Chapter 4 p3 - Magnetics
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Why do the orbital electrons of atoms in magnetic materials tend to spin predominantly in one direction?
such atoms create tiny magnetic dipoles.
when these dipoles or “atomic magnets” form groups of similarly aligned atoms, they create magnetic domains
How does the Lines of Flux travel?
from south pole to north pole inside the magnet
from north pole to south pole outside the magnet.
Magnetic fields are distorted by:
magnetic materials and are unaffected by nonmagnetic materials
There are three laws of magnetism that may help explain electromagnetism:
every magnet has a north and south pole.
like poles repel each other and opposite poles attract each other.
the force of attraction or repulsion varies directly with the strength of the poles and inversely with the square of the distance between them
The strength of the magnetic field is measured in:
the SI unit Tesla (T), named after Nicolas Tesla
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) units used for medical imaging are referred to by their:
magnetic field strength and operate with fields from 0.5 to 5 T
There are 4 types of Magnetic classifications:
nonmagnetic, diamagnetic, paramagnetic, ferromagnetic
Nonmagnetic materials are not attracted to:
magnetic fields at all
(e.g., glass, wood, plastic)
Diamagnetic materials are:
weakly repelled by magnetic fields
(e.g., water, mercury, gold)
Paramagnetic materials are:
weakly attracted to magnetic fields
(e.g., platinum, gadolinium, aluminum)
Ferromagnetic materials are:
strongly attracted to magnetic materials
(e.g., iron, cobalt, nickel)
Any flow of electrons, whether in space or in a conductor, will be surrounded by:
a magnetic field
A moving magnetic field can create an:
electric current
Electricity and magnetism are two parts of the same:
basic force
The principle of electromagnetism was first identified by the Danish physicist:
Hans Oersted
when he discovered that the needle of a compass is deflected when placed near a conductor carrying electric current.
Hans Oersted later, it was discovered that the:
magnetic field surrounding a conductor could be intensified by fashioning it into a coil (called a solenoid)
The strength of the magnetic field inside a solenoid depends on several factors:
number of turns: The more turns of wire in the solenoid, the stronger the magnetic field
current: The greater the current flowing through the wire, the stronger the magnetic field
length: The magnetic field strength decreases as the length of the solenoid increases
core material: A ferromagnetic core can significantly increase the magnetic field strength by concentrating the field lines within the core
What did Michael Faraday founded?
that moving a conductor through a magnetic field induces an electric current in that conductor (called electromagnetic induction)
the law of electromagnetic induction
Faraday’s experiment was:
moving magnetic field induces current
Two forms of electromagnetic induction are used in the operation of the x-ray machine:
mutual induction and self-induction
What is mutual induction:
the induction of electricity in a secondary coil by a moving magnetic field
when a moving magnetic field (AC) is placed near a secondary coil, electricity is induced to flow in that coil
Self-induction (auto-transformers) is a bit more complex requiring an understanding of Lenz’s law which states:
that an induced current flows in a direction that opposes the action that induced it
in this case, that action is the changing magnetic field
Similar to resistance, inductive reactance reduces the flow of:
the current in a circuit
An induction motor (IM) is a type of asynchronous AC motor where:
power is supplied to the rotating device by means of electromagnetic induction
The type of motor used in x-ray tubes is an:
induction motor
Electric generators are devices that:
convert some form of mechanical energy into electrical energy
Electric motors are devices that:
convert electrical energy to mechanical energy through electromagnetic induction
The Transformer law for voltage is:
Vs = Vp x Ns / Np
direct relationship
step-up transformer
The Transformer law for current is:
Is = Ip x Np / Ns
inverse relationship
step-down transformer
The relation of voltage to current in a transformer is:
Is = Vp x Ip / Vs
inverse relationship
Closed-core and shell-type transformers have a:
ferromagnetic core to maximize efficiency
Auto-transformers operates on the principle of self-induction and has how many coils of wire?
has only one coil of wire around a central magnetic core serving as both the primary and secondary coil
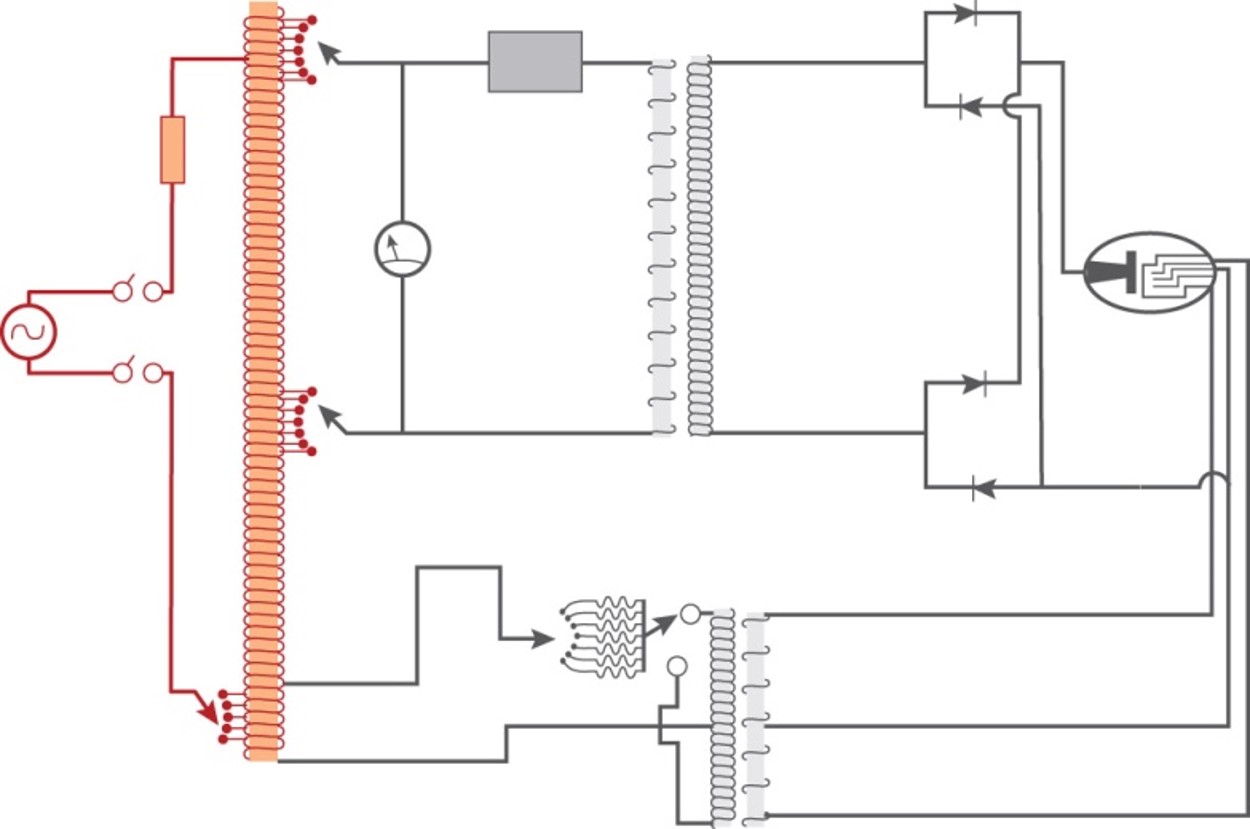
Step-up transformer:
few turns
steps voltage up and current down
Step-down transformer:
fewer turns
steps voltage down and current up