Cardiovascular
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
What are two causes of a cardiac silhouette
increase in heart size
pericardial fluid
What is the hearts response to rapid pericardial effusion/exudate
cardiac tamponade
What is the hearts response to slow pericardial effusion/exudate
adaption
What type of fluid is hydropericardium
serous fluid
What color is hydropericardium
clear/straw colored
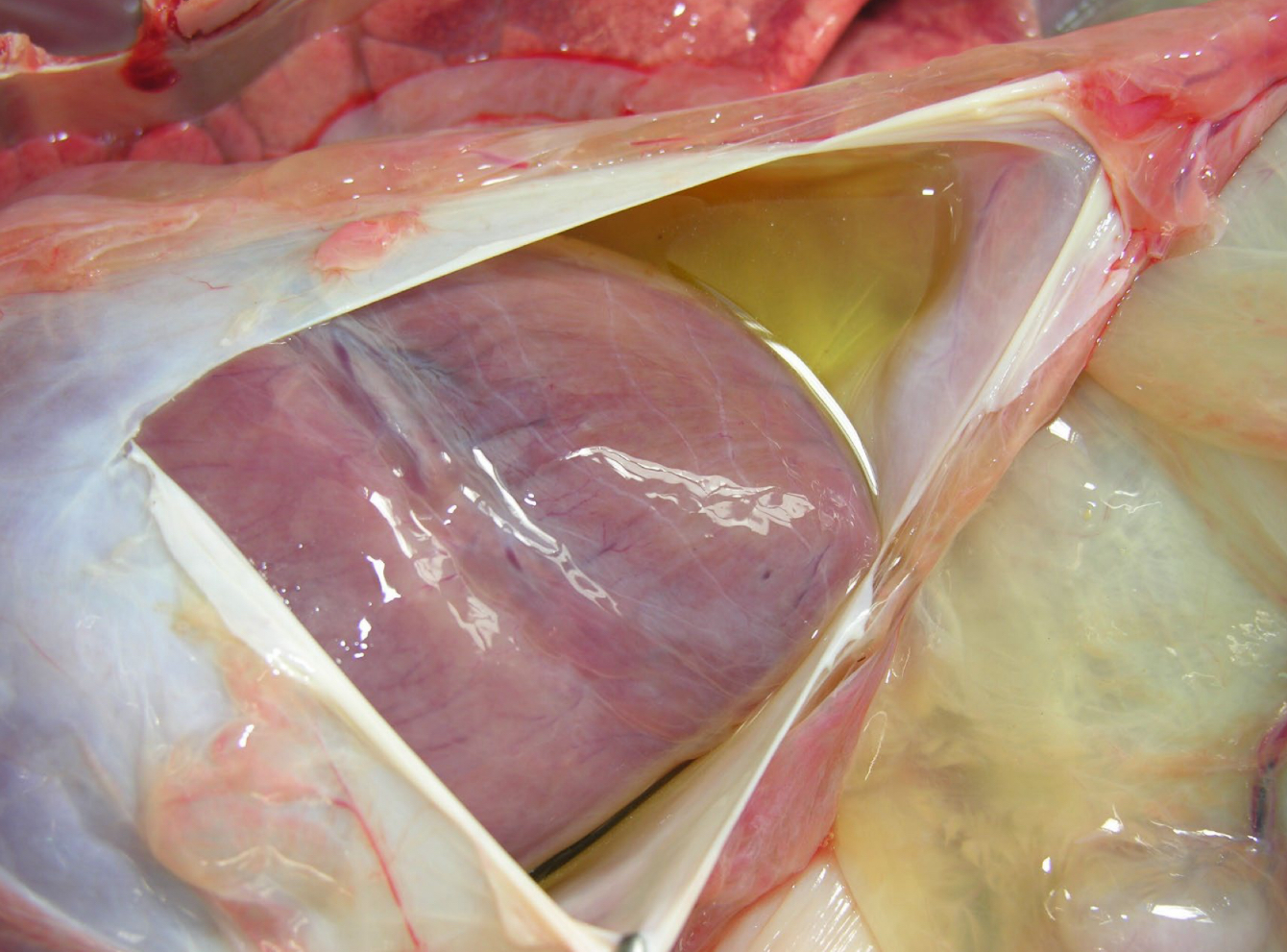
what is this
hydropericardium
Causes of hydropericardium
congestive heart failure
pulmonary hypertension- increased hydrostatic pressure
Hypoproteinemia- decreased oncotic pressure
Neoplasia
What type of fluid is a hemopericardium
pure blood
What are causes of hemopericardium
rupture of hemangiosarcoma
rupture of base of aorta in horses
rupture of left atrium secondary to mitral valve disease
trauma
anticoagulant rodenticide toxicity
Where is the most likely place for a hemangiosarcoma in a dog
right auricle
What is the likely consequence of a hemopericardium
cardiac tamponade
What is the exudate in a fibrinous pericarditis
fibrin and neutrophils
What does fibrinous pericarditis indicate
presence of bacteria in pericardial sac
Causes of fibrinous pericarditis
Septicemia
penetrating injury
extension from myocardial abscess
vascular damage
uremia (dogs)
FIP (cats)
What are the pathogens causing septicemia in fibrinous pericarditis
Neonatal infection secondary to failure of passive transfer
Glasser’s disease (Glasserella parasuis) (swine)
Histophilus somini (Cattle)
What is an example of a penitrating injury that would cause fibrinous pericarditis
hardware disease
What is a pathogen that would cause vascular damage in fibrinous pericarditis
Blackleg- Clostridium chauvoei
What is the outcome of fibrinous pericarditis
large amounts of fibrinous exudate organize into granulation tissue which causes fibrous adhesions between visceral and parietal pericardium- this prohibits filling of heart- constrictive pericarditis
What are the causes of serous atrophy of fat on the heart
Starvation or cachexia
What disease causes epicardial urate deposition
gout
What is the definition of cardiomegaly
overall increase of the external dimensions of the heart
What are the two type sof cardiomegaly
hypertrophy
dilation
What is seen with hypertrophy
increase in myocardial mass
What is seen with dilation
increase in chamber volume
Causes of dilation cardiomegaly
myocardial necrosis
myocardial inflammation
Secondary to volume overload
What type of overload causes concentric hypertrophy
pressure
What type of overload causes eccentric hypertrophy
volume
What is seen with concentric hypertrophy
heart wall thickness increases- decreased chamber size
What is seen with eccentric hypertrophy
increase in chamber size, dilation and hypertrophy
Pathogenesis of myocardial hypertrophy secondary to hyperparathyroidism
increase hypothyroidism which acts on adrenergic receptors to vasodilate peripheral vessels- increase venous return. Concentric hypertrophy occurs in response to increase peripheral tissue demand for oxygen and dissipation of heat
what is eccentric hypertrophy associated with
severe valvular insufficiency and atrial/ventricular septal defects
What is cardiomyopathy
primary disease of cardiac muscle
What are the primary cardiomyopathis in SA
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Restrictive cardiomyopathy
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy
dilated cardiomyopathy
Macroscopic signs of HCM
concentric hypertrophy of left ventricle
secondary dilation of left atrium
pulmonary edema
Microscopic signs of HCM
myofiber hypertrophy
interstitial fibrosis
cardiomyofiber disarray
HCM is a ___ disorder
diastolic
Blood backs up into what in HCM
lungs
What is the most common cardiomyopathy in cats
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Breed predisposition for HCM in cats
Maine Coon
Ragdoll
What gene gets changed in cats predisposed to HCM
myosin binding protein C3 gene
What is a common effect of HCM
thrombi development in dilated left atrium- thrombembolism blocking at terminal branch of aorta (saddle thrombis)- blocking blood flow to hind limbas
What is seen in feline restrictive cardiomyopathy
endocardial fibrosis
left ventricular hypertrophy
reduction of left ventricular lumen
left atrial dilation
What breeds are predisposed to ARVH
Boxers and English bulldogs
What is commonly seen with arrhythmogenic right ventricular hypertrophy
right ventricular dilation
replacement of cardiomyocytes with adipose tissue and fibrosis
What is seen with dilated cardiomyopathy
dilation of both atria and ventricles- particularly left side
Dilated Cardiomyopathy is a ___ disfunction
systolic
What is the most common form of cardiomyopathy in dogs
dilated cardiomyopathy
Nutritional causes of myocardial degeneration/necrosis in ruminants
selenium and/or vitamin E deficiency
What type of muscle is affected by selenium toxicity in ruminants
skeletal and cardiac muscles- turn pale
What is a nutritional cause of myocardial degeneration and necrosis in pigs
vitamin E deficiency
What is seen with vitamin E deficiency in pigs
vascular necrosis- hemorrhage and necrosis of heart
What are toxicity causes of myocardial degeneration and necrosis
ionophore (horse)
Blister beetle toxicity (horses)
Senna occidentalis
Nerium oleanderW
hat toxin is specific for cardiac muscle
nerium oreander
What is a cause of secondary myocardial degeneration and necrosis
Neural injury- brain heart syndrome
emboli- myocardial infarcts
Antineoplastic agents- doxorubicin
Causes of bacterial myocarditis
clostridium chauvoei
Histophilus somni
Staphylococcus aureus
What will we seen with bacterial mocarditis
neutrophils and necrosis
Causes of viral myocarditis
porcine circovirus 2 and 3
Canine parvovirus type 2
Causes of fungal myocarditis
disseminated aspergillosisP
Causes of protozoal myocarditis
Trypanosoma cruzi
Toxoplasma gondii
Neospora caninum
Where is hemangiosarcoma most often
Right auricle
Where is malignant lymphoma most often
right atrium
HULAS- heart uterus lymph node abomassum spinal canal
Retrobulbar
Where is chemodectomas most often
heart base
Causes of endocardial/intimal mineralization of aorta
Subendocardial mineralization
seondary to necrosis- dystrophic mineralization
secondary to imbalances in calceium and phosphorous- metastatic mineralization
AGASACA
lymphoma
Uremia
Johnes disease
Vitamin D analogs/rodenticidez
What is myxomatous valvular degeneration
chronic degenerative atrioventricular valve disease
Where does MVD commonly occur
mitral valve
What dose the valve look like with MVD
increased size and thickness but smooth
What are sequela of MVD
valvular insufficiency
left sided heart failure
jet lesions- caused by turbulent blood flow
Mitral valve prolapse
Thickening of cordae tendinae
What pathogenesis of endocarditis
underlying damage to epithelium of valve- bacteria hold on to valve- fibrin occurs because of damage- neutrophils are attracted to the site and causes friable massses
What are sequela of Endocarditis
thromboembolisms causing infarcts
valvular insufficency or stenosis
Breed predisposition of MVD
small dog breeds
Cardiac changes due to subaortic stenosis
left sided pressure overload- left sided concentric hypertrophy
poststenotic dilation of aorta
left sided heart failure
Cardiac changes due to Pulmonic stenosis
Right sided pressure overload- right sided concentric hypertrophy
Post-stenotic dilation of pulmonary artery
Right sided heart failure
Cardiac changes due to ventricular septal defect
Right concentric ventricular hypertrophy
left ventricluar dilation and hypertrophy
Ventricular septal defect pathogenesis
Blood shunt from LV to RV- increased blood volume and pressure in RV- hypertrophy of RV- equalization of pressure across ventricles- LV hypertrophy- cardiomegaly
Cardiac changes due to patent ductus arteriosis
pulmonary hypertension
Pressure overload of RV- RV concentric hypertrophy
Volume overload of LV- LV eccentric hypertrophy
Pathogenesis of Patent ductus arteriosis
Blood shunts Left to right via PDA- increase blood flow into the lung
increased venous return to LA and LV- volume overload of LV- LV eccentric hypertrophy
Pulmonary hypertension- pressure overload of RV- RV concentric hypertrophy
What is persistent right fourth aortic arch
congenital anomaly causing constriction of esophagus at the base of the heartW
What is the result of persistent right fourth aortic arch
dilated esophagus- megaesophagus
What is atherosclerosis
fat being deposited into vascular wall
What are causes of atheroschlerosis
dogs: hypothyroidism and diabetes mellitus
Birds: high fat diets
Virchow’s triad
endothelial damage
altered blood flow
hypercoagulability
What is vasculitis
inflammation of vessel wall
Viral causes of vasculitits
classical swine fever
bluetongue
African horse sickness
Equine viral arthritis
Epizootic hemorrhagic diseases
Bacterial causes of vasculitits
rickettsia rickettsii
bacterial endotoxins
erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
histophilus somni
Fungal causes of vasculitis
aspirgillosis
What causes caval syndrome
in the vena cava the worms cause right atrial turbulence and shear-induced mechanical hemolysis
Lesions of Strongylus vulgaris
arteritis
aneurysm formation
thrombosis