PDA IB Lecture 5: Second Messenger Systems
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
What are 2 functions of receptors? **
(1) sensing the ligand/chemical
(2) transmitting the message/signal
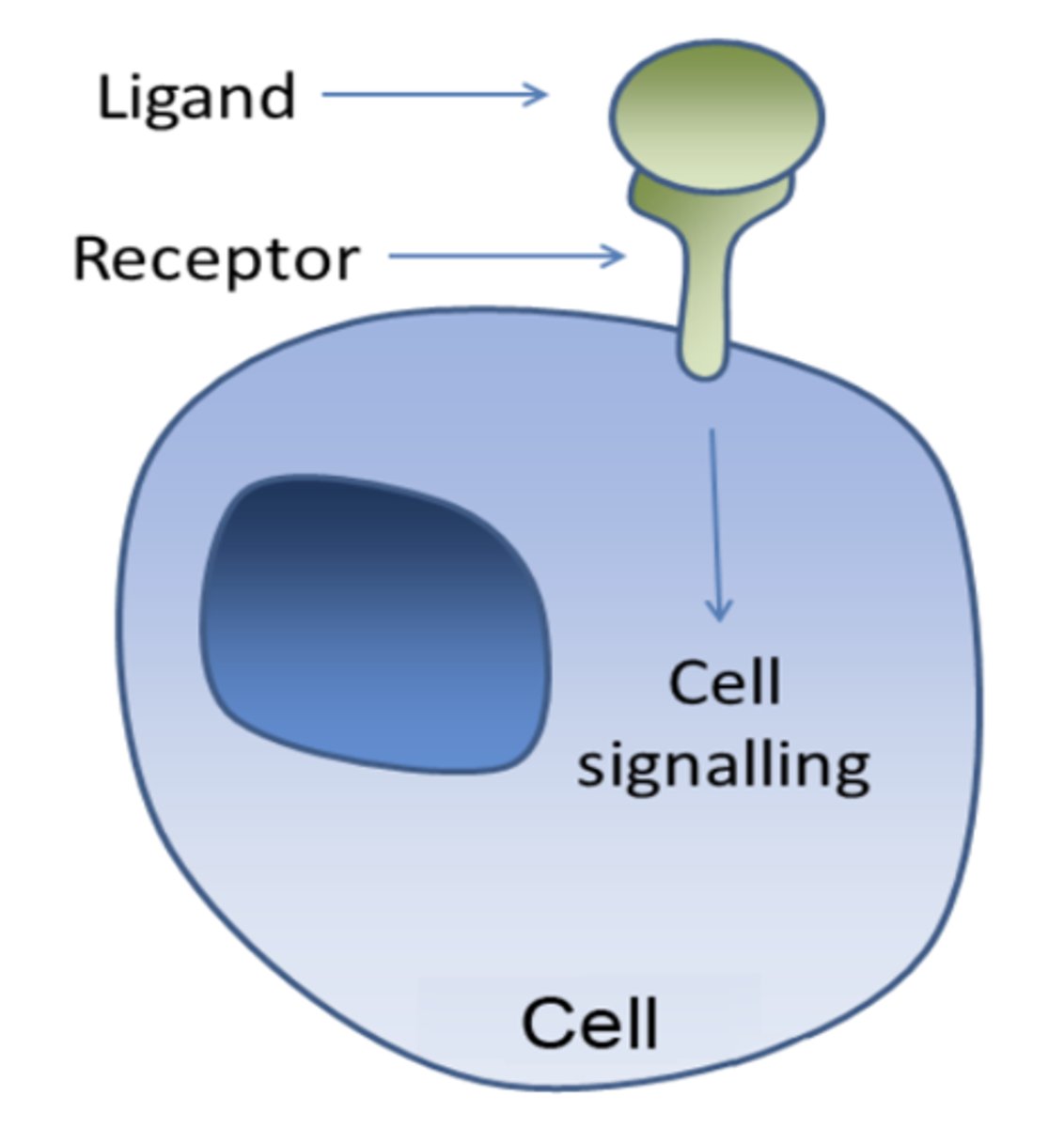
What does a signal transduction pathway involve?
a signal, a receptor, and a response
What can receptors be classified by?
their location in the cell (determined by whether their ligand can diffuse through membrane)
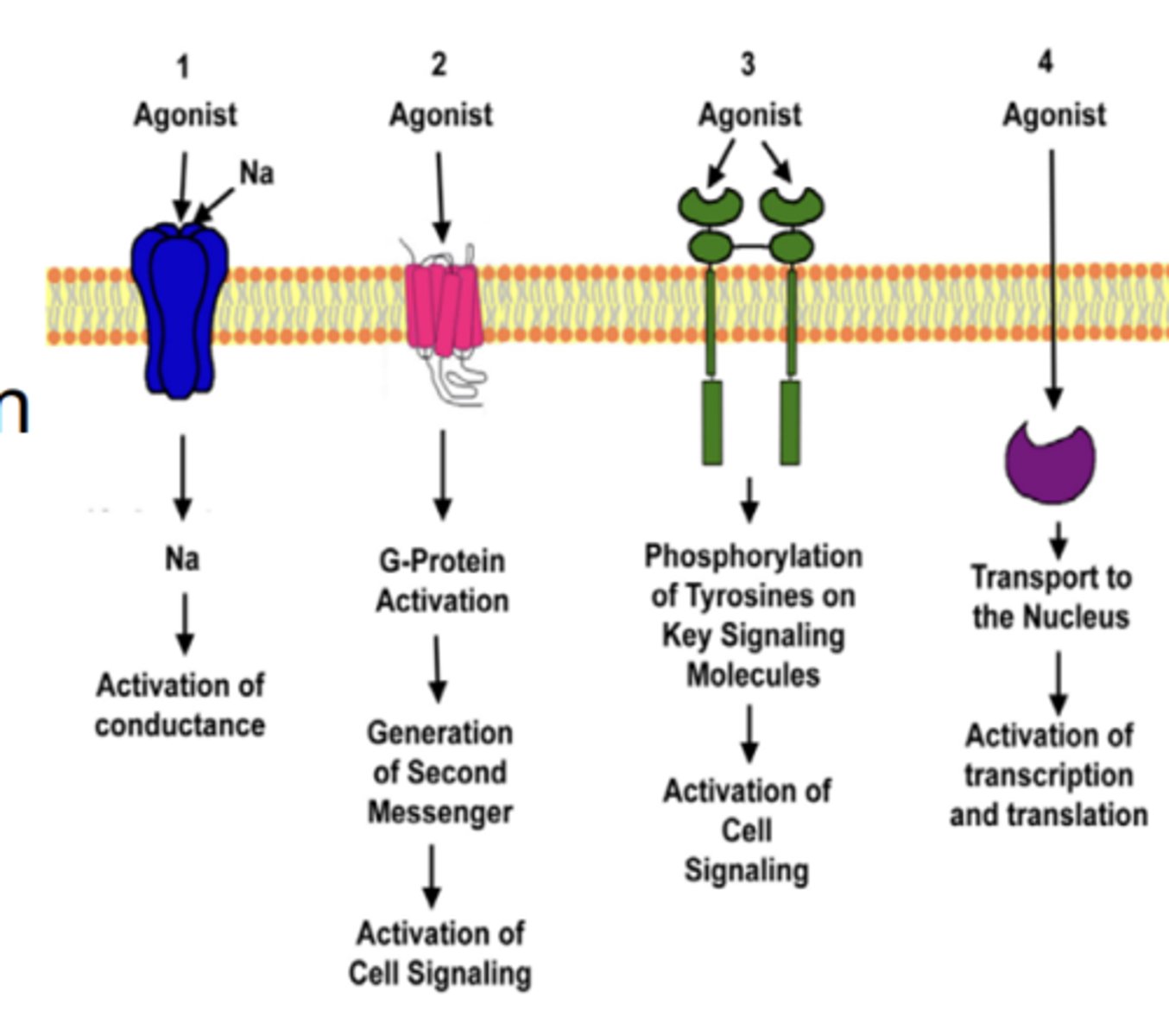
Membrane Receptors (3):
What type of ligands do they have?
- ion channels
- G-protein coupled receptors
- receptor tyrosine kinase
(usually have large or polar, hydrophilic ligands)
Cytoplasmic receptors (1):
What type of ligands do the have?
- intracellular hormone receptors
(usually have small or nonpolar, hydrophobic ligands)
Ligands are considered ___________________, directly interacting with ___________________ to initiate ___________________, activating primary effectors
- first messengers
- signal transducers (receptors)
- cellular signal
What are first messengers?
the signaling molecules
- stimulate cell from the extracellular fluid and bind to specific receptors
T/F: First messengers are typically biochemically hydrophobic small molecules
FALSE
they are typically hydrophilic large molecules
First messenger --> receptor --> ______________
transducer/protein effector
Transducer
molecules transducing signals (receptor and G protein)
Protein effector
protein (enzyme) involved in cellular signal transduction cascades
- produces downstream effects (molecular changes or producing/regulating secondary messengers)
(ex. adenylyl cyclase & protein kinase A)
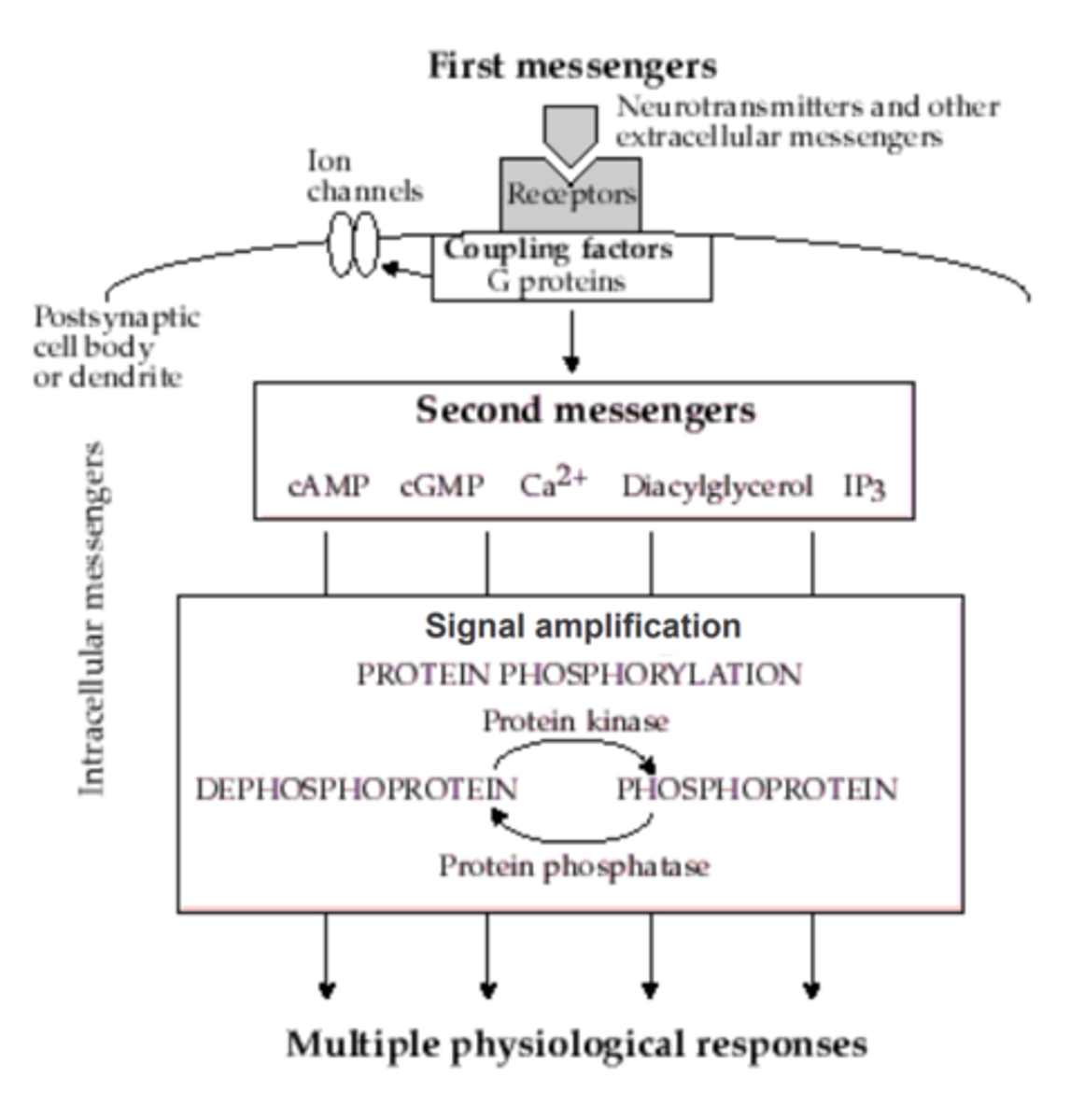
Second messengers
intracellular molecules that are generated/activated due to receptor activation by binding of ligand
A second messenger is an intermediary between the _______________ and the __________________________________
- receptor
- cascade of responses
Second messengers serve as _____________________ from the plasma membrane to the cytoplasm
chemical relays
Second messengers can activate _________________________ and serve to _________ the strength of the signal
- secondary effectors
- amplify
Three basic types of secondary messengers ****
- Hydrophobic molecules*** (water-insoluble, membrane-associated, diffuse from membrane)
- Hydrophilic molecules*** (water-soluble, within cytoplasm)
- Gases*** (small, diffuse through membrane)
Secondary Messengers: Hydrophobic molecules** (membrane-assocaited) (2)
- PIP 3 (Phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-triphosphate)
- DAG (diacylglycerol)
Secondary Messengers: Hydrophilic molecules** (cytoplasm associated) (4)
- cAMP (cyclic adenosine monophosphate)
- cGMP (cyclic guanosine monophosphate)
- IP3 (inositol triphosphate)
- Ca2+
Secondary Messengers: Gases*** (3)
- nitric oxide (NO)
- carbon monoxide (CO)
- hydrogen sulfide (H2S)
The generation of second messengers and activation of specific secondary effectors (i.e., protein kinases) results in....
changes in the activity of the target cell, characterizes the response that the agonist evokes
T/F: Changes evoked by the actions of second messengers are usually rapid
TRUE
Second messengers can cause multiple changes including....(3)
- open/close ion channels
- trigger gene expression (transcription)
- affect protein production
What 2 categories can neurotransmitter receptors be classified into?
Metabotropic (slow) and ionotropic receptors (fast)
Ionotropic receptors (fast neurotransmission)
- consists of an ion channel
- rapid (milliseconds)
- effects are direct, do not require multiple steps leading to second messengers or activation of a signaling pathway
Metabotropic receptors (slow neurotransmission)
- slower (but still fast, seconds)
- neurotransmitters bind to metabotropic receptors
- upon activation, receptors generate second messengers
- major group of receptors consists of membrane heptaspanning GPCRs (G Protein-coupled Receptors)
Ion-Channel Receptor Activation steps (5)/what do the ions act as?
1. neurotransmitter binds to receptor ligand binding domain of ion channel
2. Ion channel is activated
3. Channel opens
4. Ion's influx/enters cell
5. Ions act as secondary messengers and maintain the signaling cascade
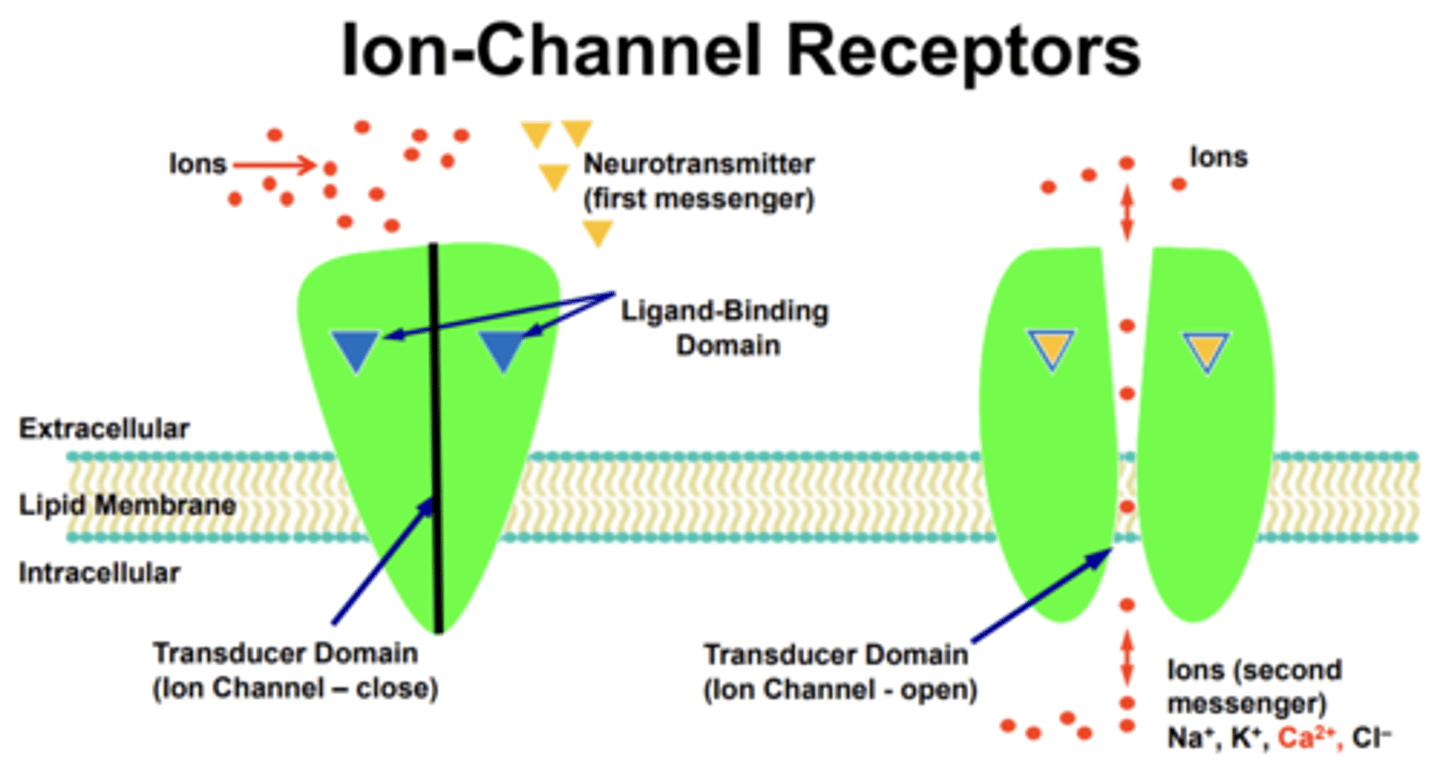
Ions act as...
secondary messengers and maintain the signaling cascade
Are metabotropic receptors directly or indirectly linked with ion channels on the membrane?
indirectly linked with ion channels through signal transduction mechanisms, often G proteins
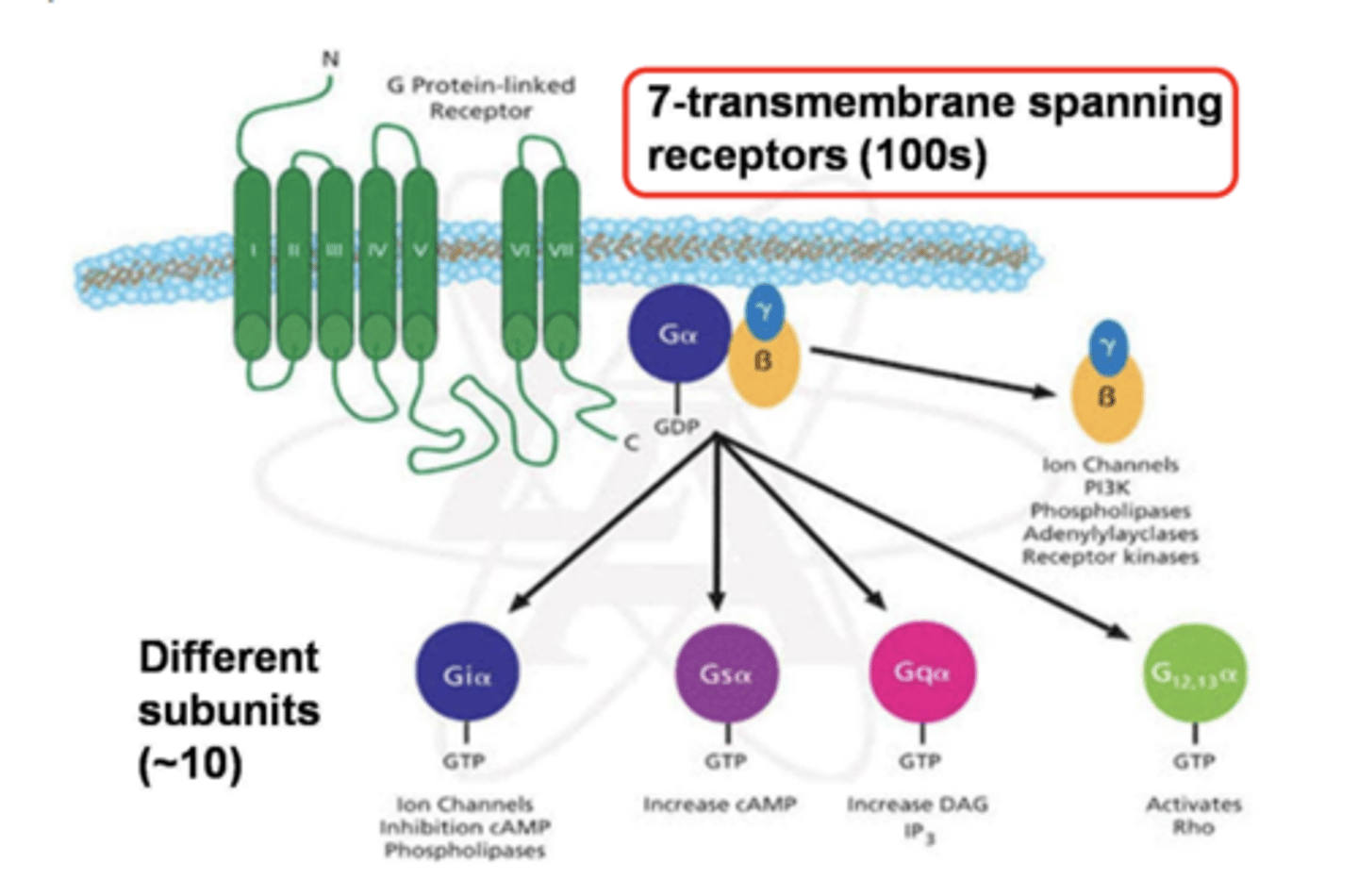
T/F: G protein-coupled receptors are inherently metabotropic
TRUE
In addition to G protein-coupled receptors (7-transmembrane spanning receptors), what are other metabotropic receptors? (2)
tyrosine kinases and guanylyl cyclase receptors
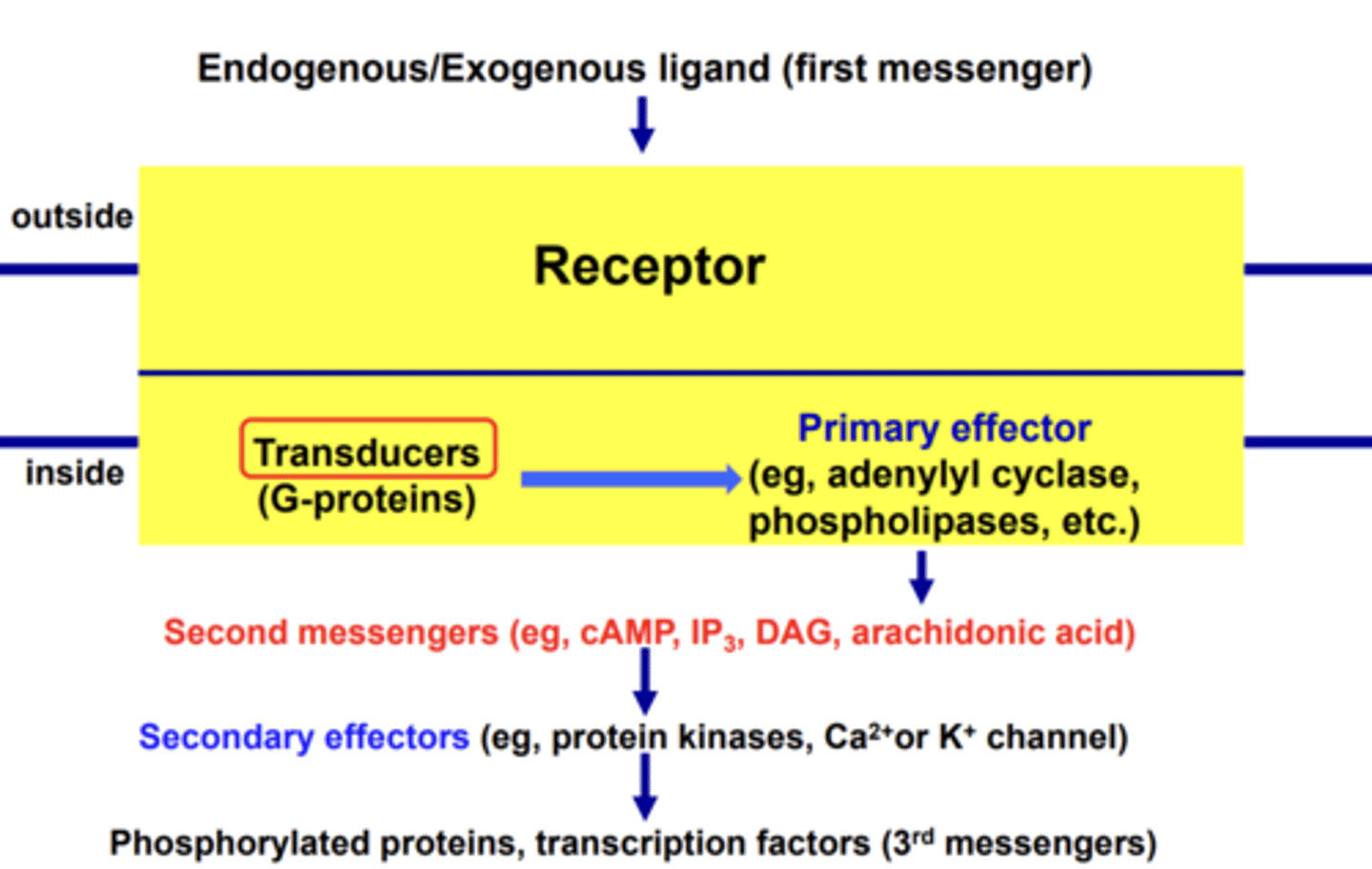
Metabotropic Receptor (Chart)
ligand binds to receptor--->activates transducer--->transducer activates primary effector--->activates secondary messengers and secondary effectors
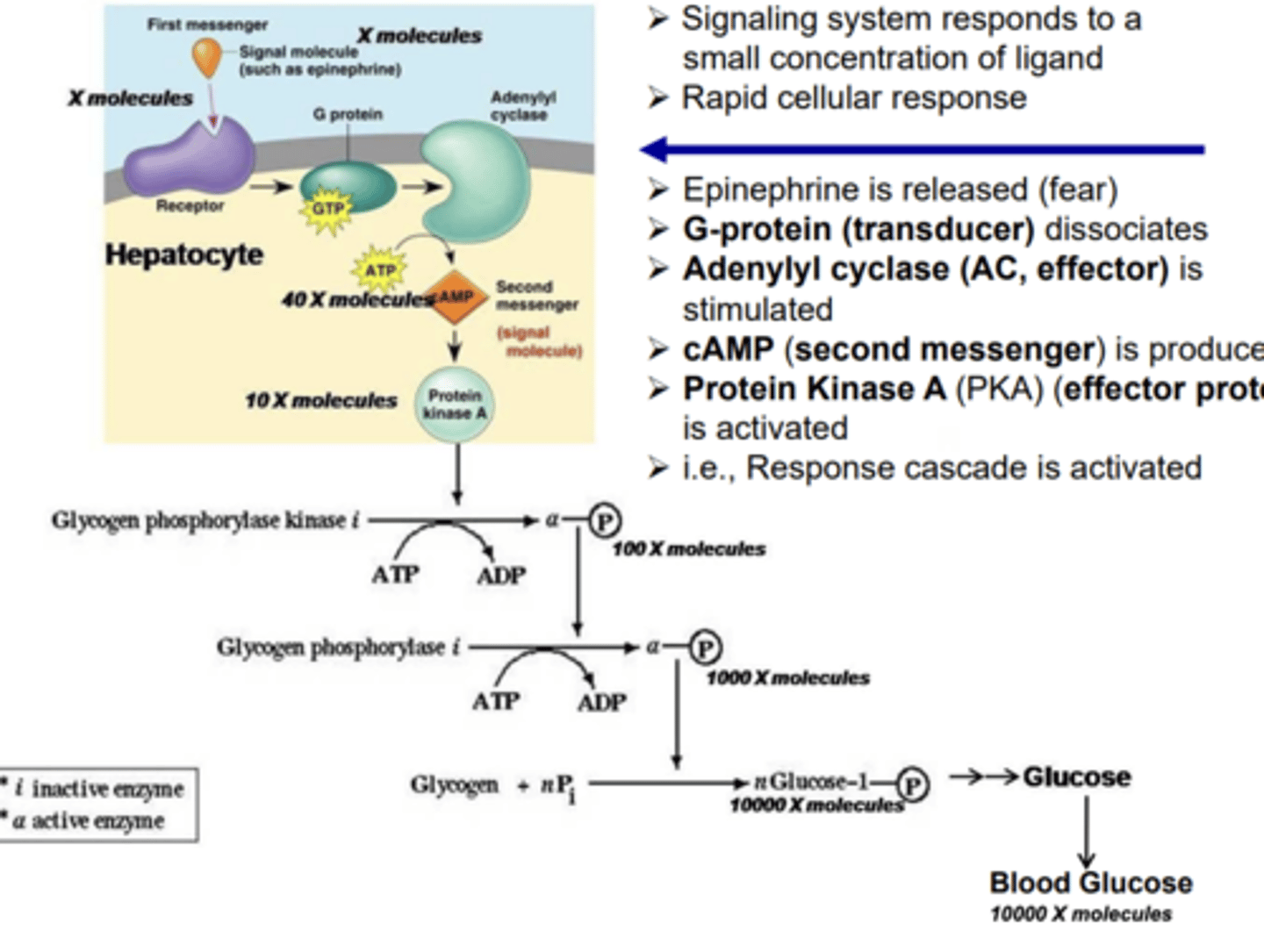
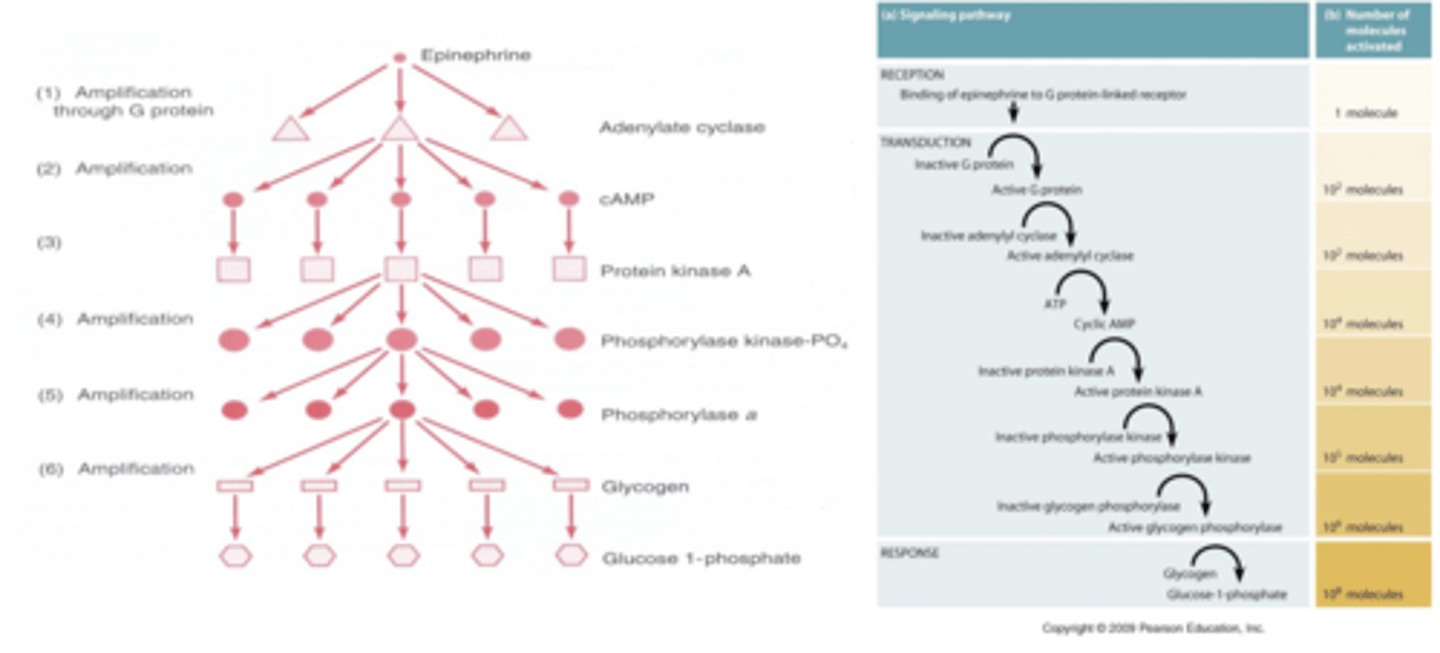
Protein Kinase A Cascade
- responds to small concentration of ligand
- rapid cellular response
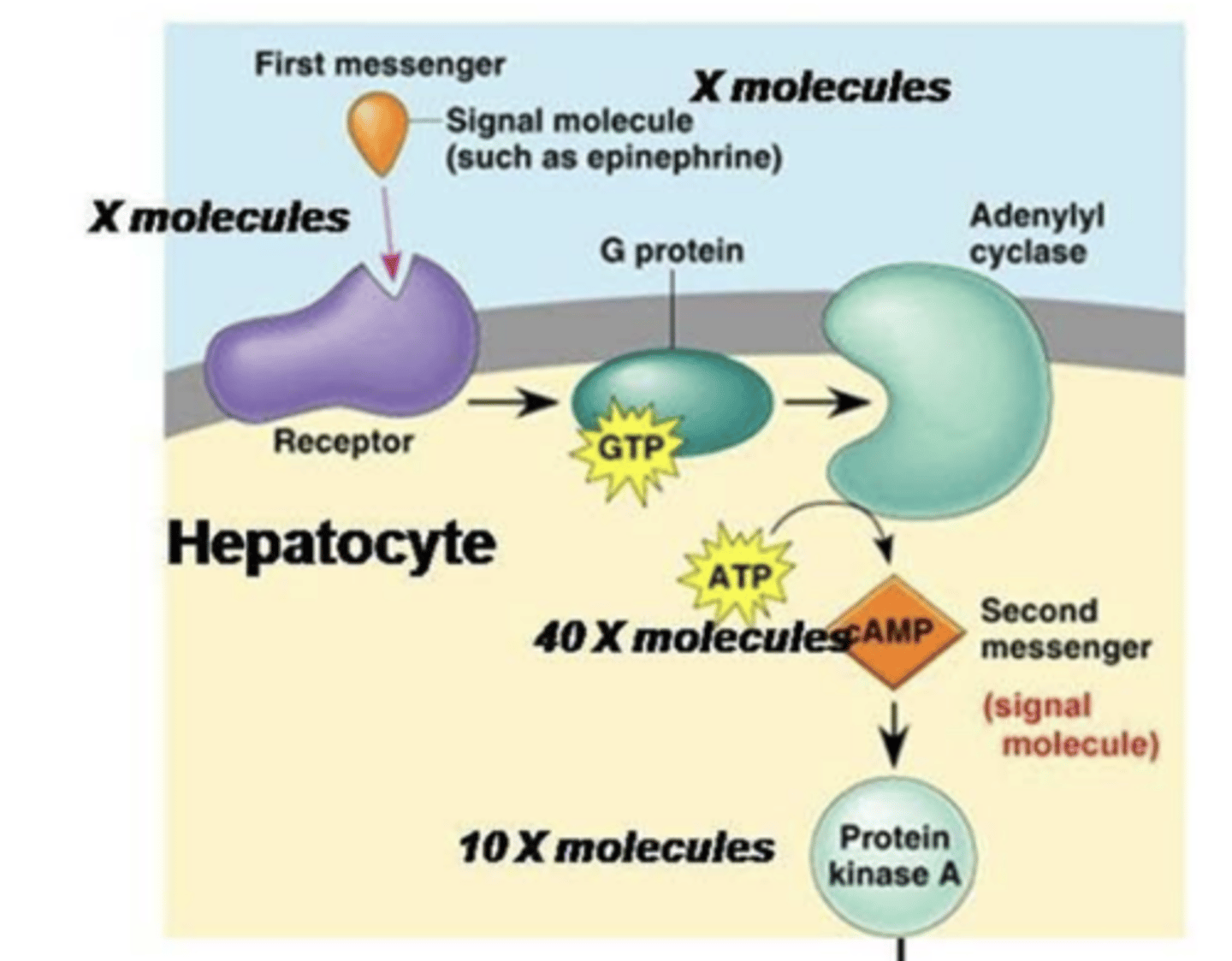
Protein Kinase A Cascade Steps:
- ______________ is released
- _____________________ dissociates
- ___________________________ is stimulated
- ____________________ is produced
- ______________________ is activated
- Response cascade is activated
- epinephrine released
- adenylyl cyclase ( effector) stimulated
- cAMP (second messenger) produced
- Protein Kinase A (effector protein) activated
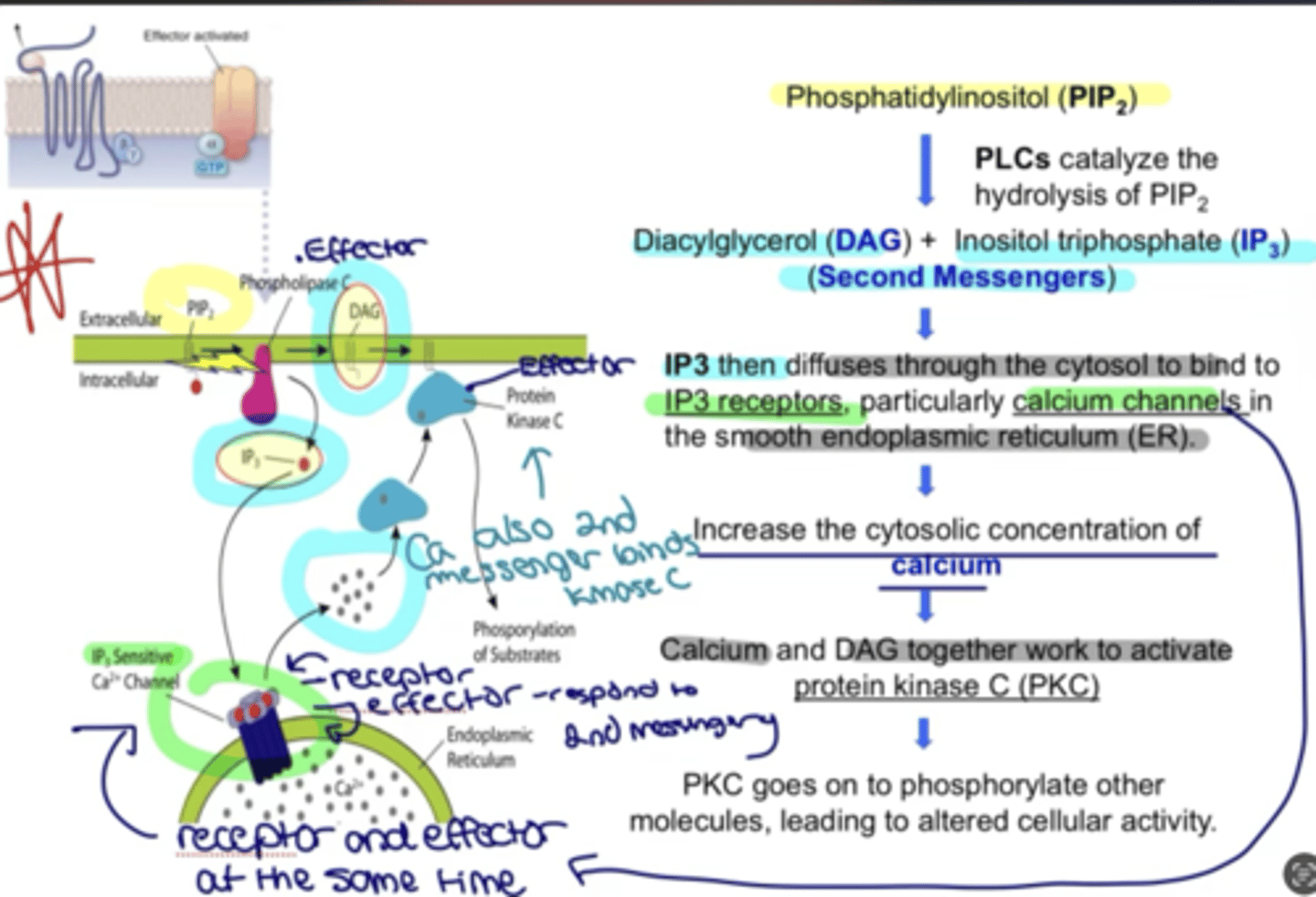
Phospholipase C Cascade*****
- Phosphatidylinositol (PIP2) binds to receptor
- second messengers DAG and IP3 are activated
- IP3 activates IP3 receptors (calcium channels) (receptors and effectors) in the smooth ER
- calcium (2nd messenger) concentration increases
- calcium and DAG work together to activate protein kinase C (effector)
- PKC phosphorylates other molecules
What is Nitric oxide (NO) synthesized by?
What does it oxidize and release?
- synthesized by nitric oxide synthase (NOS)
- oxidizes guanidine nitrogen of L-arginine, releasing NO in the form of a free radical and citrulline
- 3 isoforms of NOS: endothelial (eNOS or NOS-3), neuronal (nNOS or NOS-1), and inducible (iNOS or NOS-2)
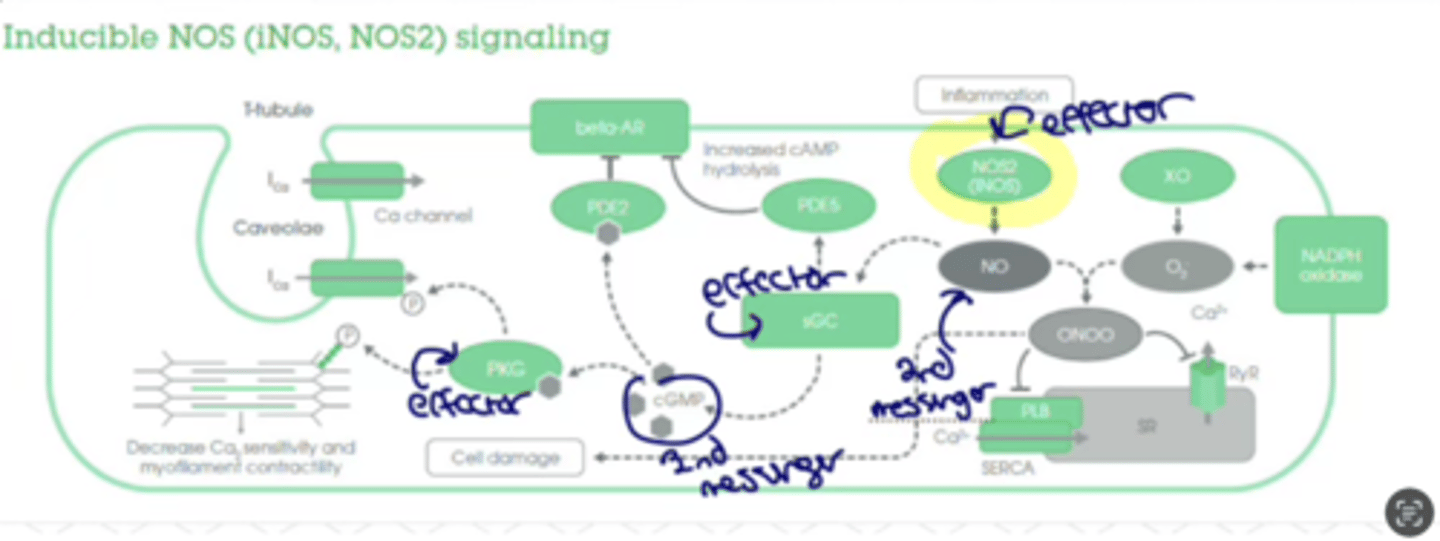
NO acts as a messenger in functions including....
vasodilation, neutrotransmission, anti-tumor, and anti-pathogenic activites
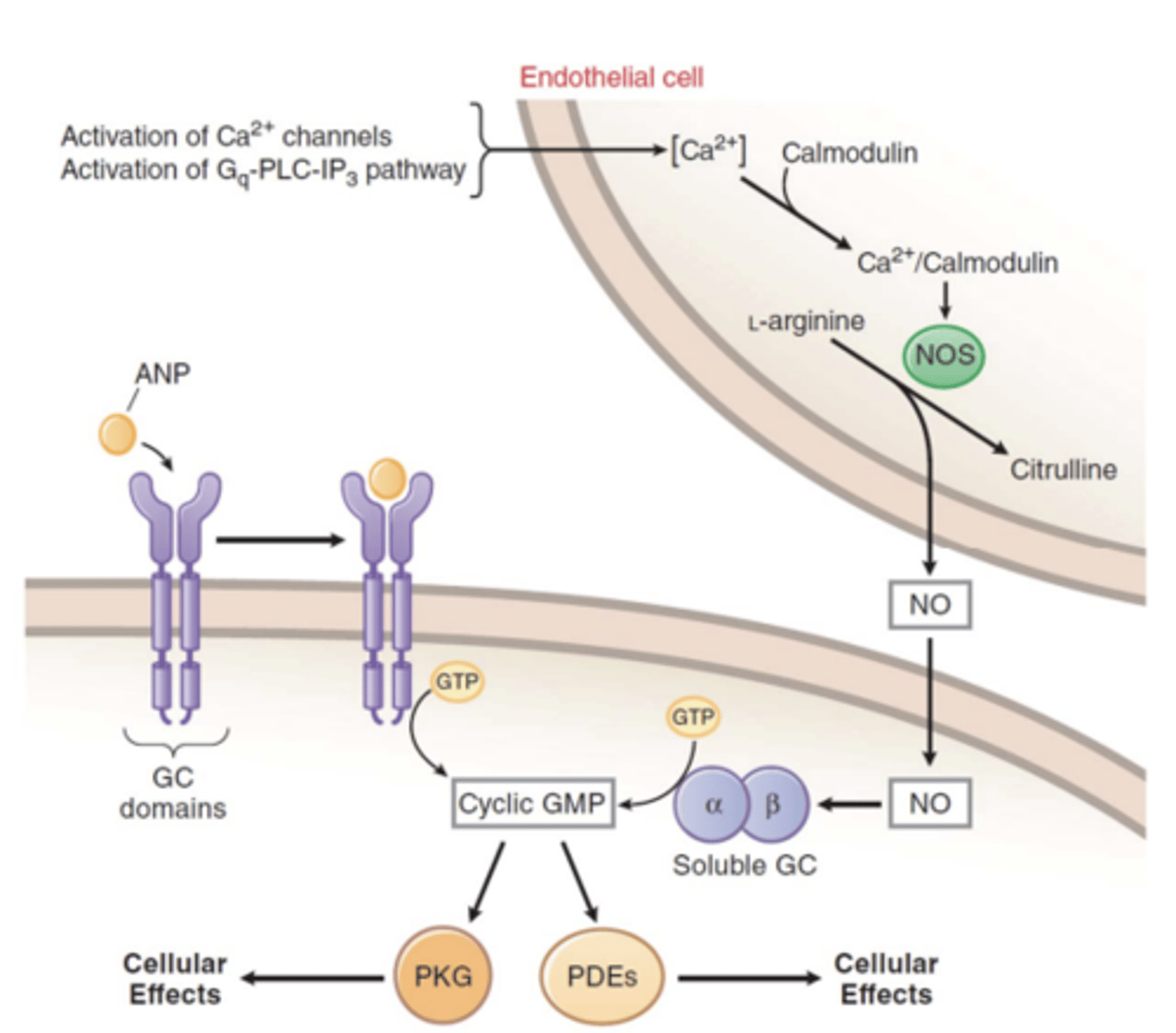
Nitric Oxide-induced cGMP
- What does it stimulate? What is generated?
- What does this result in?
- stimulates soluble guanylate cyclase to generate cGMP
- smooth muscle relaxation (dilation)
- drop in blood pressure
(NO → Endothelium-derived relaxing factor)
T/F: Neurotransmitters, hormones, and other ligands are often present at the LBD of a receptor in very high concentrations
FALSE
they are often present in low concentrations (nanomolar to micromolar levels)
The effector domain or the signal transduction pathway often contain enzymes that.....
catalytically amplify the intended signal (respond to 2nd messengers)
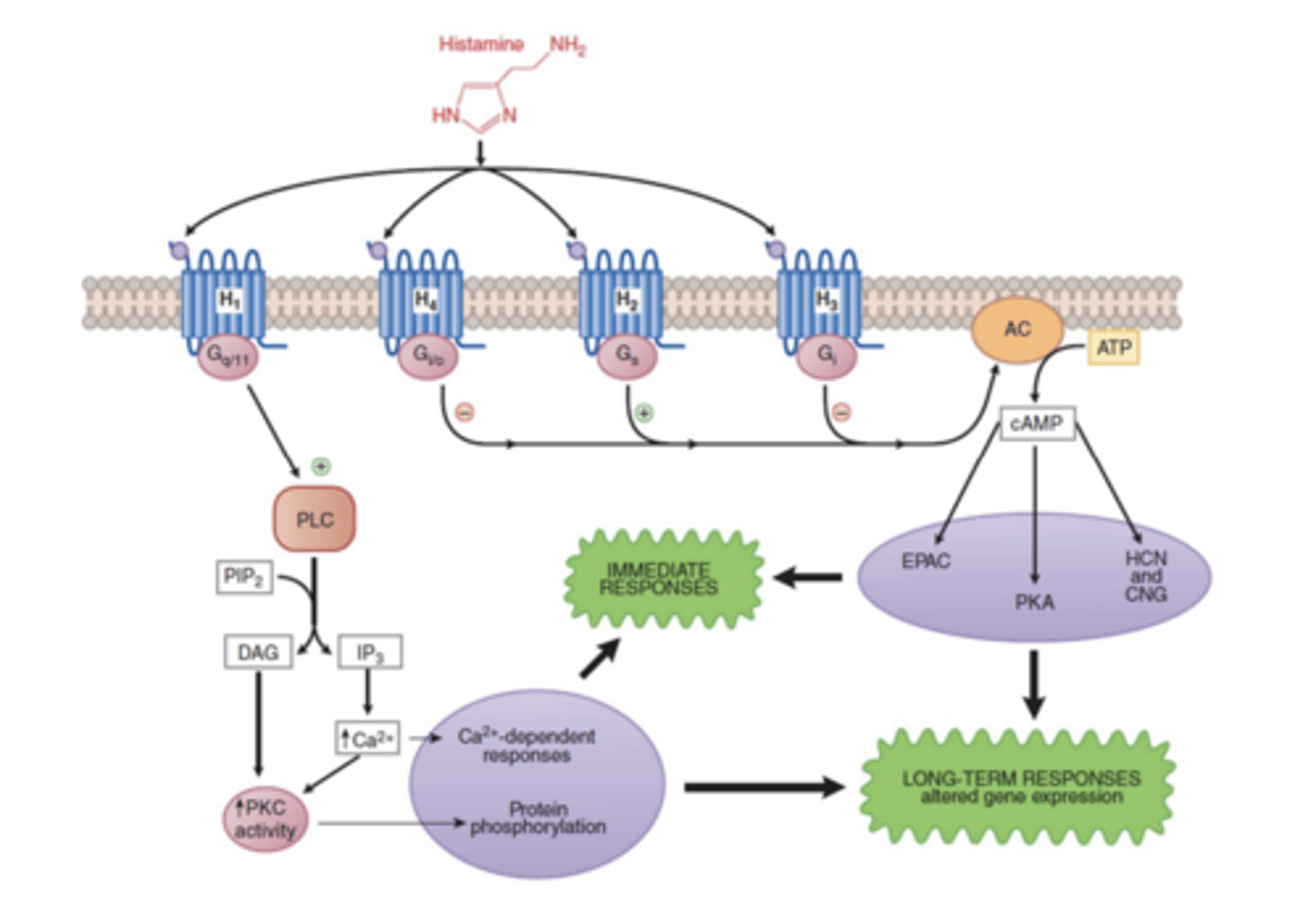
Multi-specific ligand
a ligand that can bind to different isoforms of receptors (ex: histamine can couple to a variety of G-protein linked signal transduction pathways via 4 different receptors)
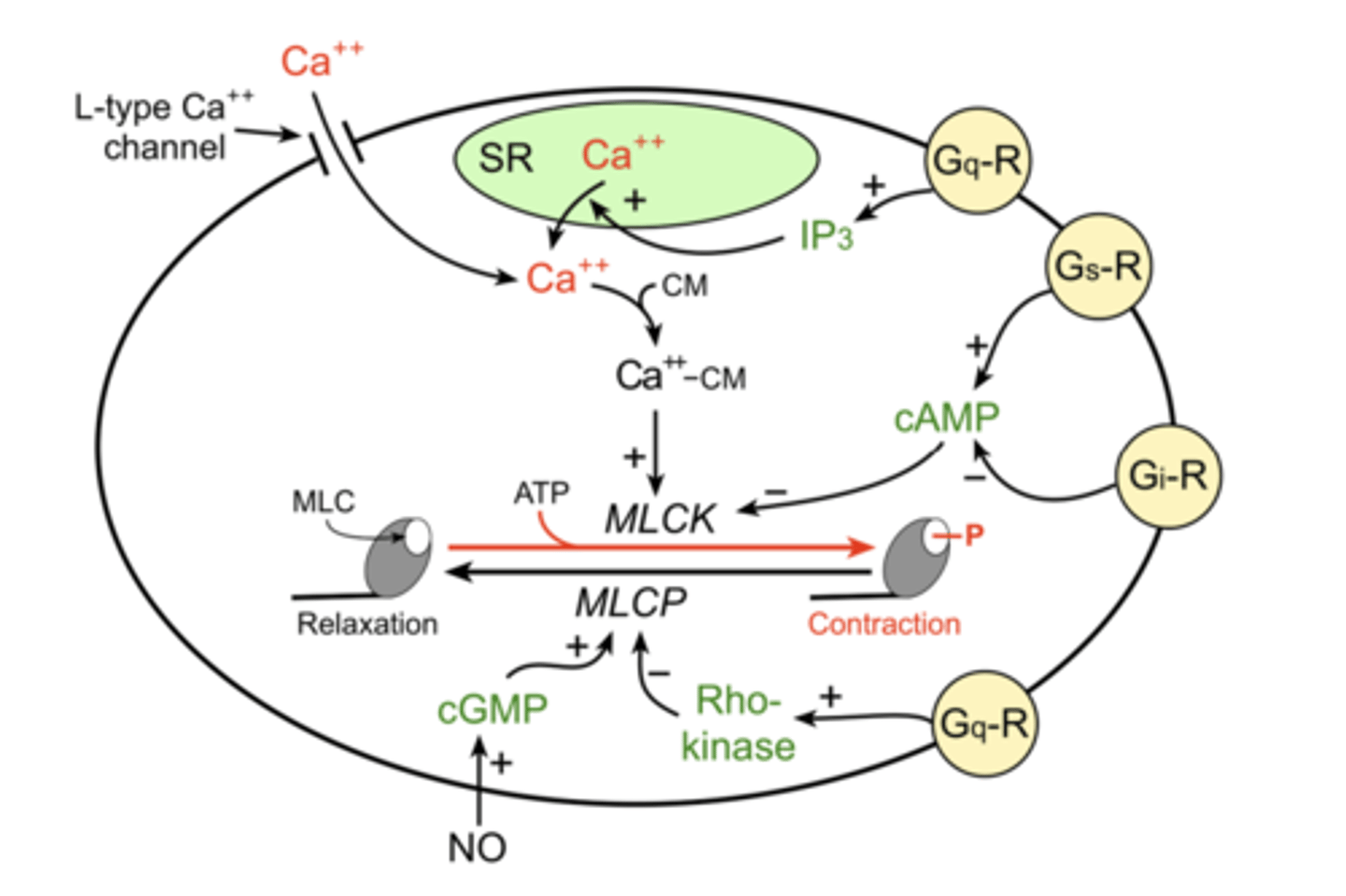
Different secondary messengers can act at the same molecular pathway/tissue to produce....
different effects
(ex: vascular smooth muscle contraction and relaxation)
- Ca2+ --> contraction
- NO ---> relaxation
Enzyme/kinase-linked receptors
linked directly or indirectly to an enzyme
- signal transduction requires this enzyme/enzyme activity
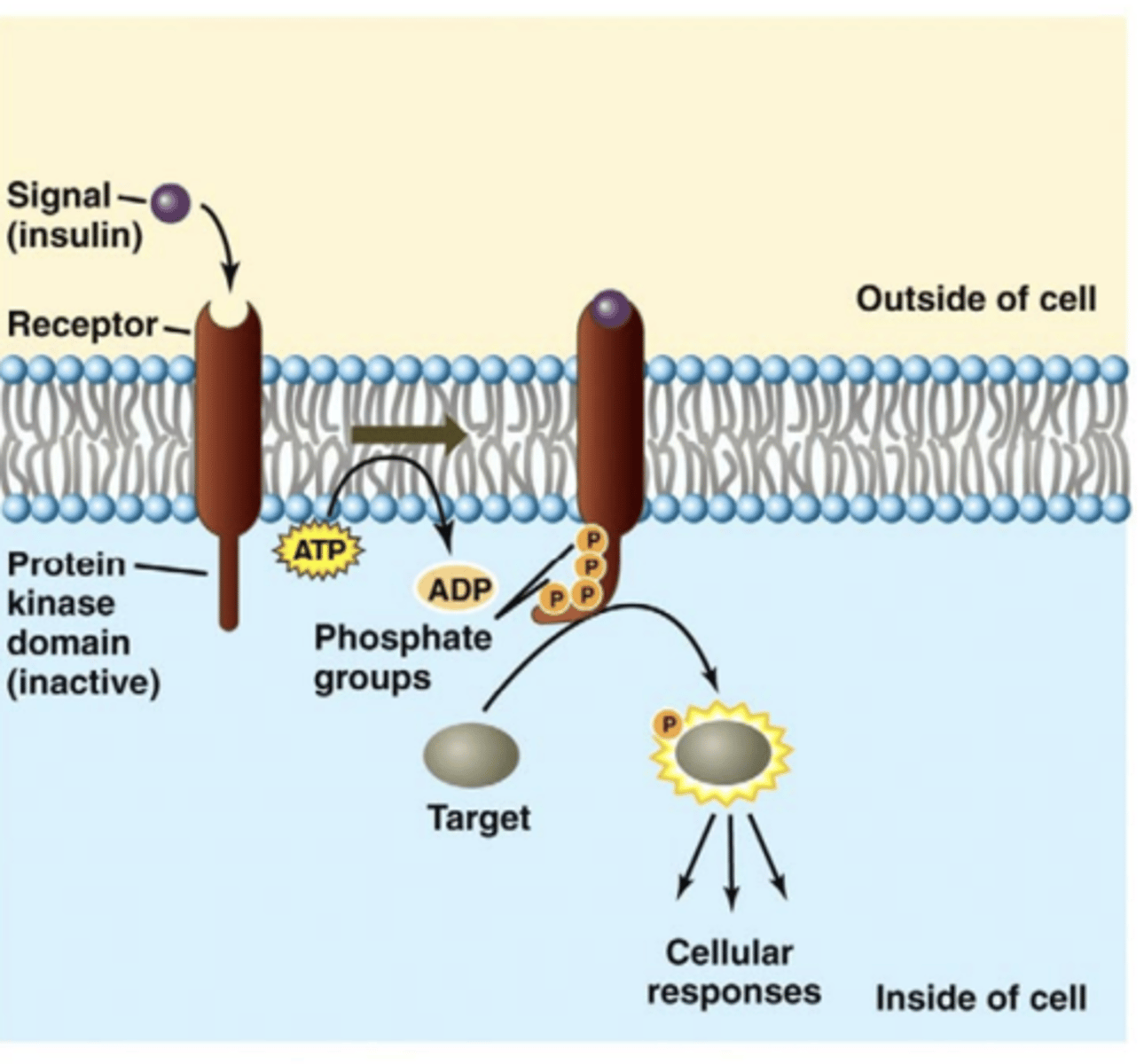
Protein kinase receptors
the high-affinity cell surface receptors for many growth factors, cytokines, and hormones
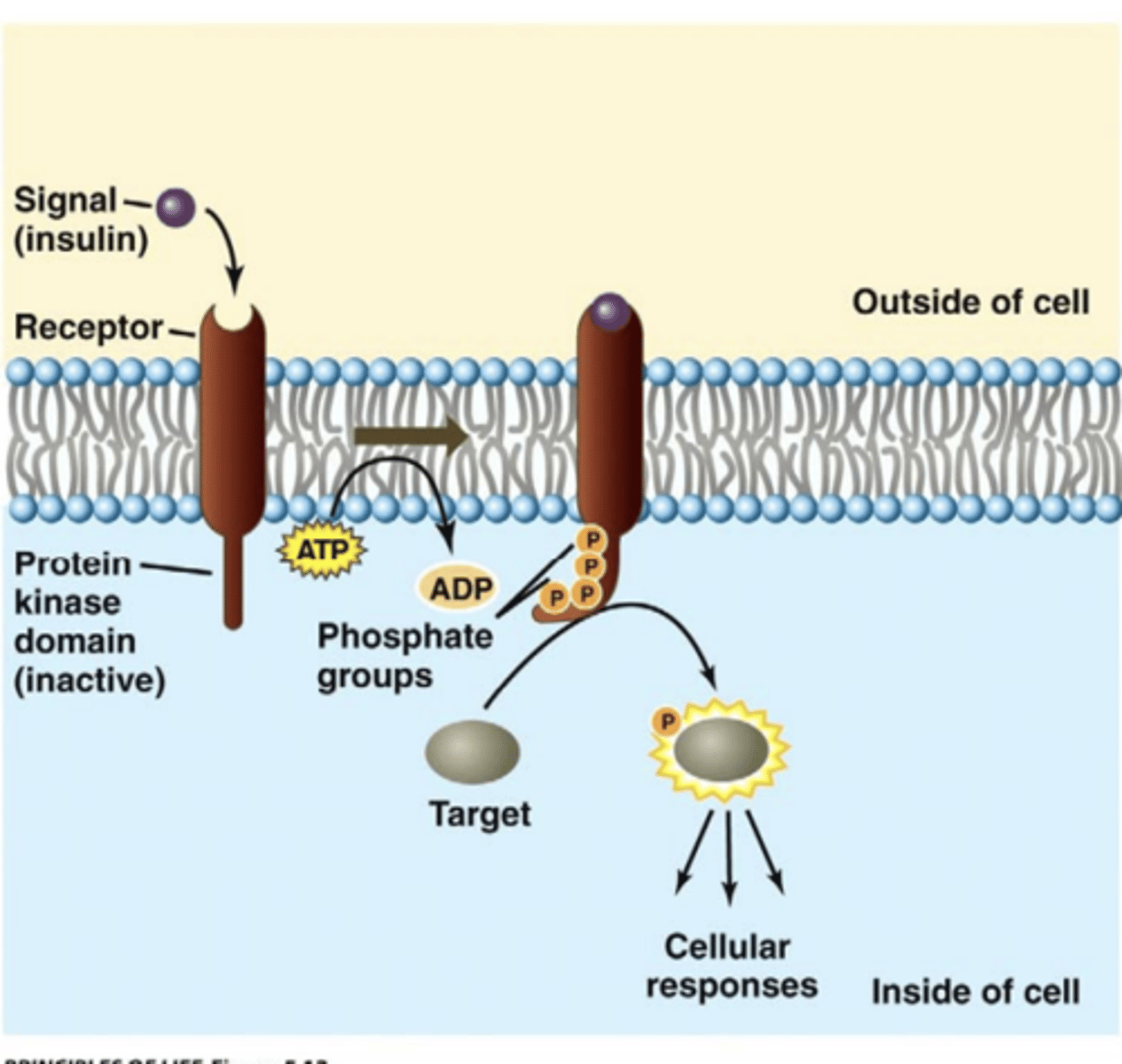
The majority of kinase receptors are....
receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs)
- specifically phosphorylate tyrosine on protein/receptor
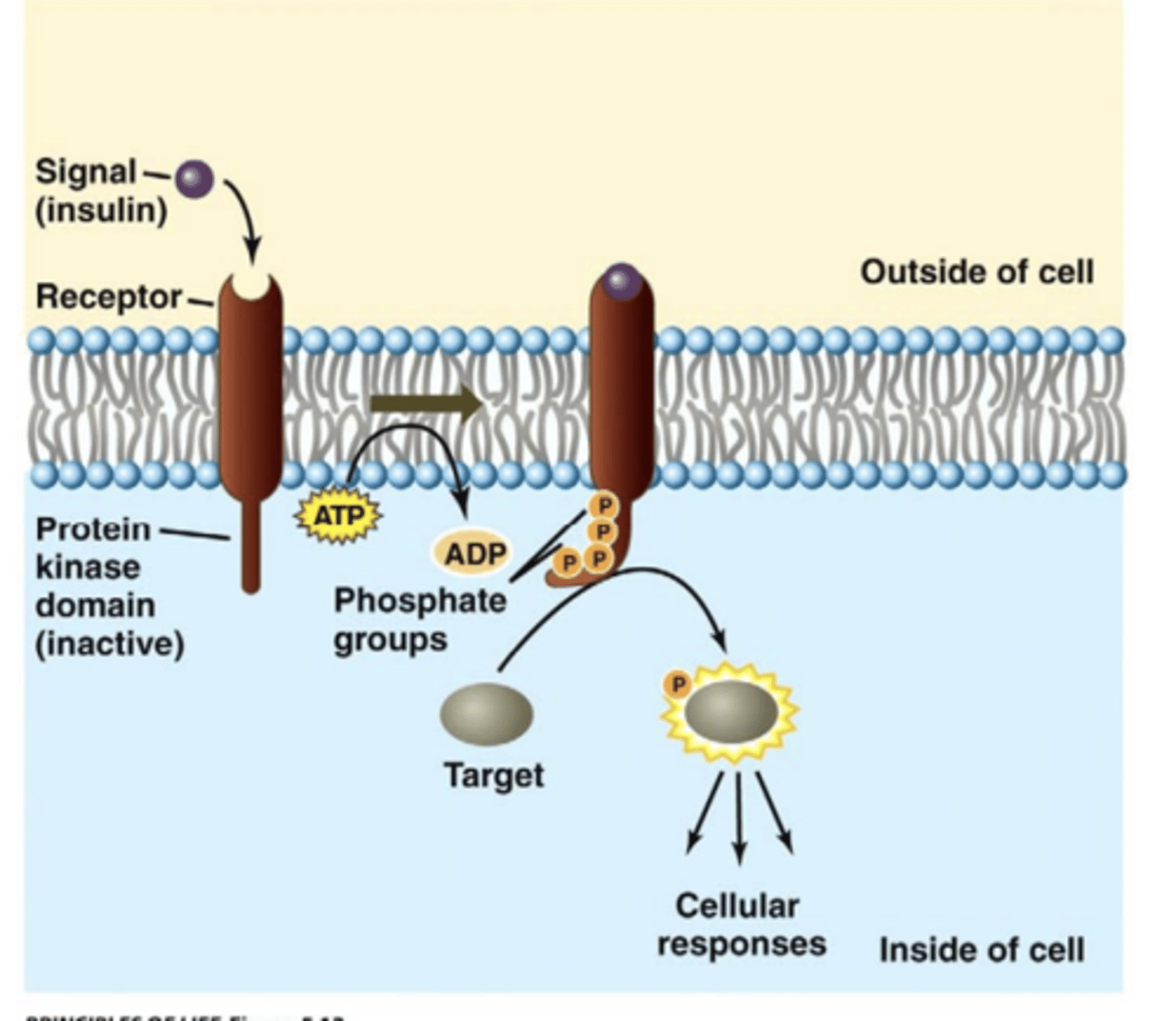
A small group of kinase receptors are....
receptor serine/threonine kinase (RTSK)
- specifically phosphorylate serine/threonine on protein/receptor
- ALKs (activin)
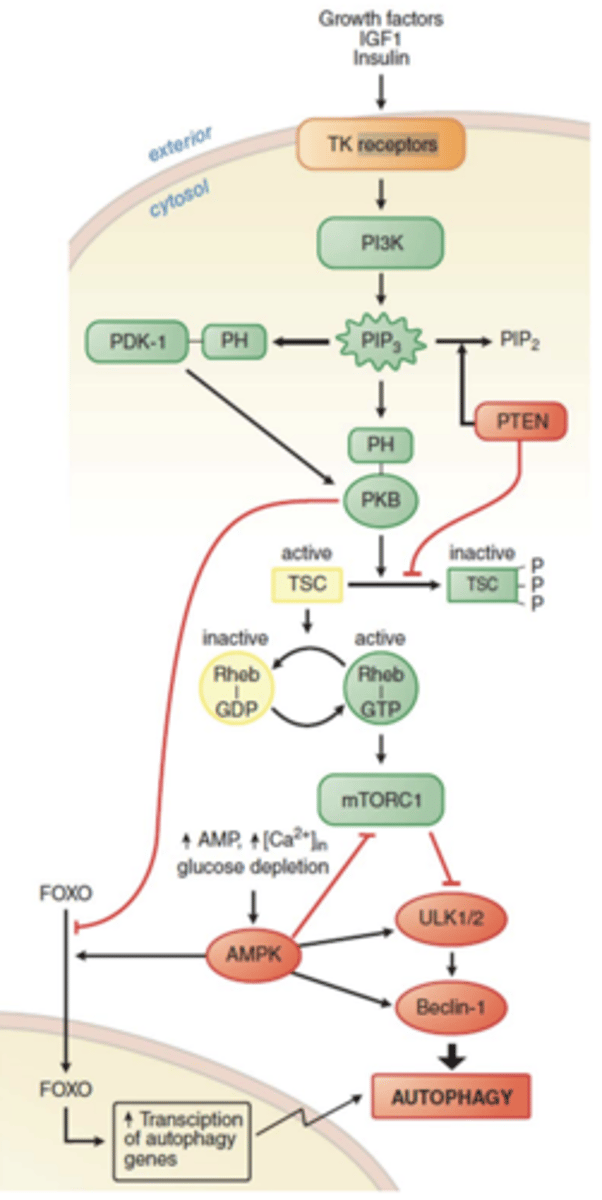
Pathways regulating autophagy: Growth factor signaling pathways activate ___________ and inhibit __________
- mTROC1
- autophagy
(PKB/Akt inhibits the TSC complex, TSC inhibits the activity of Rheb, mTROC1 is activated by the small GTPase Rheb, mTROC1 inhibits autophagy)
Why are kinases (phosphotransferases) important drug targets? (3)
due to their roles in cell growth, death and production of inflammatory mediators
(has been effective in anticancer therapies and immune-mediated diseases)
Second messenger systems (diagram)