Brain and Behavior Exam
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
119 Terms
Which of the following can be done WITHOUT the involvement of the cortex?
Release of hormones to prevent dehydration
The best term to describe the part of the spinal cord that is closest to a person's back is
Dorsal
Which of the following is a correct match between cortical lobe & function?
occipital lobe & vision
The thalamus is part of the
diencephalon
The cranial nerves are different from the spinal nerves in that
only the cranial nerves carry information for all five senses
Which of the following is NOT part of the brain?
Spinal cord
The sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system BOTH
have an effect on cardiac muscle
Which part of the brain is especially important for long-range planning, keeping inhibitions in check, and following the rules of society?
Prefrontal Cortex
Which of the following is NOT true about the hypothalamus and brainstem?
they allow you to find an object in your environment and pick it up
Damage to the hypothalamus is UNLIKELY to affect which of the following?
auditory perception
Which of the following is NOT part of the limbic system?
Midbrain
The membrane potential of a particular location along an axon
Changes over time
During an action potential, an individual potassium ion might
move from the inside of the cell's axon to the outside
Why does potassium leave a neuron during an action potential?
because it is positively charged, and the inside of the cell is positive at the time when it leaves, and also because it flows down its concentration gradient (with high potassium inside the cell and low potassium outside)
What useful function does myelin perform?
increasing the velocity of action potentials
Which of the following is NOT a function carried out by astrocytes?
Wrapping axons in myelin
During an action potential, potassium channels open because
the cell's membrane potential has become more positive
Which of the following is UNLIKELY to be affected by multiple sclerosis?
spinal nerves
Dilation of the pupils can be caused by activation of the
Sympathetic nervous system
Which of the following is NOT true about the sympathetic nervous system?
It promotes rest and digestion
Which cortical lobe is important for making decisions, controlling movements, and allowing proper social behavior?
frontal
Cocaine enhances dopamine action by
blocking reuptake of dopamine
Which of the following is NOT an important factor in determining whether binding of neurotransmitter to a post-synaptic receptor will make the post-synaptic cell fire an action potential?
how much of the neurotransmitter's precursor is present
Dendrites and axons are similar in terms of
having a resting membrane potential of about -70 mV
Which of the following steps occurs the EARLIEST in synaptic transmission?
neurotransmitter is released into the synaptic cleft
The use of G-proteins by a post-synaptic neurotransmitter receptor, relative to the use of an ionotropic receptor, has the advantage of
amplifying a small signal
During an action potential, which of the following travels the farthest?
the depolarization of the cell’s membrane potential
During an action potential, potassium ions leaving an axon cause its membrane potential to
repolarize
Axons and dendrites are different in that
action potentials occur only at axons
A new neurotransmitter that has only one kind of receptor was just discovered. To determine whether the neurotransmitter is generally excitatory or inhibitory, which of the following is the most important factor to consider?
which kind of ion passes through the post-synaptic membrane after the neurotransmitter binds
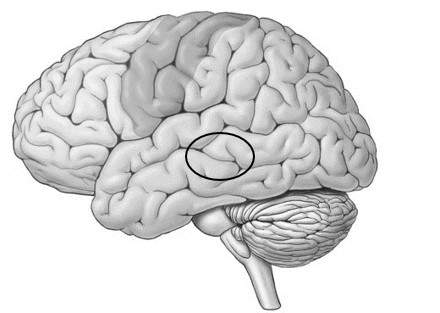
The lobe of cortex that is circled can be described as having what kind of function in general?
a "what" function related to object recognition
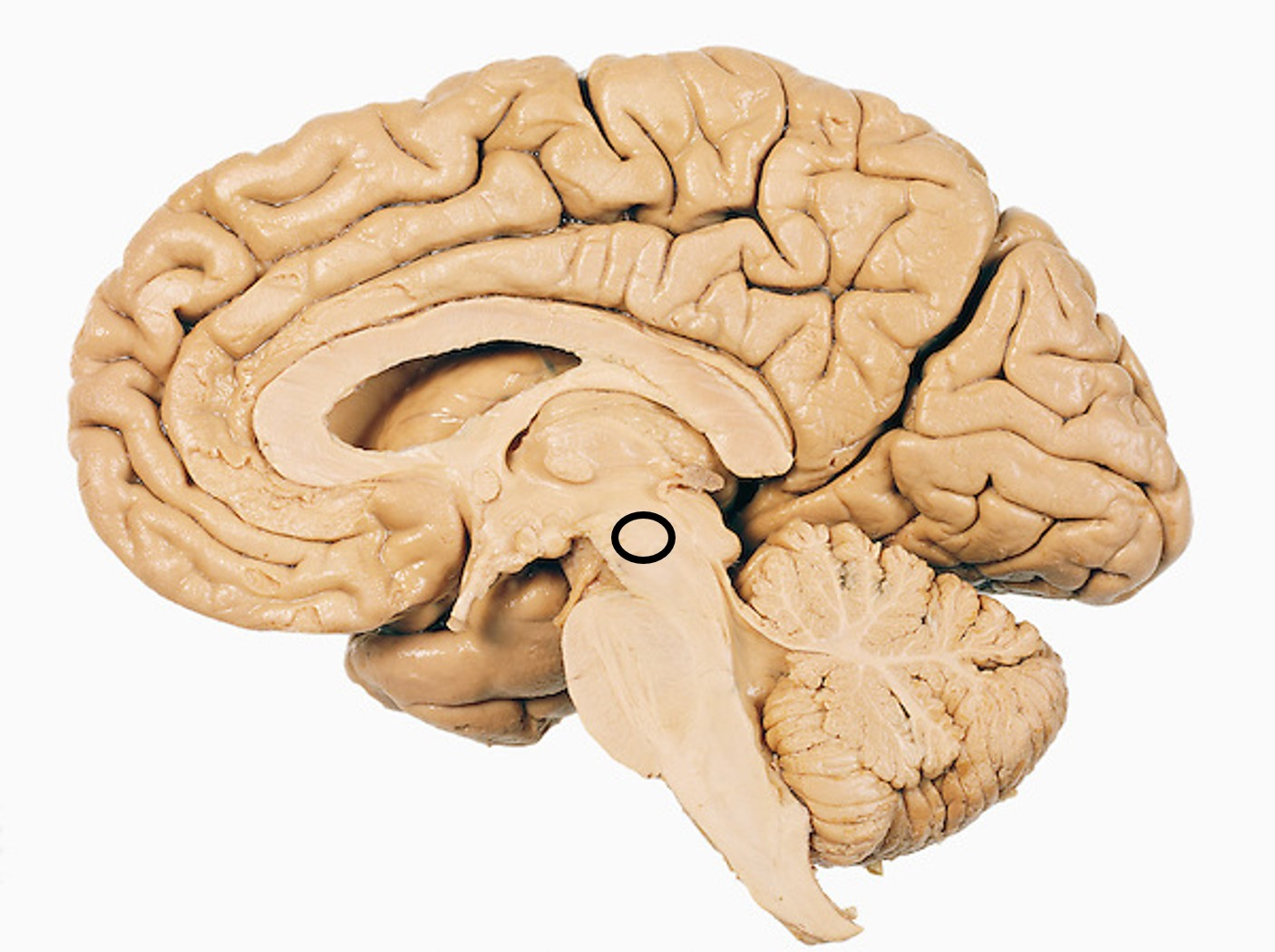
The circled area is the
midbrain
Giving muscarine to a person would be likely to make them
salivate
At a certain moment in time a presynaptic cell starts to release fewer molecules of inhibitory neurotranmitter than normal. As a result
the postsynaptic cell will be likely to increase its firing rate
Which of the following steps must occur between calcium entering the axon terminal and degradation of the neurotransmitter?
release of neurotransmitter into the synapse
Which of the following is NOT a real difference between ionotropic and metabotropic neurotransmitter receptors?
whether they can bind acetylcholine
Which ion is essential for allowing vesicles at the axon terminal to fuse with the cell membrane and release neurotransmitter?
calcium
What comes standard on your genuine model human brain?
Consciousness
Double-edged sword; knowing the actual state of the world we live in, unlike other animals.
Movement
Dexterity; having a complex brain that can send signals that allow our body to have this movement
Object Recognition
Artificial neural nets can be trained to recognize objects, but then are extremely sensitive to small changes
Language
Basic Survival
E.g. baroreflex
Central Nervous System
Consists of brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System
Contact skeletal and smooth muscle, skin, blood vessels, and visceral organs
Somatic and autonomic components
Axons bundled into nerves
Spinal for body into nerves and somatosensation
12 cranial nerves for head movement and all 5 senses
Afferent = Sensory
Efferent = Motor
Planes in the Brain
Horizontal plane
Coronal Plane = Frontal or cross-section
Sagittal plane = parasagittal
Outer part of the Brain
controls outward-looking functions
Conscious awareness, under voluntary control
Inner core of the brain controls
inward looking functions
Hypothalamus + brainstem
Unconscious, involuntary
Limbic System
Link between cortex (conscious perception) and Hypothalamus
located in between them
Mediates emotions, memory, motivation, pleasure, reward
Includes hippocampus, amygdala, nucleus accumbens
Prefrontal Cortex
Inhibitory, controls behavior
Especially large in human beings
Involved in planning foresight control of social behavior (manners, cultural customs)
Central Nervous System
Forebrain (prosencephalon)
Telencephalon
Cerebral Cortex
Basal Ganglia
Diencephalon
Thalamus
Hypothalamus
Brainstem
Midbrain (mesencephalon)
Pons
Medulla
Spinal cord
General functions of the Forebrain
Conscious perception
Control and planning of movement
Homeostasis (physiology and behavior)
E.g., water balance
Language
Memory
Cerebral Cortex - Conscious Perception
Insula not visible from the lateral surface - receives taste information
Anterior to central sulcus - generally “motor”
Posterior to central sulcus - generally “sensory”
But there are connections between them, and Both are involved in most real-world tasks
Parietal lobe: “where/how”
Temporal lobe: “what”
Basal ganglia (telencephalon)
Thalamus (diencephalon)
Egg-shaped and made up of many individual nuclei
Similar to the cortex but with a lack of conscious awareness
Hypothalamus (diencephalon)
The general function is to maintain homeostasis
Done by controlling:
Hormone release
Autonomic nervous system
Behavior
Individual functions controlled by individual nuclei
Brainstem (midbrain, pons, medulla)
general functions
Sensory processing (for some of the senses)
Control of the autonomic nervous system
Contains the reticular formation
Organization of reflected
Regulation of sleep and waking
Origin of neurotransmitter systems
Peripheral nervous system
Spinal nerves and cranial nerves
Autonomiv Nervous System
Purpose: To maintain homeostasis
Unconscious and involuntary
Targets
Smooth muscle
Glands
Cardiac muscle
Three Divisions of Autonomic Nervous System
Sympathetic nervous system (fight or flight)
Parasympathetic nervous system (rest and digestion)
Enteric nervous system (gut)
Effects of Sympathetic Activation
“Fight or flight”, stress, excitement
Increased heart rate
Increased metabolic rate
Increased blood glucose
Dilation of pupil
Effects of Parasympathetic Activation
Rest and digestion
Salivation
Increased gastric motility
Decreased heart rate
Constriction of pupil
The Autonomic Nervous System has both
sensory and motor components
Sensory
Signals related to heart rate, digestion, etc.
Motor
Control of smooth muscle
2 neuron chain
Both together
Autonomic reflects
Baroreflex
keeps heart rate approximately constant
Both sensory and motor functions are automatic
Generally opposite functions for SNS and PSNS but…
For some functions, activation of both SNS and PSNS is involved
Oligodendrocytes
Wrap axons in the central nervous system in sheath of myelin (with gaps at Nodes of Ranvier)
Potential Problem with Oligodendrocytes
Multiple sclerosis (MS)
Patches of demyelination in CNS - Causes problems with neurons communicating
Generally starts in optic nerve, spinal cord, or cerebellum
Most cases occur between ages 20 and 40
Symptoms often wax and wane
Reticular Formation
Spans brainstem dorsally
Involved in sensory-motor integration (semi-automatic movements)
Ventricles and Meninges
The brain is cushioned by cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), which also maintains the chemical environment of neurons
CSF is contained and produced in the ventricles and constantly flows out and is regenerated (blockage of CSF flow results in hydrocephalus)
3 Meninges
Dura mater - 2 layers that separate at places to form sinuses
Arachnoid - weblike, adheres to dura
Pia mater - thin, adheres to brain and surrounds blood vessel branches
Blood supply to brain
Brain has a high demand for oxygen
Blood-brain barrier regulates which molecules can enter the brain, except at certain places (circumventricular organs)
The Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB)
BBB can be crossed by some molecules, but not others relevant for drug administration
In general differences between functions of the inner and outer parts of the brain
However they interact with each other, and both are necessary
Parietal lobe
“Where/how”
Temporal lobe
“What”
Glial Cells
Equal to neurons in number
Provide support to neurons
Several Kinds
Oligodendrocytes
Schwann cells
Astrocytes
Microglia
Schwann Cells
Similar to oligodendrocytes, except:
Peripheral, not central
Do not cover multiple neurons with myelin
Astrocytes
Regulate the chemical environment of neurons
Provide neurons with nutrients
Synchronize the firing of neurons located near each other
Regulate blood flow in the brain and help form the blood-brain barrier
Microglia
The immune cells of the brain
Sensors for pathological events in the CNS (e.g. bacteria)
Involved in repair of injured neurons
Release cytokines (immune system molecules)
What makes neurons special?
Neurons are capable of carrying electrical signals without decrement, even over large distances
Transduction and Digital coding
Physical energy and chemical identity are transduced by the nervous system
Unmyelinated axons
Small diameter (pain sensation): 1m/sec
Myelinated Axons
large diameter (proprioception): 100m/sec (= 224 miles/hour)
The nervous system is derived from?
ectoderm
During development, the neural tube forms due to folding of the
Neural plate
After human beings are born…
synaptic pruning takes place
People are able to contract skeletal muscle and make voluntary movements due to
acetylcholine binding to nicotinic receptors
Which of the following is NOT true about CSF?
The same CSF continually recirculates, rather than any new CSF being produced
The Blood-Brain Barrier
can be crossed easily by lipid-soluble substances
The Reticular Formation
is important for semi-automatic movements like chewing
Multiple sclerosis involves a reduction in the number of
Oligodendrocytes
Rate Coding
Information is carried in their rate of firing not in their size (“All or none law”)
Neurons are surrounded by …
a cell membrane that is normally impermeable to ions
High concentration of organic anions (A-) inside cell
These concentration differences set up an electrochemical gradient, and ions are sometimes able to move through selective channels
Sodium is attracted by
a negative charge
Some sodium channels are
Voltage-gated and they open at a depolarization threshold
As sodium enters the cell
the cell becomes more positive (A depolarization)
When membrane potential is positive…
Potassium is repelled by positive charge and follows concentration gradient
When voltage gated potassium channels open and potassium leaves the cell…
the neuron goes back to a resting potential of -70mV
Refractory Period
Delay before the cell can fire another action potential
Transmission of an action potential resembles
A wave that propagates
At each location along an axon changes in membrane potential are the same size
Saltatory Conduction
Depolarization gets regenerated at Nodes of Ranvier
Timeline of an Action Potential
When the Threshold is passed (-50mV) neuron fires
Sodium channels open, sodium rushes in
Further depolarization, potassium channels open
Sodium channels close, potassium rushes out
Repolarization (membrane potential more neg.)
Potassium channels close, and return to resting potential
Saltatory Conduction is
Fast; depolarization gets regenerated at nodes of Ranvier (in between myelin)
The NA+/K+ pump restores the original ion concentration (requires ATP as energy)
Common Neurotransmitters
Dopamine
Norepinephrine
Serotonin
Acetylcholine
Glutamate (excitatory)
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA; inhibitory)
Many neuromodulators (small peptides)
Neurotransmitters is deactivated by
enzymatic degradation and reuptake into the cells
Ex. dopamine is taken back up into the presynaptic neuron by the dopamine-active transporter
This reuptake is blocked by cocaine, so dopamine acts for longer on the post-synaptic receptors