Main Transfusion Rxns
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Main Transfusion Reaction Types
Allergic
Anaphylactic
Febrile Non Hemolytic Transfusion Reaction
Acute Hemolytic Transfusion Reaction
Delayed Hemolytic Transfusion Reaction
TRALI
TACO
GVHD
Allergic - Cause
Donor proteins act as allergens → bind to pre-formed recipient IgE → mast cell/basophil activation → histamine release → allergic symptoms (rash to anaphylaxis)
Allergic Rxn Symptoms
may include rash, itching, hives
Anaphylactic Causes
IgA-deficient recipient developing anti-IgA
If these pts receive a transfusion containing normal donor IgA, their immune system recognizes it as foreign
Cannot be predicted w/ routine testing
Occurs very rarely
Anaphylactic Symptoms
Rapid onset: Hypotension, bronchospasm, shock
Dyspnea, cyanosis, fever, hives
must transfuse IgA-deficient products, washed products for prevention
Washed products remove donor plasma protein (IgA gone)
Can occur within minutes
Febrile Non Hemolytic Cause
HLA antibody in recipient to donor leukocyte Ags
cytokines in blood products containing WBCs and PLTS stimulates recipient’s immune system
Accumulate in storage
Prevent using leukoreduction
Febrile Non Hemolytic Symptoms
Fever ≥38 °C, chills, rigors, back pain
Normal Lab
Within 4 hrs of transfusion
Occurrence
Common in patients with multiple pregnancies and transfusions
Multiple exposures to HLA Ag
Common in women
1:200 donor units transfused
Acute Hemolytic Cause
ABO mismatch (or medications, autoimmune disorders, thalasemmia/SC)
by clerical error (most common0, wrong unit to wrong patient
Severe sudden hypotension (SBP <70-60 mmHg)
Resolves when transfusion stops
Acute Hemolytic Symptom
Fever, flank pain, DIC, hemoglobinuria
Flushing, anxiety, lightheadedness
Labs: ↓haptoglobin, ↑LDH, ↑bilirubin, positive DAT
Kidney Failure!
Onset: within minutes
Delayed Hemolytic Cause
Alloantibody (Kidd, Duffy, Kell) from previous transfusion or pregnancy
Kidd Ab are notorious for causing DHTR because they can fall below detection in screens, but rapidly rise with re-exposure
Delayed Hemolytic Symptoms
Days-weeks later
extravascular hemolysis
DAT positive, inadequate hgb rise
TRALI cause
Donor anti-HLA/neutrophil Abs react with recipient leukocytes
Women donors of child bearing age not allowed
TRALI symptoms
NON-CARDIOGENIC pulmonary edema
Hypotension
Sudden-Onset
Symptoms ≤6 hrs post-transfusion: hypoxemia
TACO cause
too much blood in pts vascular system, caused by transfusing a unit too fast
most often occurs in children and elderly pts
can be fatal
TACO Symptoms
Hypertension, pulmonary edema, ↑BNP
Dyspnea, orthopnea, cyanosis, rales, tachycardia
sudden-onset - within 6 hrs
GVHD Cause
Transfused T cells react against recipient, rare occurrence
Even just one can compromise weak immuno pt, unable to locate
GVHD Symptoms
3–30 days posttransfusion, fever, erythematous maculopapular rash, abnormal liver function
Sequelae: Sepsis, hemorrhage, 90% mortality rate
Intravascular Hemolysis
Primarily caused by IgM antibodies
IgM efficiently activates complement system
Leads to direct lysis of RBCs within blood vessels
Common IgM antibodies: Lewis (Le), I (I), P (P1, anti-P1), MNS (MN)
Extravascular Hemolysis
Mainly mediated by IgG antibodies
IgG coats RBCs → marks them for destruction
Clearance occurs via macrophages in spleen and liver
Common IgG antibodies: Rh, Kell (K), Duffy (Fy), Kidd (Jk), Lutheran (Lub), MNS (Ss)
Note: Lutheran Lua = IgM (not usually clinically significant), Lub = IgG
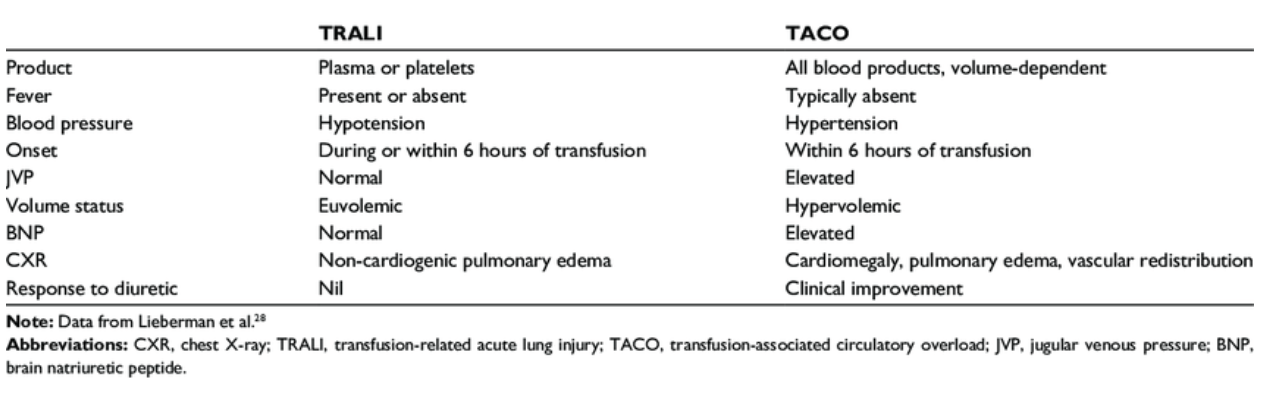
TRALI vs TACO
TACO (Circulatory Overload) | Hypertension, pulmonary edema, JVD, ↑BNP, dyspnea | Cardiogenic cause → ↑BNP, hypertension → improves with diuretics |
TRALI (Acute Lung Injury) | Dyspnea, hypoxemia, bilateral infiltrates ≤6 hrs | Normal BNP → no hypertension → donor anti-HLA/neutrophil Abs implicated |
Intravascular Hemolysis
Primarily caused by IgM antibodies
IgM efficiently activates complement system
Leads to direct lysis of RBCs within blood vessels
Common IgM antibodies: Lewis (Le), I (I), P (P1, anti-P1), MNS (MN), Lutheran (Lua)
Extravascular Hemolysis
Mainly mediated by IgG antibodies
IgG coats RBCs → marks them for destruction
Common IgG antibodies: Rh, Kell (K), Duffy (Fy), Kidd (Jk), Lutheran (Lub), MNS (Ss)