Aerobic Gram Positive Bacilli (Exam 2)
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
Bacillus species are found in ______ and are mostly saprophytic.
nature
Bacillus species are isolated as ______.
contaminants
Bacillus anthracis
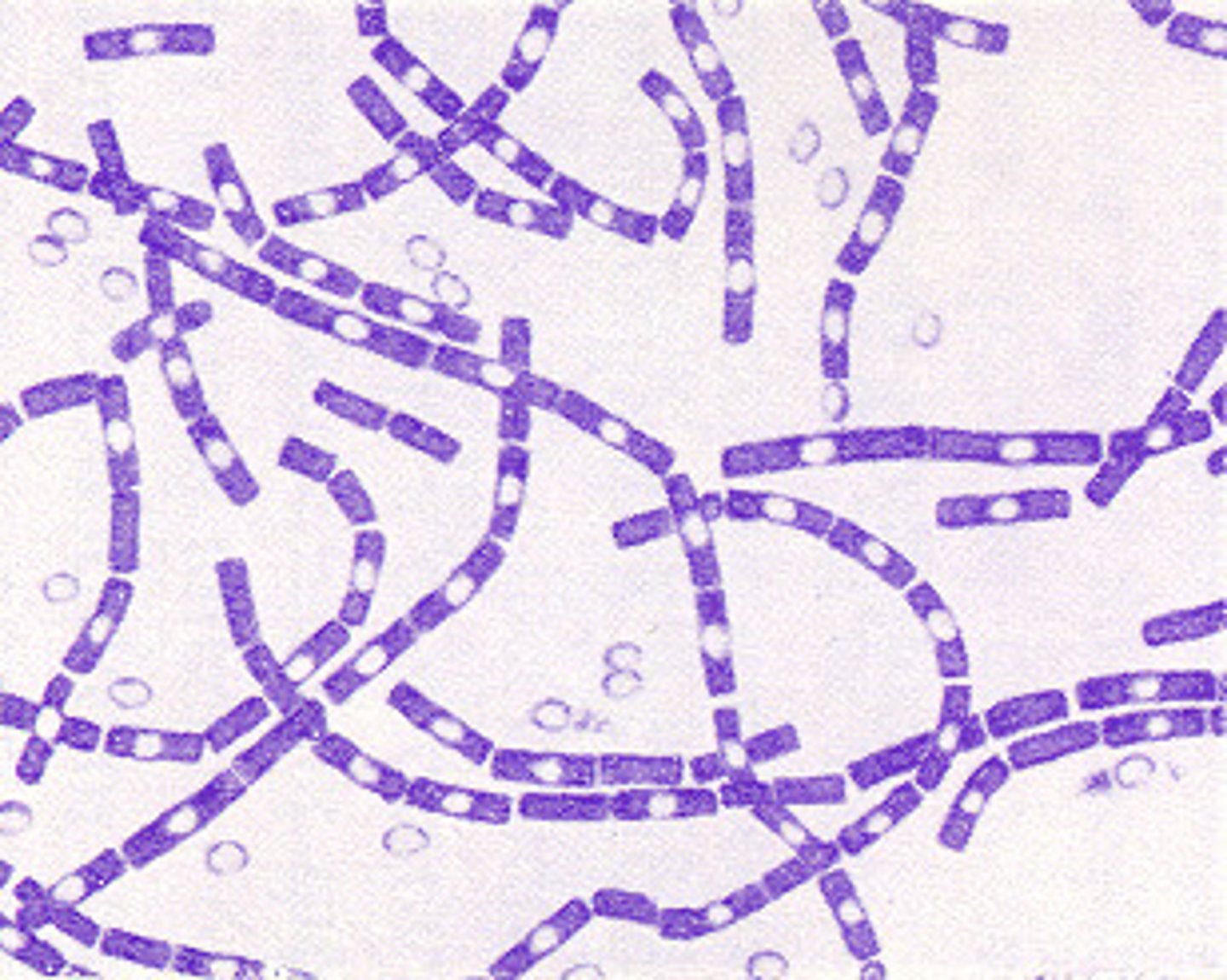
Bacillus anthracis is the agent of ______, a disease in livestock.
anthrax
Humans can contract anthrax through what methods?
- Wound contamination
- Inhalation
- Ingestion
Anthrax specimen collection
Inhalation: use ______
Cutaneous: use ______
Gastrointestinal: use ______
Inhalation: use sputum and blood
Cutaneous: use vesicles and eschar
Gastrointestinal: stool and blood
Does Bacillus anthracis exhibit motility?
No
Bacillus anthracis is catalase ______.
positive
Gram stain characteristics of Bacillus anthracis
- Large, square-ended rods
- Gram positive
- "Bamboo appearance"
What is unique about Bacillus anthracis gram staining?
They have unstained spores in the cells
When Bacillus anthracis cells are stained from blood, they are _______ and don't have ______.
encapsulated, spores
Bacillus anthracis is ______ hemolytic on blood agar.
non
Bacillus anthracis colonies look like ...
- Raised
- Large
- Gray/white
- Irregular
- Beaten egg white look
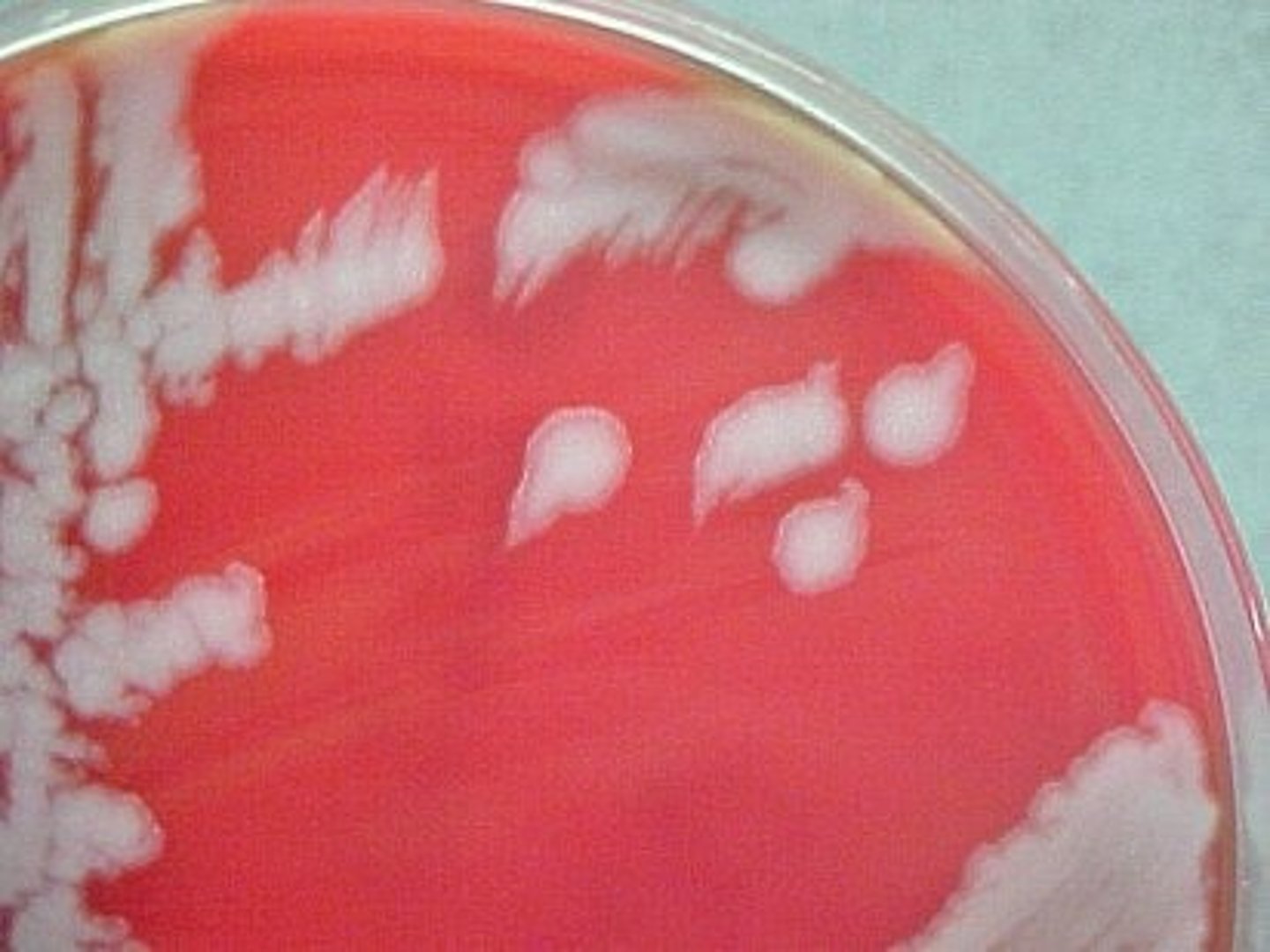
On blood agar, Bacillus anthracis exhibits ______.
"stickiness"
Can Bacillus anthracis grow on PEA?
No
Does Bacillus anthracis exhibit gelatin hydrolysis?
No
Bacillus anthracis is ______ to penicillin.
susceptible
Bacillus cereus
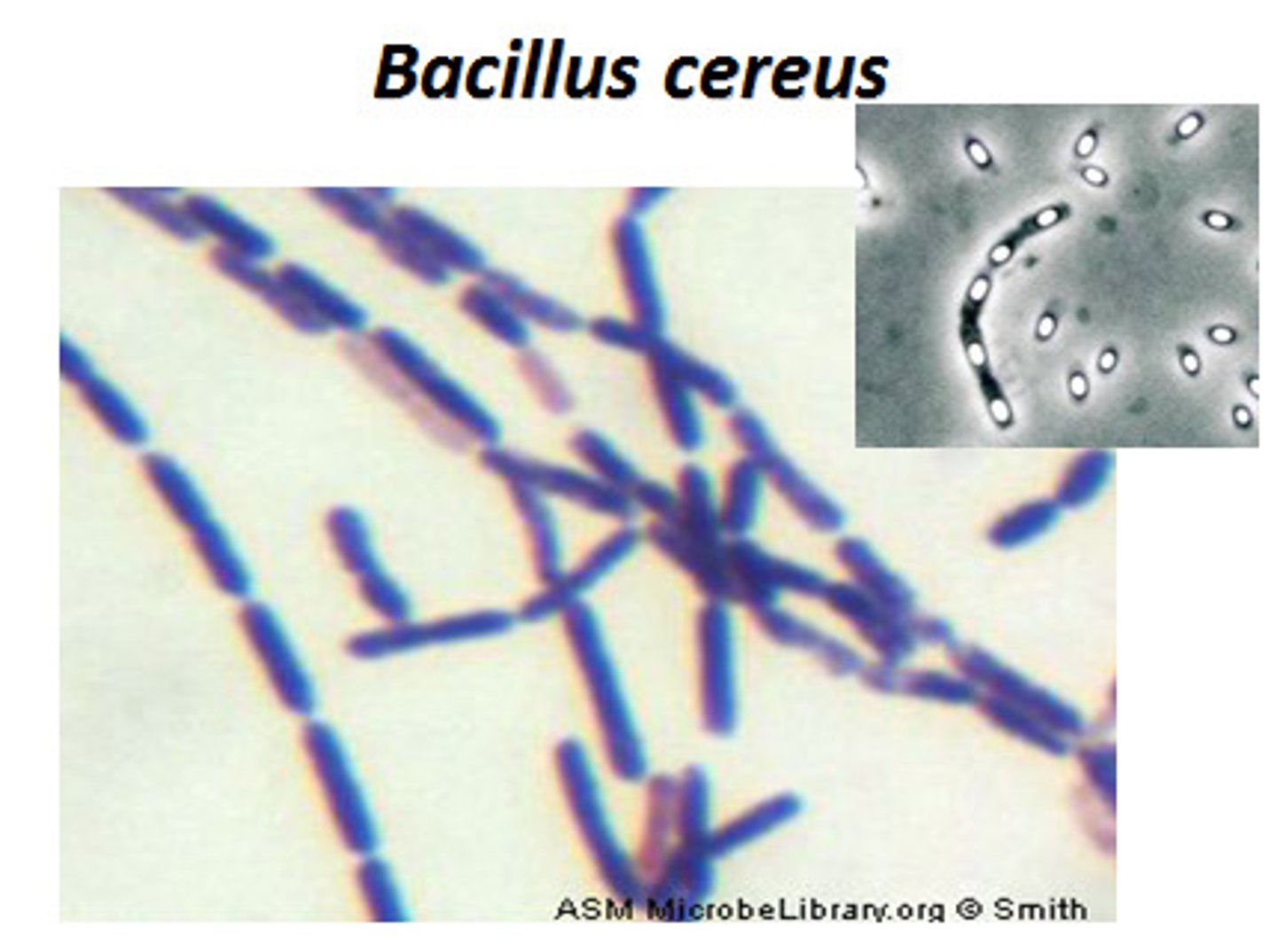
Bacillus cereus is implicated in ______.
food poisoning (diarrheal or emetic)
Bacillus cereus infections occur in ______ hosts.
immunosuppressed
Eye infections, meningitis, septicemia, osteomyelitis
Bacillus cereus is found as a contaminant in ______.
drug paraphernalia
Bacillus cereus exhibits ______ hemolysis on blood agar.
beta
Bacillus cereus ______ (has/doesn't have) motility.
has
Bacillus cereus are not found in ______.
"chains"
Can Bacillus cereus grow on PEA?
Yes
Bacillus cereus is ______ to penicillin.
resistant
The genus Listeria are what shape?
Coccobacilli/small rods
Listeria are Gram ______ and may be pleomorphic and ______.
positive, palisade
Listeria is part of the ______ of many hot and cold blooded animals.
normal flora
Listeria is found on ______ and in ______.
vegetables/plants, fresh water
______ is the clinically significant species of Listeria.
Listeria monocytogenes
Listeria monocytogenes
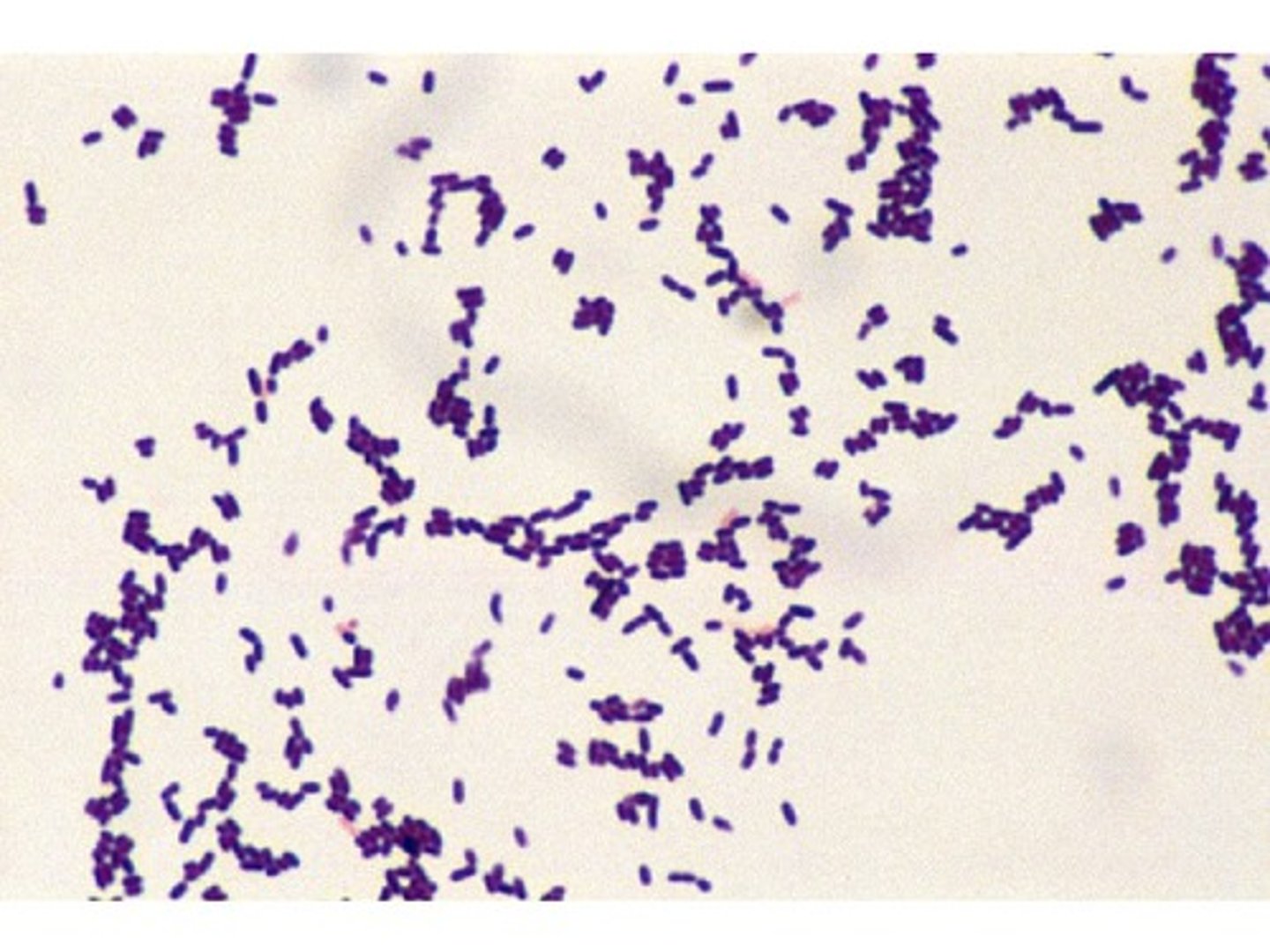
Listeria is found in ______, and can survive in ______ temperatures.
food (processed meats, dairy products, sprouts, melons), low
What demographics does Listeria primarily affect?
- Pregnant women (miscarriages, still birth)
- Young children
- Older adults >65
- Immunocompromised
Listeria is intracellular and ______.
flagellated
Listeria polymerizes ______, moving within and between cells.
actin
Listeria can cause ______.
diarrhea/vomiting
Invasive Listeriosis occurs when Listeria ...
leaves the GI tract
(fever, muscle aches, fatigue, AMS, headache, neurological deficits)
What specimens are tested for Invasive Listeriosis?
Blood and CSF
Listeria is ______ hemolytic and catalase ______.
beta, positive
Listeria exhibits ______ motility at 25C, with tumbling motility in broth culture.
umbrella
Listeria is bile esculin ______.
positive
Listeria is H2S on TSI ______ and CAMP test ______.
negative, positive (matchstick shape)
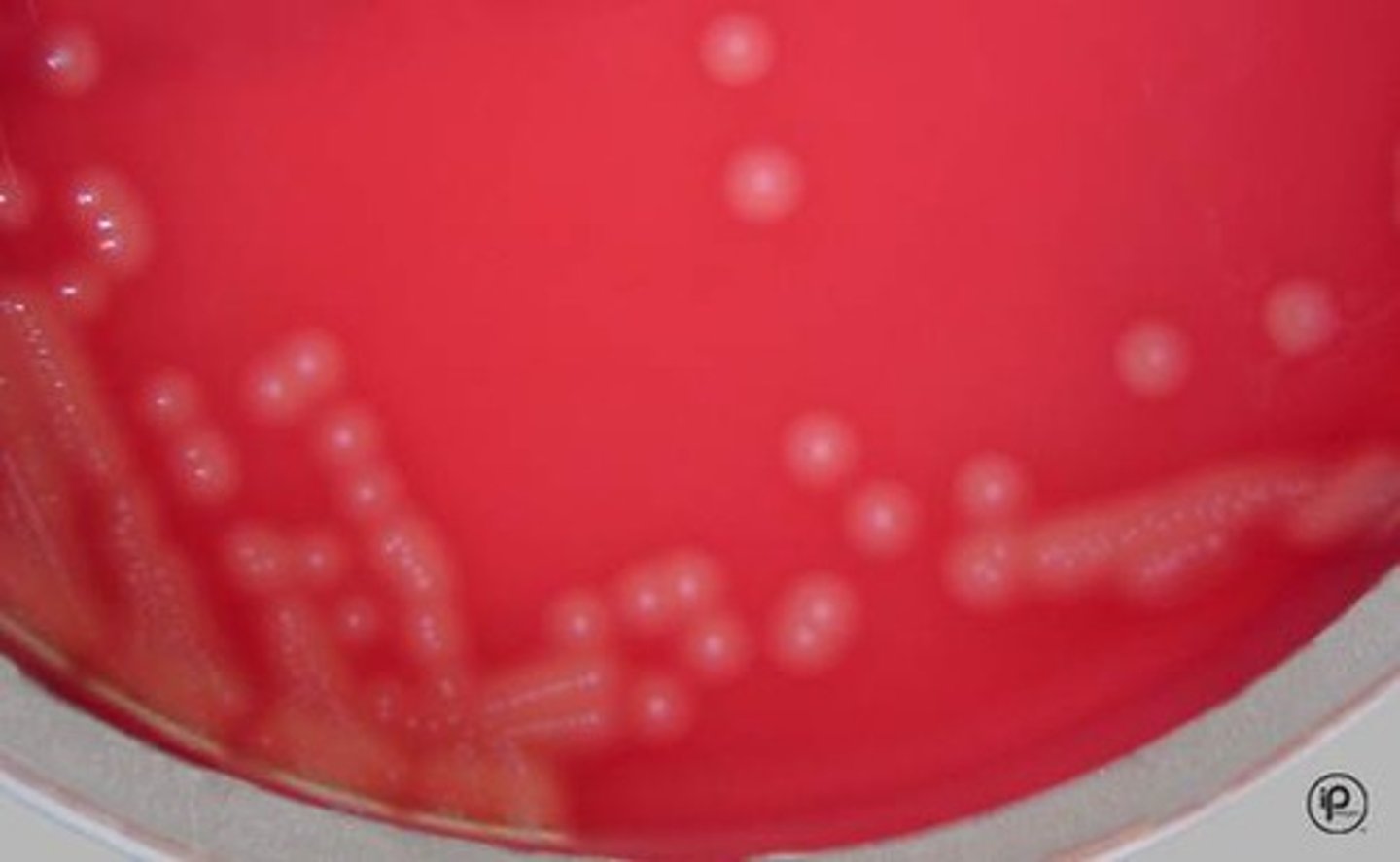
Listeria colonies
What are the categories of catalase positive Gram positive rods?
- Extensive branching
- Rudimentary branching
- Motile
- None of the above
What catalase positive Gram positive rods are within the "extensive branching" category?
- Nocardia
- Rhodococcus
- Rothia
- Actinomyces
- Rapidly growing Mycobacterium
What catalase positive Gram positive rods are within the "rudimentary branching" category?
- Actinomyces
- Oerskovia
- Rothia
What catalase positive Gram positive rods are within the "motile" category?
- Oerskovia
- CDC gps A3/4/5
- C. aquaticum
What catalase positive Gram positive rods are within the "none of the above" category?
Corynebacterium
Rhodococcus equi is found in ______.
soil
Rhodococcus equi causes ______ in immunocompromised patients with impaired ______ mediated immunity (HIV, immunosuppressive therapy).
pneumonia, cell
Rhodococcus equi is intracellular, inhibiting ______ fusions.
phagosome-lysosome
Rhodococcus equi colonies
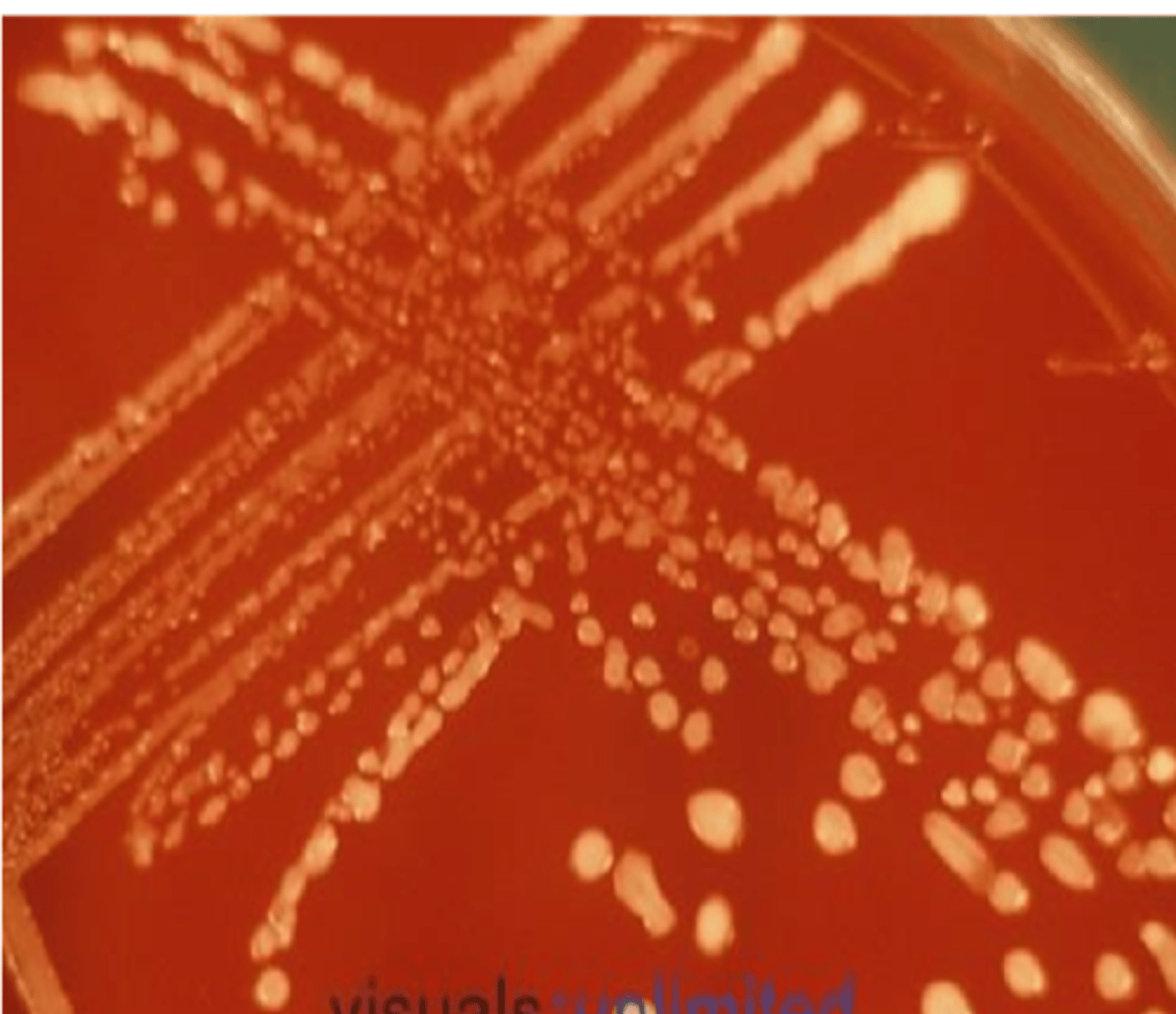
Rhodococcus equi can grow on ______ and ______ agar only.
blood, chocolate
Rhodococcus equi is a Gram positive ______ coccobacillus.
aerobic
Rhodococcus equi is partially ______ and catalase ______.
acid-fast, positive
Rhodococcus equi produces a ______ pigment in young cultures and ______ in older cultures.
salmon/pink, red
Oerskovia are opportunistic and found in ______.
soil
Oerskovia exhibits ______ filaments that fragment into coccobacilli on long incubation.
branching
Oerskovia produces ______ colonies, and is usually ______.
bright yellow, motile
Oerskovia hydrolyzes ______.
esculin
Oerskovia are not partially ______.
acid-fast
Oerskovia
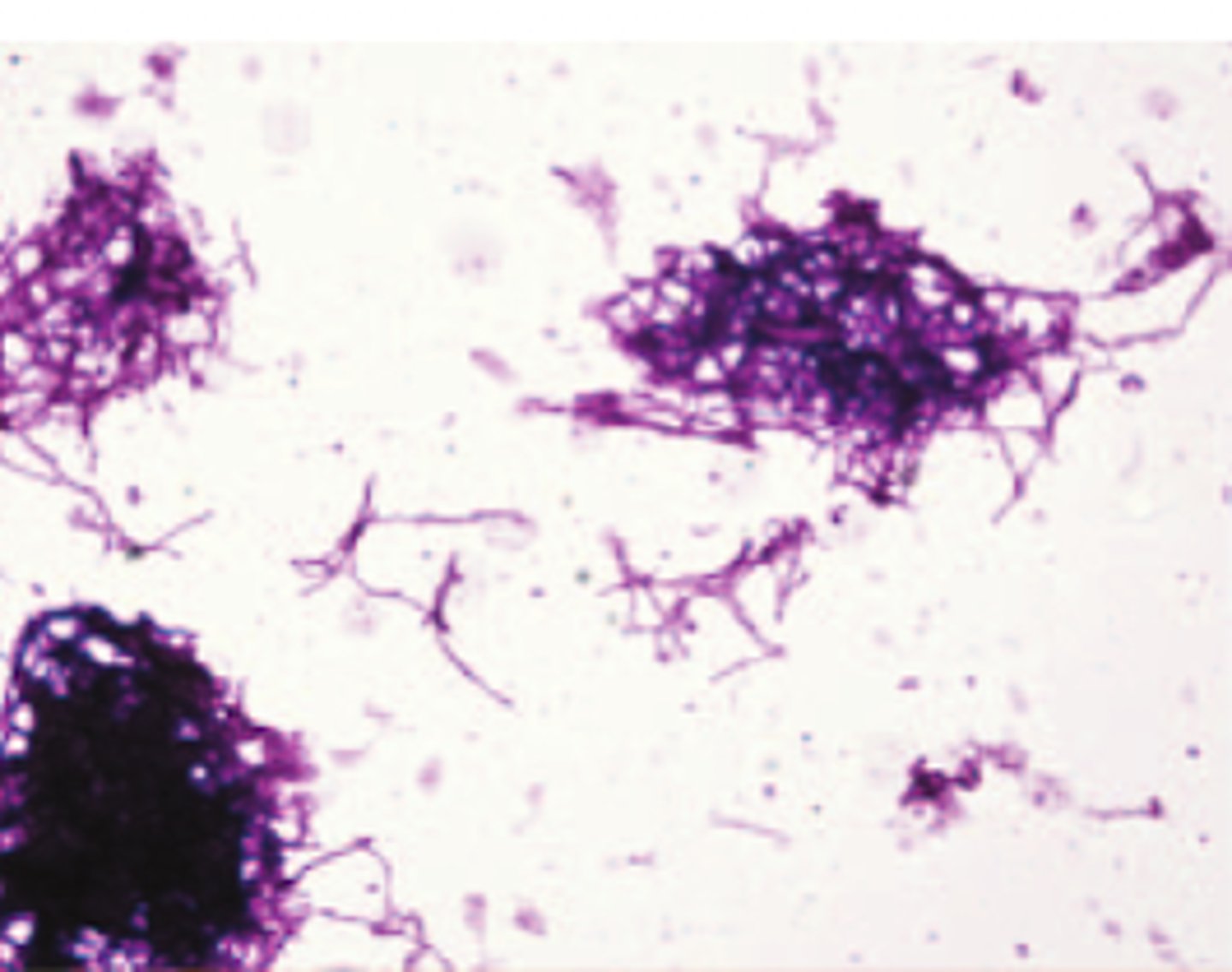
Oerskovia colonies
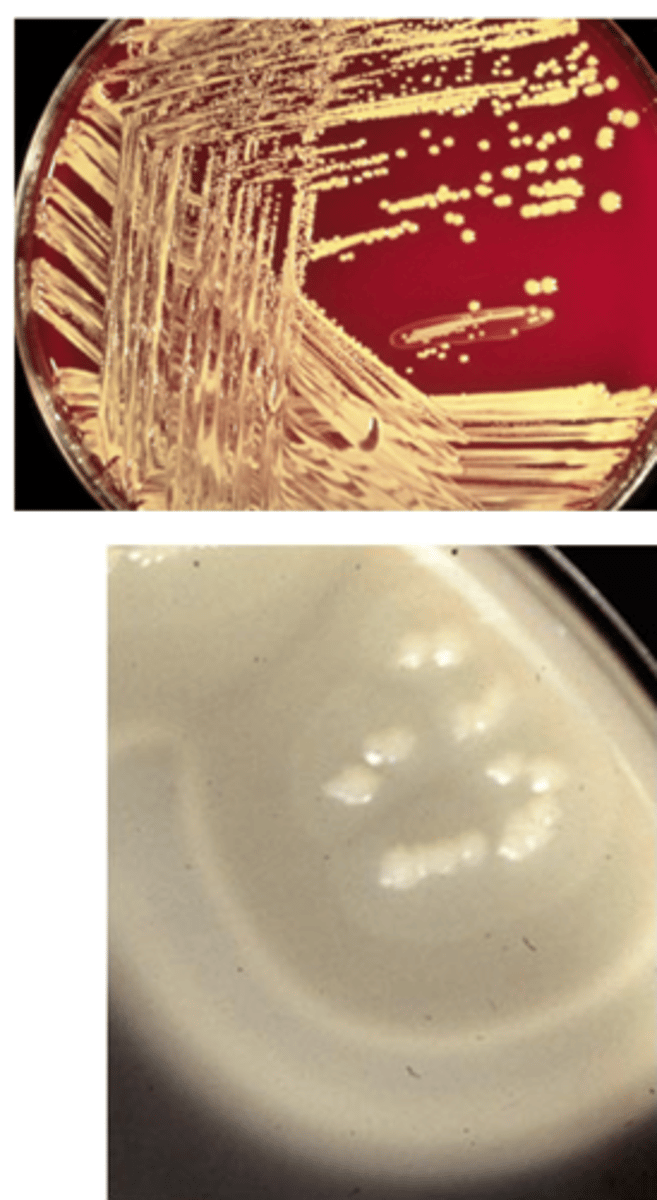
Nocardia are typically Gram positive, ______ and branched.
filamentous
Nocardia is considered to be ______ soil organisms.
saprophytic
Nocardia is an aerobic ______.
actinomycete
Nocardia
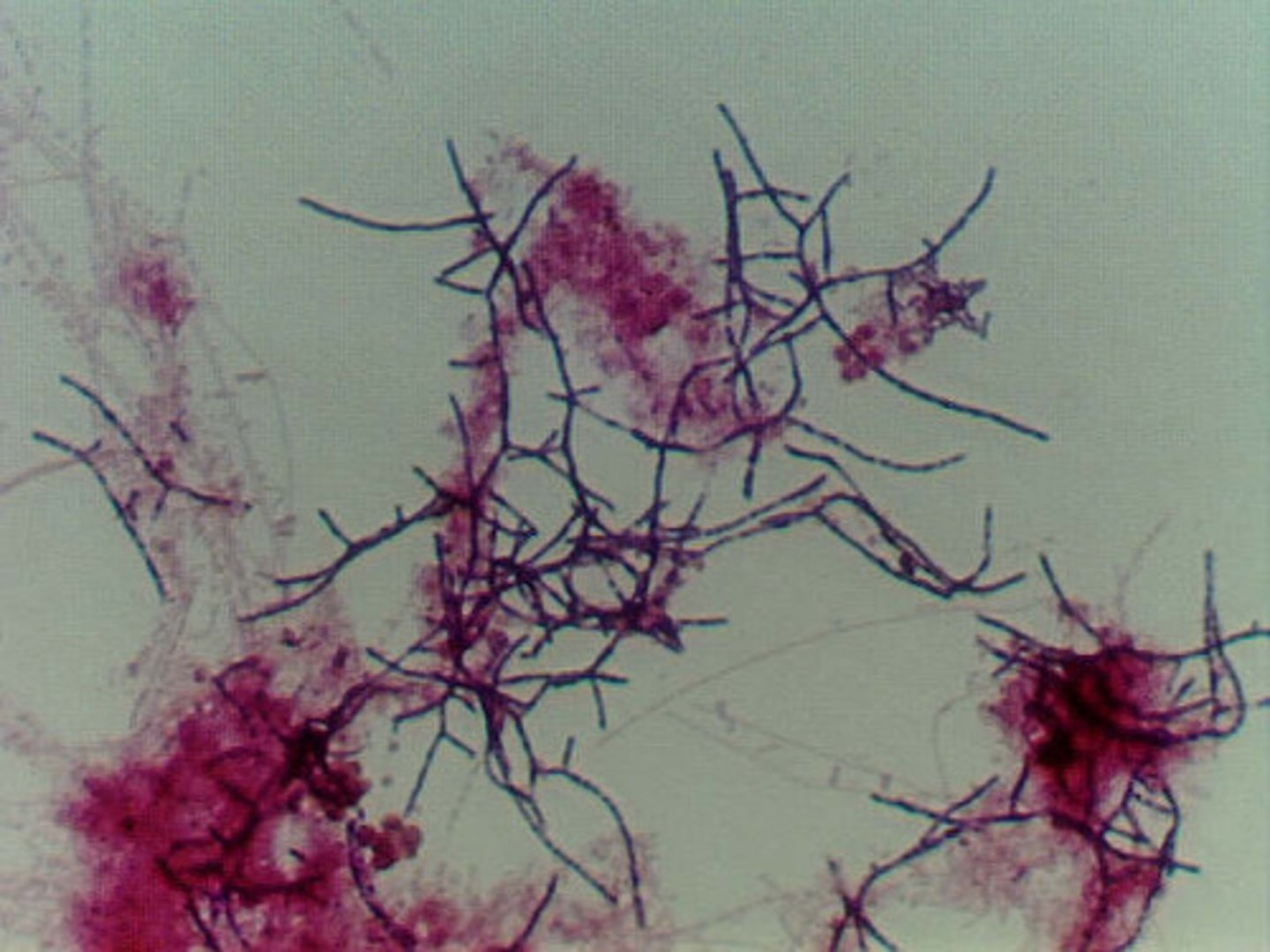
Nocardia colonies
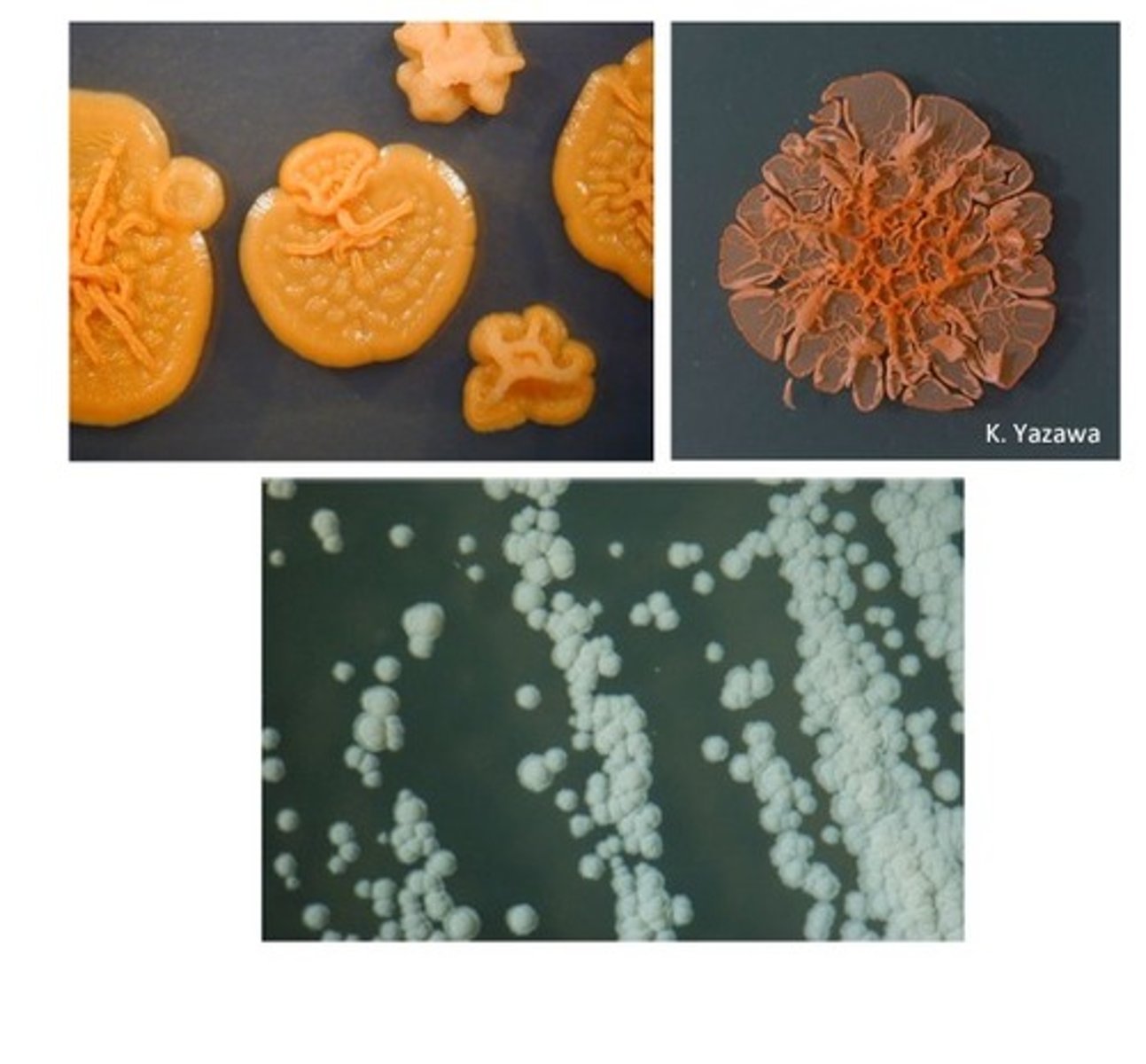
Nocardia can cause infection via ______ or the ______.
inhalation, skin
Chronic Nocardia infection resembles ______.
TB
Nocardia are branching Gram positive rods that may be ______.
coccoid
Nocardia are catalase and urease ______.
positive
Nocardia are partially acid fast, and can be stained via ______ method.
Modified Kinyoun
______ can be used as the sole carbon source for Nocardia.
Paraffin
Nocardia grows better at ______ CO2.
10%
Corynebacterium
Corynebacterium is clinically significant if it is a predominant or co-predominant organism in what specimens?
- Sputum
- Wound or abscess
- Normal sterile site
Corynebacterium is also significant when it is found in ______ or more blood culture bottles, or at certain ______ as the only/predominant isolate in urine culture.
2+, concentrations
Corynebacterium diphtheriae generally begins in the ______ with a mild sore throat and low grade fever.
tonsils/pharynx
Corynebacterium diphtheriae rapidly spreads in ______ cells.
epithelial
Toxigenic strains of Corynebacterium diphtheriae release a toxin locally causing tissue ______, exudate and an inflammatory response.
necrosis
A combination of cell necrosis and exudate forms a ______ in the throat.
pseudomembrane
For Corynebacterium diphtheriae to cause diphtheria, an ______ must be produced.
exotoxin
Corynebacterium diphtheriae can be tested from what specimens?
Nose, throat, nasopharyngeal or wound swabs
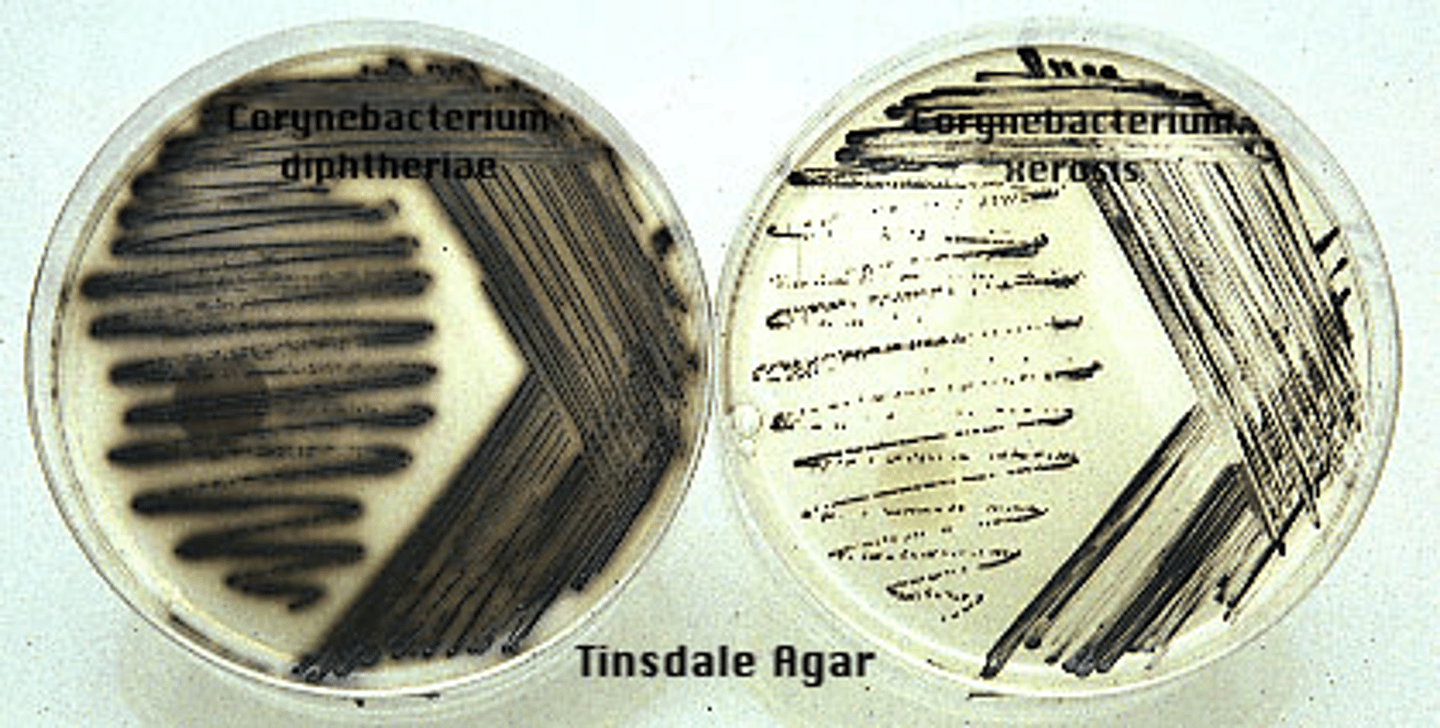
Corynebacterium diphtheriae can be isolated on what agars?
- Cysteine-tellurite (black colonies)
- Loeffler's
- Tinsdale
The ______ test can be used for definitive Corynebacterium diphtheriae identification.
Elek
The capsule of Corynebacterium diphtheriae is made of ______.
protein
Corynebacterium diphtheriae colonies
Corynebacterium jeikeium is an etiological agent of serious infections among ______ and ______ patients.
hospitalized, immunocompromised
Corynebacterium jeikeium is catalase ______, and urease/nitrate ______.
positive, negative
Corynebacterium jeikeium is susceptible to ______.
vancomycin
Corynebacterium urealyticum is associated with ...
- UTIs
- Cystitis
- Pyelonephritis
- Nosocomial pneumonia and bacteremia
Infection with Corynebacterium urealyticum produces ______ urine and promotes struvite formation.
alkaline
Corynebacterium urealyticum is slow growing, so is usually missed on ______.
urine cultures
Corynebacterium urealyticum is susceptible to ______ and ______.
vancomycin, quinolones
Rothia dentocariosa is known to cause _______ and ______.
oral abscesses, endocarditis
Rothia dentocariosa has ______ as a cell wall component.
fructose
Rothia dentocariosa is coccoid, branching after several ______ of incubation.
days
Rothia dentocariosa is catalase and VP ______ and lactose ______.
positive, negative