Biology Fall Final Study Guide
1/60
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Primary Succession
Barren rock/ no soil
Secondary Succession
Forest Fire, with soil
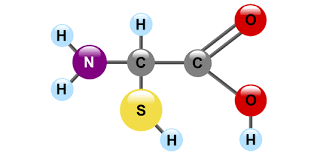
Protein Structure
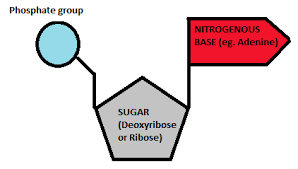
Nucleic Acid Structure
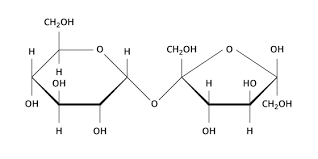
Carbohydrate Structure
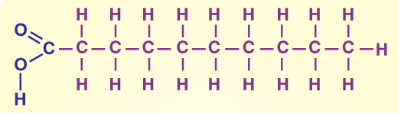
Lipid Structure
Enzymes
Protein Catalyst
DNA Fingerprinting
identifying living organisms at the molecular level.
PCR
(Polymerase Chain Reaction)Copy or duplicate DNA strands
Prophase
Chromosomes start to condense
Metaphase
Spindle fibers from the center
Anaphase
Chromosomes break, and sister chromotids move to opposite sides of the cell.
Telaphase
2 nuclei
Autotroph
Organism that makes their own food.
Mitosis
division of the Nucleus
Carrying Capacity
The maximum amount of organisms in a population.
Birth Rate
Amount of organism born in a year per 1000 individuals.
Density Dependent Limiting Factors
Has to do with the density of a population.
Density Independent Limiting Factors
Does not have to do with the density of a popualtion.
S curve
logistic growth
J curve
Exponential Growth
R-strategy
Lots of babies, not much parenting
K-strategy
Generally 1 at a time, a lot of parenting