AP Bio Unit 1: Chp 3: Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life - Functional Groups
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Functional groups
The components of organic molecules that are most commonly involved in chemical reactions; give each molecule unique properties
Hydroxyl
(-OH) or (HO-)
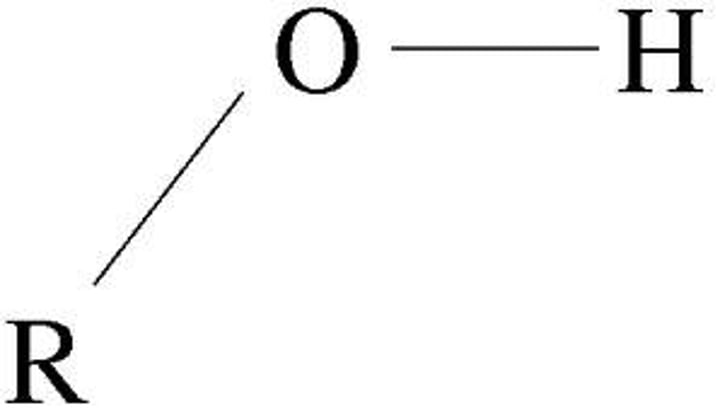
Properties of Hydroxyl
Polar (ex: Alcohol) (usually ends in -ol)
Methyl
(-CH3)
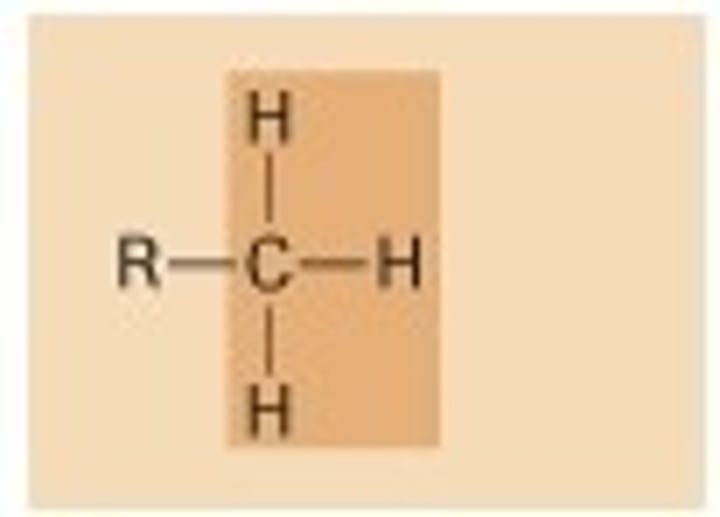
Properties of Methyl
Nonpolar (ex: methylated compound)
Carbonyl
>C=O
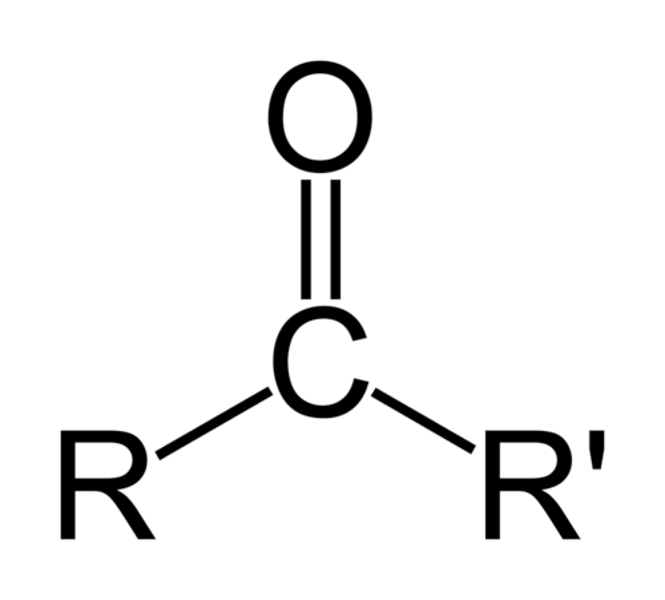
Properties of Carbonyl
Polar (ex: ketone, acetone, aldehyde)
Carboxyl
-COOH
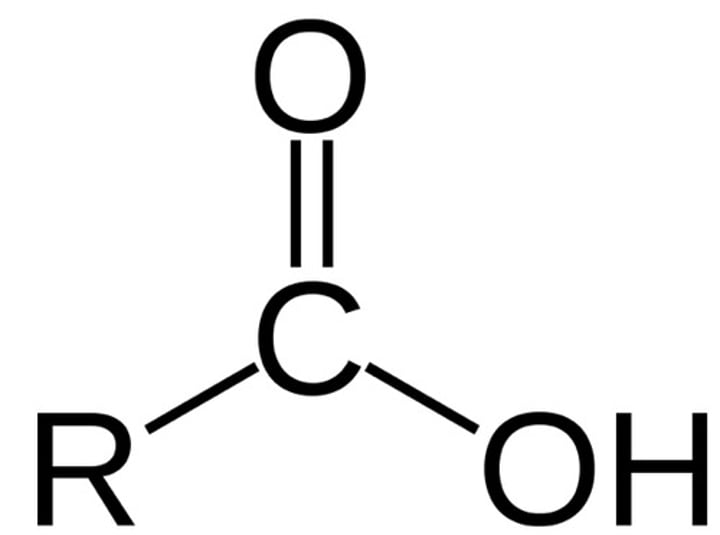
Properties of Carboxyl
Charged, ionizes to release H+ Since this group can release H+ ions into solution they are considered acidic (Ex: vinegar)
Amino
-NH2
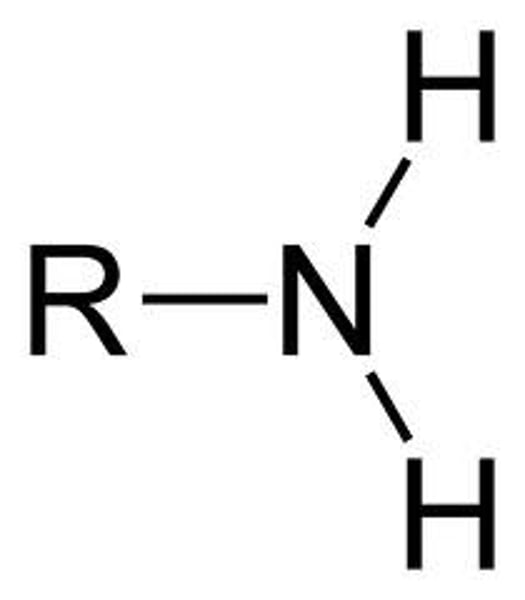
Properties of amino
Charged accepts H+ to form NH3+ Since this group can remove H+ from solutions they are considered basic (Ex: Amine)
Phosphate
-OPO3^2-
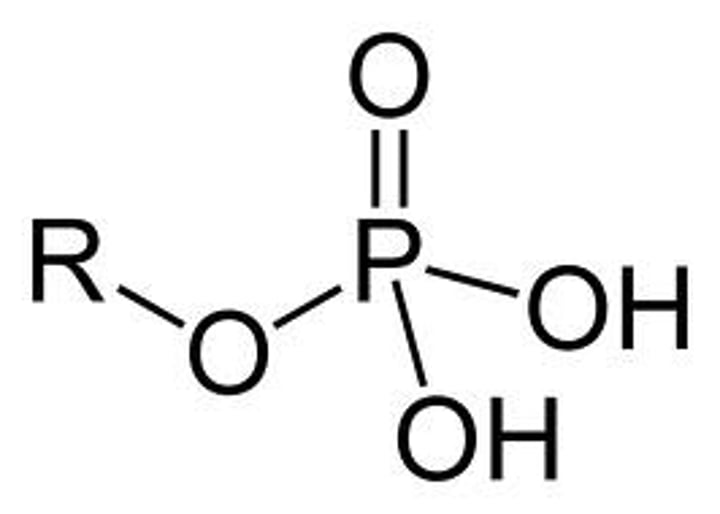
Properties of Phosphate
Charged, ionizes to release H+, Since they release H+ ions into solution, acidic
Sulfhydryl
-SH

Properties of Sulfhydryl
Polar (ex: Thiol)