Fluids
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
why do we incorporate surface pressure when calculating absolute pressure?
think of a lake, to find the pressure at the bottom of the lake we have to include both the pressure from the water of the lake and the atmosphere above (surface) exerts a pressure too (hydrostatic pressure = P0 + pgh; P0 not always 1 atm)
how the hydraulic lift shows pascal’s principle?
the tube on one side has SA1 and a piston pushes down on the water for d1 with F1, on the other side, a tube with SA2 has a piston pushed with force F2 over d2. the V displaced from tube 1 to tube 2 is the same. W = Fd, you apply a smaller force over a larger distance to exert a larger force
F1/SA1*(SA1d1) = F2/SA2*(SA2d2)
P1V = P2V (pressure is the same as it moves through the fluid and to the walls of the container)
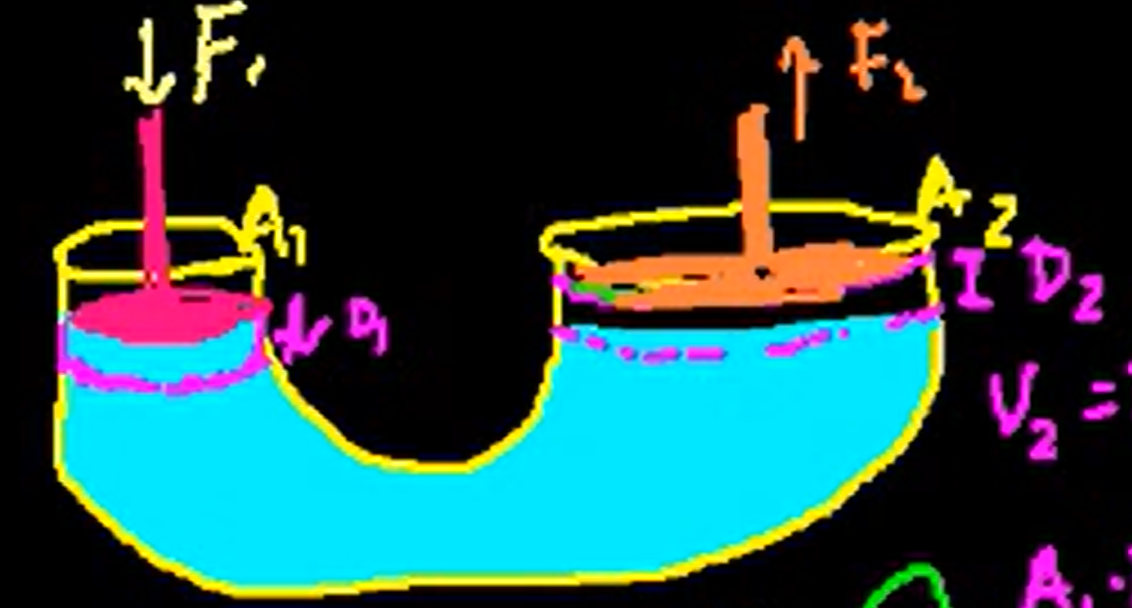
Pascal’s principle
is an external pressure is applied to a confined fluid, the pressure at every point within the fluid and to the walls of the container increases by that amount
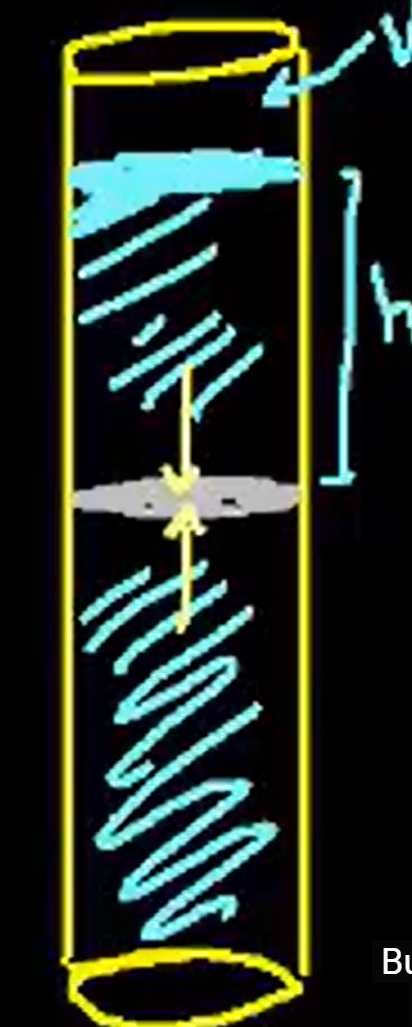
how is the pressure of the disk found at some height h in the tube?
the disk has Fnet = 0, so the down and up forces are the same. Fd = mg due to the liquid above the disk. mass of the liquid can be found from pV, Fd = pVg. V is determined by SA times h Fd = pSAhg. P = F/SA so P = phg
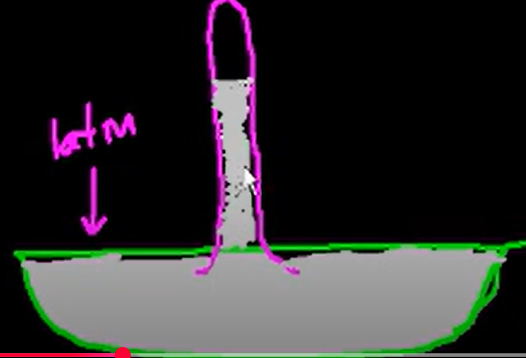
Why is there mercury that gets in the tube?
the space in the tube is a vaccum (no atm/P). there is 1atm of pressure on the mercury, so the mercury pushes 1 atm up into the tube (F net = 0). thus, the mercury in the tube has same pressure as 1 atm

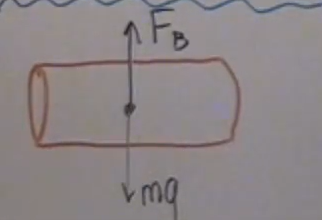
how is net F acting on the block equal to its weight that was displaced?
the P at top is diff than the bottom (bottom is lower) so Fnet = Pbx2 - Ptx2
Fnet = (pg(h+x) - pgh)x2
Fnet = (pgh + pgx - pgh)x2
Fnet = pgx3 = pgV = mfluidg; the weight of the fluid displaced (same as block) is keeping it floating there; Fbuoyancy > Fgravity
why is most of an iceberg submerged underwater?
ice has a specific gravity of 0.92 (p = 920 kg/m3) so about 92% of the ice will be submerged
why is density an intensive property?
because increasing the size of the object does not impact its density; increasing size increases both mass and volume (ratio stays same)
why do we say an object is ‘heavier’?
there are more atoms (has more mass) for the same amount of volume, making it more dense
density of water at 4C
1000kg/m3 or 1g/cm3 or 1g/mL
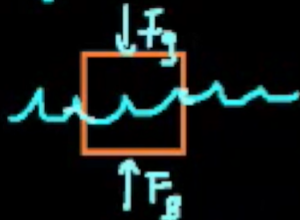
Block of wood has density of 130 kg/m3, what percent is submerged?
the forces must be equal since block is floating, so Fg = V(of block)p(of block)g
FB= V(of submerged)p(of water)g
Vbpbg = Vspwg
Vs/Vb = pb/pw
Vs/Vb = 130/1000 ×100
Vs/Vb = 13%
what is flux?
how much of something (volume) crosses a surface in some amount of time (V/t)
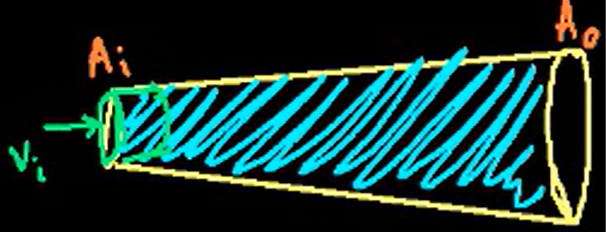
how is the continuity equation derived?
if some fluid is flowing through this tube, then the volume flowing in is equal to the volume flowing out. the distance the fluid moves in can be found by vit, multiplied by area of tube opening gives volume = Aivit = Aovot which equals to the output. therefore, Aivi = Aovo. this means that the mass of fluid flowing through the pipe at any point is the same
compare laminar and turbulent flow
laminar flow has little resistance because each fluid particle follows a smooth pathway which don’t cross with other particles
turbulent flow involves a lot more resistance because the fluid motion contains eratic, small circular currents (eddy currents)
explaining buoyant force between ball of water, racquet ball and billard ball all placed in the middle of a tub
the buoyant forces are all the same for each ball as their volumes are all the same (diff in pressures are the same, displaced water is the same) but the billard ball has a greater mass than the water, so its mg is greater than FB making it sink, for the racquet ball its mass is less than water so the FB is greater making it float (displaced water can keep it afloat)
equation for pressure
P = F(magnitude of normal force)/A (no direction)
conversions of Pa
1.013 × 105 Pa = 760 mmHg = 760 torr = 1 atm
how a difference in pressure causes air to rush in and out of the lungs, windows to burst outward during a tornado etc.
when unequal pressures are exerted against objects, the forces acting on the object will add in vectors, could result in acceleration (a net force present). pressure on one side greater than the other
what is gauge pressure?
the difference between absolute pressure inside a tire for ex. and the atm pressure outside the tire. amount of pressure in a closed space above and beyond atm pressure
hydrostatics
the study of fluids at rest and the forces and pressures associated with standing fluids

a) 0.53m
b) 0.24m
c) 0.18m
d) 0.37m
b) 0.24m

Water is flowing through a pipe with a variable radius. Is pressure the same at the input and output of the pipe?
No, velocity of the water molecules change in different areas, meaning a net force (changing v means acceleration). plus, if the pipe goes uphill, pressure will decrease