Cardiomyopathy
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
What is cardiomyopathy?
A disease of the heart muscle that affects the heart's ability to pump blood.
What are the three main types of cardiomyopathy?
Dilated, hypertrophic, and restrictive cardiomyopathy.
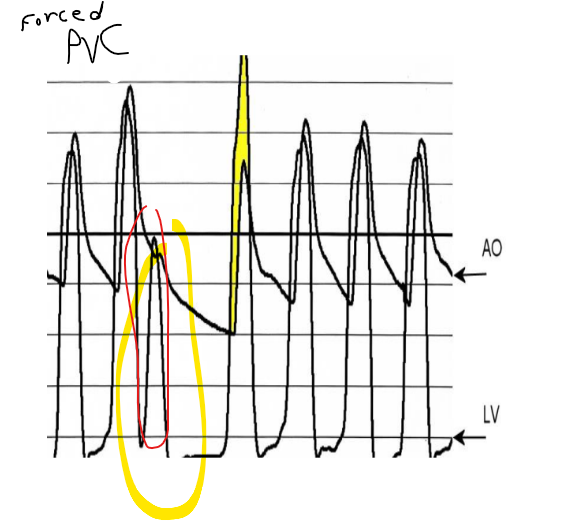
post PVC ao systolic gradient you could only have a ****
HOCM
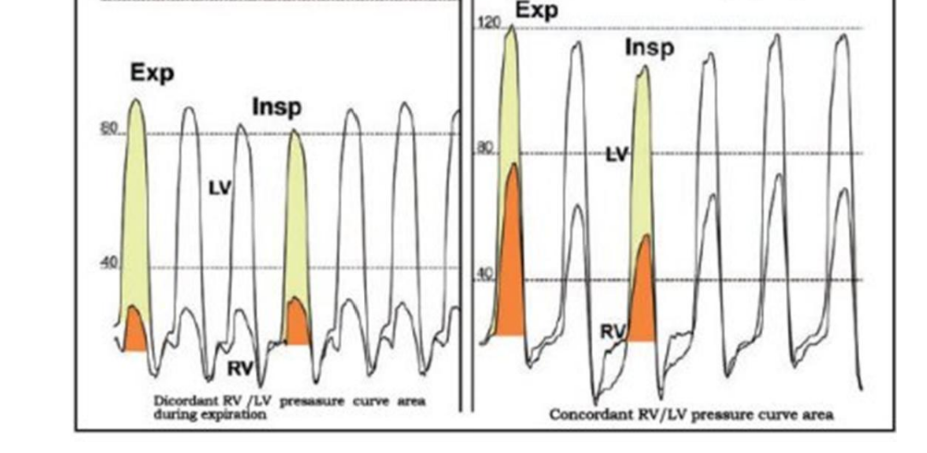
What wave form are these two
left is constrictive pericarditis
right is RCM
Which cardiomyopathies result in systolic heart failure
DCM, or dilated cardiomyopathy
cath lab treatment for HOCM/hcm
alcohol septal ablation
surgical treatment for HOCM/hcm
myectomy or septal myectomy
Coarctation of the aorta causes hypertension in how many ways.
two ways
reduced kidney blood flow causing RAAS and *** *** *** are two ways coarctation o faorta causes HTN
stiffened aortic wall (impairing baroreceptor function)
ways
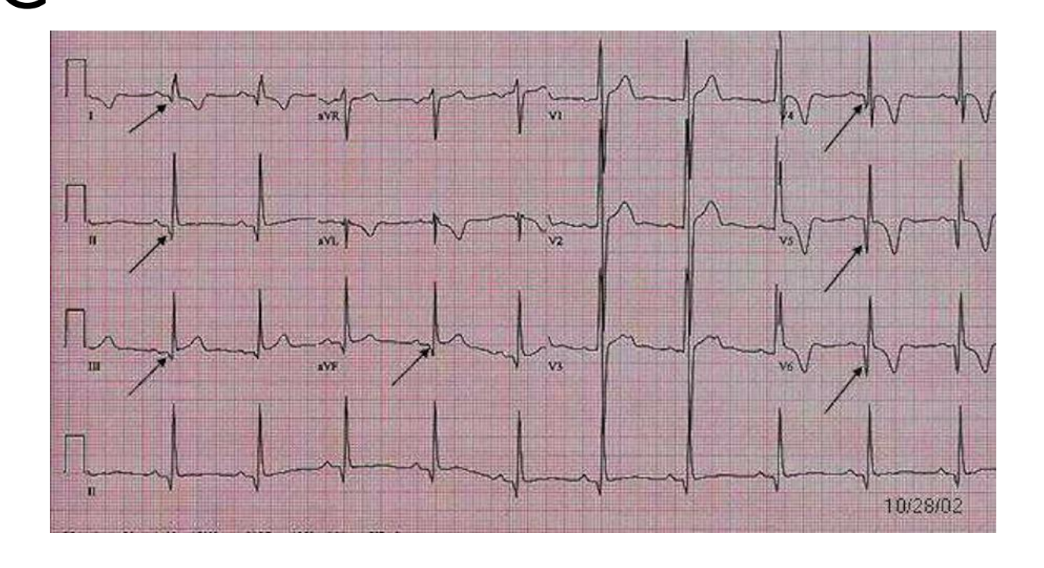
giant t wave inversion is what cardiomyopathy
HCM HOCM
What is dilated cardiomyopathy?
A type of cardiomyopathy where the heart chambers are enlarged, leading to systolic dysfunction.
What is hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
A condition characterized by thickening of the heart muscle, often affecting the left ventricle.
What is restrictive cardiomyopathy?
A form of cardiomyopathy where the walls of the ventricles become stiff, limiting their ability to fill with blood.
What are common symptoms of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
Dyspnea, angina, syncope, and palpitations.
What diagnostic test is used to confirm hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
Echocardiogram.
What is the most common cause of sudden cardiac death in young athletes?
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
What are the typical findings on an ECG for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
Abnormal Q waves, left ventricular hypertrophy, and ST-segment abnormalities.
What is the treatment goal for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
To improve ventricular filling and relieve left ventricular outflow obstruction.
What medications are commonly used to manage hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
Beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, and antiarrhythmic medications.
What is the significance of the 'square root sign' in restrictive cardiomyopathy?
It indicates poor diastolic filling with a prominent y descent in pressure traces.
What is a common cause of dilated cardiomyopathy?
Genetic factors, viral infections, and autoimmune diseases.
What are the symptoms of dilated cardiomyopathy?
Labored breathing, poor appetite, slow weight gain, and signs of heart failure.
What is the prognosis for dilated cardiomyopathy?
The 9-year survival rate is approximately 69.8%.
What is the role of an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) in cardiomyopathy?
To prevent sudden cardiac death by treating life-threatening arrhythmias.
What diagnostic test is used to identify causes of restrictive cardiomyopathy?
Myocardial biopsy.
What is the typical ECG finding in restrictive cardiomyopathy?
Low voltage QRS complexes and possible atrial fibrillation.
What are potential treatments for restrictive cardiomyopathy?
Mild diuretics, vasodilators, and management of associated conditions.
What is the main difference between restrictive cardiomyopathy and constrictive pericarditis?
Restrictive cardiomyopathy is related to the stiffness of the myocardium, while constrictive pericarditis involves thickening of the pericardial sac.
What can trigger HCM symptoms during exercise?
Increased cardiac demand leading to outflow obstruction.
What is the effect of beta-blockers in the treatment of cardiomyopathy?
They reduce heart rate and myocardial oxygen demand.
What genetic testing is commonly associated with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
Testing for mutations in genes responsible for cardiac muscle proteins.
What is the role of surgical interventions in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
To remove excess muscle and relieve outflow obstruction.
What are common presentations of dilated cardiomyopathy on imaging?
Enlarged heart chambers and reduced ejection fraction.
What is the characteristic hemodynamic feature of restrictive cardiomyopathy?
Elevated filling pressures with preserved systolic function.
What kind of ventricular dysrhythmias may occur in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
Ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation.
What type of myocardial abnormalities can be seen in restrictive cardiomyopathy?
Amyloidosis or hemochromatosis.
What is the role of echocardiography in cardiomyopathy assessment?
To evaluate heart structure and function, including wall thickness and chamber size.
What is the main goal of dilated cardiomyopathy treatment?
To improve heart function and quality of life.
What are signs of restrictive cardiomyopathy on physical examination?
Lower extremity edema, distended neck veins, and pulmonary congestion.
What are common findings on the echocardiogram in dilated cardiomyopathy?
Decreased left ventricular function and enlarged heart chambers.
What types of abnormal heart rhythms may indicate a poor prognosis in restrictive cardiomyopathy?
Atrial fibrillation and complex ventricular arrhythmias.
What is the purpose of blood pressure monitoring in patients with cardiomyopathy?
To assess effectiveness of treatment and detect potential complications.
What types of medications are typically avoided in patients with restrictive cardiomyopathy?
Calcium channel blockers due to hypotension risks.
What is the impact of genetic mutations in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
They contribute to the development of the disease and can affect family members.
What are common preventive treatments for people with cardiomyopathy at risk for sudden death?
Implantable devices such as ICDs or pacemakers.
How does hemodynamics differ in restrictive vs dilated cardiomyopathy?
Restrictive cardiomyopathy usually shows preserved EF, while dilated cardiomyopathy shows reduced EF.
What is the clinical significance of diastolic dysfunction in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
It can result in elevated left atrial pressure and symptoms of heart failure.
What lifestyle changes are recommended for patients with cardiomyopathy?
Dietary modifications, regular exercise as tolerated, and avoidance of strenuous activities.
What imaging findings can help differentiate between constrictive pericarditis and restrictive cardiomyopathy?
Thickened pericardium in constrictive pericarditis vs. normal pericardium in restrictive cardiomyopathy.
What can ejection fraction indicate in patients with cardiomyopathy?
It can reveal the severity of heart dysfunction.
What are characteristic features of apical hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
Localized hypertrophy at the apex of the heart, often seen in Japanese patients.
What are the primary characteristics of cardiac MR in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
LV/RV thickness and gadolinium enhancement.
What pharmacological treatments are generally avoided in systolic heart failure?
Certain antiarrhythmics due to their potential negative impact on contractility.
What is the prognosis of patients with restrictive cardiomyopathy?
It often depends on the underlying cause and associated conditions.
What is Kussmaul's sign, and where is it commonly seen?
It's a paradoxical rise in JVP during inspiration, seen in constrictive pericarditis.
What leads can show deep Q waves in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
Lateral (V5-6, I, aVL) and inferior (II, III, aVF) leads.
What lifestyle changes can help manage symptoms of dilated cardiomyopathy?
Maintaining a healthy weight, following a low-sodium diet, and regular follow-up with a cardiologist.
What tests are used to diagnose restrictive cardiomyopathy?
Echocardiogram, CXR, ECG, and sometimes MRI.