nervous system
1/149
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
150 Terms
what does the somatosensory system do
awareness of body sensation - touch, temperature, position, pain
what are the 3 types of sensory neurons
general somatic: pain, touch, temp
special somatic: muscles, tendons, joints
general visceral: fullness, discomfort
difference between first, second, and third order neurons
first: periphery to CNS, sensory
second: spinal cord to thalamus, ascending in dorsal column
third: thalamus to cortex, processing
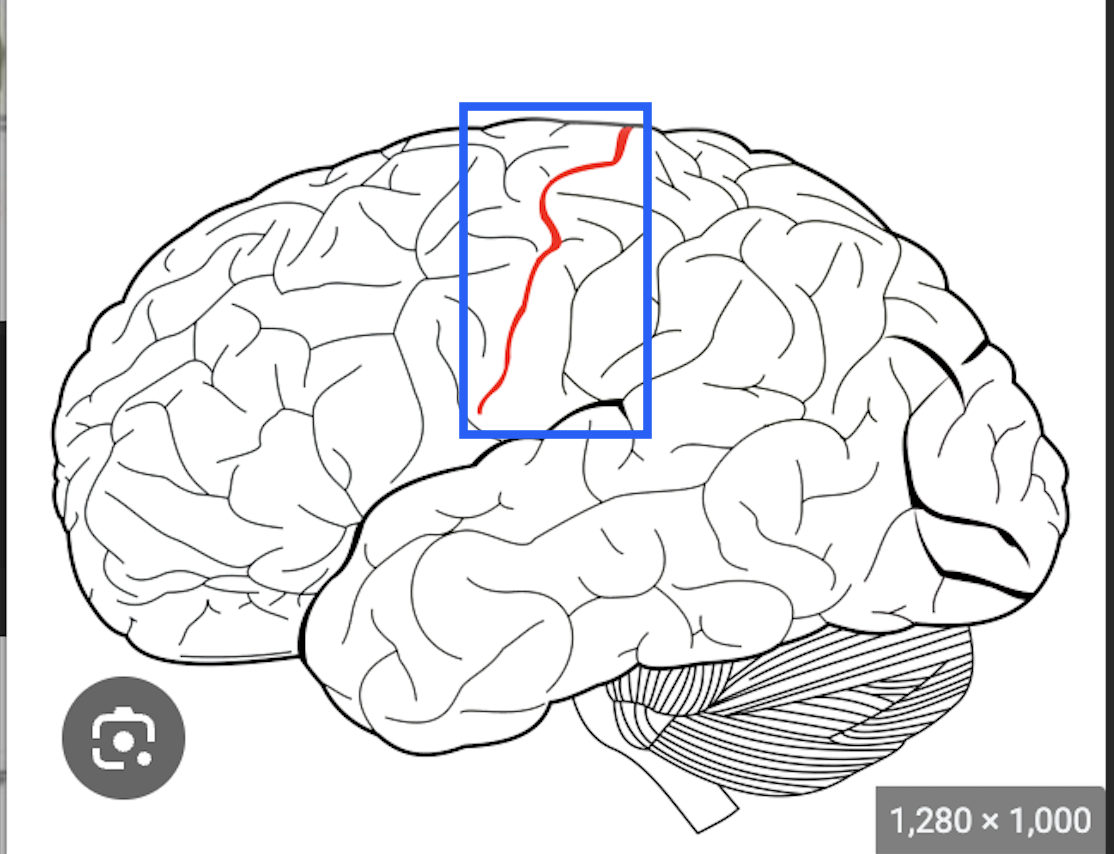
what is this
central sulcus
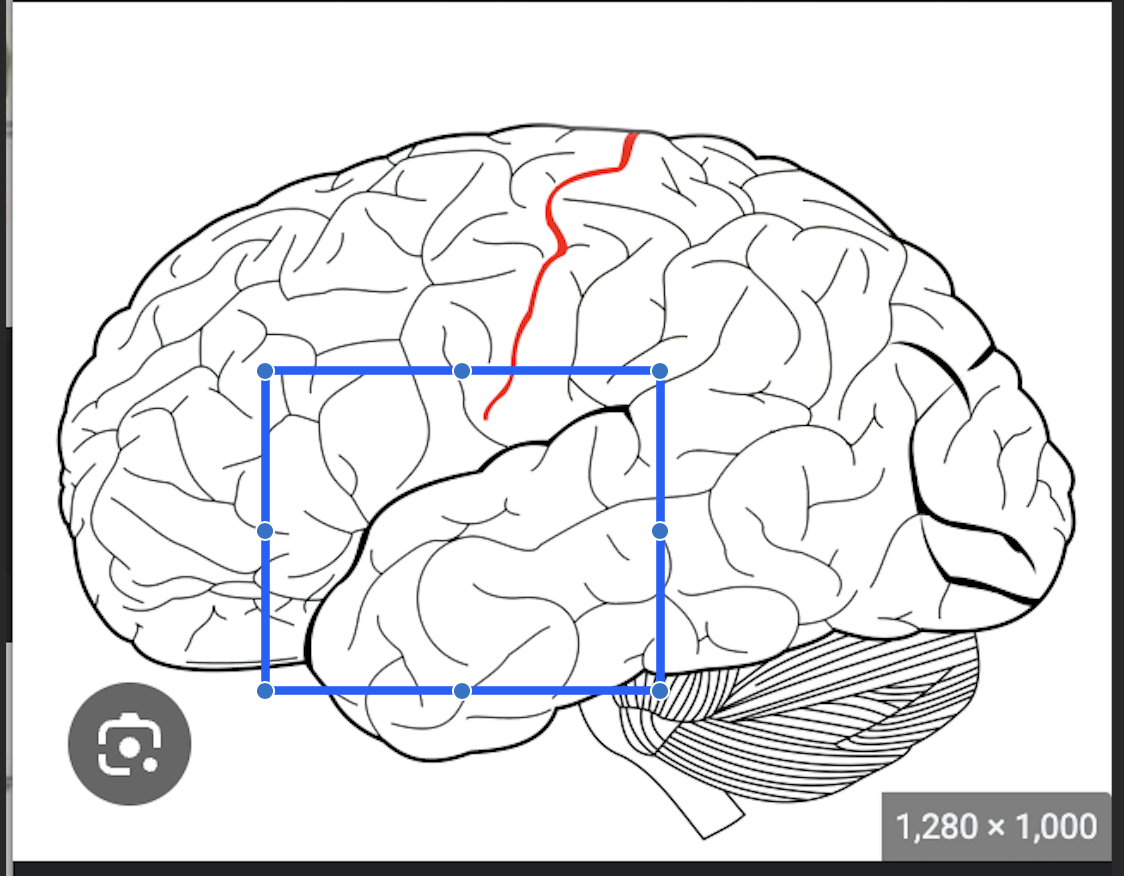
what is this
sylvian/lateral fissure
where is the precentral gyrus and what is its main job
anterior to central gyrus, primary motor cortex
where is the postcentral gyrus and what is its main job
posterior to central gyrus, somatic sensation
sensory info from limbs and trunk share what common structure
dorsal root ganglion neurons
what is part of the sensory unit
body of dorsal root ganglion, peripheral branch, central axon
what are the 3 types of nerve fibers
A: myelinated - touch, pressure, heat, cold pain
B: myelinated - cut/subcut mechanoreceptors
C: unmyelinated - mechanical/chemical/intense hot or cold pain, warm/hot sensation - delayed transmission
UE dermatomes C5-T2
C5 deltoid, C6 thumb, C7 middle finger, C8 pinky, T1 M epicondyle, T2 axilla
LE dermatomes L1-S2
L1 inguinal ligament, L2 distal M quad, L3 M epicondyle, L4 M malleolus, L5 third MTP, S1 calcaneus, S2 popliteal fossa
facial dermatomes CN5
V1 frontal bone, V2 maxilla, V3 mandible
important thoracic dermatomes
T4 nipple line, T10 umbilicus
where does all general sensation and pain enter the spinal cord
dorsal root
describe the discriminative pathway
dorsal column, medial lemniscus
type A fibers, mechanoreceptors - somatosensory input ascends ipsilaterally, crosses over at medulla
spatial orientation, discrimination, delicate touch, joint position
first, second, and third order neurons of discriminative pathway
first: primary dorsal root ganglion - projects to dorsal column
second: dorsal column neuron - axon through M lemniscus
third: thalamic - projects axons to primary sensory cortex
what happens after an association neuron (3ON discriminative) is damaged
can feel and describe, cannot identify
describe the anterolateral pathway
spinothalamic tracts
type C fibers, free nerve endings
input crosses over at the spinal cord, ascends contralaterally
pain, temperature, crude touch, pressure
difference between lateral and anterior spinothalamic tracts
lateral: contralateral pain, temp, crude touch - fibers cross immediately in spinal cord
anterior: contralateral crude touch, pressure - most fibers ascend a few levels before crossing over, some fibers do not cross at all
when do anterolateral fibers synapse
before reaching thalamus in reticular formation of spinal cord
what happens in a brown sequard lesion
one side of spinal cord is lesioned - lose ipstlateral fine touch, contralateral pain and temperature
what is the point of the homunculus
proportion of cortex dedicated to peripheral areas
what happens with an anterior cerebral artery lesion
weak LE
lose sensation of genitals, foot, ankle
what happens with middle cerebral artery lesion
weak and lost sensation in face and UE
what happens with posterior cerebral artery lesion
impaired vision
why does referred pain from the viscera happen
not much cortex for pain perception in viscera, stimulus confused by different areas
difference between broca and wernicke’s areas
broca: speech production, near motor cortex
wernicke: speech understanding, near auditory cortex
what happens in the prefrontal cortex
reasoning, logic, decision making
difference between somatic and special senses
somatic: touch, pressure, temperature, proprioception
special: requires complex sensory organs - vision, hearing, smell
what is 2 point discrimination an early indicator of
neuropathy and healing
where is the highest and lowest acuity for 2 point discrimination
highest: lips, cheek, fingertips
lowest: back, upper arm
what do free nerve endings detect
pain perception, touch, temperature
what do meissner corpuscles detect? where are they? adaptation rate?
light movement over skin, vibration
in hairless parts of skin
quick, fraction of second
what do merkel disks detect? where are they? adaptation rate?
steady state sensation to touch (like clothes)
dome shaped receptors on skin
stimulus starts strong, diminishes slowly
what does a pacinian corpuscle detect? where is it? adaptation rate?
deep pressure changes, tissue vibration - should stimulate with palpation
subcutaneous area and fascia
quick, hundredths of a second
what does a hair follicle end organ detect? where is it? adaptation rate?
movement on body surface
unmyelinated fibers around hair follicle
quick
what do ruffini end organs detect? where are they? adaptation rate?
deformation (heavy/continuous pressure)
joint capsules, skin, deeper structures
little adaptation
what happens (neurologically) with diabetes
chronic high blood sugar damages nerves → diabetic neuropathy, lose ability to sense pain
what weight monofilament is considered the threshold for protective sensation
5.07
what does someone that cannot feel the 5.07 monofilament need to do
regular foot checks for breakdown, lesions, blisters, etc
what temperatures do warmth receptors detect
25-46 C
77-114 F
what temperatures do cold receptors detect
10-30 C
50-104 F
what temperatures are thermal pain receptors stimulated at
<10 C or >46 C
why can getting in a hot tub feel painful
receptors detect CHANGES - strong stimulus can be perceived as painful
will adapt slowly
describe when the 2 proprioceptors are active and what their result is
golgi tendon organs: catching 300 lbs - quick tension or load on muscle → loosen or give out as protection
muscle spindle receptors: DTRs - quick lengthening of muscle → shorten as protection
what are tonic proprioceptors for?
phasic proprioceptors?
tonic: limb positioning - orient, info at rest and movement
phasic: kinesthesia - triggered by change in position
what happens in sensory adaptation? what receptors adapt quickly/slowly
magnitude and rate of conduction of impulse decreases
touch receptors: quick
proprioceptors: slow
when is desensitization therapy commonly performed
amputations, CRPS (complex regional pain syndrome)
describe desensitization therapy
start with soft material stimulus, progressively rougher
frequently throughout day → decrease pain sensation in hypersensitive region
describe the gold standard treatment for BPPV (benign paroxymal positional vertigo)
habituation - repeated exposure, maneuver to slowly move stones back to inner ear
describe the gate control theory
pain fibers are slower and smaller, stimulate larger and faster fibers to temporarily block pain sensation (close the gate)
outdated, pain is more complex
describe the 2 types of nociceptors
A Delta: acute, myelinated - somatic pain, sharp/intense pain from superficial trauma
C fibers: chronic, unmyelinated - visceral pain, dull/aching pain originating from viscera
what can you educate your patient about pain?
what can pain education do for a patient?
pain is more than just tissue damage. it’s like an alarm - you have more control over pain than you think
decreased risk of chronic pain, healthcare costs, and pain catastrophization
what are 2 big factors that contribute to pain
anxiety and stress
describe acute pain
activated nociceptors at site of local tissue damage - short duration, associated with anxiety
what psychological factor plays a role in chronic pain behavior
depression
difference between cutaneous and deep somatic pain
cutaneous: sharp, burning - localized or dermatomal
deep: diffuse - originates from deep structures
describe visceral pain
low density of nociceptors → pain is referred
travels along pathways of autonomic nervous system
describe how referred pain happens
deep structures have little nociceptors → pain felt by area innervated by the same spinal segment, location of pain is misinterpreted
where is referred pain of the heart
T1-T5
T1: medial epicondyle
T2: axilla
jaw in females
where is referred pain of the kidney
thick band around abdomen
3 ways pain is often quantified by patients
numeric pain intensity: 0-10
visual analog scale: straight line 10cm long, mark pain level
verbal descriptor scale: ranked words to evaluate pain
how to manage acute vs chronic pain
acute: aggressive, pain meds before symptoms are severe
chronic: preventative, noncurative methods if not treatable illness
cognitive-behavioral interventions for pain management
more effective if enacted before pain starts
relaxation, distraction, cognitive reappraisal, imagery, meditation, biofeedback
physical/infared agents of pain management
heat: vasodilation, increased extensibility, reduced tension on nociceptive nerve endings
cold: vasoconstriction to prevent fluid pooling in tissues, reduce afferent activity
what kind of infared therapy shows benefit for pain
contrast therapy (alternating hot and cold)
what is the result of a cold plunge
reduced protein synthesis, inhibit hypertrophy
stimulus induced analgesia for pain management
foundation in gate control theory, TENS estim, placed directly over painful area or in dermatome
acupuncture for pain management
reduce spasm, LACK HIGH QUALITY EVIDENCE
neurostimulation for pain management
low volt estim directly to spinal cord or targeted peripheral nerve
blocks pain sensation
may be surgically implanted
difference between COX 1 and 2
1: maintain stomach acidity, vasodilation
2: local tissue inflammation, vasoconstriction
what is an NSAID?
what can happen with overuse?
non steroidal anti-inflammatory drug
GI bleeding
what adverse events can happen with COX2 inhibitors
block vasoconstriction, small clots move straight to heart
adverse cardiac events in 4-6 weeks
describe the 2 nonnarcotic analgesics
aspirin/NSAIDs: block pain impulses, block both COX enzymes, anti-inflammatory
acetaminophen: like aspirin but not anti-inflammatory
describe opioid analgesics
aka narcotics, morphine-like actions
relieve short term pain or manage severe long term pain
when are opioids most effective
before pain starts or before pain becomes extreme
fewer doses associated with early return to daily activity pain free
what kind of responses do opioids cause? what cranial nerves are affected?
parasympathetic - pinpoint pupils, aletred mental status, decreased HR RR and BP, n/v, constipation
3, 7, 9, 10
opioid withdrawal effects
uncomfortable, mot life threatening
dilated pupils, flu like symptoms, rhinorrhea, joint pain, hypertension, n/v, cramps
what needs to happen with opioid intoxication
naloxone/narcan as antagonist if RR dangerously decreased
5 minutes intramuscularly, within 2 minutes intravenously
what can help ween off opioid use
methadone
what are the 2 neurotransmitters released from autonomic neurons
antagonists - norepinephrine, acetylcholine
describe the 2 types of adrenergic receptors and what they cause
bind norepinephrine
alpha: stimulatory, vasoconstriction
beta: inhibitory, vasodilation
what do beta receptors cause in the HEART
stimulatory, increase HR
what do beta blockers do
block beta receptor, block norepinephrine
decrease HR and BP
where is norepinephrine released from?
what kind of receptors?
adrenergic fibers - post ganglionic sympathetic neurons
beta and alpha receptors
describe the 2 types of cholinergic receptors and what they cause
bind acetylcholine
nicotinic: preganglionic neuron (symp and parasymp)
muscarinic: post gangiolic parasymp → bronchoconstriction
where is acetylcholine released from?
what kind of receptors
cholinergic fibers - preganglionic sympathetic neurons, pre and post ganglionic parasympathetic neurons
nicotinic and muscarinic
where are nicotinic receptors found?
muscarinic?
beta and alpha?
nicotinic: preganglionic sympathetic and parasympathetic
muscarinic: post ganglionic parasympathetic
beta nad alpha: post ganglionic sympathetic
what is trigeminal neuralgia
aka tic douloureux
stabbing pain from compression, inflammation, or degeneration of CN5
how is trigeminal neuralgia treated
tegretol relieves in most cases
can surgically remove trigeminal ganglion if severe → permanent loss of sensation in face, teeth, gums
what is postherpetic neuralgia? how does it present
herpes zoster, shingles - chicken pox stays dormant in dorsal root ganglia
presents with dermatomal rash, intermittent shooting pain
how is shingles treated
zostavax vaccine → 60% protection
antivirals: acyclovir, valacyclovir
what are dorsal root ganglia
peripheral sensory cell bodies
what is the biggest conern for a secondary headache
TBI, tumor
symptoms of a migraine headache
Pulsatile, photophobia, phonophobia
One day
Unilateral pain
Nausea/vomiting
Dysfunctional, debilitating, dark room
difference between migraines with and without aura
with: 25%, 5-60min flickering vision
without: 75%, no warning sign
how does a migraine work
hyperexcited part of the brain
starts at occipital lobe to cause spotty vision
cortical spreading anteriorly to cause aura
what can trigger onset of a migraine
estrogen, MSG, milk chocolate, cheeses
how does vasoconstriction and dilation affect a migraine
vasodilation around trigeminal nerve → nerve compressed → trigger
vasoconstriction from caffeine or SSRI → eased symptoms