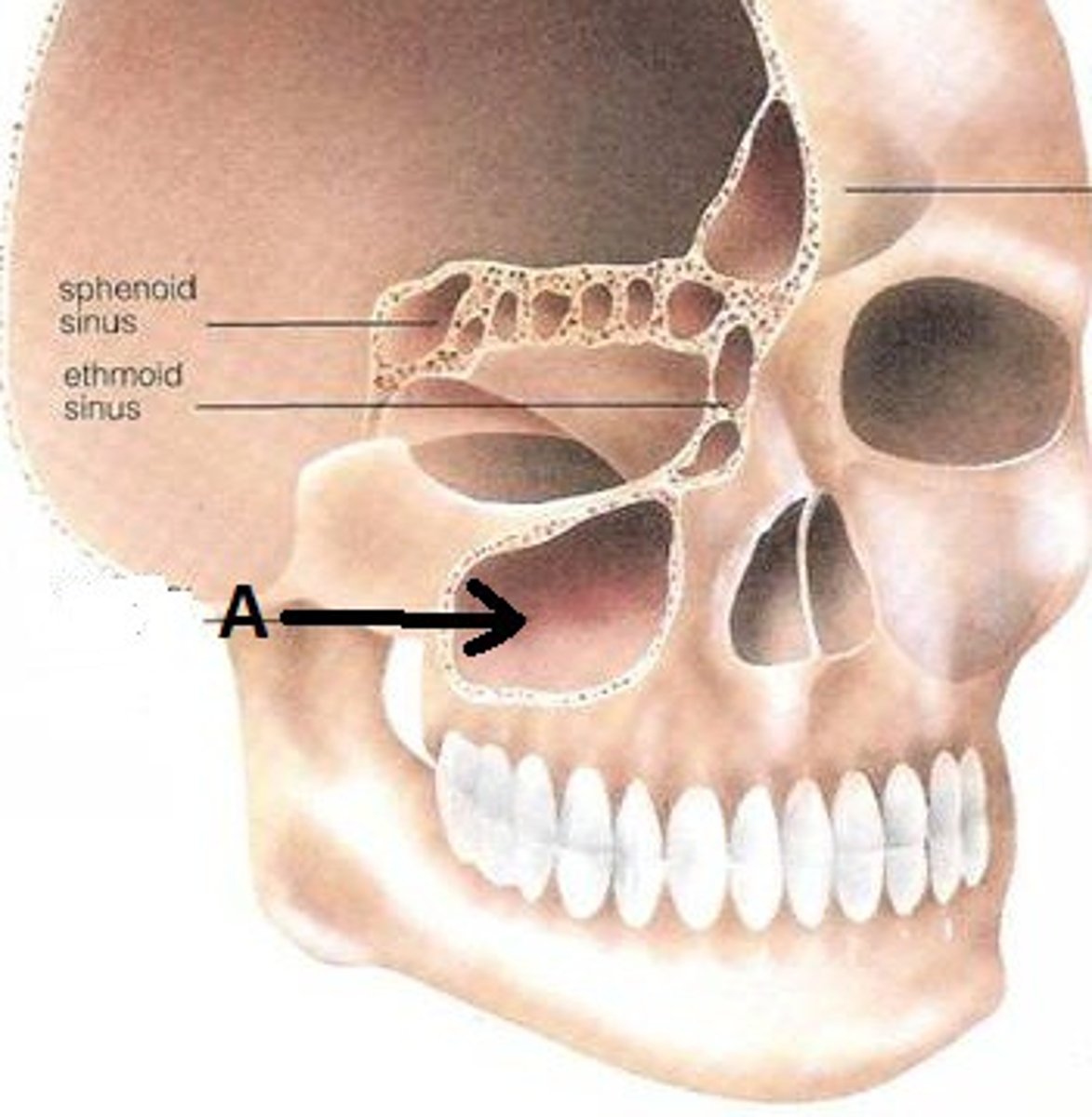
Palatine process
What is shown on the image?

Condyle
What is shown on the image?
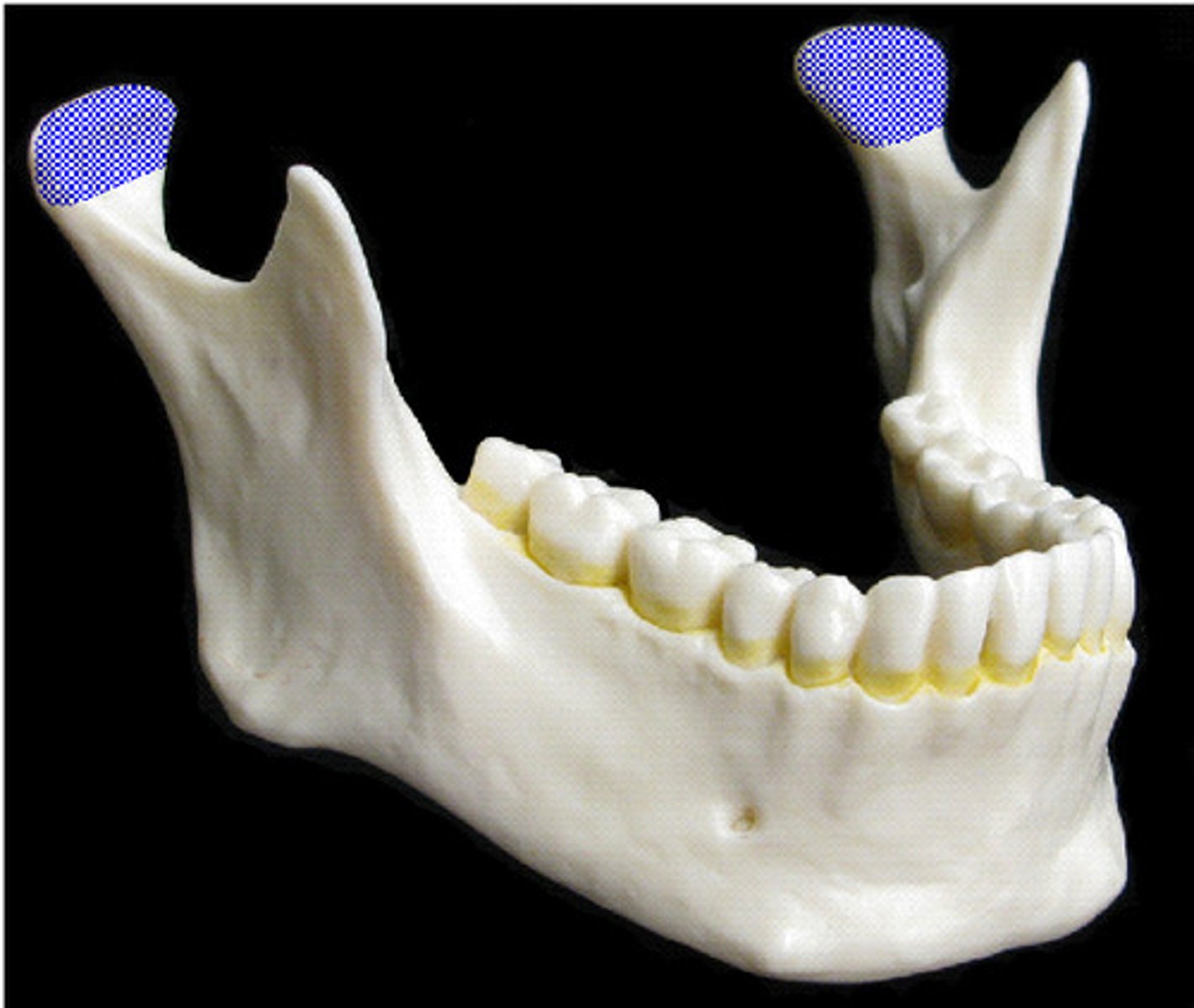
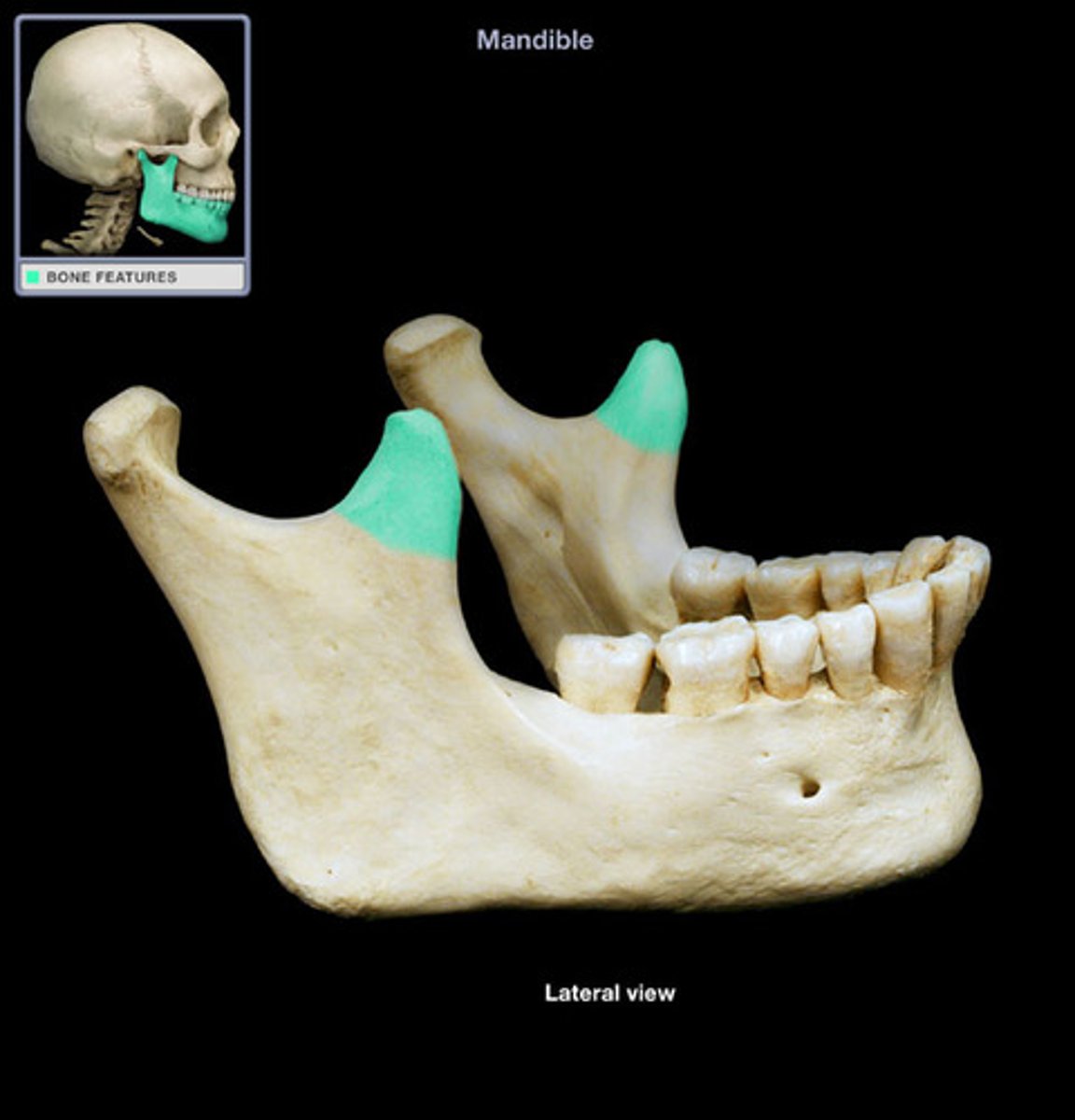
Coronoid
What is shown on the image?
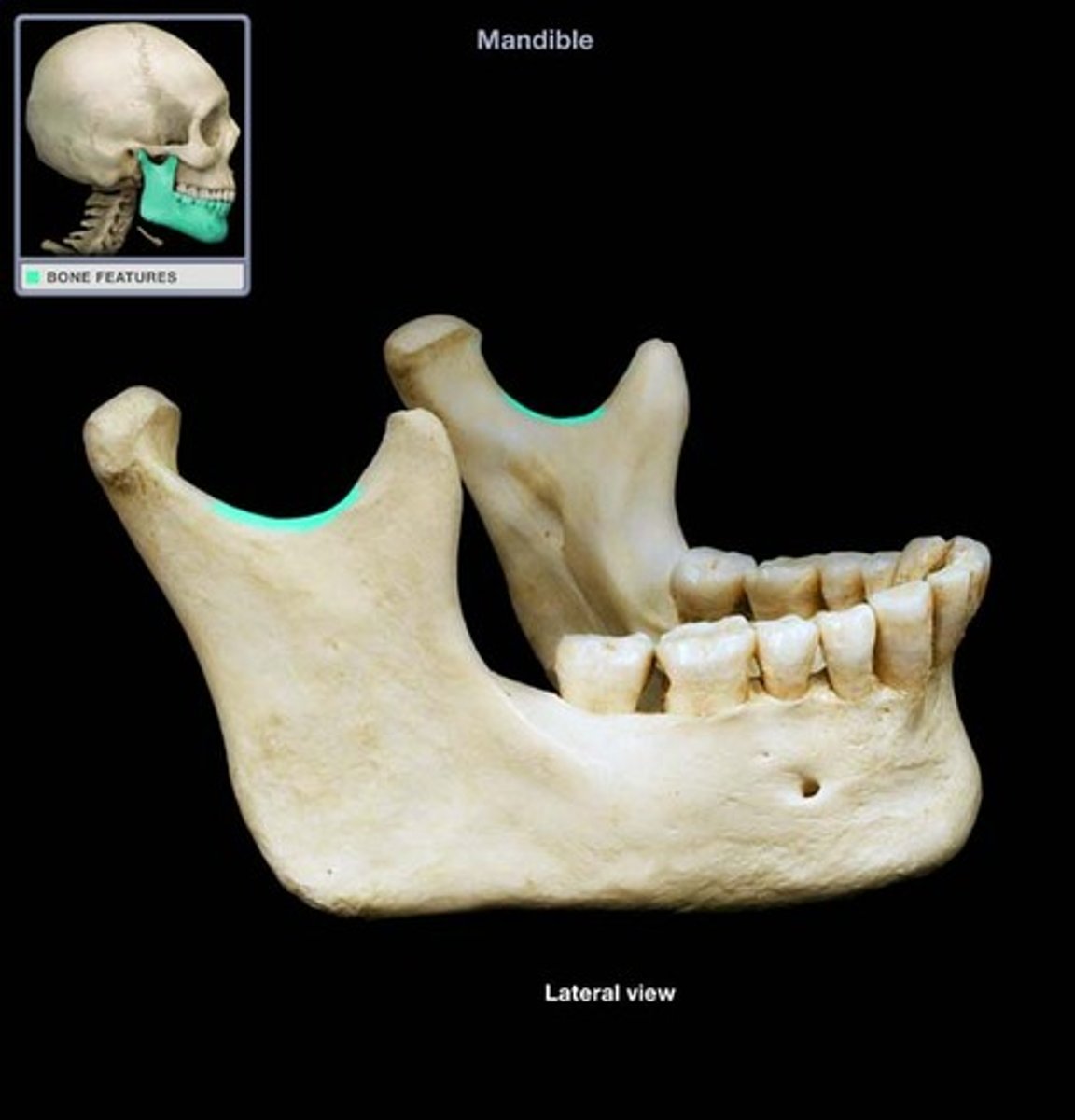
Mandibular notch
What is shown on the image?
14
The sphenoid bone has ____ articulations.
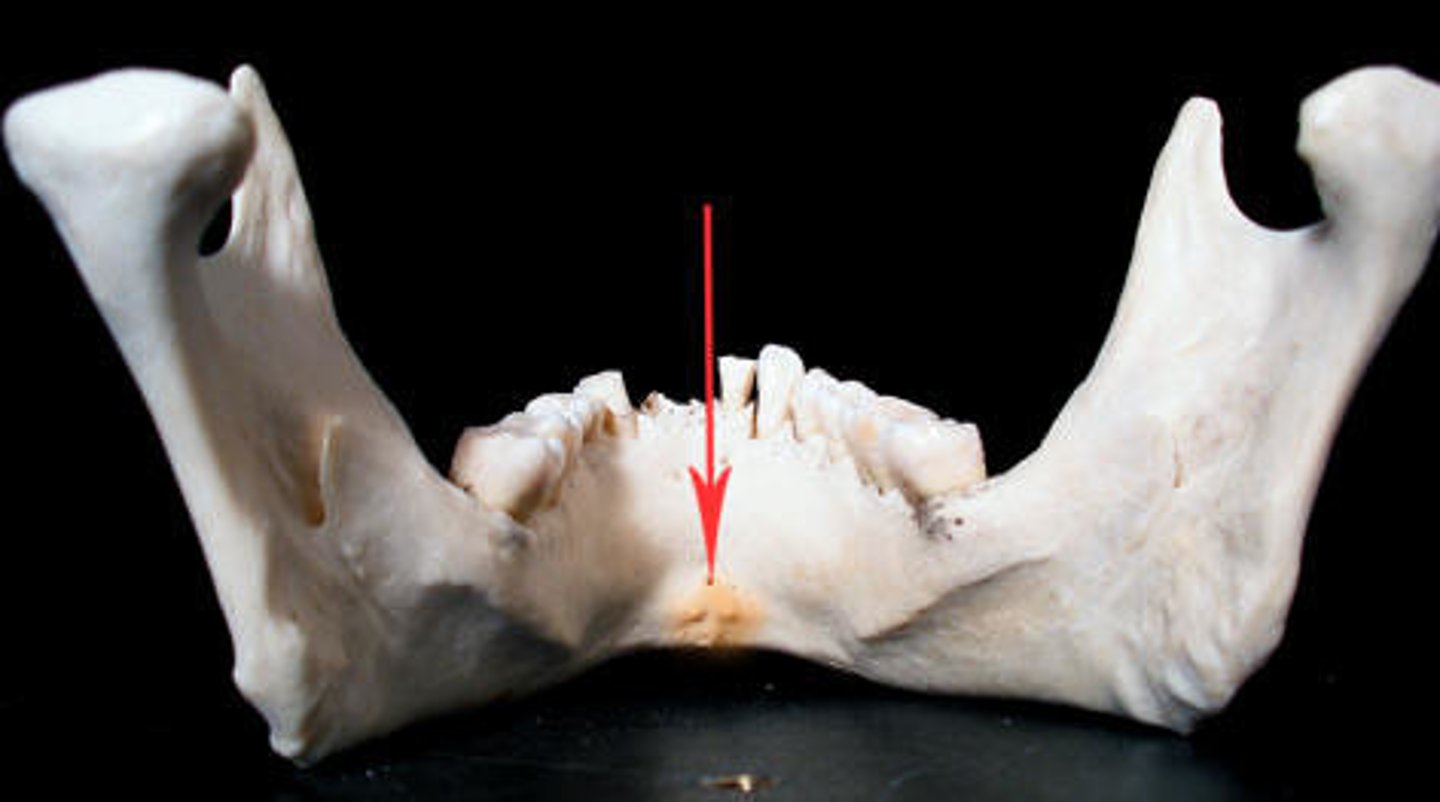
Mandibular symphysis
What is shown on the image?
Genial tubercle
What is shown on the image?
Mylohyoid line
What is shown on the image?
Pterygoid fovea
What is shown on the image?
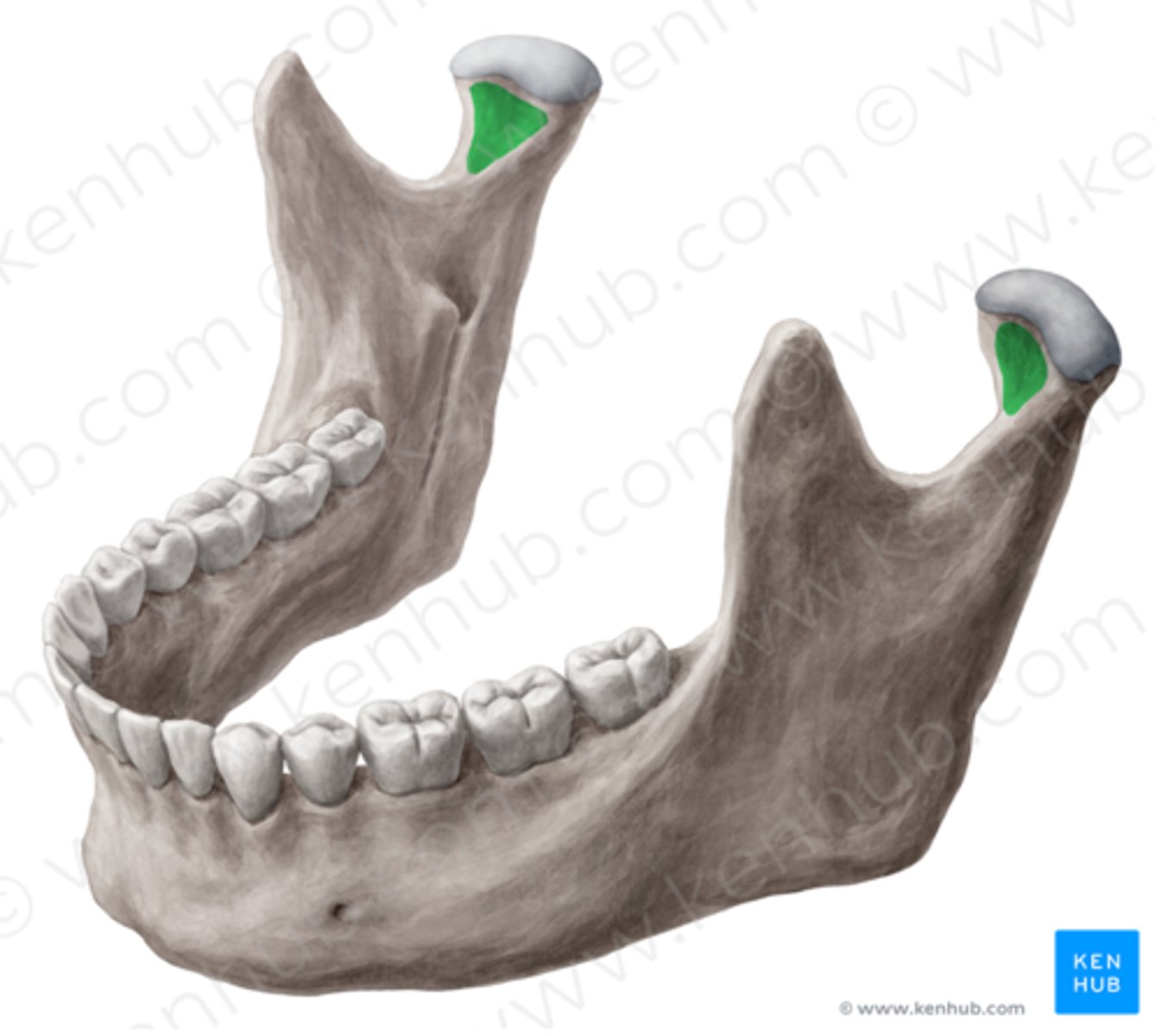
Lingula
What is shown on the image?
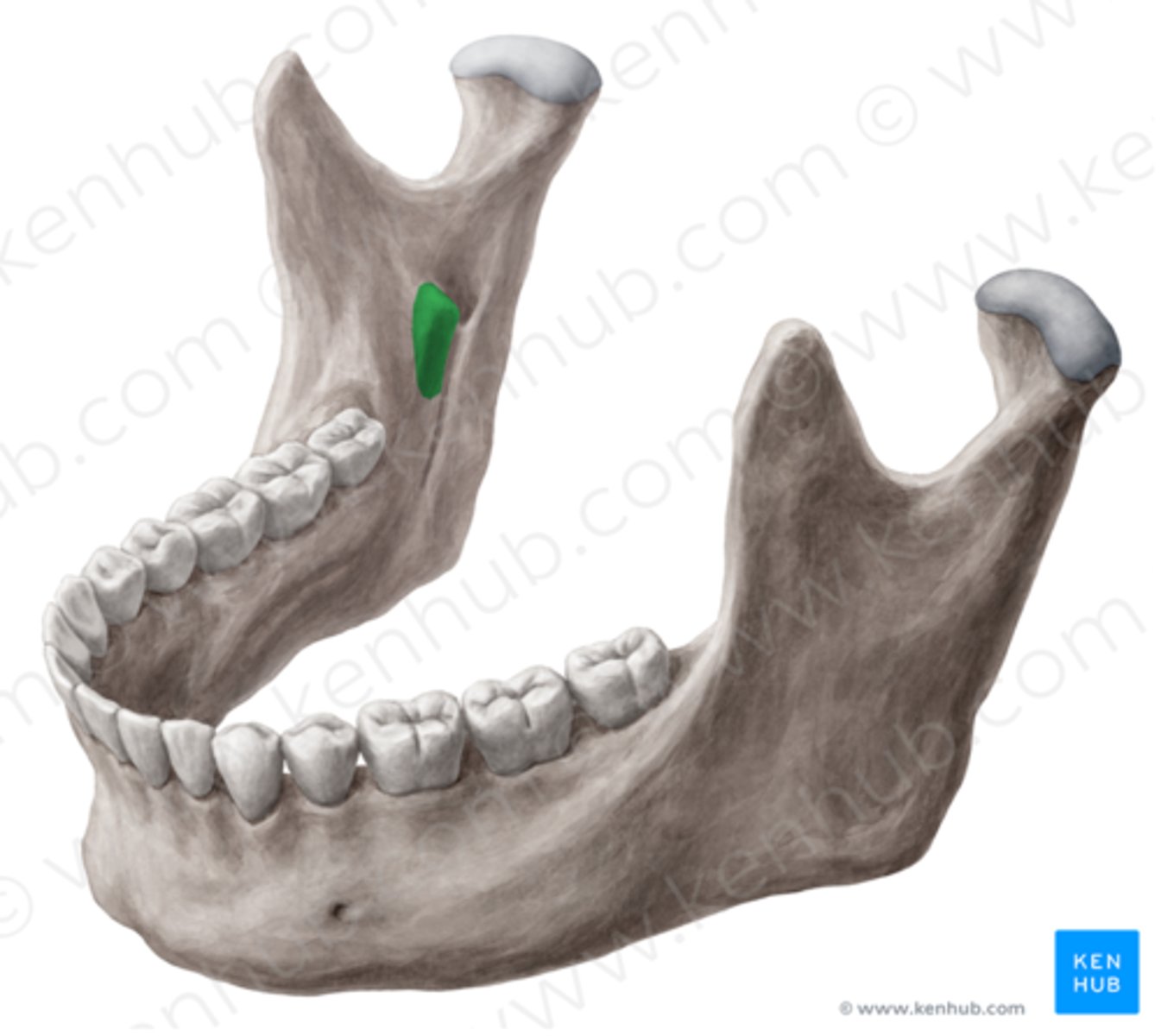
Mandibular foramen
What is shown on the image?

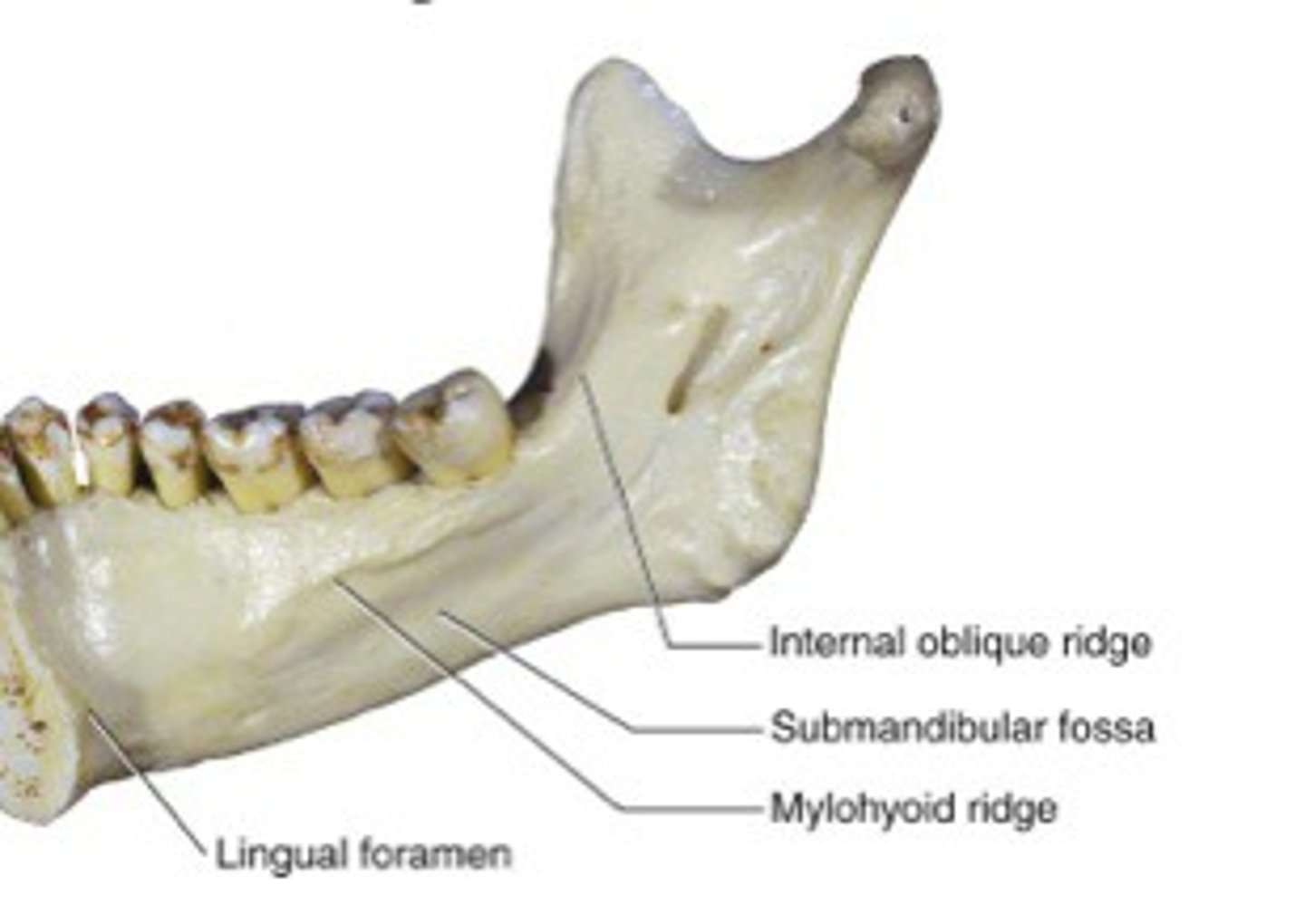
Internal oblique ridge
What is shown on the image?
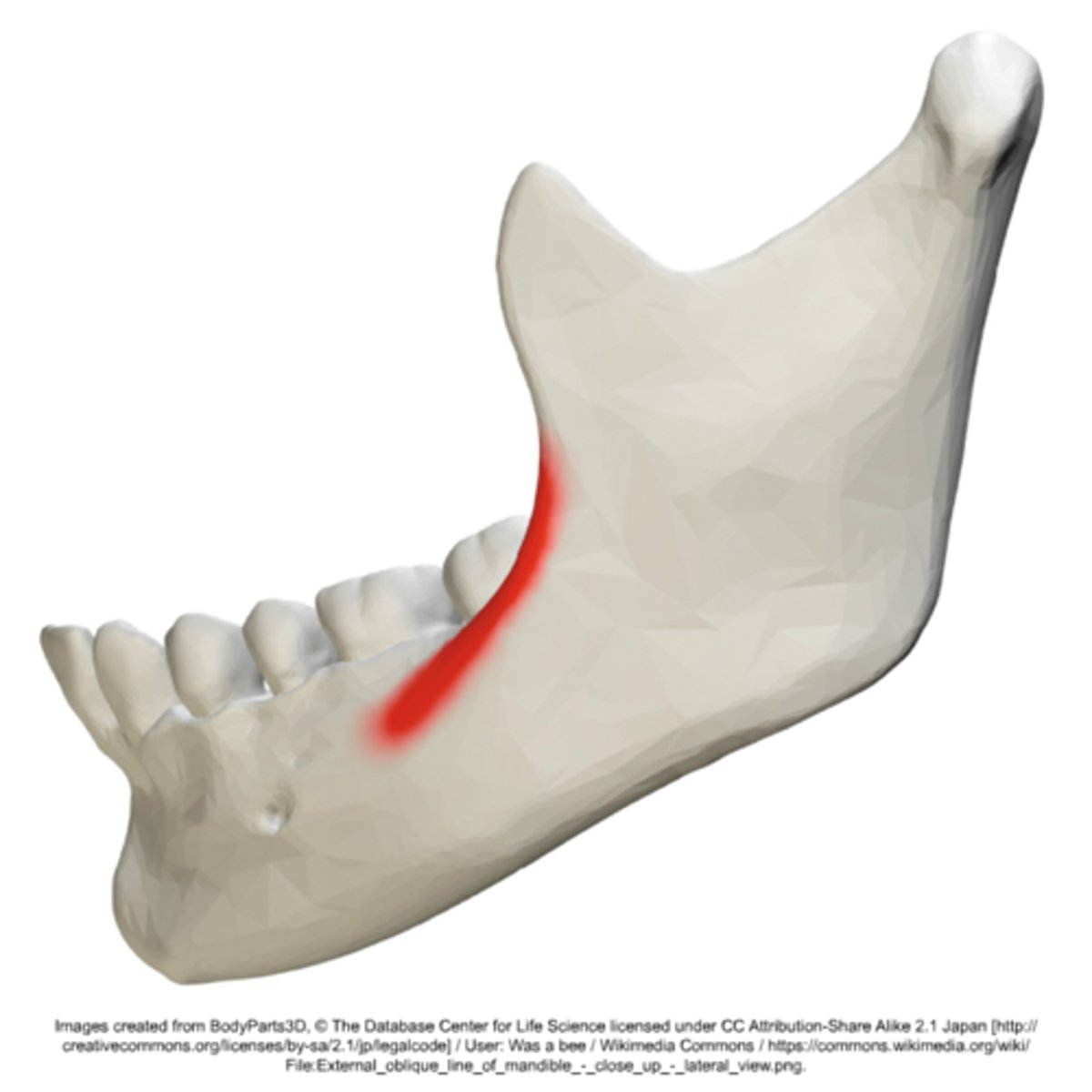
External oblique ridge
What is shown on the image?
mandible
The ________ is the only moveable bone of the skull at the temporomandibular joint.
where the muscle originates, the contraction is TOWARD the origin, the least moveable
Origin
where the muscle attaches to the more moveable structure
Insertion
True
T/F: If the name of the muscle is a 'combination' the first part is the origin.... the second part is the insertion
medial portion of the clavicle and the sternum's superior and lateral surfaces
Origin - Sternocleidomastoid
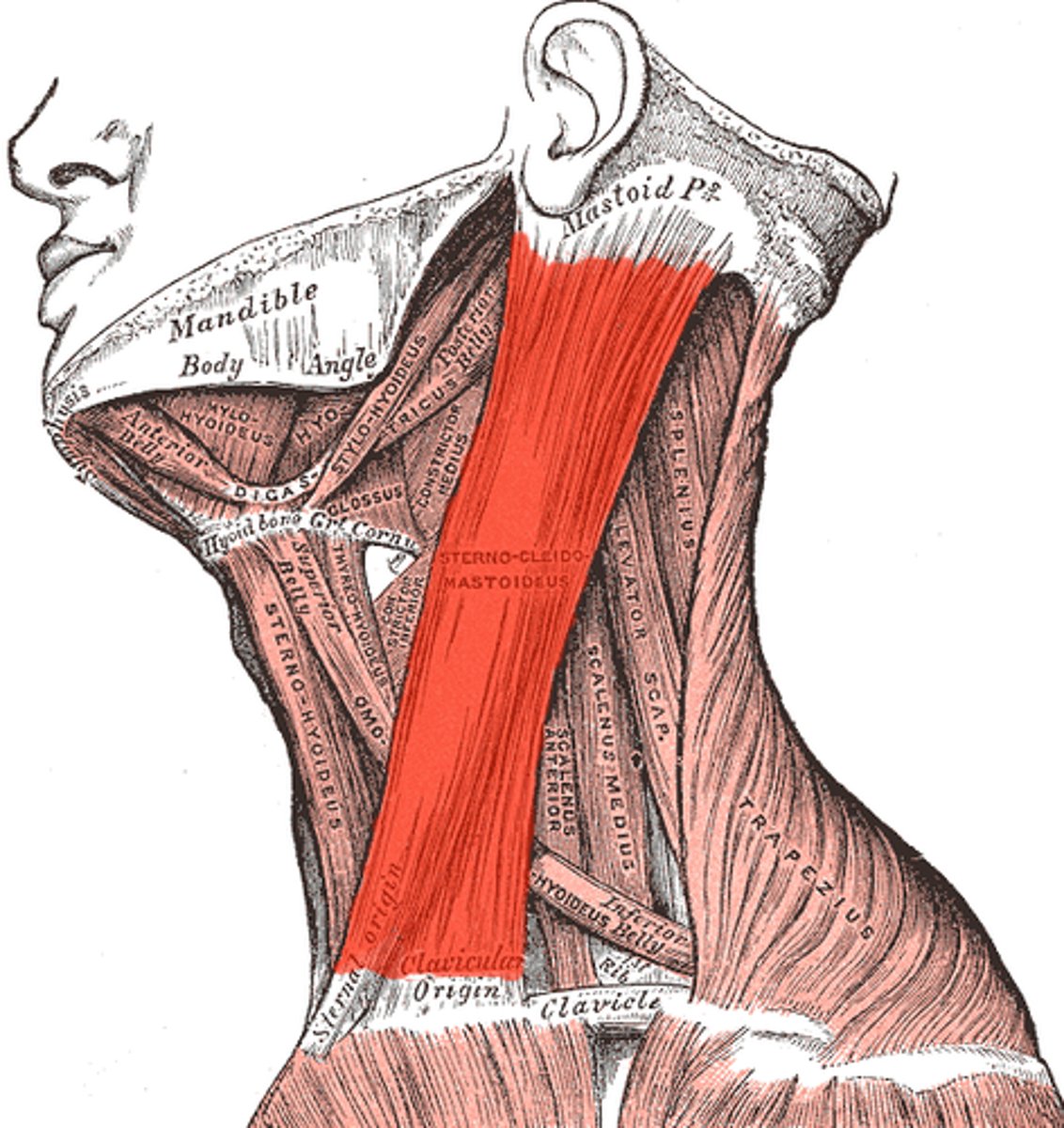
mastoid process of the temporal bone
Insertion - Sternocleidomastoid
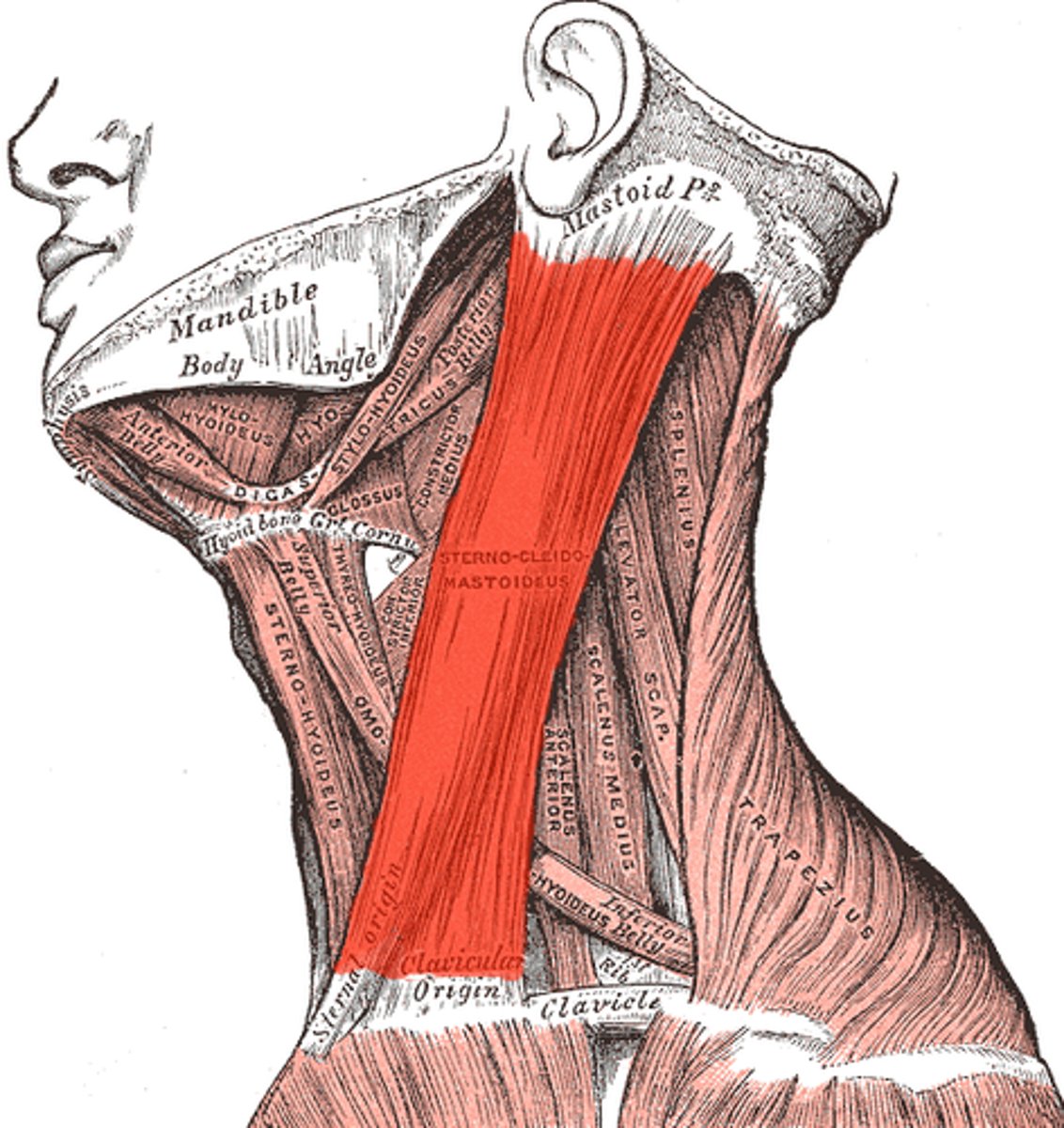
tilts and rotates head and neck; flexing of neck; stabilize neck
Movement - Sternocleidomastoid
eleventh (XI) cranial nerve or accessory nerve
Innervation - Sternocleidomastoid:
external surface of the occipital bone and the posterior midline of the cervical and thoracic regions
Origin - Trapezius
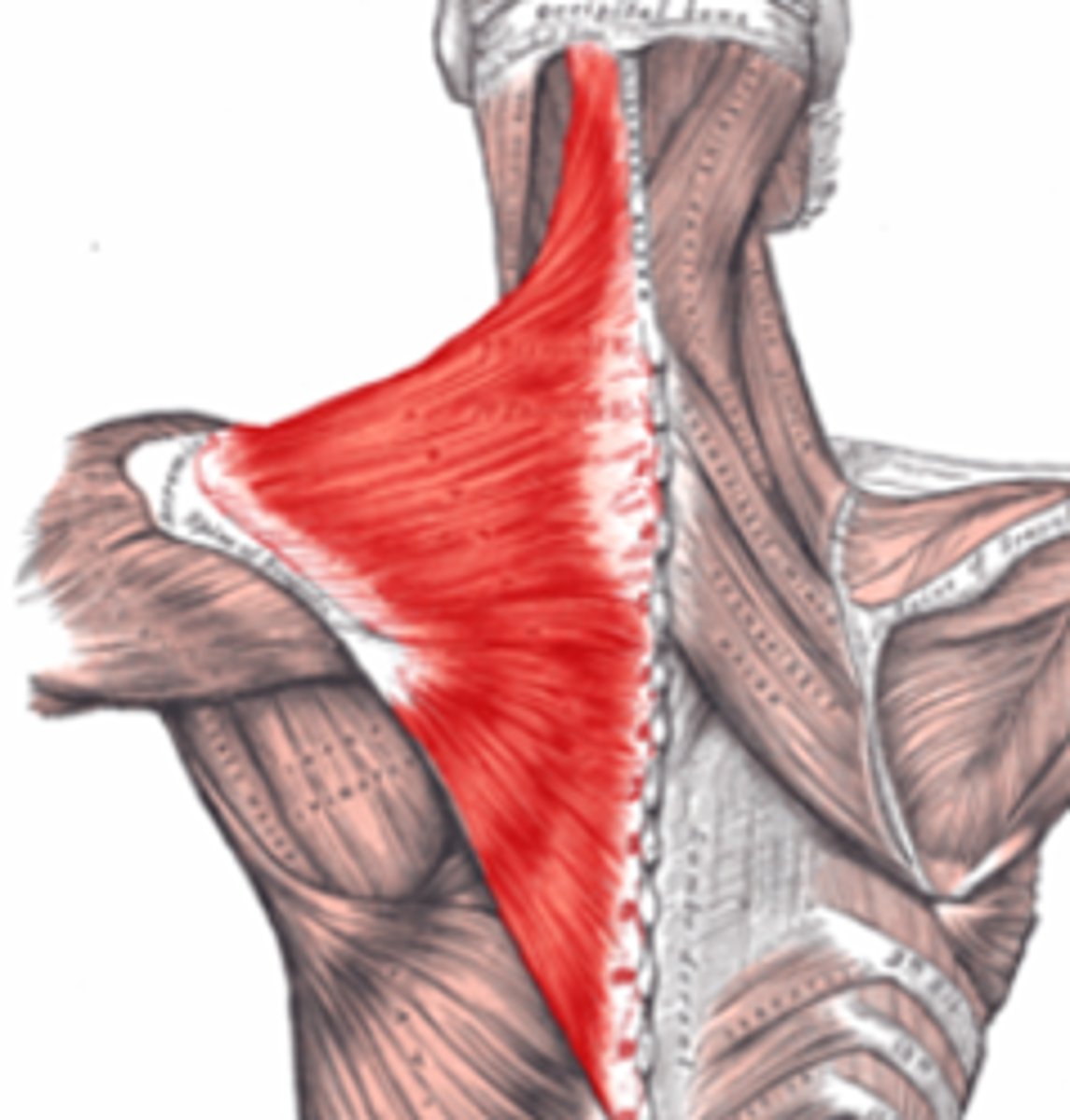
lateral 1/3 of clavicle and parts of the scapula
Insertion - Trapezius
lifts and rotates the shoulders, dorsal flexion of the head; twist head
Movement - Trapezius
eleventh (XI) cranial nerve or accessory nerve and the third and fourth cervical nerves
Innervation - Trapezius
encircles mouth
Origin - Orbicularis oris
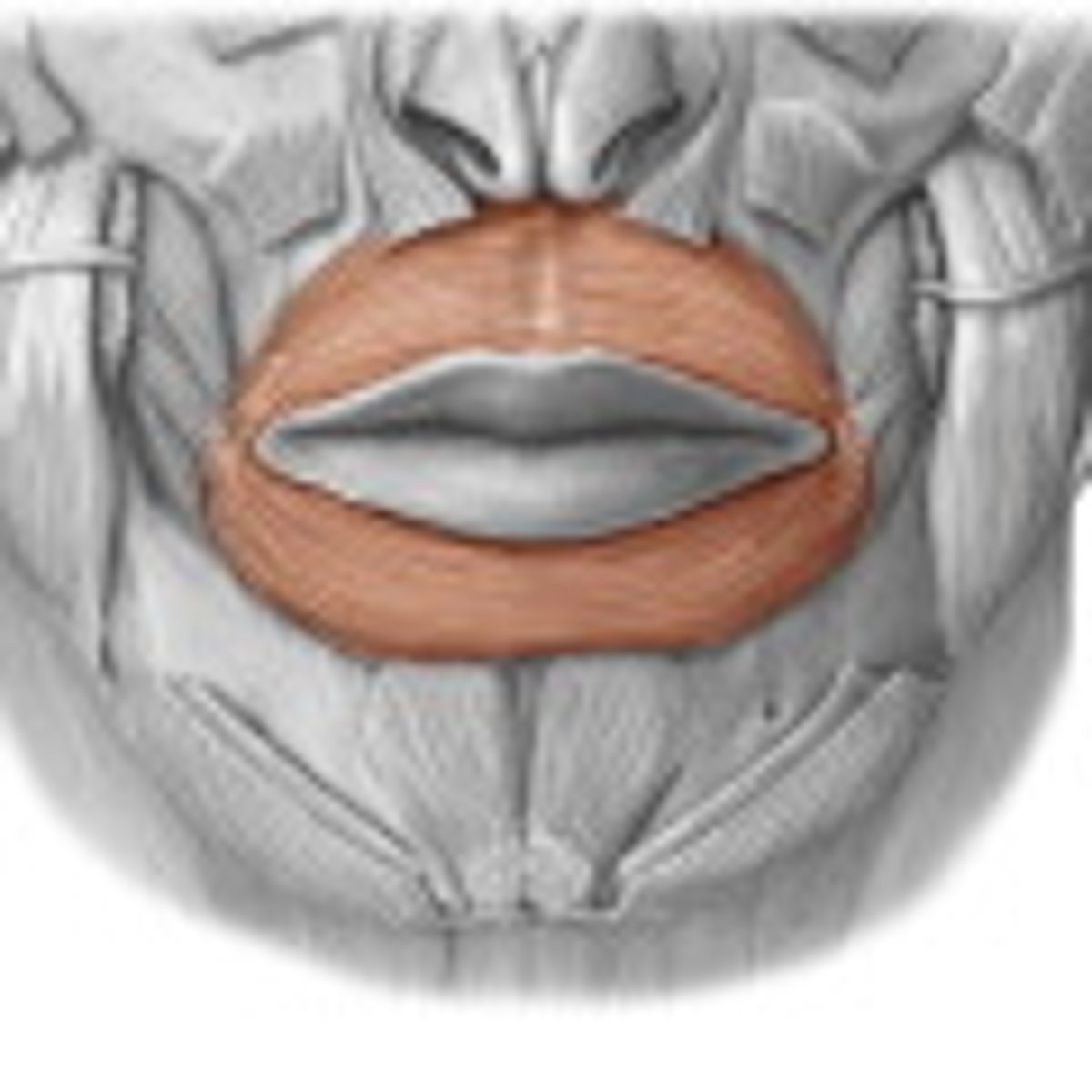
angle of mouth
Insertion - Orbicularis oris
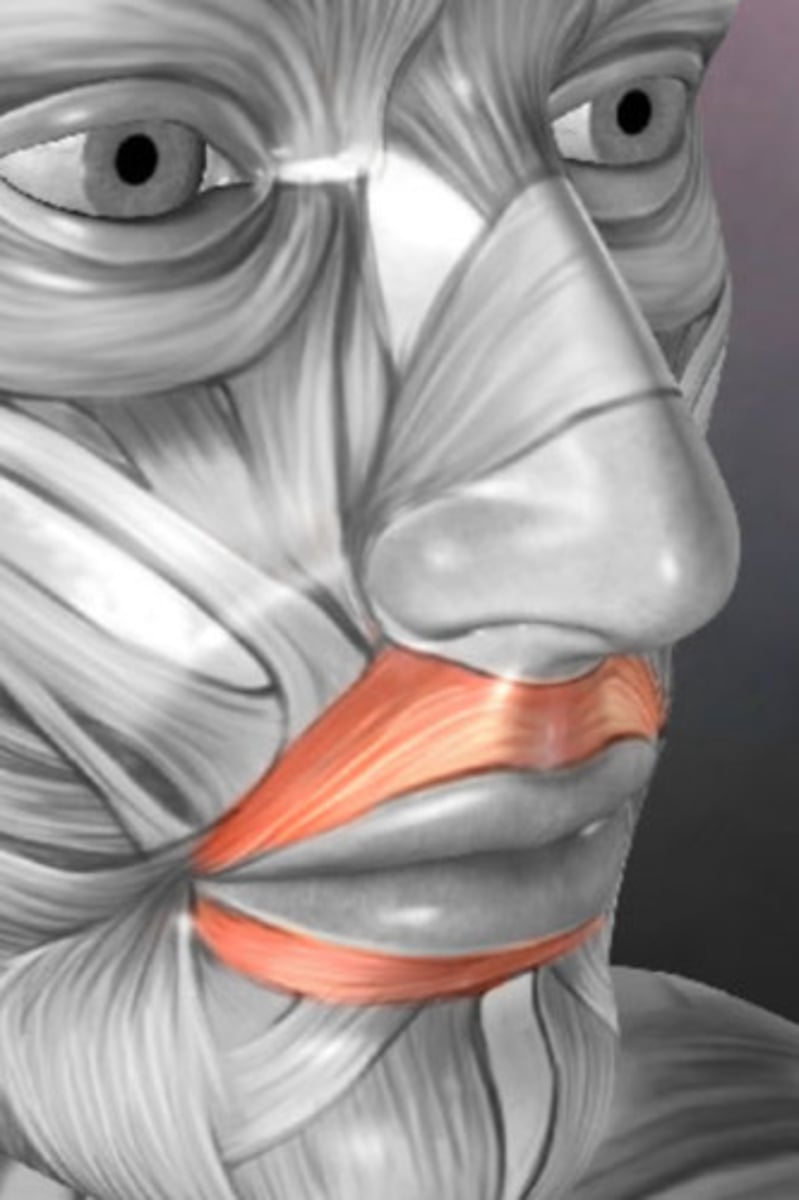
closing or pursing lips
Expression - Orbicularis oris
maxilla, mandible, pterygoid raphe
Origin - Buccinator
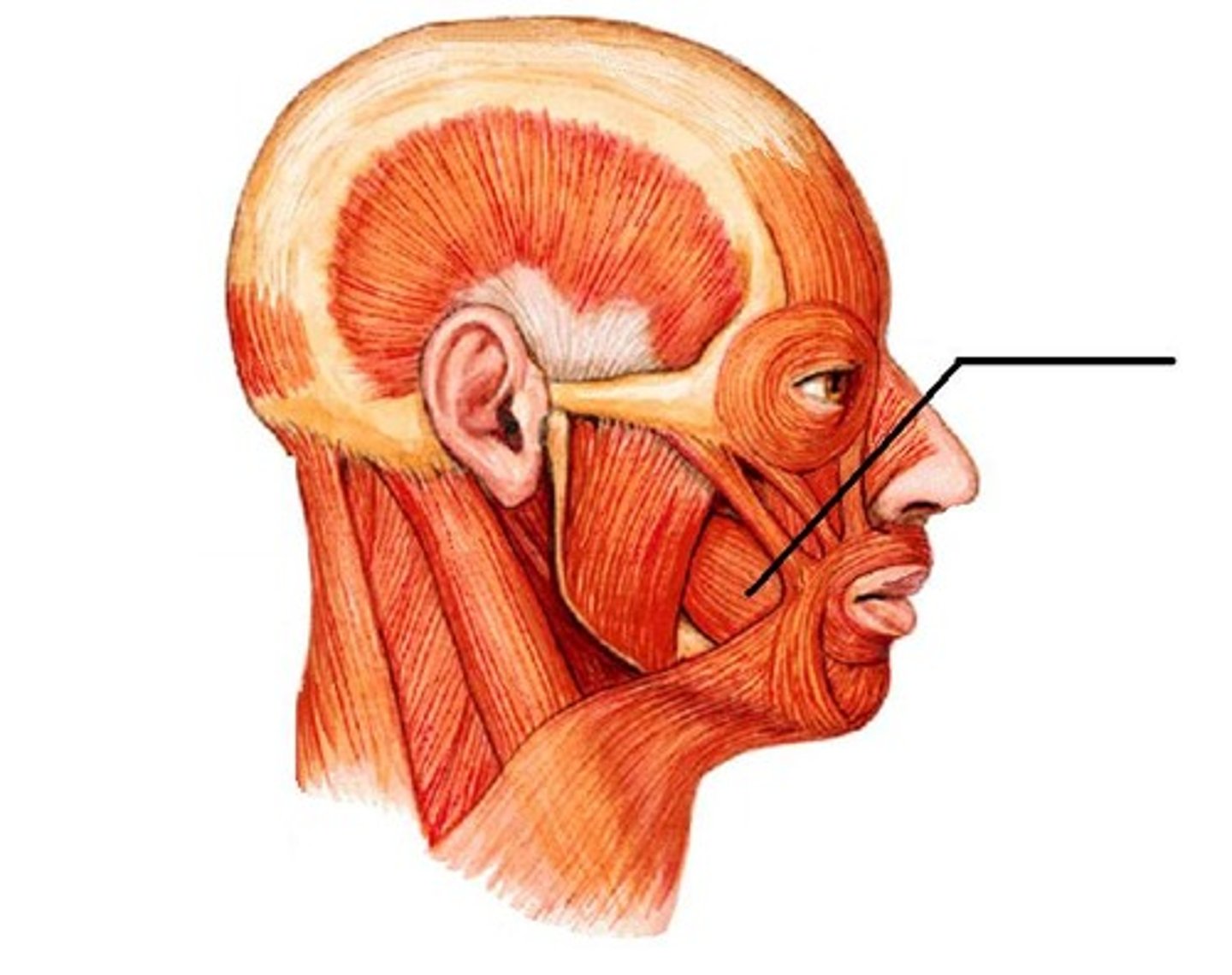
angle of the mouth
Insertion - Buccinator
flattens cheek/assists in chewing, assists the muscles of mastication
Expression - Buccinator
fascia superficial to the masseter muscle
Origin - Risorius
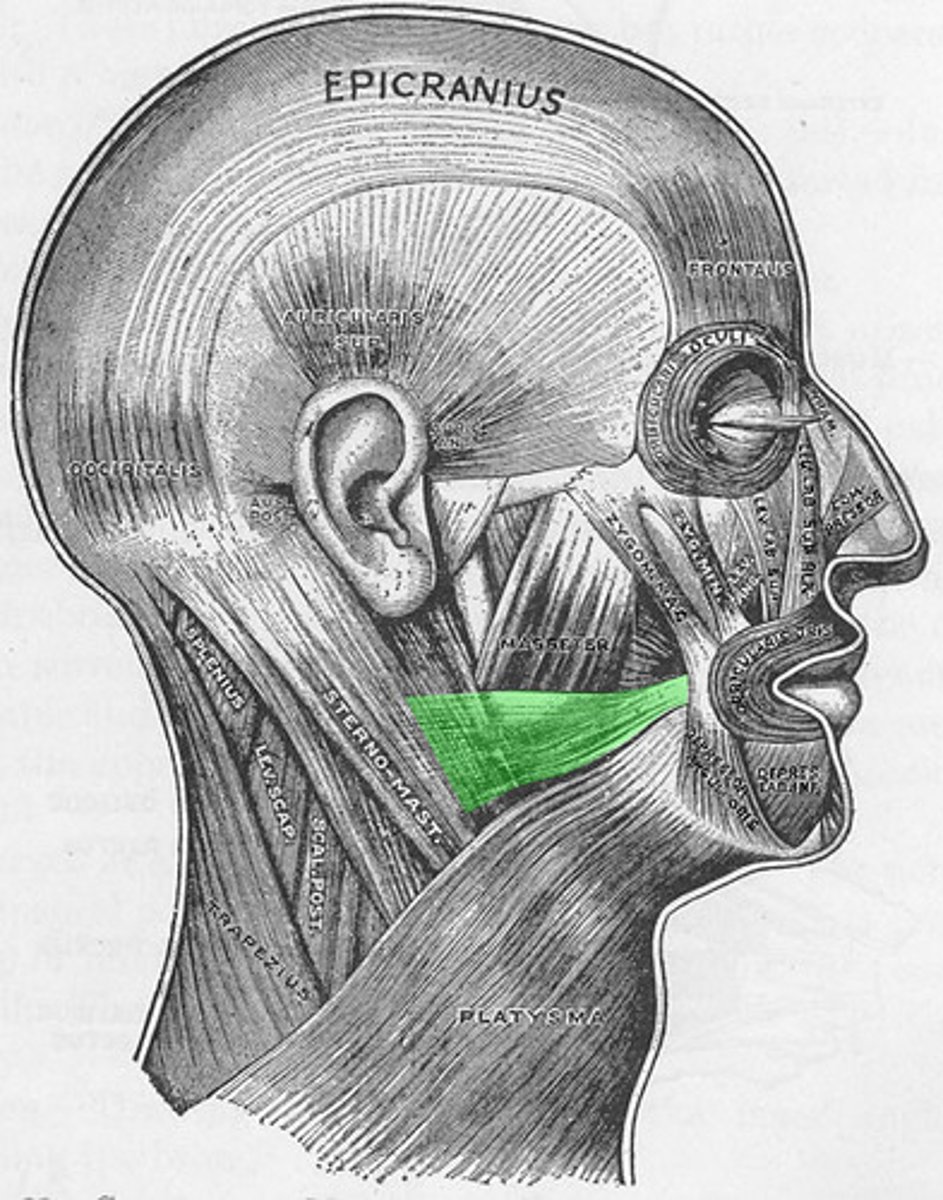
angle of the mouth
Insertion - Risorius
smiling widely
Expression - Risorius
zygomatic bone
Origin - Zygomaticus
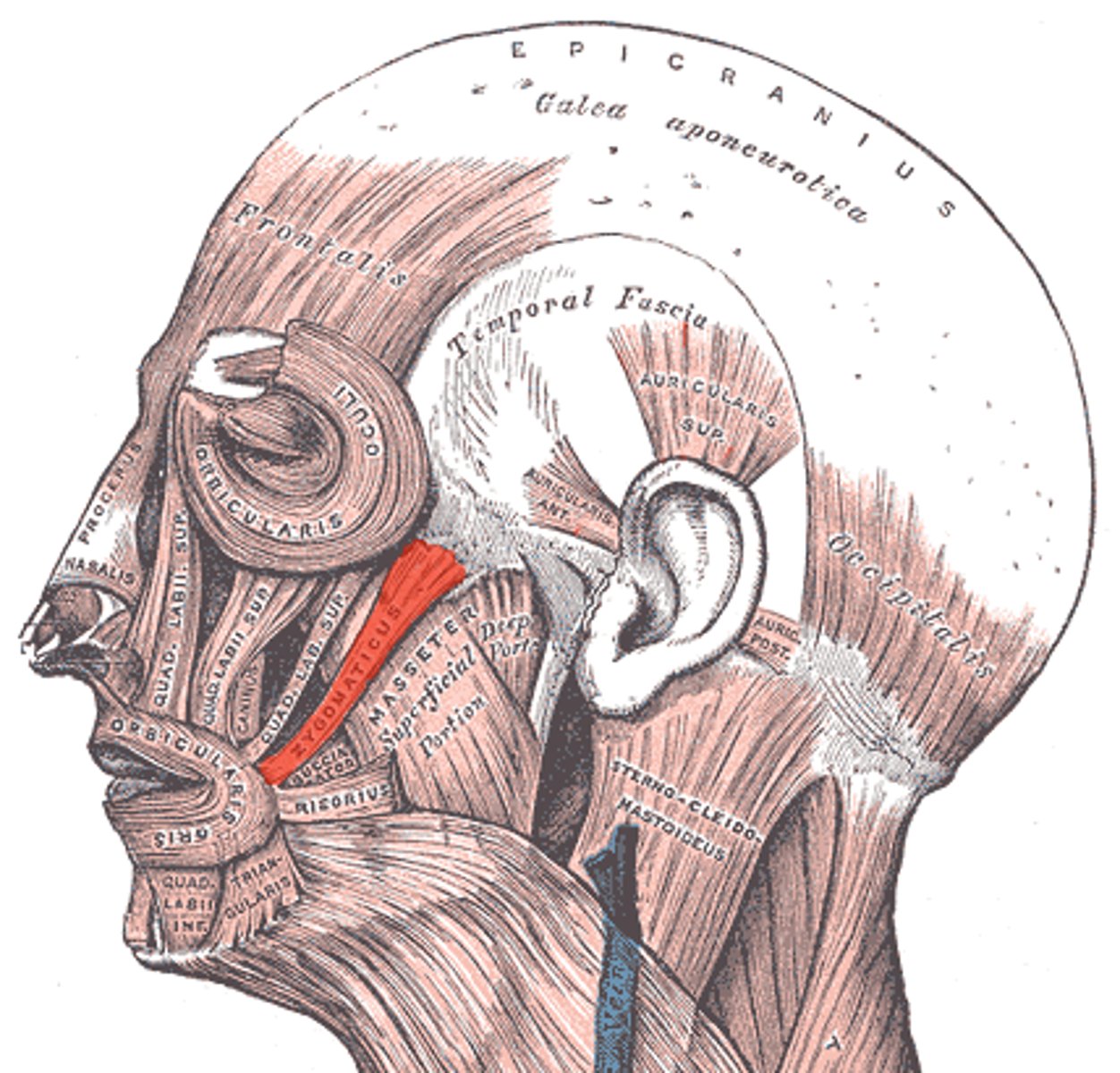
major: angle of mouth
minor: upper lip
Insertion - Zygomaticus
smiling and raising upper lip
Expression - Zygomaticus
maxilla
Origin - Levator anguli oris
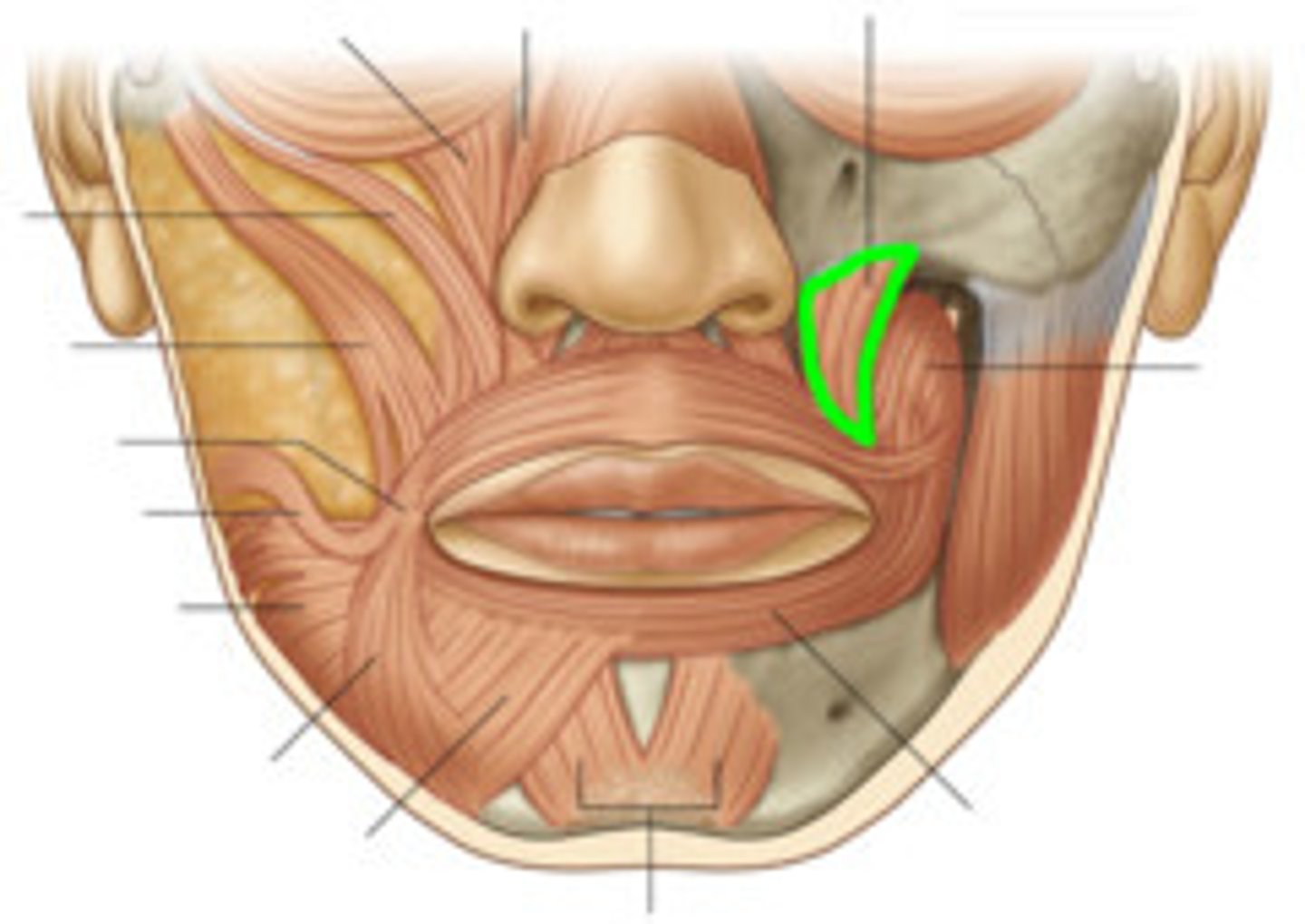
angle of the mouth
Insertion - Levator anguli oris
smiling
Expression - Levator anguli oris
mandible
Origin - Depressor anguli oris
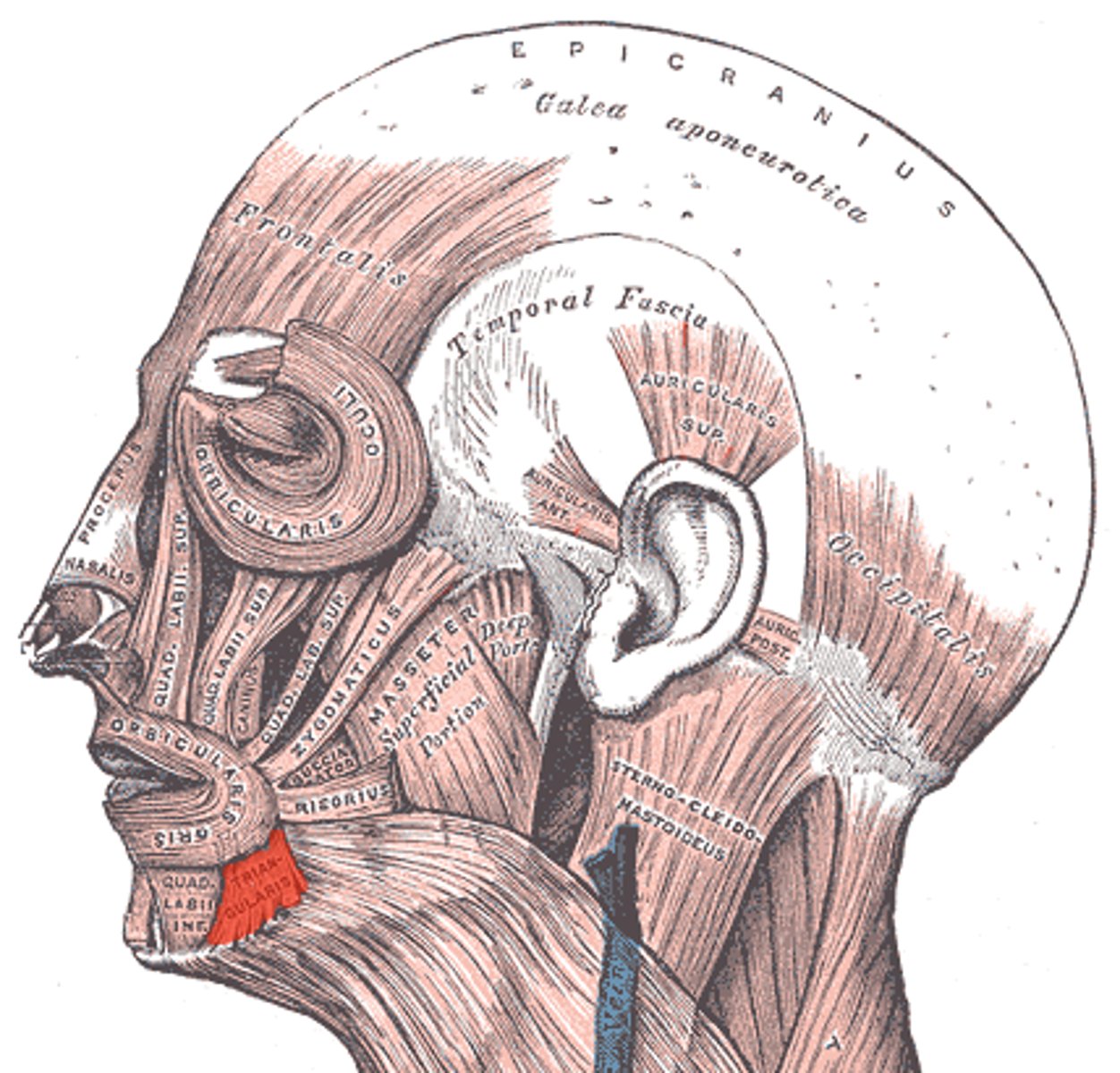
angle of mouth
Insertion - Depressor anguli oris
frowning
Expression - Depressor anguli oris
seventh cranial nerve (VII) or facial nerve with blood supply from the facial artery
All facial muscles are innervated by?
bone
NOTE: In general, facial muscles have origins with _______ and insertions with skin tissue.
superficial head: anterior 2/3 of lower border of zygomatic arch
deep head: posterior 1/3 and medial surface of zygomatic arch
Origin - Masseter