tutorial 1: prenatal development
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
how many chromosomes are their in the human genome in total?
46 in total
23 pairs
what are genes?
segments of DNA
have a specific place on chromosomes
what is the function of genes?
help cells reproduce themselves and regulate protein synthesis
what is the function of proteins?
building blocks of cells
regulate internal processes of cells
what is one important thing to remember about genes and their influence?
they dont work independent from each other but in collaboration
what is one way genes can be influenced by teh environment?
gene expression is affected by hormones and hormones are affected by the environment (eg.light, behaviour, temperature)
how does stress and radiation affect gene expression?
stress → damage of DNA
radiation → changes rate of DNA synthesis
what is the gene wide association model?
look at the whole genome to find genes linked to disease
→ compare the egentc variation in healthy individuals to the variation in individuals with the disease → variation in the sick people points to location of the possibly disease causing gene
what is linkage analysis?
used to find a disease causing gene
find location of a gene in relation to a marker gene
what is Mitosis?
process in which body cells divide to produce two identical daughter cells.
what is Meiosis?
process when gametes (sperm or egg cells) are beig formed
what happens during Mitosis?
the nucleus in the cell duplicates and then the cell divides into two identical cells with again 46 chromosomes in total
which chromosome determines the gender?
chromosome 23
male: xy
female: xx
what is a zygote?
formed when teh sperm and egg cell combine
half of the genetic material is from dad and half from mom
how does genetic variation come about?
pieces of the chromosomes in each pair are exchanged
mutations
what are monozygotic twins?
twins with 100% identical DNA
the egg seperated after fertilization into two identical copies
what are dizygotic twins?
twins that share about 50% of their genes
two different egg cells are being fertilized by two different sperm cells (division before fertilization)
what are four genetic principles?
dominant and recessive genes,
sex linked genes,
genetic imprinting
what are dominant genes?
they override the influence of recessive genes
only one needs to be resent so that trait is expressed
are most mutated genes recessive or dominant?
recessive
who is more likely to have x-linked disease?
males because they dont have a backup x chromosome if one is damaged
what are females with x linked mutations called?
carriers
what is genetic imprinting?
genes have different effect depending on wether they were derived from mom or dad
on of the genes is silenced and the other one expressed
what can happen if there is disturbed genetic imprinting?
diseases like Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome (growth disorder) or Wilms tumour (cancer)
what does polygenic inheritance mean?
not a single genes determines characteristic but the collaboration of many different ones
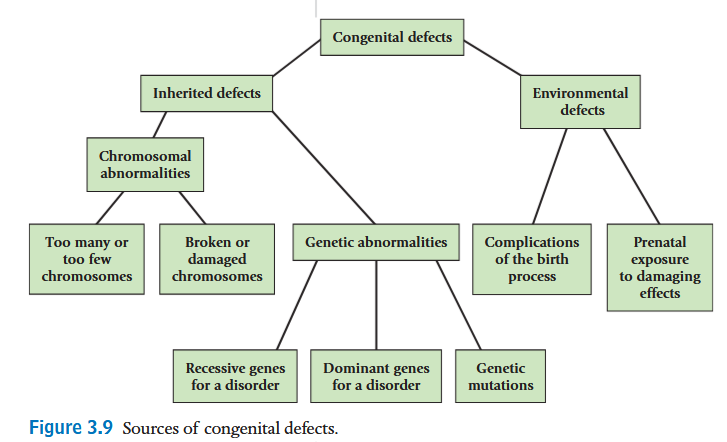
what are the two things abnormalities can be caused by?
harmful genes or something going wrongin meiosis
what are the two kinds of abnormalities ?
chromosomal and gene linked abnormalities
whats the cause of downsyndrome?
there is an extra copy of chromosome 21
may be caused by unhealthy gametes
what is the earliest you can do fetal sex determination?
7 weeks into pregnancy
what does the success of in vitro fertilization depend?
age of the mother
what are the three different heredity environment correlations?
passive, evocative and active (niche picking)
what is the passive heredity-environment correlation?
parents provide an environment to child which fits to their genotype (if they are good reader, academically inclined they might provide more books; if they are very social they will create a very social environment around them and their child)
what is the evocative envrionment-heredity correlation?
the genotype of the child causes their environment to respond to them in a specific way
(more social, smiling child might get more attention; a more loud child might receive negative responses from adults and peers)
what is the active environment heredity correlation?
according to their genetic predisposition the child selects and environment
(more atheltic genotype → seek athletic hobbies and friends)
what is the epigentic view?
believes that there is constant interaction between environment and genes
both influence each other
(eg. diet, stress toxins influence which genes are being expressed)
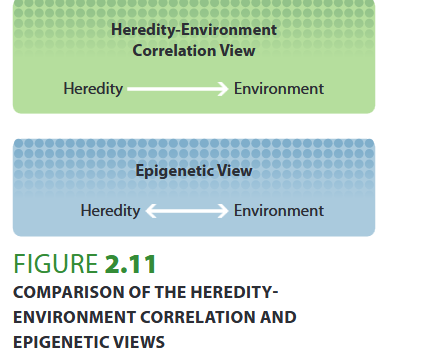
what is the G x E interaction?
specific genes interact with specific aspects of environment
eg. depression is only expressed when a stressful live is experienced as well
or attachment isssues only form if there is a certain gene
how many chromosomes do gametes have?
23
how many divisions are there in meiosis?
two divisions that result in fourcells with each 23 chromosomes
what are autosomoes and how many are there?
non sex chromosomes
22
what is independent assortment?
alleles end up in the new cell independent from each other
→ contrinuted to genetic variety
what is crossing over?
the homologous chromosome pairs exchange their information
→ contributes to genetic variation
On what levels can the interaction between environment and genes take place?
intracellular
extracellular
external-environment
what are
“experience-expectant interactions” ?
experiences influencing the genes that are the same for evry human
what are “experience dependant interactions”?
experiences interacting with genes that are different for every person
what does homozygous mean?
someone having the same allele for a trait twice
(eg. AA or aa)
what is heterozygous?
someone having two different alleles for a trait (one dominant and one recessive)
(eg. Aa or aA)
what are the four main patterns of genetic expression?
dominant-recessive inheritance
codominance
sex-linked inheritance
polygenic (multiple gene) inheritance
what is the chance of a child inheriting the recessive trait if both parents are heterozygous?
1/4
what is codominance?
both alleles are equally expressive, the one is not more dominant than the other => the expressed phenotype will be a compromise/mix
(eg. blood type)
what is incomplete dominance?
one allele is more dominant than the other however not enough to completely muter the other gene so some of the recessive gene will still be expressed
(eg. sickle cell anemia)
what is sex linked inheritance?
traits that are being inherited via genes located on the sex chromosome (mainly the x chromosome)
what is an example of a sex linked trait?
colour blindness
what happens to the number of possible genotypes and phenotypes when the number of collaborating genes increases?
the increase and follow a normal bell curve
what are congenital effects?
abnormalities and problem present at birth, caused by genes, prenatal influences or birth complications
which prenatal diagnostic test can be done the earliest?
chorionic villus sampling (8th to 9th week)
what is germ line therapy?
unhealthy genes are replaced with healthy ones in the embryo which leaves a permanent effect
what is gestation?
time during which the child develops in the uterus
what is the germinal stage and how long does it last?
the time of the zgote, two weeks after fertilization
how long is the embryonal stage?
beginning of third week until the end of the 8th week
what is the amniotic sac?
membrane around the embryo that contains the amniotic fluid and acts like a protective buffer against physical shocks
what is the placenta?
develops during pregnancy and provides the baby with nutrients and oxygen while removing waste products
→ formed by the tendrils connectign the embryo to the uterus
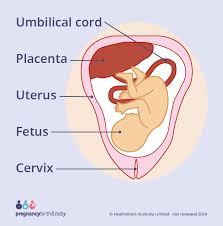
what is the umbilical cord?
connects baby to the abdomen and placenta, carries blood back and forth from baby and placenta
carries oxygen and nutrients to the baby, removes carbon dioxide and waste
why can some substances from the mothers blood reach the infant?
because the placentas membrane is semipermeable
what are the three layer called into which the embryo divides?
endoderm
mesoderm
ectoderm
what does the endoderm layer include?
gastrointestinal tract, bronchi, trachea, eustachian tubes, glands and vital organs (liver, lungs, pancreas)
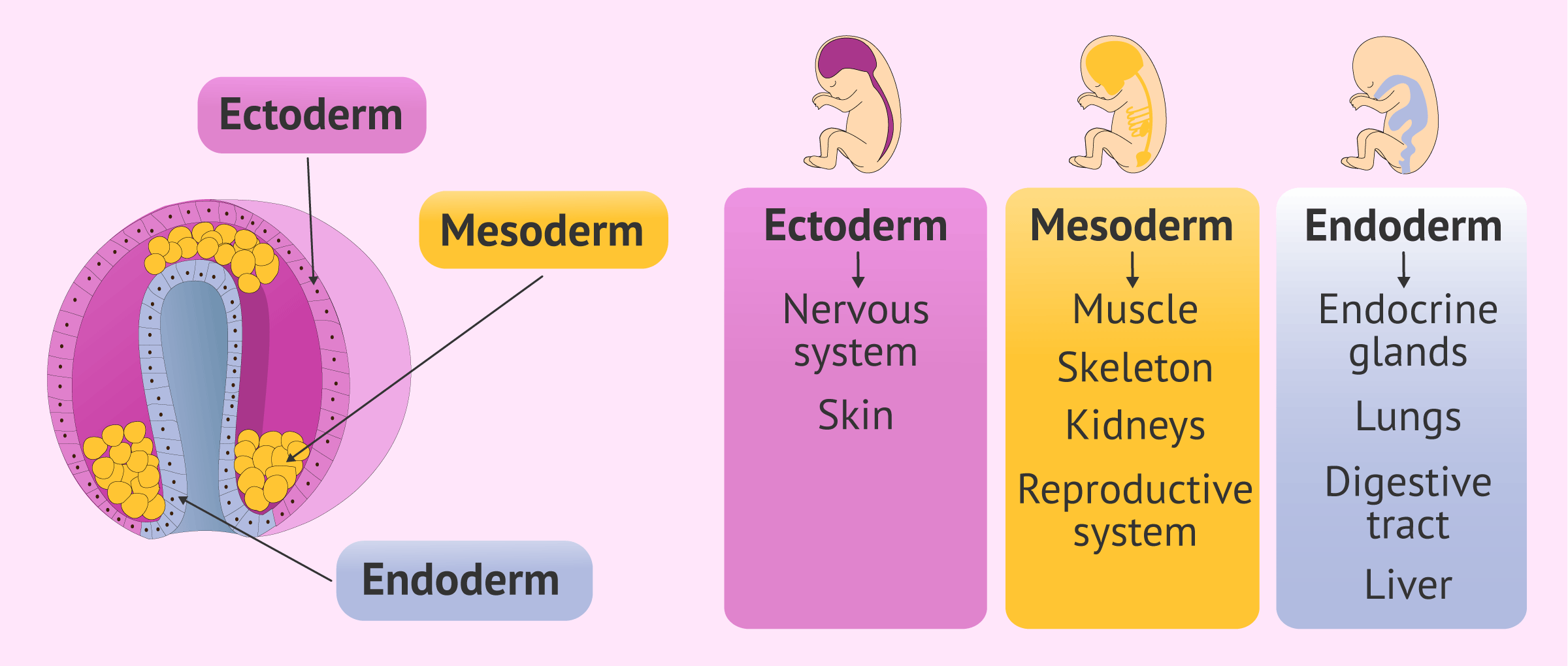
what does the mesoderm include?
muscles, sceleton, kidneys, circulatory and excretory systems, reproductive system and inner skin layer
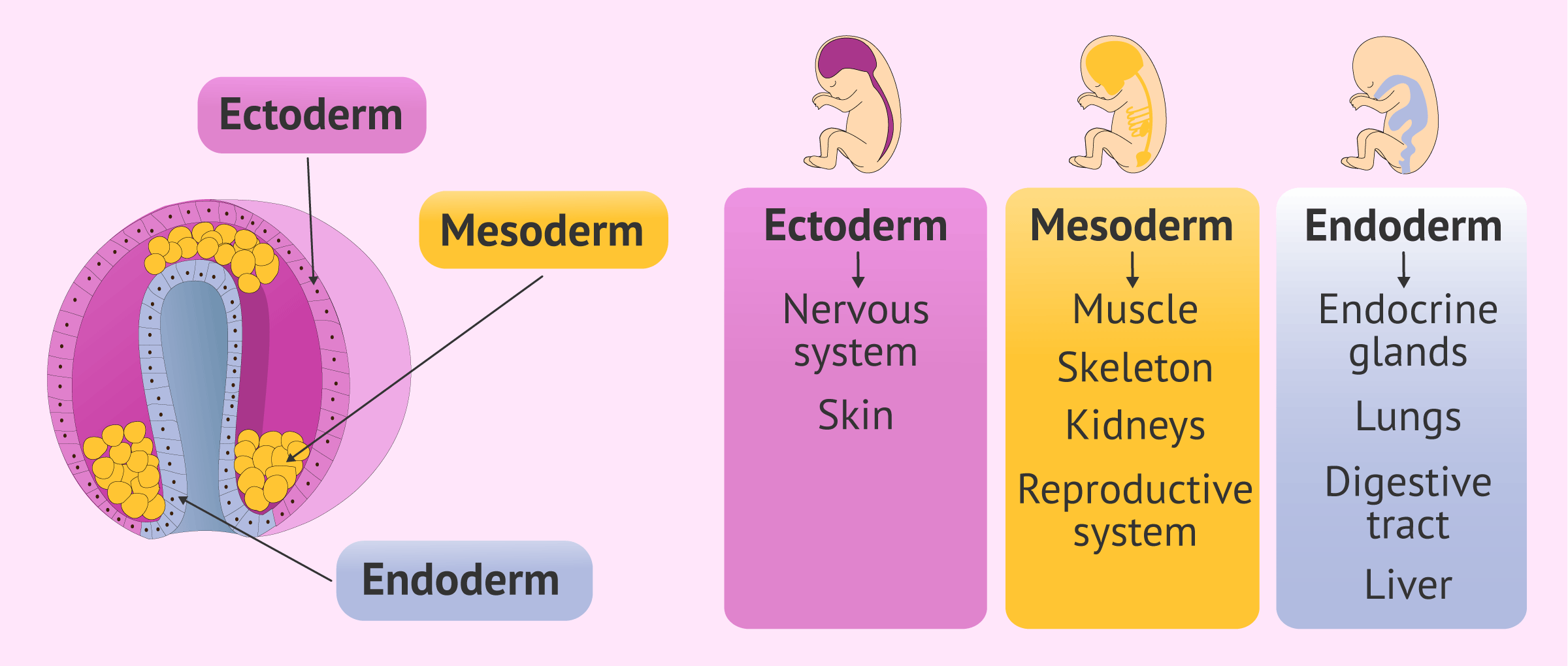
what does the ectoderm layer include?
nervous sysem and sensory organs, hair, nails, skin and skin glands
how does teh nervous system form?
when the ectoderm layer folds in on itself after 4th/5th week of gestation to form the neural tube
in what stage do most anomalies occur?
embryoic stage because the rapid development is making it especially vulnerable
what happens when the neural tube doesnt close properly?
child will have spina bifida
what does cephalocaudal developemt mean?
development is advancing from head downwards
what does proximal-distal mean?
development advances from central part od body to the outisde
when is the foetal stage?
lasts from the beginning of third month until birth
what is the age of viability?
22 to 26 weeks → if born at that point the baby would have a chance of surviving
(if born before the baby could not survive without intense intervention)
what are teratogens?
environmental factors leading to congenital abnormalities
what is neonatal abstinence syndrome?
happens to babies born addicted
→ irritable, unable to regulate arousal, trembling, shrill crying, rapid respiration and hyperactivity
what is the less severe version of “foetal alcohol syndrome”?
fetal alcohol effects (FAE), “alcohol related neuropsychological disorder”
what are the three stages of childbirth and how long do they last?
stage → contractions in 10-15 minute intervals (8-14h)
child comes through vaginal canal (1h)
placenta comes out through the vaginal canal
what are the consequences of caesarian delivery for the baby?
affected by the medications for mother
increase risk for preterm and low weight for future babies
not really affects cognition or future hospitalization
what are three perinatal risk factors?
deprivation of oxygen (foetal anoxia, switching from uterus to outside)
breech birth → starting labour with feet towards vagina
preterm, respiratory distress syndrome
how many weeks is the normal gestation period?
38 weeks