Week 8: HTML, CSS, JavaScript
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
IP (Internet Protocol)
a way by which computers can identify one another across the internet since every computer has a unique address in the world.
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)
helps keep track of the sequence of packets being sent and is used to distinguish web services from one another.
DNS (Domain Name Systems)
a collection of servers on the internet that are used to route website addresses like harvard.edu to a specific IP address; simply a table or database that links specific, fully qualified domain names to specific IP addresses.
DHCP
a protocol that ascertains the IP address of your device and defines the default gateway and nameservers your device uses.
HTTP (hypertext transfer protocol)
an application-level protocol that developers use to build powerful and useful things through the transfer of data from one place to another. HTTPS is a secure version of this protocol.
200
response code; “OK”
301
response code; “Moved Permanently”
302
response code; “Found”
304
response code; “Not modified”
307
response code; “Temporary Redirect”
401
response code; “Unauthorized”
403
response code; “Forbidden”
404
response code; “Not Found”
418
response code; “Im a teapot”
500
response code; “Internal Server Error” (always your fault as the developer when they concern a product or application of your creation.)
503
response code; “Service Unavailable”
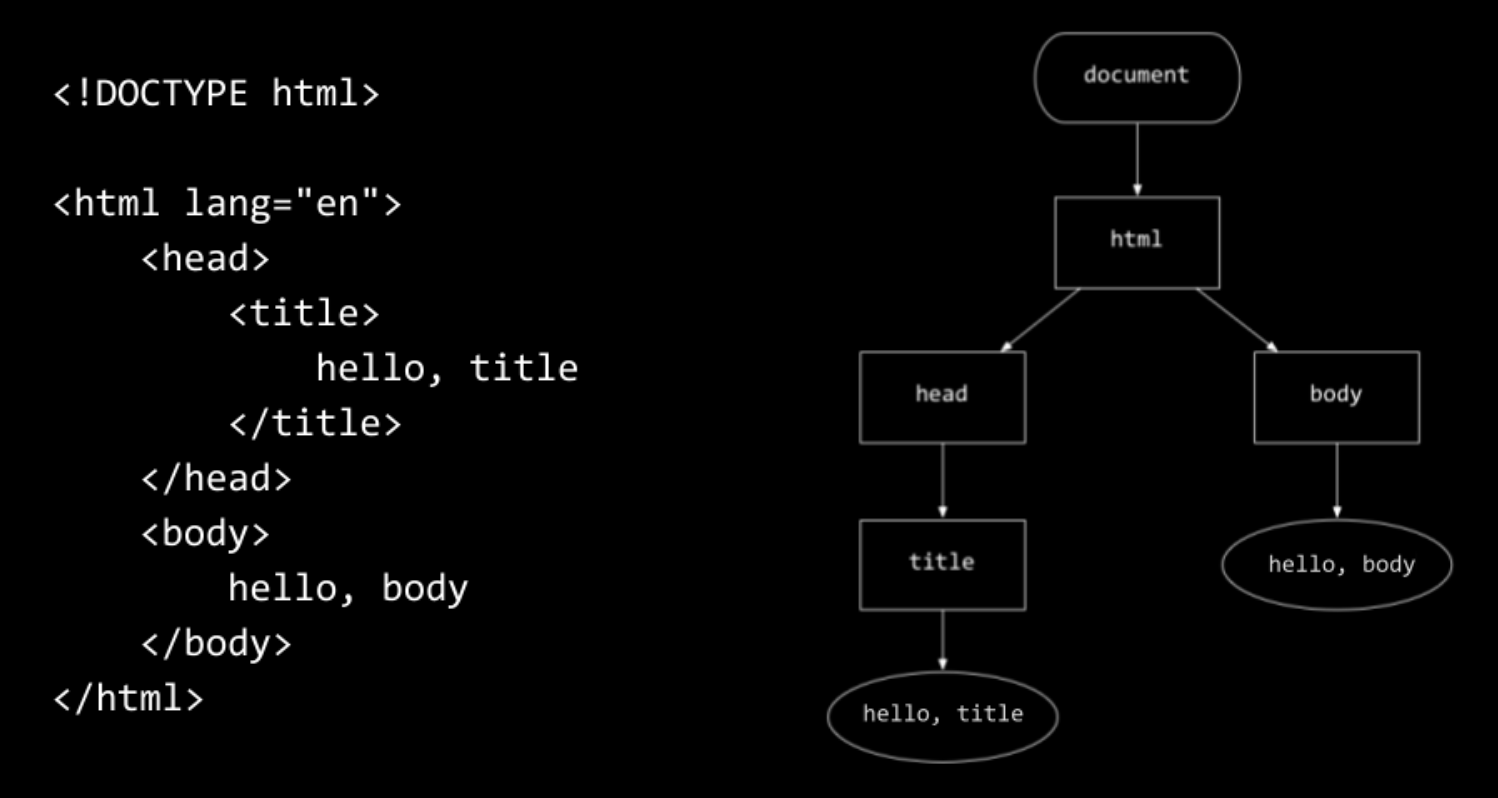
HTML (hypertext markup language)
made up of tags, each of which may have some attributes that describe it.
Hierarchy of tags
Regular Expressions/ regexes
a means by which to ensure that user-provided data fits a specific format.
CSS (Cascading Style Sheet)
a markup language that allows you to fine-tune the aesthetics of your HTML files; filled with properties, which include key-value pairs.
JavaScript
programming language that allows for interactivity within web pages.
Internet
the fundamental concepts and technologies that underpin how computers communicate and exchange information over a network
Routers
a networking device that forwards data packets between different networks
TCP/IP
a set of communication protocols used to connect network devices on the internet. It's a fundamental framework that enables global information exchange
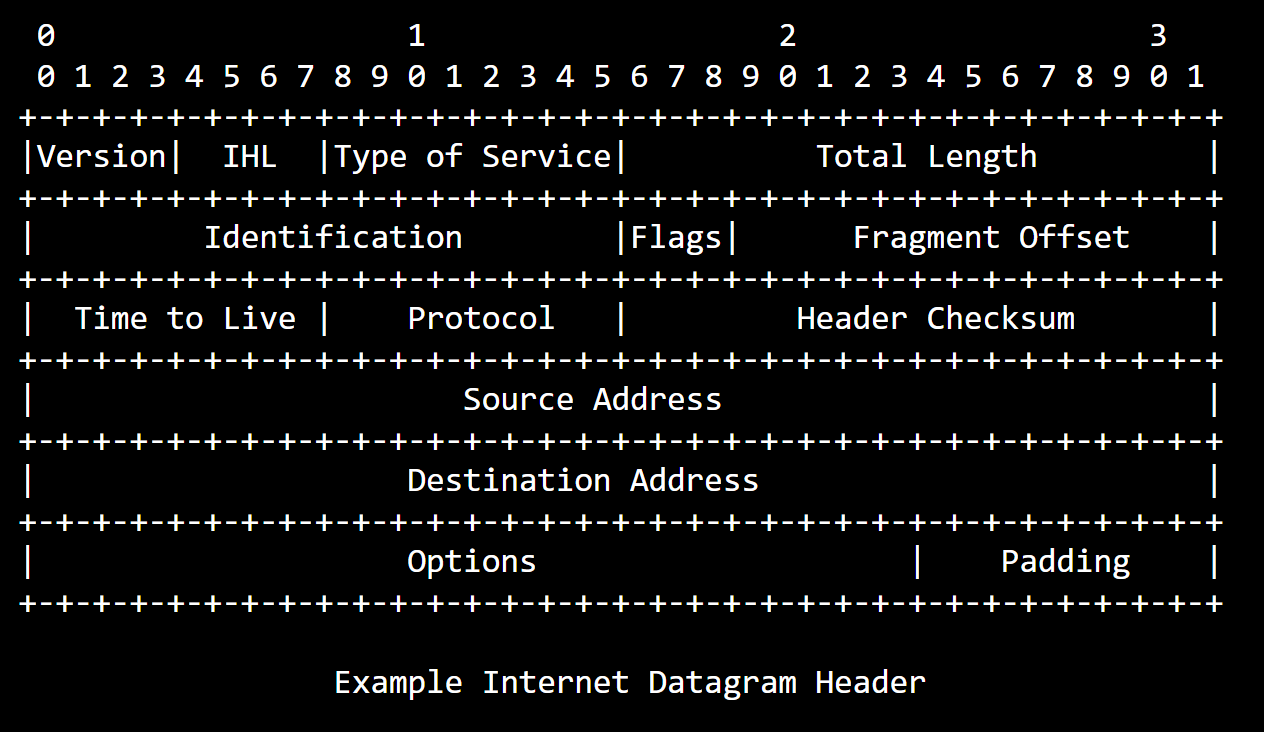
Packets
What is being sent around computers; standardized and contains the source and destination
Ports
standardized numbers that represent different services running on a computer or server
path
the specific location or route through which a file or directory can be accessed within a file system

GET
a type of HTTP request that a web browser (the client) sends to a web server.
developer tools
the environment and software used to write, compile, and debug code
frameworks
a pre-defined structural foundation that streamlines the development process for specific types of applications
Bootstrap
helps developers avoid writing extensive CSS from scratch by offering readily available styles and layouts