Manufacturing Operations
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
What is the technical definition of Manufacturing
Application of physical and chemical processes to alter the geometry, properties and/or appearance of a given starting material to make parts/products
Also means to join together multiple parts to make assembled products
What is the economic definition?
Transformation of materials into items of greater value through processing and assembly operations
Manufacturing adds value to the material e.g. iron ore to steel
3 types of industry: (same as geog)
Primary industries - obtain and provide natural resources (e.g. agriculture, oil)
Secondary industries - convert output of primary industries into products (e.g. automotive, construction etc)
Tertiary industries - Service sector (e.g. banking, teaching etc)
What are process industries?
Industries that manufacture products by processing raw materials, and dont necassarily have individual countable products e.g. food and drink, energy , basic metals etc
What are discrete product industries
Produce indidual counatble units, e.g. cars, aircraft, machinery
What do continuous and batch production look like in process and discrete industries?
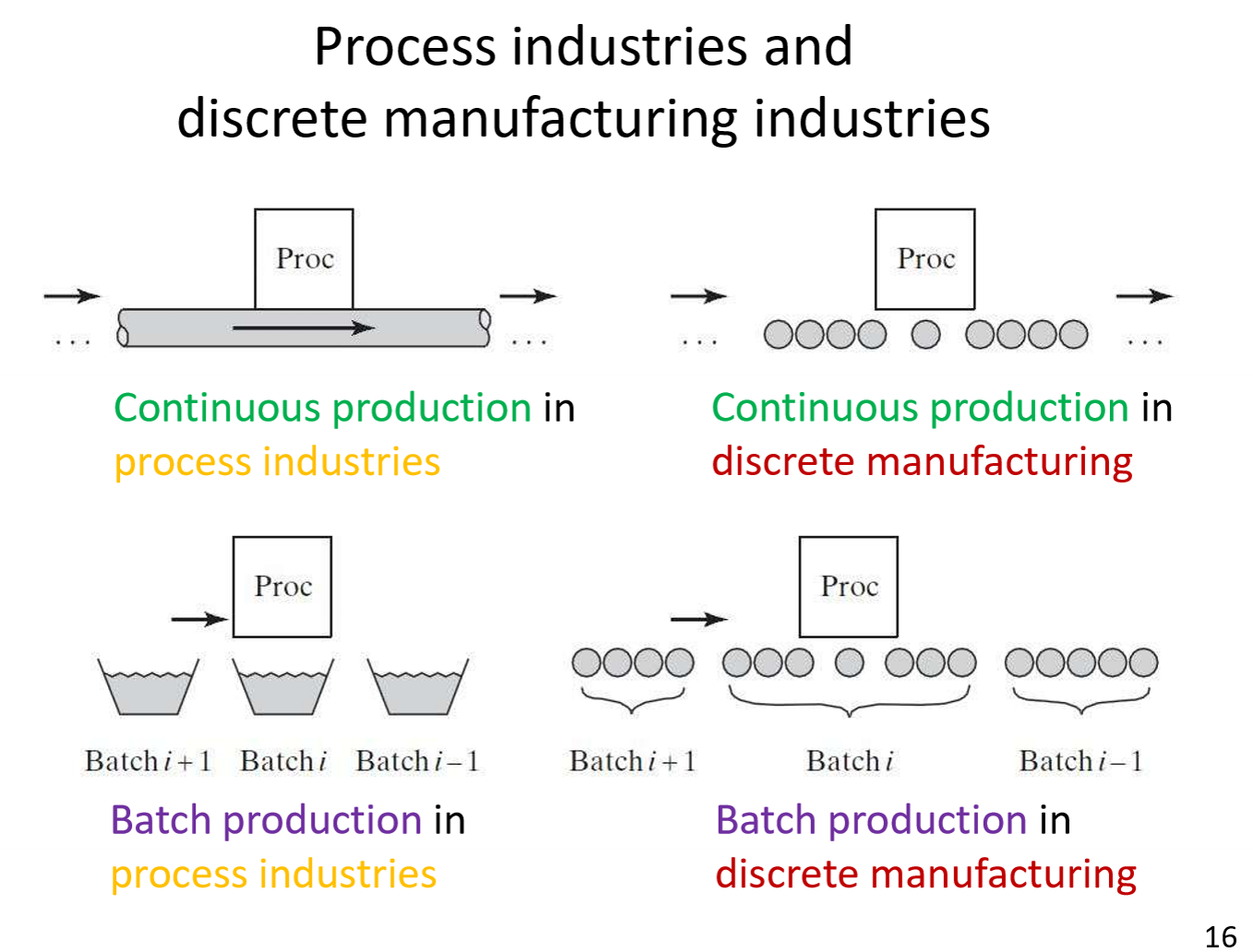
What are manufacturing operations?
Basic activities in a factory to convert raw materials into finished products
What does this consist of for discrete products:
1) Manufacturing processing
2) Material handling
3) Inspection and testing
4) Coordination and Control
What are the 2 main overall manufacturing processes
Processing operations
Assembly operations
What are the 3 types of process operation?
Shaping operations (e.g. additive and subtractive manufacturing, solidifcation processes (casting))
Property-enhancement operations (e.g. heat treatment)
Surface processing operations
What are the 2 types of Assembly operation?
Joining process (welding, adhesive etc)
Mechanical assembly process (threaded nuts and bolts, interlocking assemblies etc)
What occcurs in material handling? (3)
Material transport (e.g. veichles, conveyors, trucks)
Storage systems
Automated identification and data capture (AIDC) (e.g. bar codes)
Why is material handling significant?
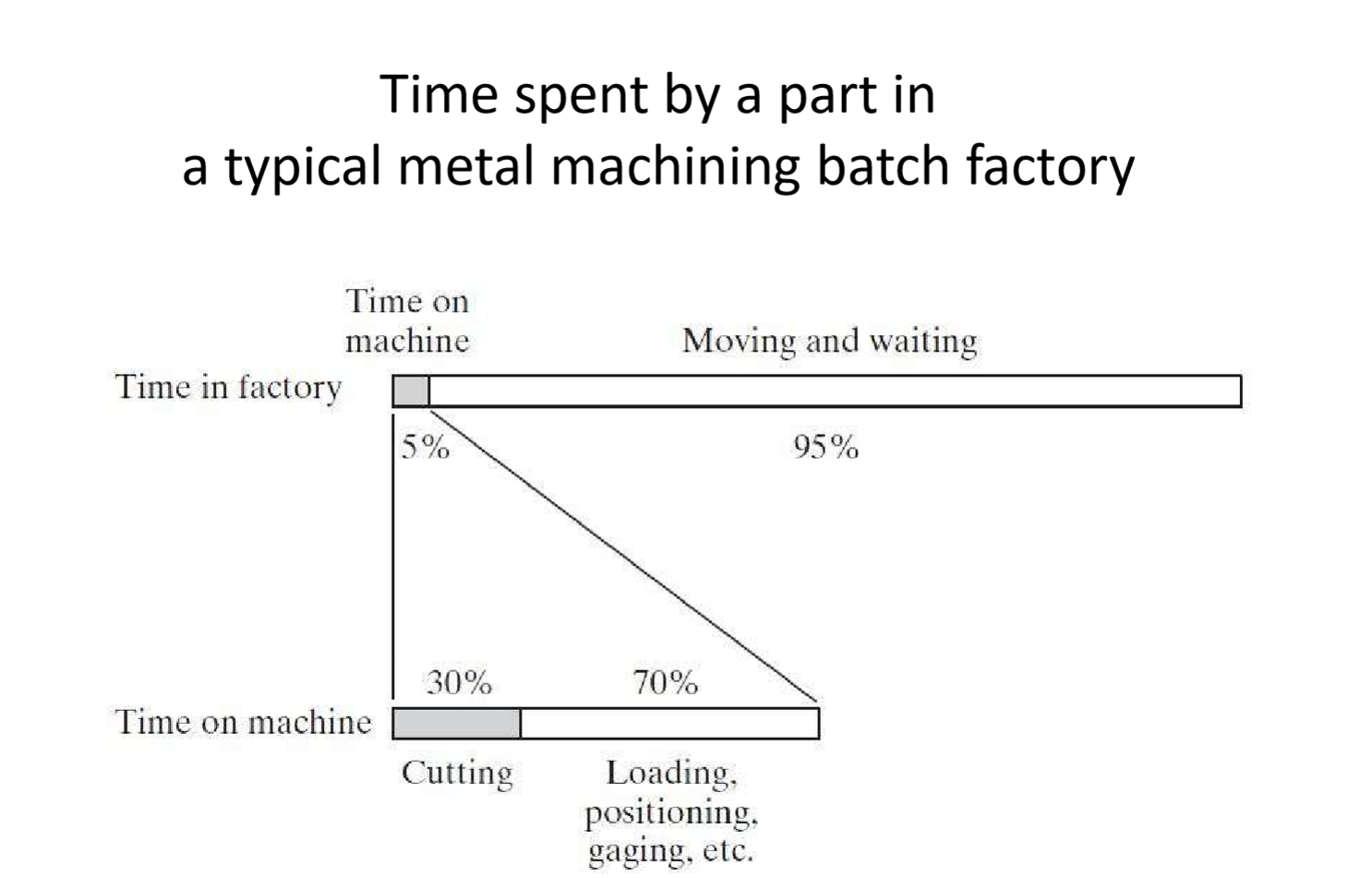
What is inspection?
What is measuring
What is gauging
Examination of the product to see if it conforms to design specifications
(inspection for variables is measuring, inspection for attributes is gauging)
What is testing?
Observing the product under actual operation (or under conditions that migh occur under operation)
What does coordination and control consist of?
Regulation of individual processing and assembly operations
Includes quality control, process control and optimisation
Management of plant-level activities
ie production, planning and control (PPC)
What does low production mean:
1-100 units anually
Medium production:
100 - 10,000 units
High production:
10,000 to millions of units
Product variety refers to
The number of different product or part variations in a design
There is an inverse relationship between
Production quantity and variety
Diff between hard and soft product variety
Hard - Products differ greatly
Soft - Products differ slightly
What are the three types of manufacturing system?
Job shop (low production)
Cellular Manufacturing System (Medium Production)
Flow Line (High production)
Can a factory consist of multiple in 1?
Yes, can be either one of a combination of them
A job shop is a manufacturing system that _____
produces unique products in low variety
Features and applications of a job shop
Complex products
General purpose equipment
Prototypes
Special machinery
What are the two types of layout in a job shop
Process layout - Equipment arranged and fixed, while materials go through the workstations (normal factory)
Fixed position layout - worker and equi[ment go to the product as its too heavy (like a fair ground ride)
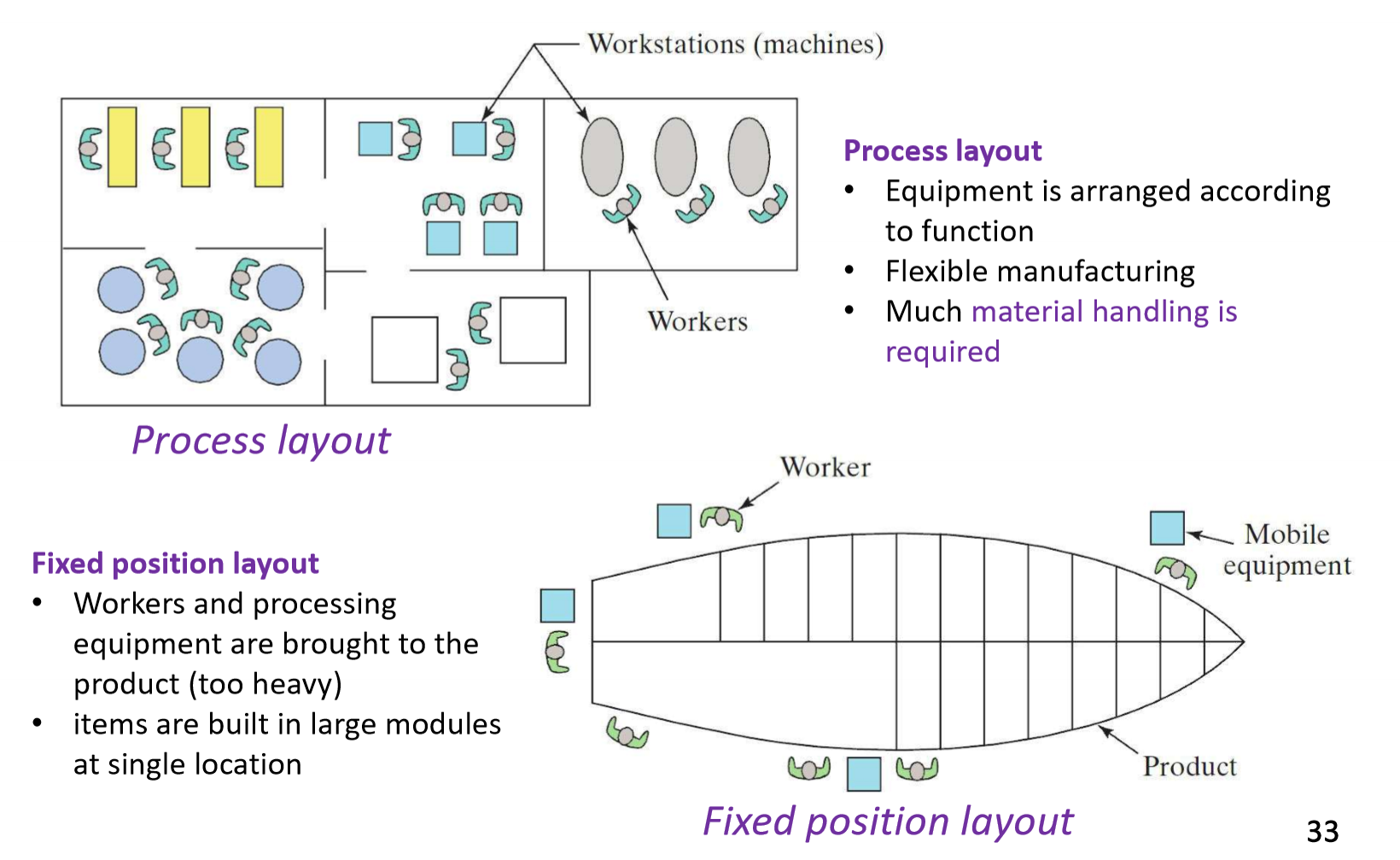
What are the two types of medium production:
Batch
Batch of product is produced, then facility is changed over to produce another product
Hard product variety
Cellular
Mixture of products is made without changeover
Soft product variety
A cellular manufacturing system is a system that
Produces several families of products in low volume
Features of a CMS:
Applications of a CMS:
Large product variety
Variable process routings
Small to Medium Volumes
Dissimilar Machines
Products customised for applications (e.g. office cabinets and aeroplane seats)
2 types of high production:
Quantity production - Mass production of single parts
Flow line production - Multiple workstations arranged in sequence, for products with assembly and processing steps
Features of a flow line:
Applications of a flow line:
Sequential config
Fixed process routings
No/little variety
Automotive final assembly, computer assembly etc
What is the total number of product units Qf equation

How can product variety P be divided
P1 → The number of distinct product lines produced by the factory
P2 → Number of models in a product line
So whats the P equation?
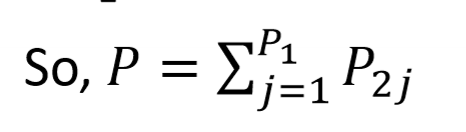
What do np and no stand for
np stands for number of parts per product (so product complexity)
no stands for number of operations per part (so part complexity)
What are the simplified equations?
Qf = PQ
(Qf = total number of parts
P = number of diff product styles
Q = average quantity per style)
What is the average Q eq?
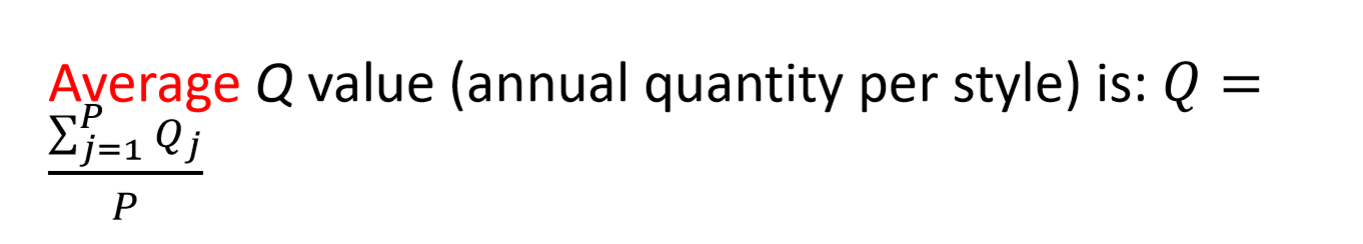
What is the number of parts produced eq?
(Number of products x number of parts per product)

What is the number of operations eq?
(number of parts x number of operations per part)
