Unit 5 - Fourier Analysis of CT Signals + LTI Systems
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
130 Terms
Fourier Analysis
one of the most widely used techniques in signal processing; about representing signals as sums of pure sinusoids of different frequencies (e^jwt); merely a special case of LT analysis in which sigma = 0
Fourier Analysis allows for?
convenient visualization of the frequency or “spectral” content of a signal
Spectra
basically a plot of a signal vs frequency instead of time; used to analyze bio signals
Sinotrial Node
the heart’s pacemaker; innervated w/ parasympathetic and sympathetic fibers for neural heart rate control
Spectra Analysis of HR(t)
allows selective assessment of the integrity of the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems
Fourier analysis is simplier than what?
LT bc no ROC so can be applied to causal or non-causal signal, symmetry properties can be exploited in FA
Fourier vs LT
fourier: 1D (w), simplier bc no ROC, applied to causal or non-causal signals, sinusoids instead, and studies of signals
LT: 2D (sigma + w), ROC, applied to just causal signals, permits frequencies domain analysis of exponentially-growing signals, and study of unstable systems
Fourier Analysis is not applicable to what?
exponentially-growing signals and unstable systems no matter how sinusoids are added, a growing signal is never possible
Fourier analysis is preferred for what?
when the signals for study are bounded
Basis Set of Vectors
any vector can be represented as a sum of vectors which span the entire vectors space
Orthogonal
vectors perpendicualr to each other
Signals may be similarly represented as what?
a sum of “orthoginal basis of signals”; ex. representing signals as a sum of shifted impulse fcns (convolution and output to any input) and representing signals as sums of sinusoids (multiplication and input limited)
Fourier Series (FS)
an expansion of usually a periodic signal on a set of orthogonal basis signals; individual coefficients contain the amplitude and phase information for thier respective basis signals
Orthogonal Series Expansion
a set of signals orthogonal signal set on [t1, t2] are pairwise orthogonal on [t1, t2] (have to signify time interval); if Kn = 1 for all n, then the set is said to be “orthogonal” (unity length)
![<p>a set of signals orthogonal signal set on [t1, t2] are pairwise orthogonal on [t1, t2] (have to signify time interval); if Kn = 1 for all n, then the set is said to be “orthogonal” (unity length)</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/cdb7557c-e1d2-4630-b522-f1cc1648ebb5.png)
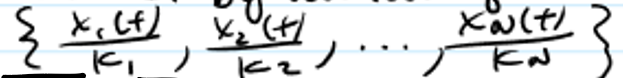
Orthogonal Signal Set
can be always be made orthogonal by dividing each signal by its length; ex. sinusoids

Exponential (or complex) FS
several forms of the FS; forms use different but closely related basis signal sets; has compactness and ease of mathematical manipulation
EFS of a Signal
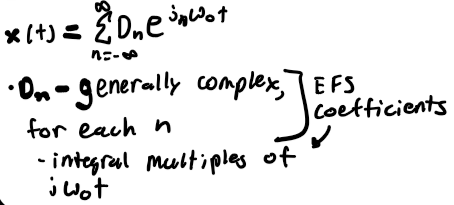
How to compute Dn
take inner product between x(t) and each e^(jnwot)
EFS Pair
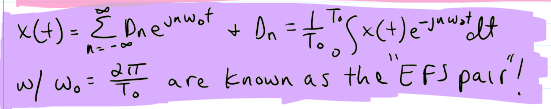
EFS can be computed over what?
a single period of a periodic signal x(t) and it will be valid for all time t; replace t w/ (t +To) in the sum
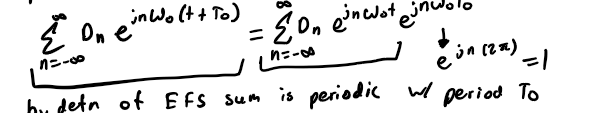
Customary to use what to compute Dn
the primary period [0,To]; can be shown that any period may be employed
![<p>the primary period [0,To]; can be shown that any period may be employed</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/bd3fffd2-5308-4040-9f8a-c79848731efc.png)
If Dn is computed over some range [to, to + To] for a signal, periodic or not?
the EFS sum will represent a periodic version of that signal over the “expansion range”
EFS can be computed over what?
any finite interval and will be valid over that interval; if an interval is a period of a periodic signal then EFS will be valid for all t; why EFS is most commonly used for periodic signals
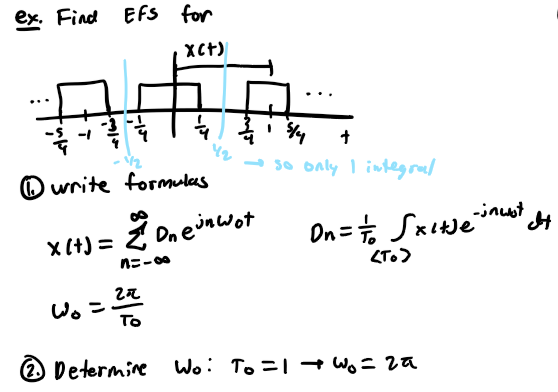
put example in

nth Harmonic
combination of the +- terms of the EFS sum; of the signal being expanded
Conjugate Symmetry
most important symmetry in Fourier analysis; Dn = Dn* → if go same amount in either direction, Dn is conjugates of eachother


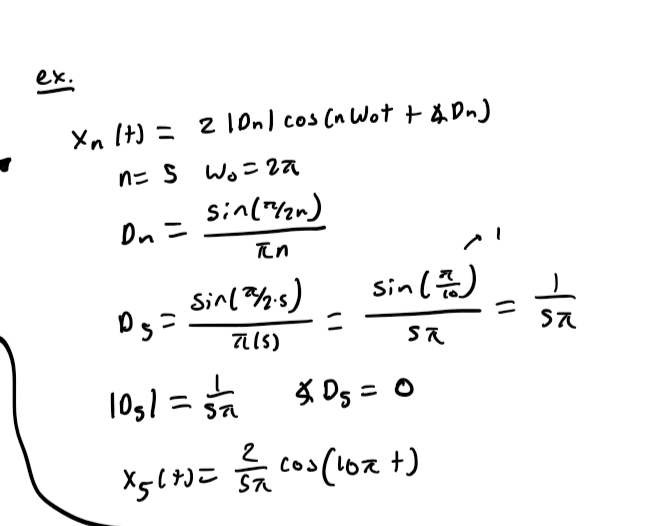
Symmetry Properties
helpful in Fourier analysis;
x(t) real → Dn is conjugate symmetric (D-n = Dn*)
x(t) real and even → Dn real and even (D-n = Dn)
x(t) real and odd → Dn purely imaginary and odd (D-n = -Dn)
x(t) is odd-half-wave-symmetric (OHWS) → only odd harmonics “survive” (Dn = 0 for all even n)
Do represents average value of x(t) over the expansion integral
Odd-half-wave-symmetric
OHWS; shift signal to the left or right by ½ of its period and then flip it over the x-axis; if it is the same signal as the original, it has this
A level (DC) shift in a signal causes what?
a change in only Do and vice versa
Scaling a signal by A has the effect of what?
scaling the EFS coefficients by A
Shifting a signal in time has no effect on OHWS but does affect what?
even and odd symmetry
Line Spectra
sketch of the EFS coefficients as a function of n → Dn vs n; Dn usually complex so there are 2 plots
2 Dn Plots
amplitude spectrum and phase spectrum
Amplitude Spectrum
plot of the magnitude of Dn vs n (|Dn| vs n)
Phase Spectrum
plot of the angle of Dn vs n
Line spectra allows for what?
visualization of the harmonic content of a signal
Finite # of harmonics can be used to approximate x(t) if
|Dn| is decreasing as n increases
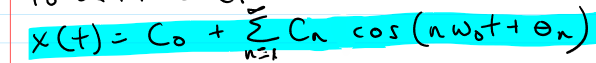
Compact Trigonometric FS (CTFS)

How to compute CTFS coefficients?
compute Dn
Go from An, Bn → Cn, deltan → Dn

Symmetry Properties
x(t) is even, Bn = 0 for all n (sum of sines is odd)
x(t) is odd, An = 0 for all n (sum of cosines is even)
x(t) is OHWS, An = Bn = 0 for even n
Ao represents the avgerage value of x(t)
How to get Dn for n < 0
D-n = Dn* bc x(t) must be real to use TFS
Line Spectra
used as informative to sketch then line spectra for the CTFS as the EFS; 2 plots: amplitude spectrum (Cn vs n, n = 1,2,3) and phase spectrum (deltan vs n, n = 1,2,3)
n-harmonic
if know n, know frequency nWo
Bandwidth of x(t)
frequency beyond which there is no power in x(t)
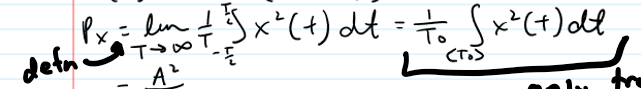
Power Relations
the second one is only true for periodic signals
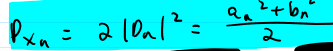
Parseval’s Relations
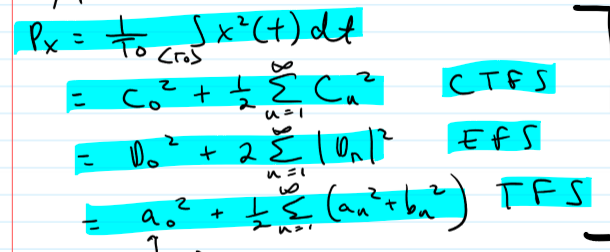
Power is conserved in what
the frequency-domain; summing the square of a signal in time or frequency gives the same value for power; most signals are aperiodic
Fourier Transform (FT)
w/ the FS, periodic signals can be represented for all t as a sum of everlasting sinusoids (only certain discrete frequencies needed); permits the representation of aperiodic signals as a sum of everlasting signals (a continium of frequencies is required)
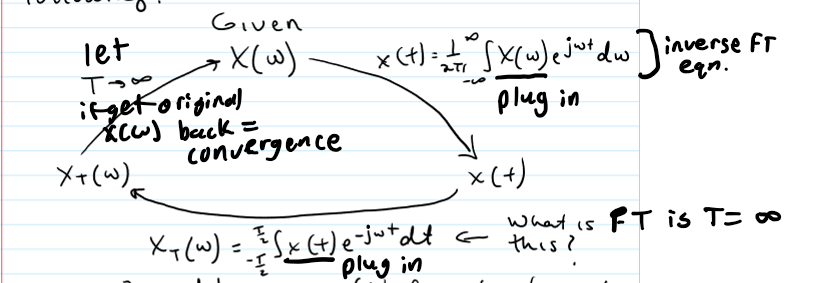
How to derive the FT?
a limiting process is applied to the FS (EFS)
Periodic Extension Signal
has a period To; constructed by repeating the signal every To sec; ex. XTo(t)

FS representing XTo(t)
is periodic and also represents x(t) which is aperiodic in the limit as To → infinity

Example

An aperiodic signal can be represented as what?
a sum of sinusoids w/ a continium of frequencies
Coefficients of the Sinusoids
for any given signal x(t) can be computed as X(w) = integral from - infinity to inifinity of x(t)*e^(-jwt)dt (FT eqn.)
FT Pairs
x(t) and X(w); x(t) ←> X(w)
Periodic Signal - Comment
Dn reflects the extent to which the nth harmonic contributes to the signal
Aperiodic Signal - Comment
X(w)dw reflects the extent to which e^(jwt) contributes to the signal
Spectral Density
amount of frequency component per unit frequency; ex. X(w)
At any single frequency, X(w)dw = what?
0; amplitude of any one sinusoidal component is 0; a whole lot of nothing is something; ex. infinity * 0 = a finite value
X(w)
represents the relative amount of component at frequency w
FT can represent what?
finite duration signals w/ everlasting sinusoids
Relationship between FS and FT
X(w) - FT of an aperiodic signal x(t)
DN - FS of the periodic extension signal XTo(t)
FS Coefficients
scaled “sampler” of the FT of one period of the periodic signal; as To increases, Wo decreases and as To → infinity, Dn → 0
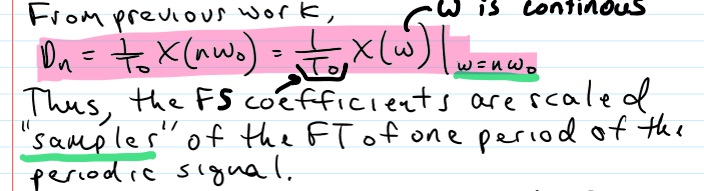
FT Examples

Sinc Function
important in signals and systems; even fcn of w; = 0 when sin(w) = 0 except at w=0; sinc(0) = 1; exhbits osicallating behavior w/ period 2pi and amplitude decreasing as 1/w; never goes to 0
FS Example
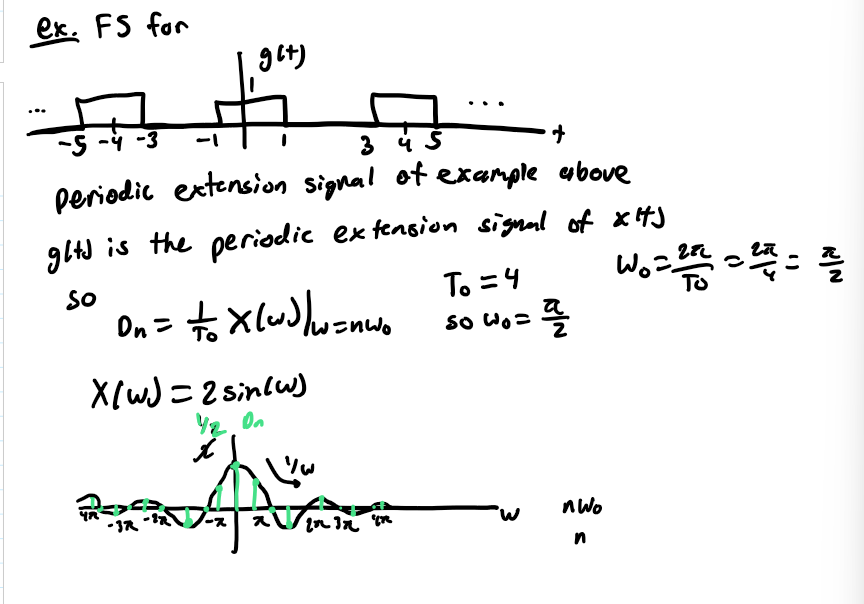
FT Pair
any time you have an infinite intergral it could blow up or diverge so FT does not exist for all x(t)
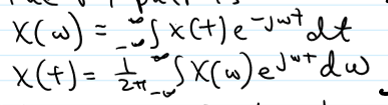
Convergence of the Integrals
x(t) Conditions thet Guarantee Convergence
x(t) is absolutely integrable (all BIBO stable impulse responses are Fourier transformable)
x(t) is square integrable (if get a finite value) → all energy signals are FTable
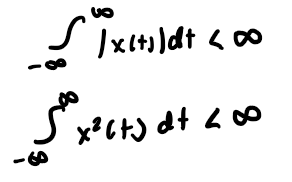
Neither Signals
do not have a FT bc they blow up over time; no matter how you add sinusoids, can’t produce a growing signal
Fourier Transform → Laplace Transform
by setting s = jw; “evaluating LT along jw-axis”; can only do this if ROC includes jw-axis (“causal signals” need all poles to be in the LFP so ROC is right of right most pole)
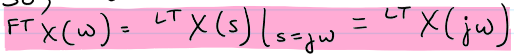
Plot of X(w) vs w
allows visualization of the frequency content or “spectral” content of a signal x(t)
X(w) is generally complex
2 plots
amplitude/magnitude spectrum (plot of |X(w)| vs w)
phase spectrum (plot of angle X(w) vs w)
analogous to EFS line spectra
|X(w)|² vs w
energy density spectrum plot; given instead of magnitude spectrum sometimes
Example

For real x(t)
|X(w)| vs w is always an even fcn; angle X(w) vs w is always an odd fcn; X(w) is a conjugate symmetric
Sketch the Spectra for x(t)
EFS Line Spectra
indicate harmonic content of a periodic signal
FT Spectra
provides similar info that EFS line spectra does for periodic signals but for aperiodic signals
Why does X(w) over a range of frequencies must be approximated?
contribution of any 1 frequency is nothing; need every frequency for aperiodic signals
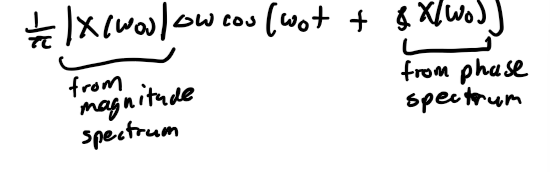
Parseval’s Relation for the FT
energy conserved in FT domain (sum the square of a signal in time or frequency gives the same value for energy)
Energy Density Spectrum
plot of |X(w)|² vs w
|X(w)| is what at any single w?
0; reflects the realtive energy at that frequency
Power Signals
include periodic signals as well as constants and the step fcn; niether absolutely nor square integrable
FT of Power Signals
does not exist in the conventional sense
What has to happen if a signal has periodic and aperiodic parts?
analyzed separately
FT of a Power Signal
may be determined with a trick in which impulses (delta(w)) are allowed in X(w); so X(w) is infinite at some frequencies
A complex sinusoid of frequency Wo has a FT given by what?
an impulse fcn located at the same frequency
Power Signals and the FT
doesn’t exist in the conventionl sense; only the inverse FT works
FT of the Periodic Signal
let Dn be the EFS coefficients for an arbiterary periodic signal w/ period (2pi)/Wo; now use lineraity + the result from pervious example to get

2 Steps to Compute the FT of a Periodic Signal
determine EFS (Dn and Wo) then put in formula
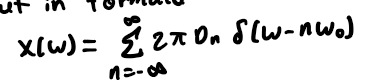
FT of a real sinusoid contains what?
2 impulses; at +- frequency of the sinusoid
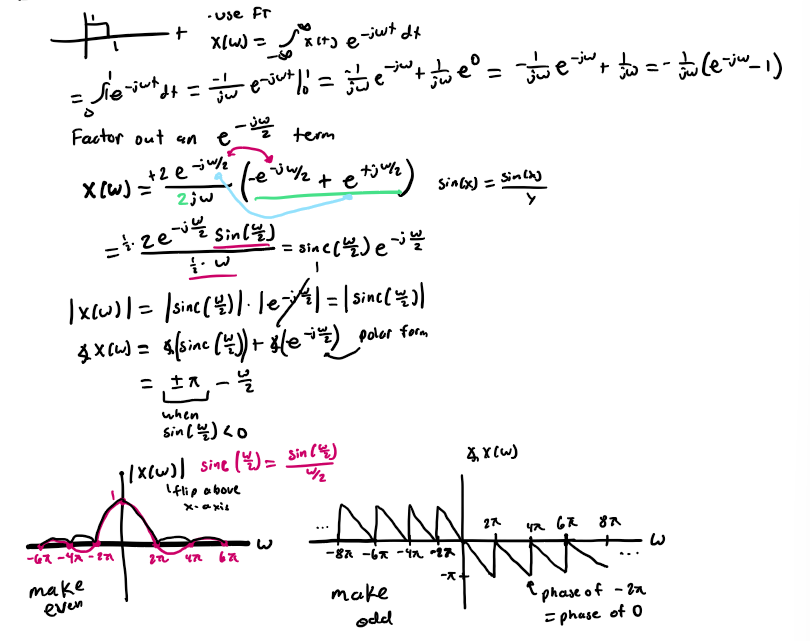
Time-Frequency Duality of the FT
operations required to go from x(t) to X(w) and then from X(w) to x(t) are nearly identical (w/ the exception of the 1/(2pi) scale factor and sign on the exponent); ex. time-shifting and frequency-shifting

FT and Inverse FT are essentially Symmetric Formulas
means that for any result or relationship but with x(t) + X(w), there exists a dual result or relationship obtained by interchanging the roles of t and w in the original result
Properties of the LT
linearity, symmetry, scaling, reversal, time-shifting, and frequency shifting
Linearity
if x1(t) ←> X1(w) and x2(t) ←> X2(w), then ax1(t) + bx2(t) ←> aX1(w) + bX2(w)
Symmetry
if x(t) ←> X(w), then X(t) ←> 2*pi*x(-w); if 1 pair of an FT is known, another pair automatically results