2.4 - quarks and antiquarks
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
what are strange particles?
particles that decay into:
pions
pions and protons
what are kaons?
strange particles that decay into pions only
which strange particles decay into pions only?
kaons
how are other strange particles (such as sigma) different to kaons?
kaons decay into pions only (they don’t decay into protons as well)
otheres have different rest masses which are always greater than the proton’s rest mass
others decay either in sequence or directly into protons and pions
whhat do kaons decay into?
only pions (i.e., not pions and protons)
what are some examples of strange particles?
kaons
sigma
what is the rest masses of strange particles (excluding kaons) like?
each have different rest masses
always greater than the a proton’s rest mass
rest masses of strange particles
other strange particles (including sigma) > proton > kaons
what is the rest mass of other strange particles (excluding kaons) always larger than?
the rest mass of a proton, and therefore also the rest mass of a kaon (as protons > kaons)
how do other strange particles (excluding kaons) decay?
either in sequence or directly into pions + protons
via which interaction do strange particles decay?
weak nuclear
in what quantity are strange particles created?
created in 2s, as a quark-antiquark pair
what must be conserved in strange changes?
strangeness
how is strangeness conserved in strong interactions?
always conserved
how is strangeness conserved in weak interactions?
it may change by 0, +1, or -1
how can we explain why hadrons have the properties they do (charge, strangeness, rest mass)?
by assuming they’re composed of smaller particles called quarks and antiquarks
quarks and antiquarks
up (u)
down (d)
strange (s)
anti-up (s-)
anti-down (d-)
anti-strange (s-)
charge, strangeness, baryon number of quarks and antiquarks
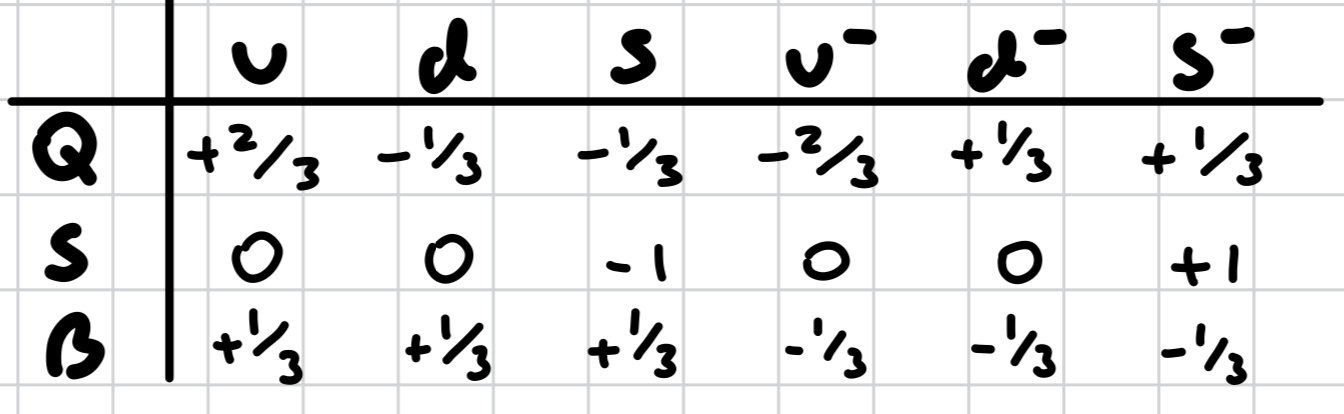
what is the charge of an up quark?
+ 2/3
what is the charge of a down quark?
- 1/3
what is the charge of a strange quark?
- 1/3
what is the strangeness of an up quark?
0
what is the strangeness of a down quark?
0
what is the strangeness of a strange quark?
-1
what is the baryon number of an up quark?
+ 1/3
what is the baryon number of a down quark?
+ 1/3
what is the baron number of a strange quark?
+ 1/3
what is the charge of an up antiquark?
- 2/3
what is the charge of a down antiquark?
+ 1/3
what is the charge of a strange antiquark?
+ 1/3
what is the strangeness of an up antiquark?
0
what is the strangeness of a down antiquark?
0
what is the strangeness of a strange antiquark?
+1
what is the baryon number of an up antiquark?
- 1/3
what is the baryon number of a down antiquark?
- 1/3
what is the baryon number of a strange antiquark?
- 1/3
what is the quark composition for a baryon?
3 quarks
what is the quark composition for an anti-baryon?
3 antiquarks
what are sigma particles (Σ)?
baryons with a strange or anti-strange quark in any amount
what is a baryon with a strange / anti-strange particle in any amount?
a sigma (Σ)
how many strange / anti-strange particles must there be to constitute as a sigma particle?
any quantity
quark composition of a proton
uud
charge = +2/3 +2/3 -1/3 = +1
baryon number = +1/3 +1/3 + 1/3 = +1
quark composition of a neutron
udd
charge = +2/3 -1/3 -1/3 = 0
baryon number = +1/3 +1/3 +1/3 = +1
quark composition of an antiproton
u-d-d-
charge = -2/3 -2/3 +1/3 = -1
baryon number = -1/3 -1/3 -1/3 = -1
what is the only stable baryon? why?
a proton, because it’s the only one with both a charge and baryon number of +1
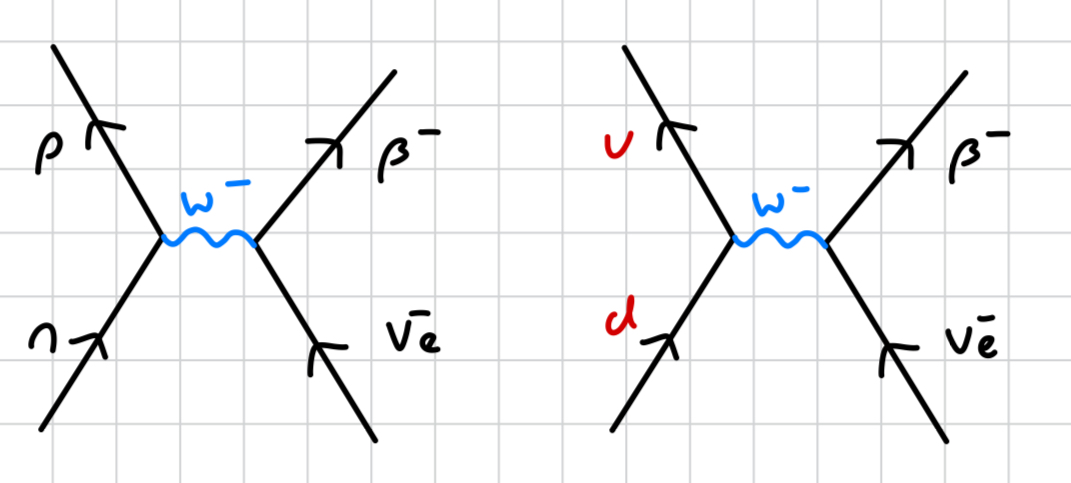
what does a free neutron decay into?
a proton, releasing an electron and electron antineutrino (i.e., β- decay)
n → p + e- + ve
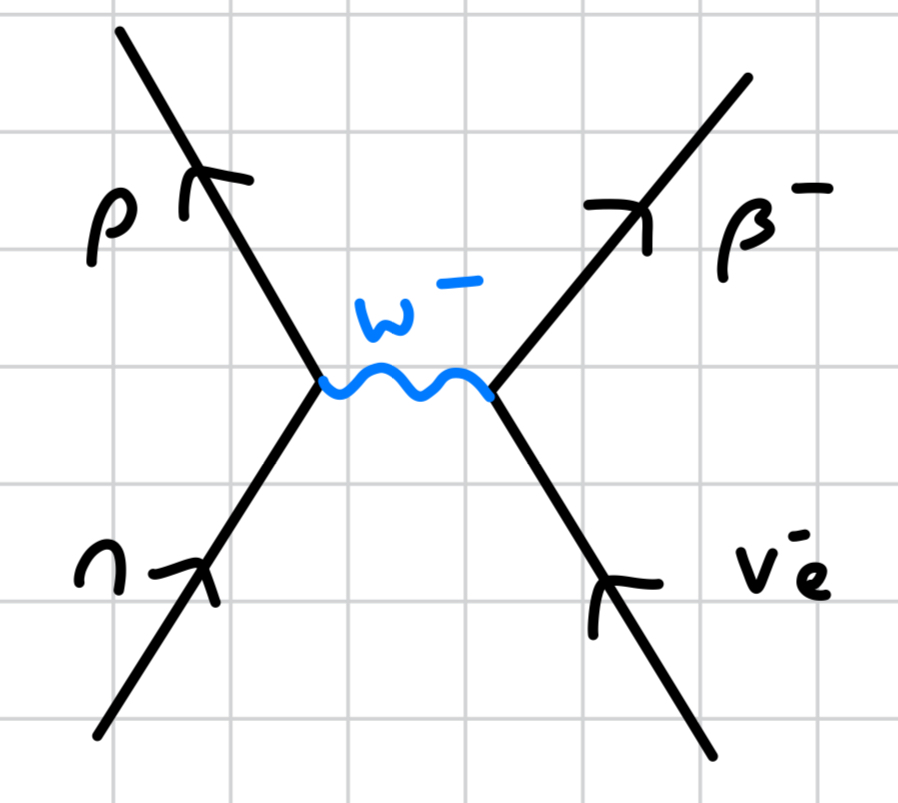
what is the decay of a free neutron the same as?
β- decay
what is the quark composition for mesons?
quark-antiquark pair
9 combinations
which hadrons is composed of a quark-antiquark pair, and which are composed of 3 quarks / antiquarks?
mesons = quark-antiquark pair
baryons = 3 quarks / antiquarks
how many quark-antiquark combinations can there be for mesons?
9
what is a meson when strangeness = 0?
pion
what is a meson when strangeness doesn’t = 0?
kaon
what is this combination?;
u + u-
charge = +2/3 -2/3 = 0
baryon number = +1/3 -1/3 = 0
strangeness = 0 + 0 = 0
no charge, not a baryon, and no strangeness, so π0
what is this combination?;
d + d-
charge = -1/3 +1/3 = 0
baryon number = +1/3 -1/3 = 0
strangeness = 0 + 0 = 0
no charge, not a baryon, and no strangeness, so π0
what is this combination?;
s + s-
charge = -1/3 +1/3 = 0
baryon number = +1/3 -1/3 = 0
strangeness = -1 +1 = 0
no charge, not a baryon, and strangeness cancels out, however this is not a pion as it decays much faster
why is s + s- not a π0 meson?
because it decays much faster than a pion
what is this combination?;
u + d-
charge = +2/3 +1/3 = +1
baryon number = +1/3 -1/3 = 0
strangeness = 0 + 0 = 0
charge of +1, not a baryon, and no strangeness, so π+
what is this combination?;
d + u-
charge = -1/3 -2/3 = -1
baryon number = +1/3 -1/3 = 0
strangeness = 0 + 0 = 0
charge of -1, not a baryon, and no strangeness, so π-
what is this combination?;
u + s-
charge = +2/3 +1/3 = +1
baryon number = +1/3 -1/3 = 0
strangeness = 0 +1 = +1
charge of +1, not a baryon, and strangeness of +1, so K+
*strangeness included, so a kaon
what is this combination?;
d + s-
charge = -1/3 +1/3 = 0
baryon number = +1/3 -1/3 = 0
strangeness = 0 +1 = +1
no charge, not a baryon, and strangeness of +1, so K0
*strangeness included, so a kaon
*if a down quark is involved with strangeness, then charge cancels out
what is this combination?;
s + d-
charge = -1/3 +1/3 = 0
baryon number = +1/3 -1/3 = 0
strangeness = -1 + 0 = -1
no charge, not a baryon, and strangeness of -1, so K0
*strangeness included, so a kaon
*if a down quark is involved with strangeness, then charge cancels out
what is this combination?;
s + u-
charge = -1/3 -2/3 = -1
baryon number = +1/3 -1/3 = 0
strangeness = -1 + 0 = -1
charge of -1, not a baryon, and strangeness of -1, so K-
*strangeness included, so a kaon
what is the antiparticle of a meson? why?
antiparticle of a meson is a meson, because mesons are uncharged
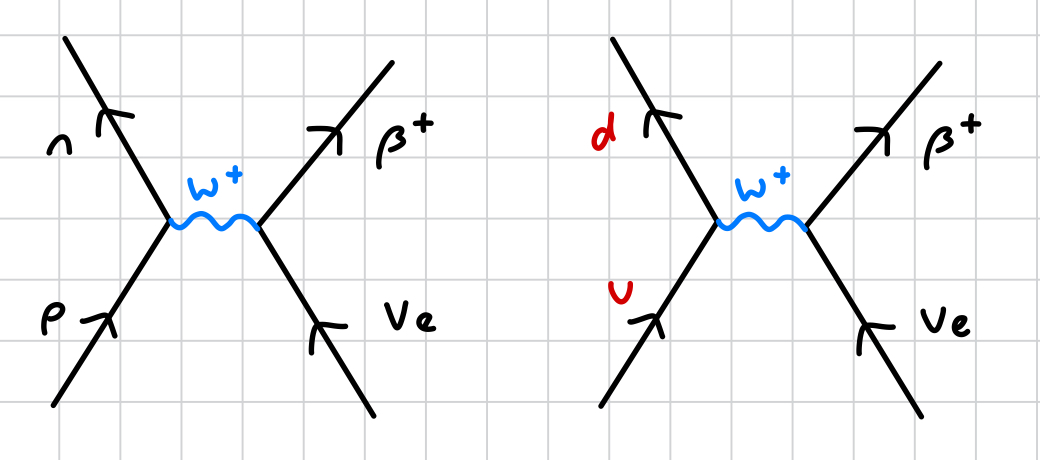
what happens to the quark composition during β+ decay?
proton (uud) turns to a neutron (udd)
up quark turns to a down quark
up quark releases a W+ boson, which releases a down quark that turns the proton to a neutron
what happens to the quark composition during β- decay?
neutron (udd) turns to a proton (uud)
down quark turns to a up quark
down quark releases a W- boson, which releases a up quark that turns the neutron to a proton