science notes 3rd quarter
1/149
Earn XP
Description and Tags
note: i may have made a few mistakes so pls don't solely rely on this!!! check ur book and own notes as well to be sure ^^
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
150 Terms
central dogma of molecular biology
is a fundamental principle that explains the flow of genetic information in living organisms. it states that genetic information flows from dna to rna to proteins, but not the reverse.
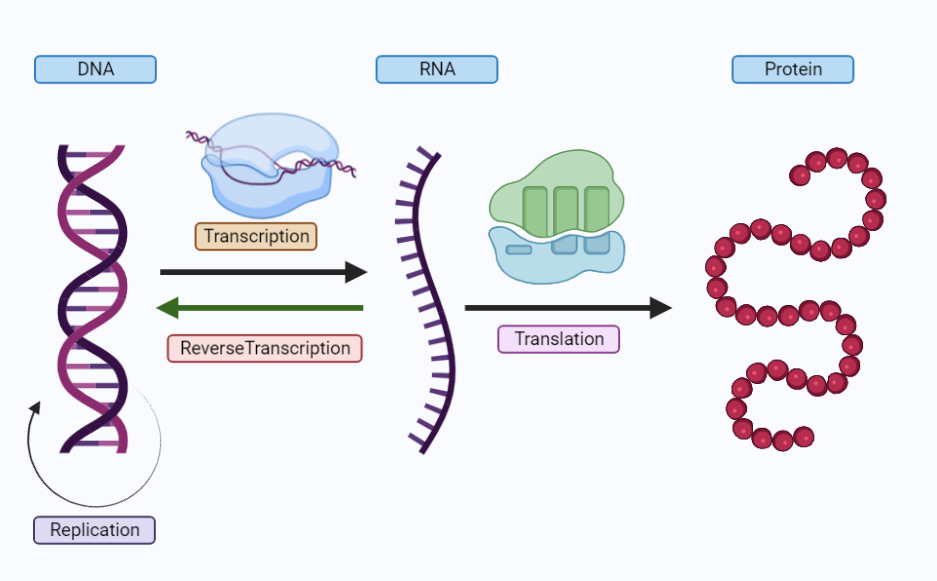
central dogma of molecular biology
this principle was first proposed by francis crick in 1958 and has since been a fundamental concept in the field of molecular biology.
dna (deoxyribonucleic acid)
hereditary material in humans and organisms, carrier of genetic information
rna (ribonucleic acid)
is a polymeric molecule that is essential for most biological functions, either by performing the function itself or by forming a template for the production of proteins
components of dna
adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine
components of rna
adenine, cytosine, guanine, uracil
dna replication
process of copying double-stranded dna molecules
semi-conservative replication
origin of replication; replication fork
pyrimidines
single = 1 ring
purines
double = 2 rings
chargaff’s rule of pairing
adenine - thymine (2 hydrogen bonds) | guanine - cytosine (3 hydrogen bonds)
enzymes (-ase)
they make the process of dna replication easier and faster
1st step of dna replication
‘unzip’ the double helix structure
helicase
essential during dna replication because they separate double-stranded DNA into single strands
2nd step of dna replication
separation of two single strands will form into a replication fork
leading strand
3’-5’ direction
lagging strand
5’-3’ direction
rna primase
makes the primer which acts as the starting point for dna synthesis. functions by synthesizing short RNA sequences that are complementary to a single-stranded piece of DNA
dna polymerase
adds new complementary nucleotide bases towards the replication fork. it completes the dna sequence. are enzymes that create DNA molecules by assembling nucleotides
okazaki fragments
rna primase given by lagging strand
exonuclease
strips away the primer(s), proofreads and serves as an editor, also removes primer
dna ligase
seals up the sequence of dna into 2 continuous double strands (serves as a glue), also fills in the gap of the removed primer
semi-conservative strand
1 old strand, 1 new strand
location of dna replication in plants and organisms
cytoplasm of prokaryotes
location of dna replication in humans
nucleus of eukaryotes
protein synthesis
process of creating protein
2 main process of protein synthesis
transcription and translation
transcription
template of dna the rna is copying from
translation
rna goes to ribosome (cell organelle) to be translated into protein
codon
sequence of three nucleotides in dna or rna that encodes information in creating amino acids or protein
natural selection
a theory proposed by charles darwin and the process through which populations of living organisms adapt and change.
biodiversity
different species, habitats, organisms
carolus linneaus
father of taxonomy, classified animal names and organisms, implemented the terms genus and species and created their scientific names
george louis leclerc de buffon
proposed the theory that organisms shared ancestors but are unrelated to each other
erasmus darwin
proposed the theory that all living things were descended from a common ancestor
jean-baptiste lamarck
proposed the theory that all organisms evolved toward perfection and complexity
charles darwin
proposed the theory of natural selection and that it is a survival of the fittest and adaptability is what makes organisms survive
galapagos island
a very sensitive island that preserves wildlife and only a few can visit this island
variation
heritable differences among single species resulting from differences in genetic traits
overproduction
increase in reproduction, greater chance to survive
adaptation
cope with the fast-changing type of environment
descent for modification
present-day organisms are descendants of ancestral species, many individuals possess the traits
evidence
can be classified as fossil, embryological, anatomical
fossil evidence
fossils are preserved remains of an organisms. most common fossils are bones, shells, seeds, teeth, and pollen grains.
embryological evidence
embryology; study of embryos and their development. embryonic development are further evidence that living things evolved
anatomical evidence
comparing the body structures of living species also provide clues pointing to evolution and the common ancestry of organisms
homologus structure
physical structures of the organisms that have the same evolutionary origin and position yet have different functions
vestigial structure
structure of animals that is gradually disappearing; inherited body parts which are smaller and often unused
analogus structure
have similar functions but have a different anatomy
genetics
basic heredity for all of life
fossils
remnant, impression, or trace of an animal or plant of a past geologic age that has been preserved in earth’s crust.
water, temperature, light, atmospheric pressure, chemical components
factors affecting survival
water and atmospheric pressure (air)
organisms need this to survive
temperature
helps maintain the ideal homeostasis
light
main source of energy; plants use this for photosynthesis
chemical compounds
derived mostly in plants and other food sources
balance of nature, diversity and stability, finiteness of resources, stewardship
core principles to attain biodiversity and stability
balance of nature
can only support a given number of individuals at a time
diversity and stability
more diverse ecosystems, more resilient and stable
finiteness of resources
limitation on the most common resources
stewardship
act of protecting, conserving, and preserving our nature
population density, spatial distribution patterns, population range, reproduction patterns
population characteristics
population density
number of individuals over a unit area
spatial distribution patterns
capability to spread and occupy a specific area
uniform, random, and clumped dispersion
types of dispersion
uniform dispersion
a dispersion in which there are equal spaces in between organisms
random dispersion
a dispersion in which there are no equal or have random spaces between organisms
clumped dispersion
a dispersion in which organisms’ group and stay together
population range
how organisms are distributed
reproduction patterns
expanding, stable, declining
density-independent factor, density-dependent factor
limiting factors
density-dependent factor
biotic factor—interactions, competition for food, water, space, parasites, and diseases. population matters
density-independent factor
abiotic factor—atmospehric conditions, human-intervention. population doesn’t matter
birth rate, death rate, immigration, emigration
population variables
formula for population change
(birth + immigration) - (death + emigration) if answer is positive, increase. if answer is negative, decrease.
exponential growth
constantly increasing, unlimited resources and no diseases at all, population size will increase, an ideal concept for organisms. (j - shape)
r-strategists
bacterias, yeast, fungi - can reproduce more
logistic growth
type of growth that exhibits a steady expansion followed by an abrupt slowdown. influenced by the limited resources in the environment known as the carrying capacity (s-shape)
resilience and resistance
these two values will equate to stability and an ideal ecosystem
logistic growth phases
(1) unlimited supply; will experience exponential growth, favorable time for population to increase (2) increase in population (3) no decline, constant increase in population (4) overpopulation will lead to scarcity, do not exceed carrying capacity or else it will lead to competition - death - and extinction
seminal vesicles
these are sac-like pouches that attach to the vas deferens near the base of the bladder. It can produce a sugar-rich fluid (fructose) that provides sperm with a source of energy and helps with the sperms' motility. (ability to move).
vulva
the female external reproductive organs consist of the mons pubic, which is covered with pubic hair; two folds of tissue, called the labia majora and labia minora, which surround a space called vestibule.
mons Pubis
it is formed at the upper margin of the symphysis pubis and is shaped like an inverted triangle. It is located over the two pubic bones of the pelvic. This structure is composed of fatty tissue lying beneath the skin and from puberty on, is covered with varying amount of hair.
labia Majora
are two folds of fatty tissue that form the lateral boundaries of the vulva. they are covered with coarse skin and pubic hair on the outer aspect and are smooth and moist on the inner aspect, where the openings of numerous small glands are found.
labia Minora
are soft folds of skin that are rich in sebaceous glands. it is moist and composed of erectile tissue containing loose connective tissue, blood vessels, and involuntary muscles. Its functions are to lubricant and waterproof the vulvar skin and to provide bactericidal secretion that help prevent infections.
clitoris
it is a small, sensitive structure that, like the penis, is composed of erectile tissue, nerves, and blood vessels; it is covered at the tip with very sensitive tissue. It exists primarily for female sexual enjoyment.
vaginal vestibule
it is a boat shaped depression enclosed by the labia minora and is visible when the labia minora are separated. it contains the introitus.
urethra
this is just below the clitoris. although it is not related to sex or reproduction, it is included in the vulva and is actually used for the passage of urine. connected to the bladder.
hymen
it is a thin, elastic, mucous membrane that partially covers the vagina in young females. does not seem to have a specific physiological function or purpose. many shapes are possible.
perineum
it is the short stretch of skin starting at the bottom of the vulva and extending to the anus. It is a diamond shaped area between the symphysis pubis and the coccyx. this area forms the floor of the pelvis and contains the external sex organs and the anal opening. it may tear during the birth of an infant.
vagina
it is a curved tube leading from the uterus to the external opening at the vestibule. it lies between the urinary bladder and the rectum. it consists of muscle and connective tissue and is lined with epithelial tissue, which contains folds called rugae.
purposes of a vagina
it receives the penis and semen of a male. the pathway of the baby during childbirth. provides the route of menses from the uterus to leave the body. may hold the diaphragm and female condom.
cervix
it consists of a cervical canal with an internal opening near the uterine corpus called the internal os and an opening in to the vagina.
purposes of a cervix
providing lubrication for the vagina. acting as bacteriostatic agent. providing an alkaline environment to shelter the sperm from the acidic vagina. producing a mucous plug in the cervical canal during pregnancy.
uterus
it is a womb, is a hollow, pear-shaped, muscular organ. It is supported by two important pairs of ligaments, the round and broad ligaments. this is divided into three portions and parts: fundus (upper portion), the corpus (body), the cervix. It also has three layers: (perimetrium, myometrium, endometrium).
purposes of a uterus
for menstruation, pregnancy, labor and birth
fallopian tube
it can extend laterally from the uterus, one to each ovary. they are small, narrow tubes. the tubes carry the ovum from the ovary to the uterus by the contraction of the cilia: hair like projections found in the lining of the tubes. Extending from the ends of these tubes are small, fingerlike projection called fimbriae.
purposes of the fallopian tube
a passageway in which sperm meets the ovum. a site of fertilization. a safe nourishing environment for the ovum or zygote. a means of transport of the ovum or zygotes to the corpus of the uterus.
ovaries
these are two small, almond shaped organs located on each gland. they are responsible for producing the female sex hormones: progesterone and estrogen. also responsible for the development and maturation of the ovum.
breasts
it is composed of glandular, ductal, connective, and adipose tissue. embedded in the fibrous tissue are fat and lobules which make up the mammary glands, accessories to reproduction in women, but rudimentary and functionless in men.