WBC
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
- Marrow <3%
- Blood none
- Nucleus is large, round or slt oval, with 2-5 nucleoli, and smooth fine chromatin
- cytoplasm is medium blue color with no granules
- Type I

myeloblast
- 15-25 um
- Marrow 1-5%
- Blood none

Promyelocyte
- Marrow 10-15%
- Blood none
- Has secondary (lilac) granules

neutrophilic myelocyte
- Size 10-15 um
- marrow 15-30%
- blood rarely

Neutrophilic metamyelocyte

Neutrophilic band
- size 10-15 um
- marrow 15-25%
- blood 50-70%

segmented neutrophil
What is the neutrophilic sequence?
granulocyte-monocyte progenitor → Myeloblast → Promyelocyte → Myelocyte → Metamyelocyte → Band → Segmented Neutrophil
What is the monocyte sequence?
granulocyte-monocyte progenitor → Myeloblast → Promyelocyte → Myelocyte → Metamyelocyte → Band → Segmented Neutrophil

Monoblast
Hint: nucleus is too convoluted to be a blast

Promonocyte
Bone marrow: <2%
Blood: <10%

Monocyte

Macrophage
What is the eosionophilic sequence?
Eosinophil-basophil progenitor → Myeloblast → Promyelocyte →eosinophilic myelocyte →eosinophilic metamyelocyte → eosinophilic band → eosinophil

Eosionophilic myelocyte

Eosinophilic metamyelocyte

eosinophilic band
- Size 12-17
- Blood 0-7%
- Abs <0.7 x 10^3/ul

eosinophil
what is the basophilic sequence?
Eosinophil-basophil progenitor → Myeloblast → promyelocyte → basophilic myelocyte →basophilic meta-myelocyte →basophilic band → basophil
- Size 10-15 um
- Blood 0-3%
- Abs. < 0.2 x 10^3/ul

basophil
Identify this inclusion and cell.
What causes this? What does it indicate?

Auer rod in a Myeloblast.
- caused by granules in the cell fusing together.
- Indicator of leukemia and that the cell is not maturing properly
What is the most important content of primary granules? What does it do?
Myeloperoxidase
- potentiates HOCl killing microbes
Size: 2-4 um
No nucleus
Light blue with red granules
Live for about 7-10days

Platelets
- Size 25-35 um

Megakaryoblast

Promegakaryocyte

Megakaryocyte

platelets
Bone marrow - not defined
Blood 0%
- the nucleoli are a flag for this cell and the outline of the cell has a crisp edge
- only seen if someone has leukemia
- hardest cell to identify because it is not much bigger than its mature kin (see slide 24 of hematopoiesis part 2)

lymphoblast
Bone marrow - Not defined
Blood - None
- Flag for this cell is that it has one large nucleolus in the center
- larger than its mature kin
- Mike Wazowski cells

Prolymphocyte
Bone marrow - 5-15%
Blood 20-40%

lymphocyte
Bone marrow - 0-1%
Blood - 0%
- rarely seen in blood

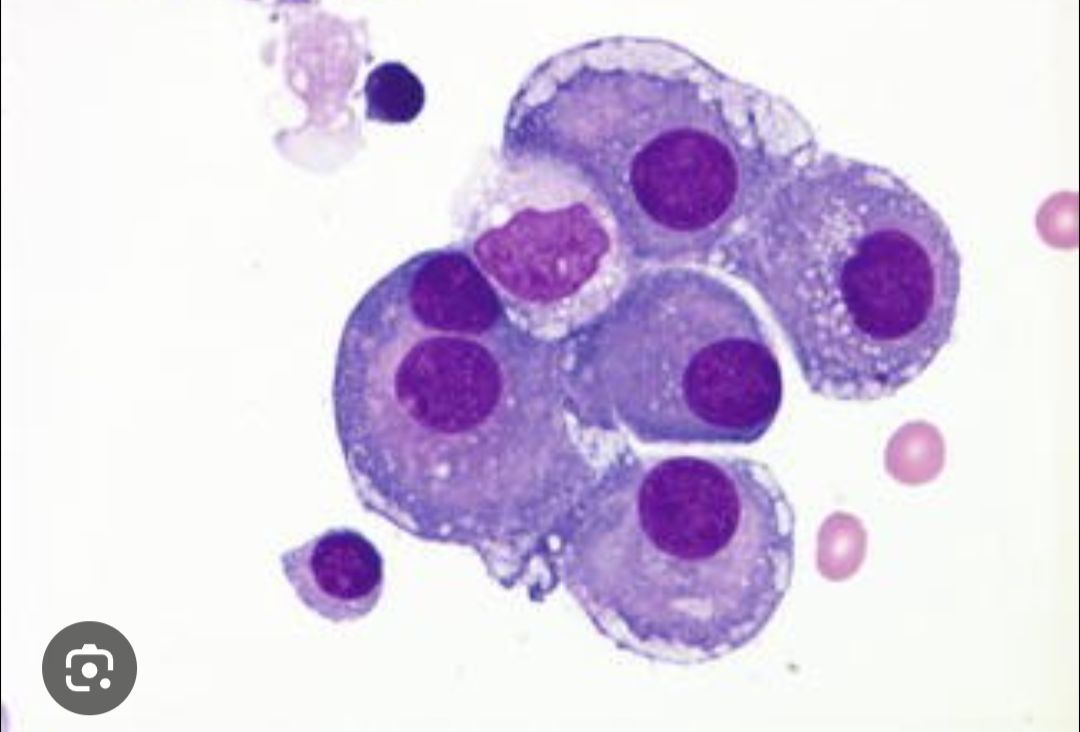
Plasma cell
5-20% of peripheral blood lymphs and count as a lymph (not any special reporting)
- have pink granules in them that are big enough to see
- Monocyte granules are not distinct enough to see them, that is how you tell the difference.

Natural killer (NK) cell
5-6% in normal blood
- Indicates functioning immune system
- See a lot in patients with EBV
- They get reported if >10 but usually lumped in with regular lymphs if only a few are seen

Variant lymph
(or atypical lymph or reactive lymph)
Precursor right before a plasma cell, does not meet all 4 characteristics of a plamsa cell
- reported as a variant lymph

Plasmacytoid
- A variant lymph

Mono-type lymph
a variant lymph

"Blast-like" lymphocyte
variant lymph

Flame cell
Bubbles are Abs being produced
- variant lymph

Mott cell or Morula cell
meso