Chapter 23: Signal Transduction Mechanisms
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
131 Terms
These are part of the body seen in the digestive system that is controlled by cell signaling pathways.
taste buds
This is secreted by the adrenal gland. Responsible for Fight or flight situation
Adrenaline/epinephrine
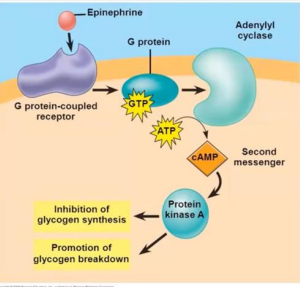
For epinephrine = adrenergic/adreno receptors. Epinephrine accepts the ligand in this pathway
Epinephrine Transduction Pathway
These are the primary messengers of the Epinephrine Transduction Pathway that resulted to the production of secondary messenger
Epinephrine
Body will respond with increased heartbeat and glycogen breakdown because of this.
Epinephrine
This is considered the secondary messengers in ETP. Activates protein kinases
cAMP
Transport movement of phosphate molecules from molecule to molecule. Power cellular reactions
Kinases
What can be seen in this photo?
Ligand-receptor binding
TRUE OR FALSE:
In the most cases the binding of a receptor and ligand resembles the binding of an enzyme and its substrate
True
The receptor specific for a certain ligand is called the
cognate receptor
A receptor bound to its ligand is said to be
occupied
Facilitate increase the binding between ligand and receptor
Co-receptors
Can you allow cell signaling to continue happening? Needs regulation or not?
Signals regulate
TRUE OR FALSE:
Cells are geared to sense fixed concentrations rather than ligand concentration changes
False
TRUE OR FALSE:
When receptors are occupied for prolonged periods, the cell adapts and longer respond to the ligand
True
When receptors are occupied for prolonged periods, the cell adapts and longer respond to the ligand. These changes are called?
receptor down-regulations
A receptor-down regulation that is accomplish to decrease response
down-regulate
A receptor-down regulation that is accomplish to increase response
up-regulated
Cells reduce the density of receptors on their cell surfaces via
receptor-mediated endocytosis
There are no more receptors, nothing to accept the ligand, no more signals. Reducing the effect of the receptors by eliminating or lessening the receptors. Small portions of the plasma membrane containing the receptors are internalize
Endocytosis
Allows cells to internalize receptors and extracellular molecules, bringing them into the cell via protein-coated vesicles
Clathrin-Dependent endocytosis
In Clathrin-Dependent endocytosis, this allows cells to internalize receptors and extracellular molecules, bringing them into the cell via?
protein-coated vesicles
Allows the selective transfer of macromolecules. Concentrates the receptor molecules and the internalized receptors are transported in the vesicles. Can down regulate via activating the clathrin.
Clathrin-Dependent endocytosis
TRUE OR FALSE:
Clathrin-Dependent endocytosis is important in the removal of the receptors from the plasma membrane
True
Cells can adapt to signals by __________, alterations to the receptor that lower its affinity for the ligand
desensitization
Refers to the decreased responsiveness. Happens upon chronic/repeated exposure to ligand or agonists
desensitization
Desensitization is like _______ feedback mechanisms that shuts off the receptor or making it less receptive to a particular ligand
negative
TRUE OR FALSE:
In desensitization, ligand activation triggers a feedback circuit that shuts off the receptors or removes it from the cell surface
False
TRUE OR FALSE:
It is possible to make synthetic ligands that bind even more tightly or selectively than the real ligand
True
Drugs that activate the same receptor they are bound to. Examples are Heroine and Morphine
Agonists
Bind receptors without triggering a change, and prevent the naturally occurring messenger from activating the receptor
Antagonists
Ligands that sort of triggering a change and prevent the activation of the receptor, the end result of the antagonist is?
No effect
TRUE OR FALSE:
Cells can be exposed to a multitude of signals at certain moments
False
TRUE OR FALSE:
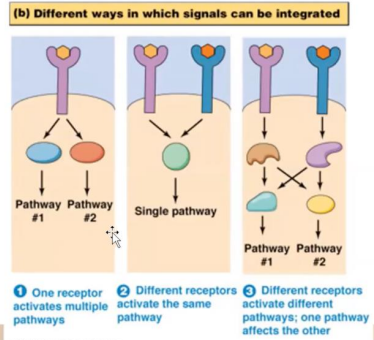
A single receptor can activate multiple pathways, or multiple pathways can converge into the same molecules
True
Sometimes activated components from one pathway affect components of another pathway, this is called
signaling crosstalk
TRUE OR FALSE:
Signaling is more of a network of linear sequence of events than a biochemical pathways
False
TRUE OR FALSE:
Components from one pathway will have an influence on the components or molecules in any other pathway
True
TRUE OR FALSE:
Very small quantities of ligand are often sufficient to elicit a response from a target cell
True
TRUE OR FALSE:
At each step in the resulting cascade of events, a signaling intermediate stimulates the production of many molecules needed for the next step
True
The multiplication of the effect of the signal is called
signal amplification
THIS IS AN EXAMPLE PROCESS OF SIGNAL AMPLIFICATION, ARRANGE THE FOLLOWING IN THE CORRECT ORDER
A. Begin with 1 molecule -> activate G protein -> Activation of 100 molecules - > so on and so forth
B. Adrenal gland will produce epinephrine in response to stressful situation
C. Moving one step to another will lead to producing 10^2 molecules
B, A, C
In here, we want to produce more glucose for energy
Fight or flight
TRUE OR FALSE:
Small quantities of ligand is not enough to elicit a major response resulting to production of many molecules
False
Controls the regulation of blood glucose levels via Negative Feedback System
Insulin and Glucagon
Causes the blood glucose level to increase. Long chains of repeating glucose units. During digestion, this is broken to glucose and absorbed by the bloodstream
Carbohydrates
Increase in blood glucose level causes the pancreas to secrete
insulin
Pancreas is a gland that secretes hormones which act on specific target organs. What target organ is stimulated to convert glucose to glycogen
liver
Long multibranched of glucose monomers stored in livers and muscle cells
Glycogen
Insulin also causes the body cells to uptake or take in glucose decreasing the blood glucose level into the optimal state. The faulty state is?
Diabetes
Secreted when blood glucose level drops (when you’re hungry)
Glucagon
The target organ of glucagon where it increases the blood glucose level to its optimal state
liver
Taste receptors responsible for sweet taste
T1r2 and T1r3
Taste receptors responsible for savory and umami tastes
T1r1 and T1r3
TRUE OR FALSE:
Receptors can be classified into several basic categories
True
Categories of Receptors
Ligand-gated channels, GPCRs
A huge family of receptors. Facilitates cell signaling and different types of cellular responses. Have a similar structure but quite different amino acid sequence
G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR)
Guanine-nucleotide Binding protein
G protein
Causes a change in receptor conformation that activates a particular G protein
Ligand binding
Each GPCR has _________________________ connected by alternating cytosolic or extracellular loops. Crosses the phospholipid bilayer. There are external and internal loops
seven transmembrane alpha-helices
Terminus that is is exposed to the extracellular fluid
N terminus
Terminus that is residing in the cytosolic region (within the cell/internally) and interacts with G proteins.
C terminus
TRUE OR FALSE:
A ligand binds to the extracellular portion of the receptor, causing an intracellular portion of the receptor (also cytosolic loops) to bind and activate a G protein
True
This is considered the first step in GPCR
Ligand Binding
This is considered the second step in GPCR. This activates a particular G protein coupled to the certain receptor
change in conformation/shape
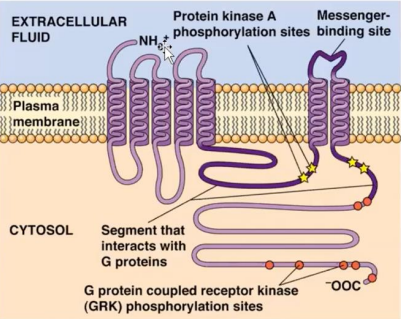
The loop itself creates the messenger-binding site for a particular messenger or chemical or ligand
Messenger binding site
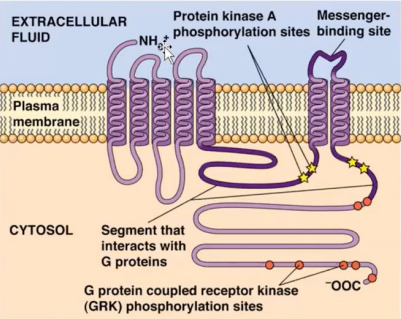
Reacts with the G protein
Cytosolic loop
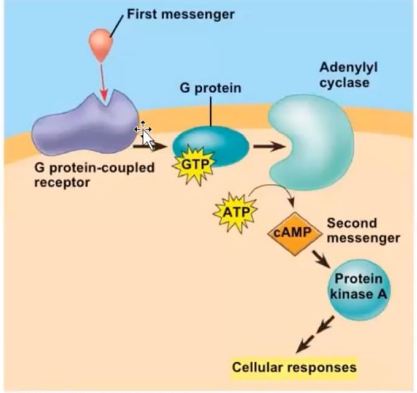
Activation will activate Adenylyl cyclase
G protein
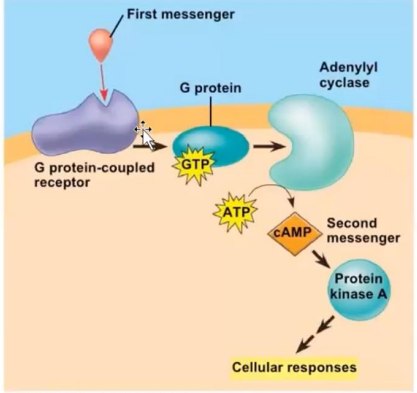
When activated, will produce cyclic AMP from ATP
Adenylyl cyclase
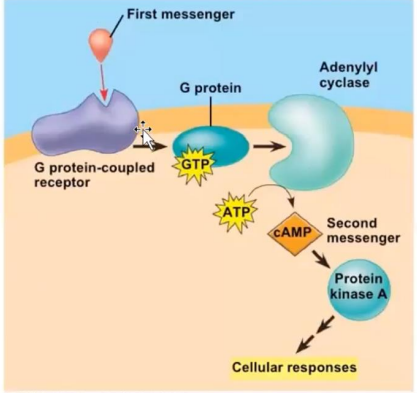
Will become the second messenger. Activates Protein Kinase A
cAMP
G protein-linked receptors examples:
olfactory, taste, beta-adrenergic, hormone, opiod receptors
Even pain and itch as well as allergic dermatitis are explained by the
GPCR
Carried out by the G-protein coupled receptor kinases (GRKs). Act on activated receptors
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation is carried out by the
G-protein coupled receptor kinases (GRKs)
Binds phosphorylated Betaadrenergic receptors and inhibits them. Proteins that are versatile, multifunctional adapter proteins that are best known for their ability to desensitize GPCRs (negative regulators) and to regulate cellular functions
Beta-arrestin
TRUE OR FALSE:
Upon GPCR activation *when phosphorylated, Beta-arrestins bind to antagonist-occupied receptors, completely inhibiting ability to associate with G proteins
False
Activated by G Protein-mediated signaling. In turn, this can phosphorylate other amino acids on the receptor and inhibit it
Protein Kinase A
are stimulators of signal transduction
Gs
are inhibitors of signal transduction
Gi
G proteins is considered?
Heterotrimeric
What are the three subunits of G proteins?
G alpha, G beta, G gamma
They mediate signal transduction coupled to the (or through the) GPCR and act like molecular switches
G proteins
TRUE OR FALSE:
G protein, like molecular switches whose “on” and “off” states depend on whether they are bound to Guanosine Triphosphate (GTP) or Guanosine Diphosphate (GDP)
True
Largest subunits. When in inactive resting stage, it is bound to GDP. When it starts binding to GTP, it is activated
Ga
When Ga is bound to GDP it is?
resting/inactive
When Ga is bound to GTP it is?
active
This Binds to GDP and GTP
GBy
TRUE OR FALSE:
When Ga binds to GTP, it detaches from GBy subunits which are permanently bound together
True
In the step 1 of G protein activation, when a ligand (messenger) binds to a ______________ the resulting change in receptor conformation causes a G protein to associate with it and release its GDP
G protein-coupled receptor
In the step 2 of G protein activation, the Ga then binds a new GTP molecule and detaches from the complex. Signal pathways govern the?
alpha subunits
TRUE OR FALSE:
In the 3rd step of G protein activation, either the Ga or the GBy initiates signal transduction depending on the G protein
True
ARRANGE THE FOLLOWING BASED ON G PROTEIN INITIAL ACTIVATION:
A. Alpha unit will separate to the beta and gamma subunits
B. GTP is binded and alpha subunits detaches from the protein complex
C. GDP is released
C, B, A
TRUE OR FALSE:
In G protein inactivation, G proteins remain active as long as the Ga subunits is bound to GTP and separate from the GBy subunit
True
TRUE OR FALSE:
In G protein inactivation, Once the Ga subunit has hydrolyzed GDP to GTP, it reassociates with GBy
False
The most important G protein function is
formation of second messenger
Production of cAMP is formed from?
ATP
Activation of adenylyl cyclase will promote the conversion of ATP to
cAMP
Activation of Protein Kinase A inhibits?
Glycogen synthesis
The entire sequence, from signal reception to cellular response is referred to as
signal transduction pathway
In the fight or flight response, the adrenal glands release the hormone __________, a signaling molecule within the body
epinephrine
Certain cells (such as _______ cells) can detect the signal, after which they process the signal and respond to it
liver