Neurodevelopment and Neurocognitive Disorders- PSYCH EXAM 2
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Neurocognitive Disorder (NCD):
Chronic, progressive decline in cognitive function affecting memory, thinking, and behavior.
What are people with NCDs vulnerable to?
Delirium, which may accelerate cognitive decline
Delirium
Sudden, reversible cognitive impairment, Often secondary to an underlying medical condition
What can increase symptoms of delirium?
Longer hospital stays
Risk Factors for Delirium
- Advanced age
- Dementia or cognitive impairment
Medical/Environmental- Polypharmacy (psychoactive meds)
- Acute illness or infection
- Metabolic or electrolyte imbalance
- Sleep deprivation or immobilization
Symptoms of Delirium
Cognitive Changes- Acute onset with fluctuations- Impaired attention- Disorientation- Memory impairment•
Behavioral & Physical• Hallucinations or delusions• Agitation or lethargy• Sleep disturbances• Emotional changes
What assessment do you use for patients with delirium?
CAM or CAM-ICU

Nursing Considerations for Delirium
Ensure safety
Identify and treat the underlying Cause
Promote Orientation and cognitive support
Avoid Deliriogenic Medications
Encourage Family involvement
Promote sleep: reduce noise/lights at night
Ensure glasses/hearing aids are used
Encourage mobility and hydration
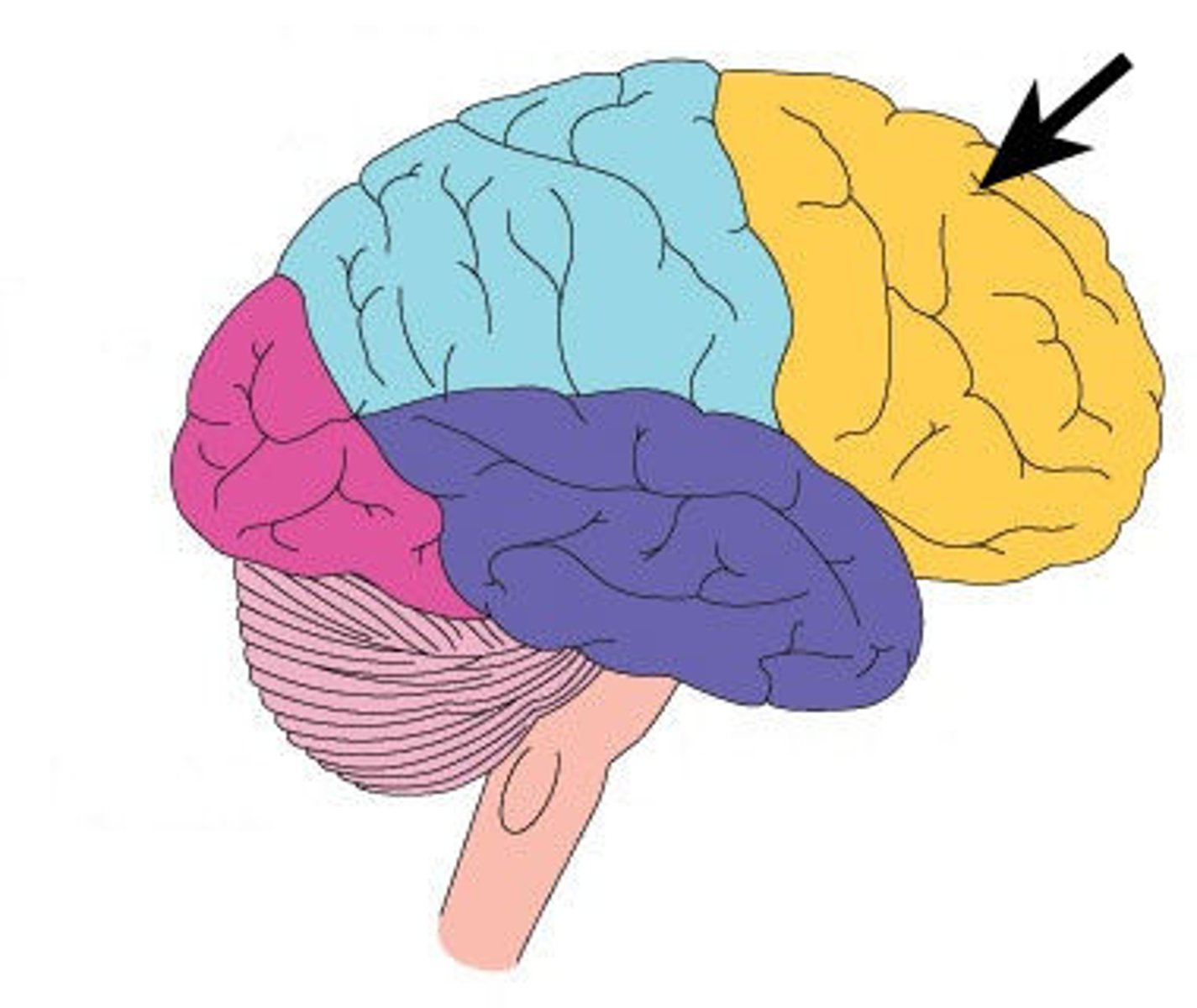
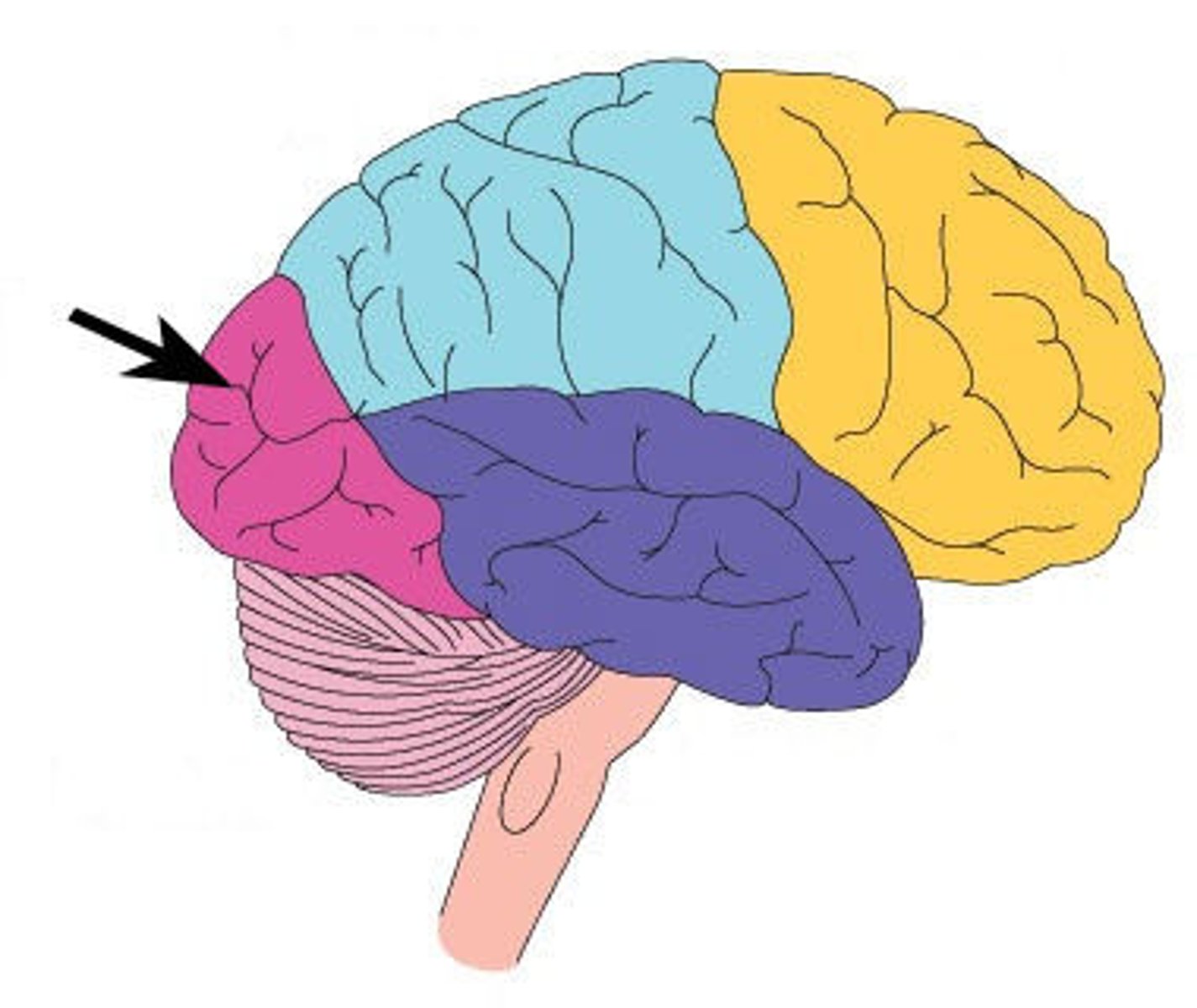
Frontal Lobe
associated with reasoning, planning, parts of speech, movement, emotions, and problem solving
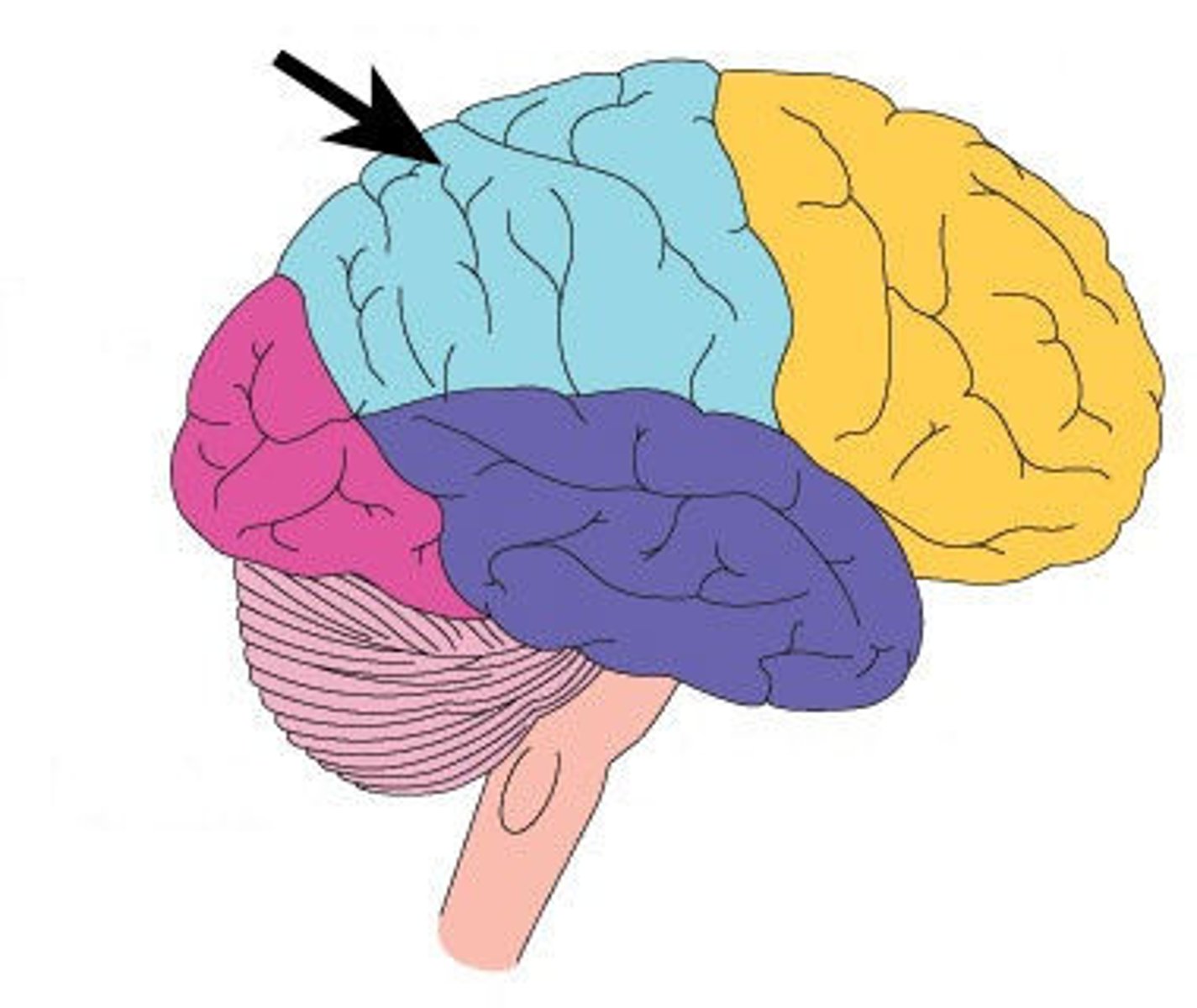
parietal lobe
portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the top of the head and toward the rear; receives sensory input for touch and body position
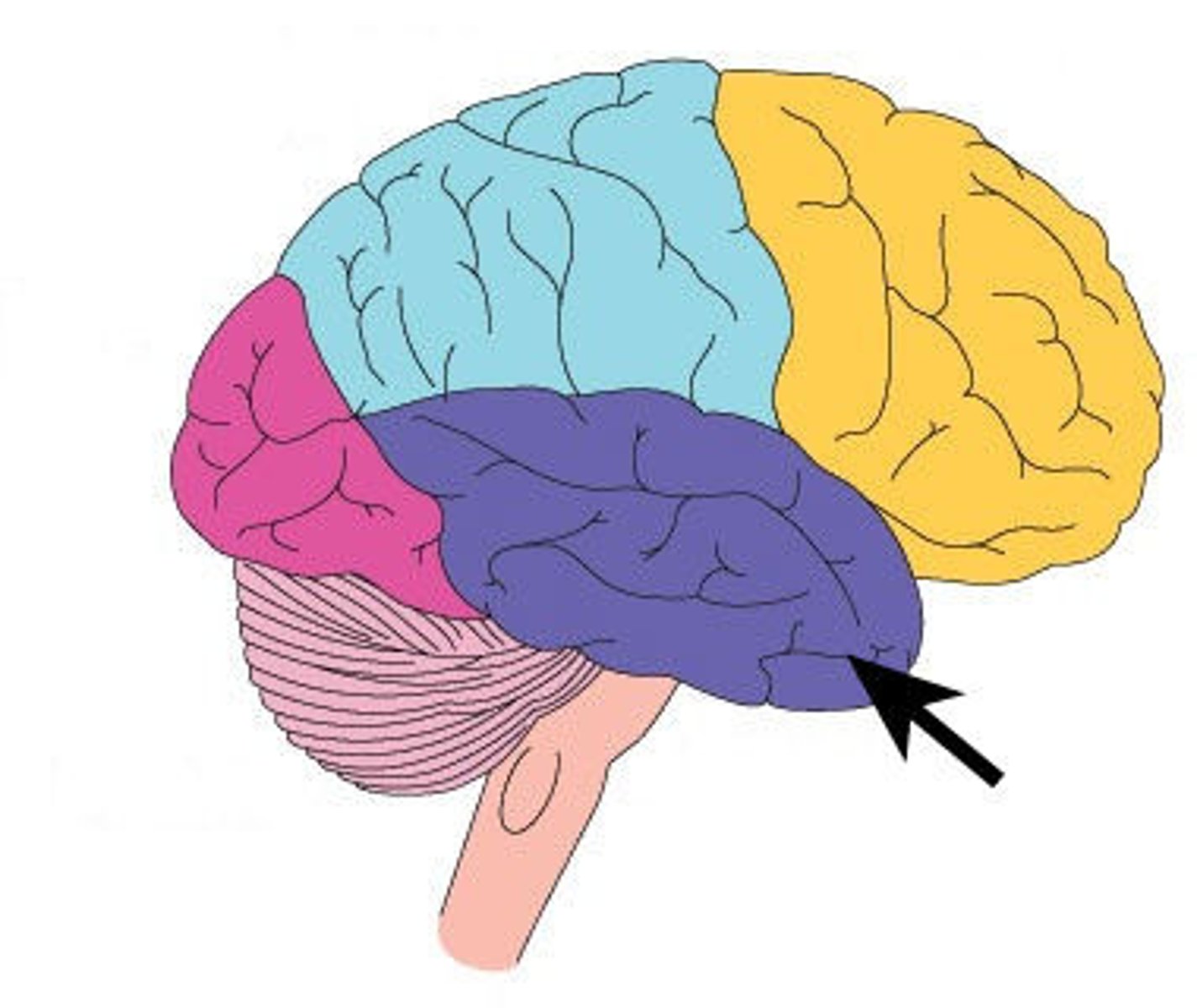
temporal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex responsible for hearing and language.
occipital lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information
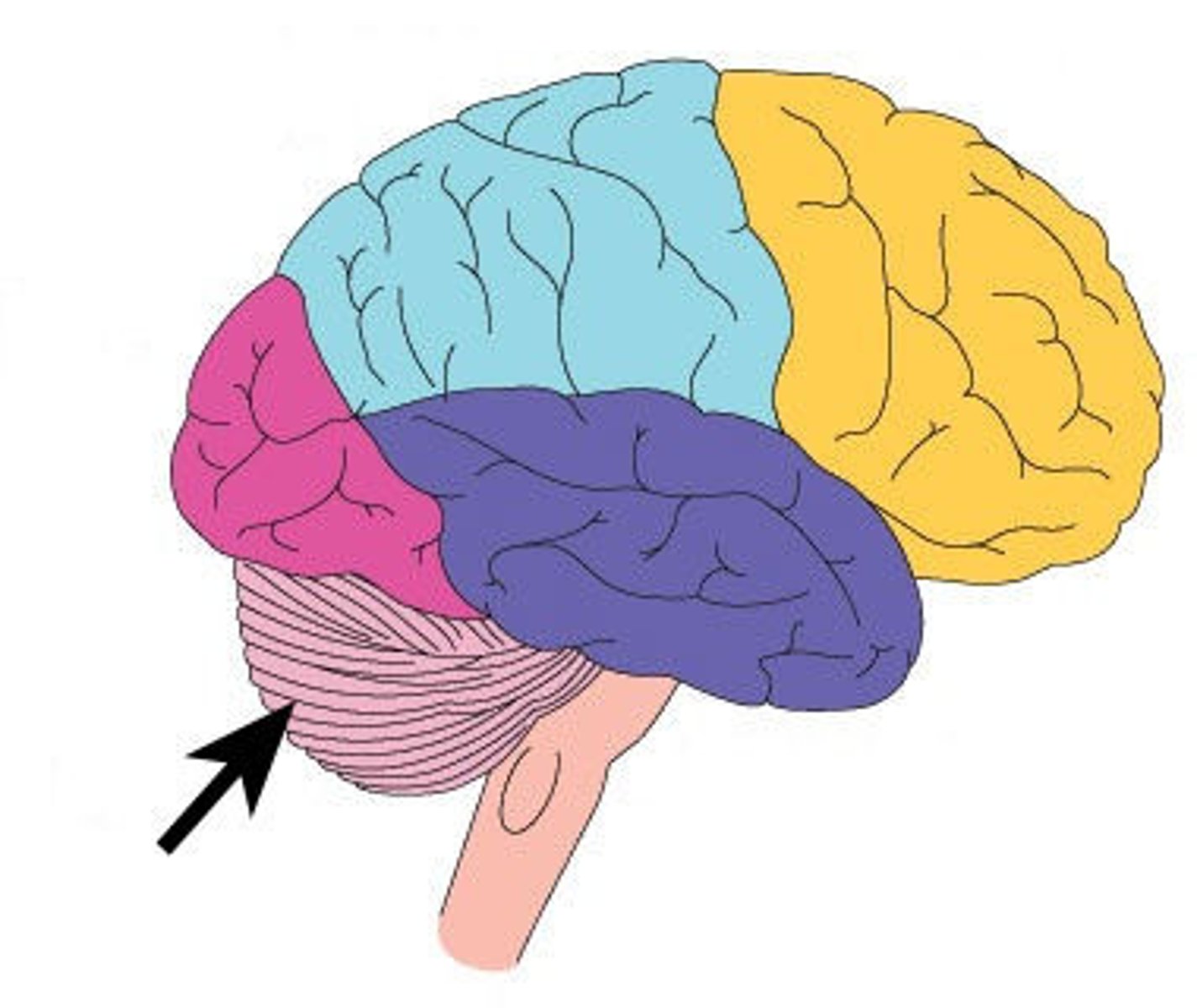
Cerebellum
the "little brain" at the rear of the brainstem; functions include processing sensory input and coordinating movement output and balance
Dementia
Chronic Decline that interferes with daily functioning and marked by at least 2 impairments to cognitive functioning
Cortical Dementia
changes in cerebral cortex (Alzheimer's disease, Pick's disease)
Subcortical Dementia
Parkinson's and Huntington's disease caused by damage to basal ganglia.
Early Onset Dementia is diagnosed when?
Before 65 yrs.
Vascular dementia are
Parkinson's and Huntingtons
Alzheimer's Disease
a progressive and irreversible brain disorder characterized by gradual deterioration of memory, reasoning, language, and, finally, physical functioning
What is the average lifespan after being diagnosed with Alzheimers?
8-10 yrs
Tau Tangles
Twisted fibers in neurons linked to Alzheimer's.
Amyloid Plaques
fragments of the protein beta-amyloid that accumulate into insoluble plaques that inhibit communication between neurons
Symptoms of Dementia
Memory impairment, apparent changes in intellect, impaired judgment, spatial disorientation (wandering), emotional changes
Mild Stage of Dementia
•Short-term memory loss interferes with everyday activities (driving, balancing checkbook)
•Moderate difficulty with orientation
•Unable to function independently in community affairs (may still be engaged)
•Moderate difficulty in handling problems
-Social judgment maintained
•Mild impairment of function at home (with regards to chores and hobbies)
Moderate stage of dementia
more frequent and extensive forgetfulness and confusion, increase in irritability and difficulty in behaviour, lack of food intake and hygeine
Severe stage of dementia
- Severe memory loss; Only fragments
- Oriented to person only
- No independent function outside the home
- Unable to make judgments or solve problems
- No significant function in the home
-Unable to perform ADLs
Cholinesterase inhibitors
Donepezil
Rivastigmine
Galantamine
Diminishing - Donepezil
Recall - Rivastigmine
Grows - Galantamine
Namenda (memantine)
Regulates the activity of glutamate in the brain, prolongs life of someone with dementia
Aducanumab
Beta-amyloid antibody- Reduce and remove the formation of beta-amyloidplaques in the brain
Home Safety for Alzheimers
no scatter rugs, install door locks good lighting especially around stairs, colored tape on edge of stairs, remove clutter, mattress on floor to prevent falls
Developmental Delay affects what?
Attention, cognitive, language, affect, social or behavior
ADHD
Neurobehavioral condition, diagnosed in childhood and often lasts into adulthood. Diagnosed during childhood based on school behavior, parents' reports, and direct observation. Trouble paying attention, controlling impulsive behaviors, or being overly active.

Causes of ADHD
genes, prenatal environment, and brain differences, toxins
Inattentive ADHD
Difficulty paying attention in the classroom, unable to concentrate on schoolwork, poor problem-solving

Hyperactivity/Impulsive ADHD
• Fidgetiness, squirming in seat
• Excessive climbing or running where inappropriate
• **Difficulty engaging in leisure activities
• Parents:
• "always losing things"
• "...like they're a hamster on a wheel."
• "driven by a motor that wont stop"

Diagnostic Criteria for ADHD
6 or more symptoms present from either the Attention or the Hyperactive/Impulsive catagories for at least 6 months. Symptoms present in at least 2 environments.
Stimulant Medications for ADHD
•methylphenidate
•dexmethylphenidate
•amphetamine
Non-stimulant medications for ADHD
Atomoxetine
Bupropion hydrochloride
Clonidine
Guanfacine
Autism
Developmental Disorder that impacts social skills, repetitive behaviors, communication
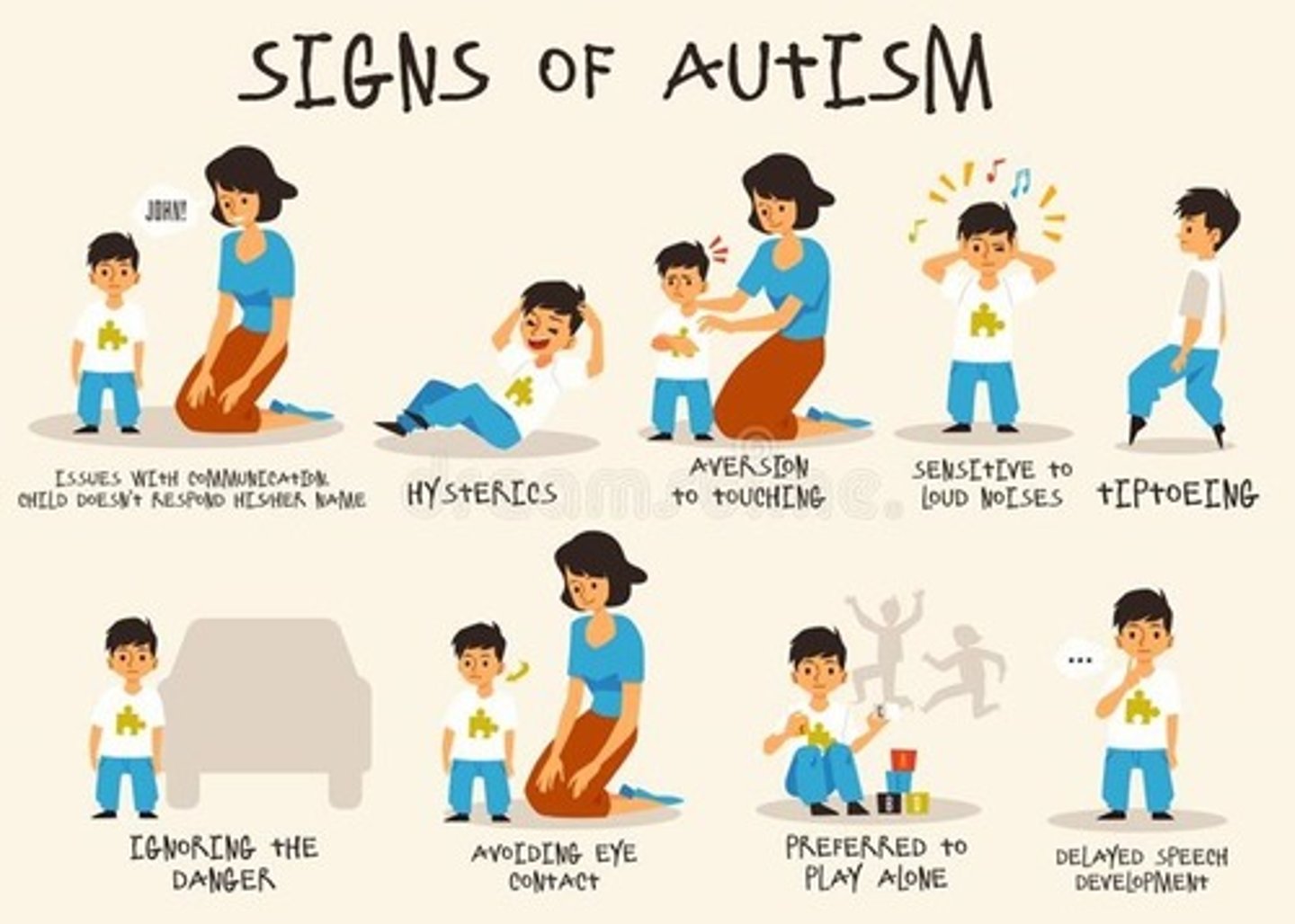
Levels of Autism
Mild, Moderate, and Severe
Intellectual Disability
IQ less than 70