AP Bio Cell Types & Structures & Cell Size
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Ribosome
makes proteins; can be on Rough ER (bound) which make proteins for membranes or for export out of cell; can be free in cytoplasm which make proteins for use in cell
Lysosome
cell organelle filled with hydrolytic enzymes needed to break down (digest) certain materials in the cell
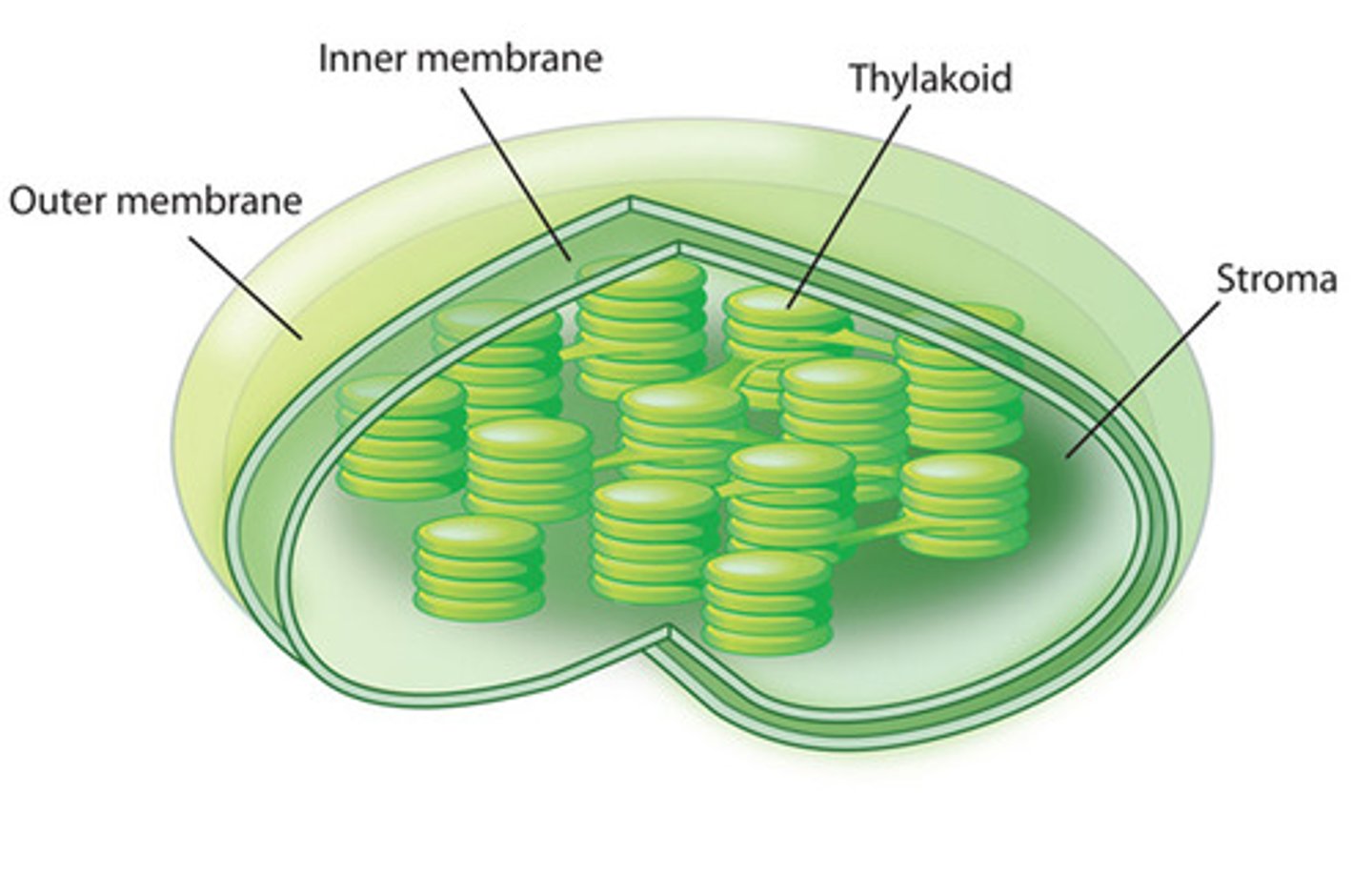
Chloroplast
Site of photosynthesis, contains its own DNA & ribosomes.
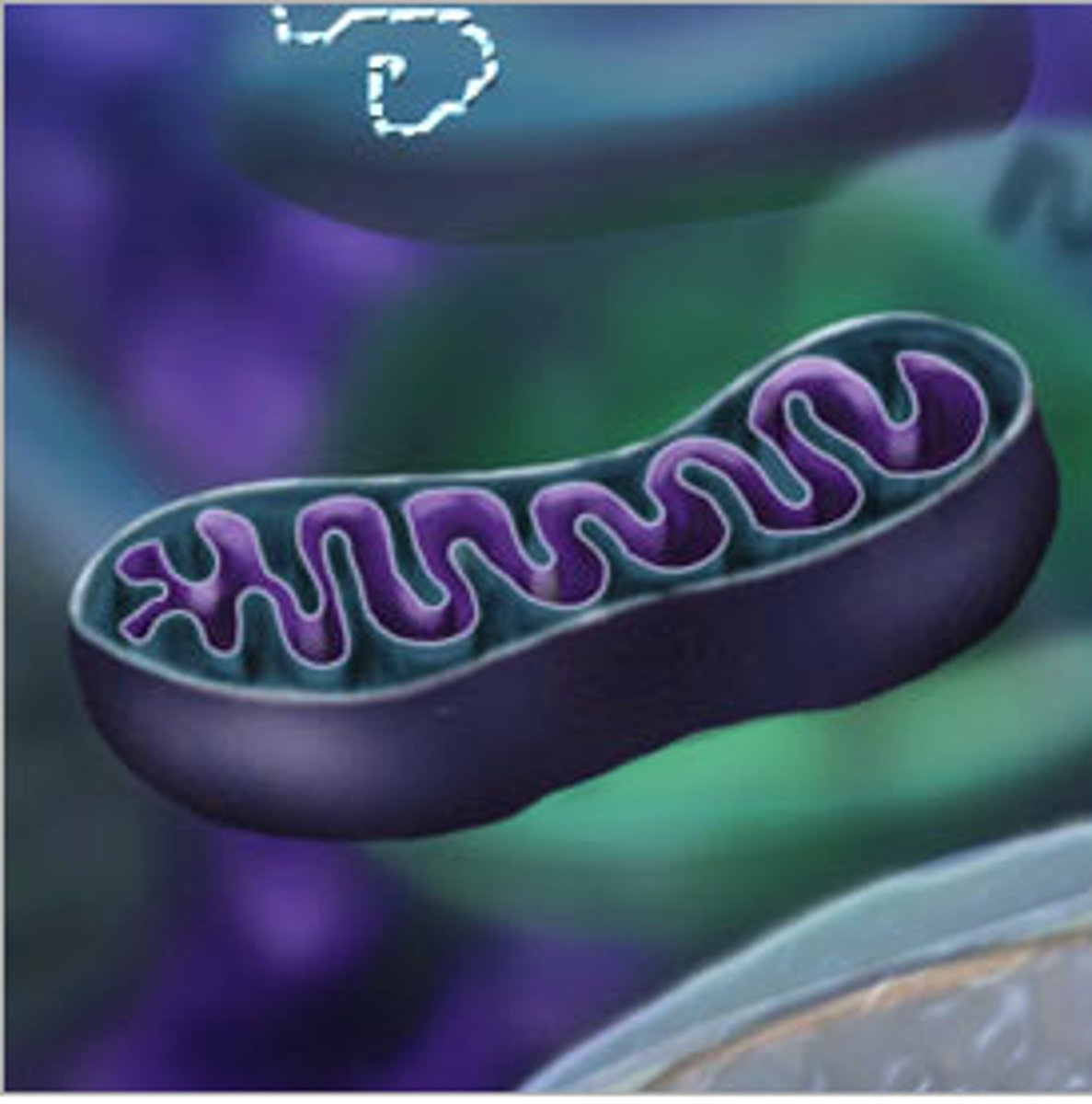
Mitochondria
organelle that is the site of ATP (energy) production, oxidizes sugar to make ATP (cellular respiration); contains its own DNA & ribosomes
Endosymbiotic Theory
A theory that mitochondria and chloroplasts were once free living bacteria.
Cell membrane (plasma membrane)
encloses the cell, regulates the passage of materials into and out of the cell.
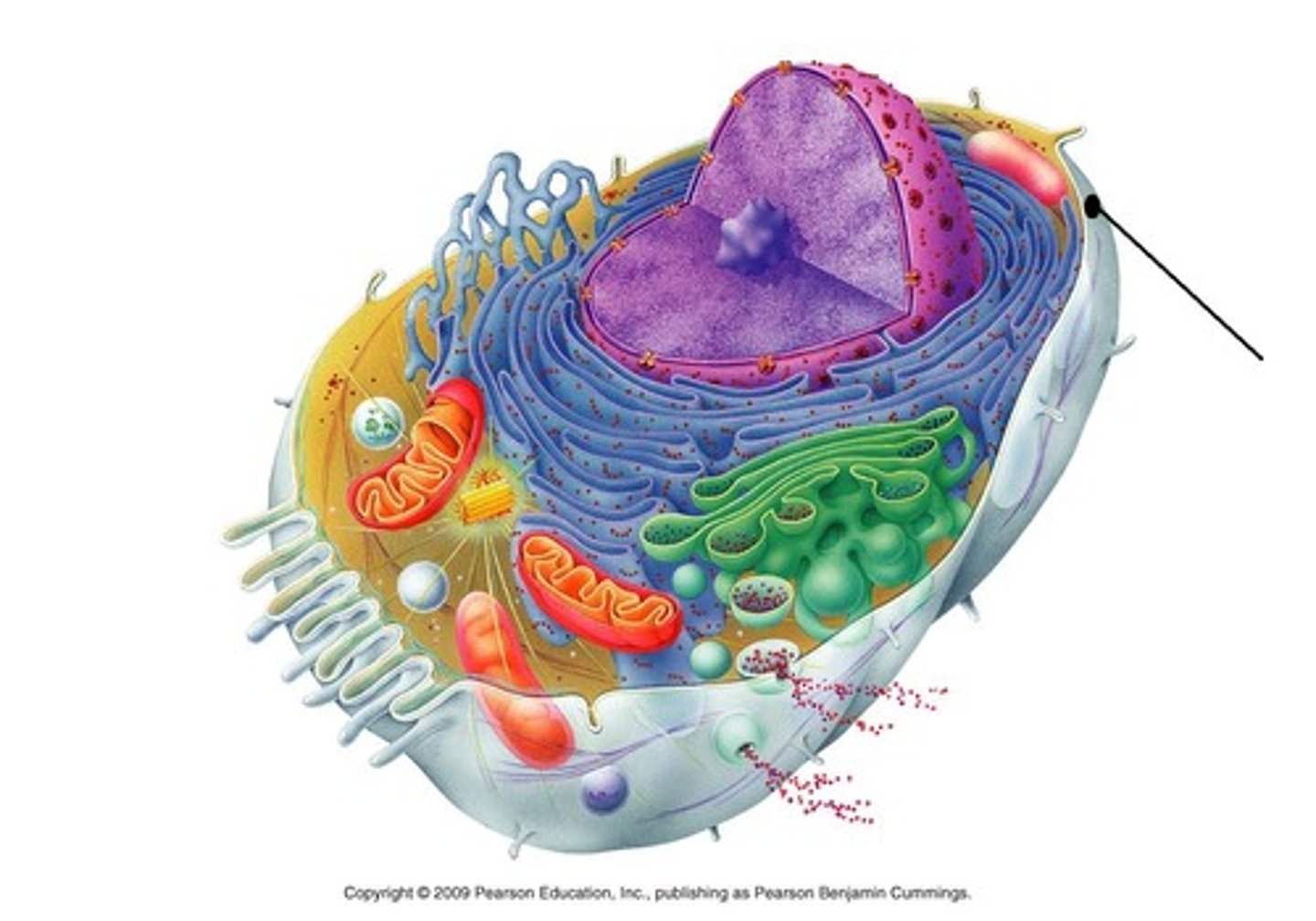
Cell wall
Surrounds cell membrane in some cells. Provides protection & support. Maintains cell shape. Prevents cell from taking in too much water. May contain cellulose, chitin, or peptidoglycan.
Nucleus
Control center of the cell. Contains DNA.
Nucleolus
Found inside the nucleus; produces ribosomes
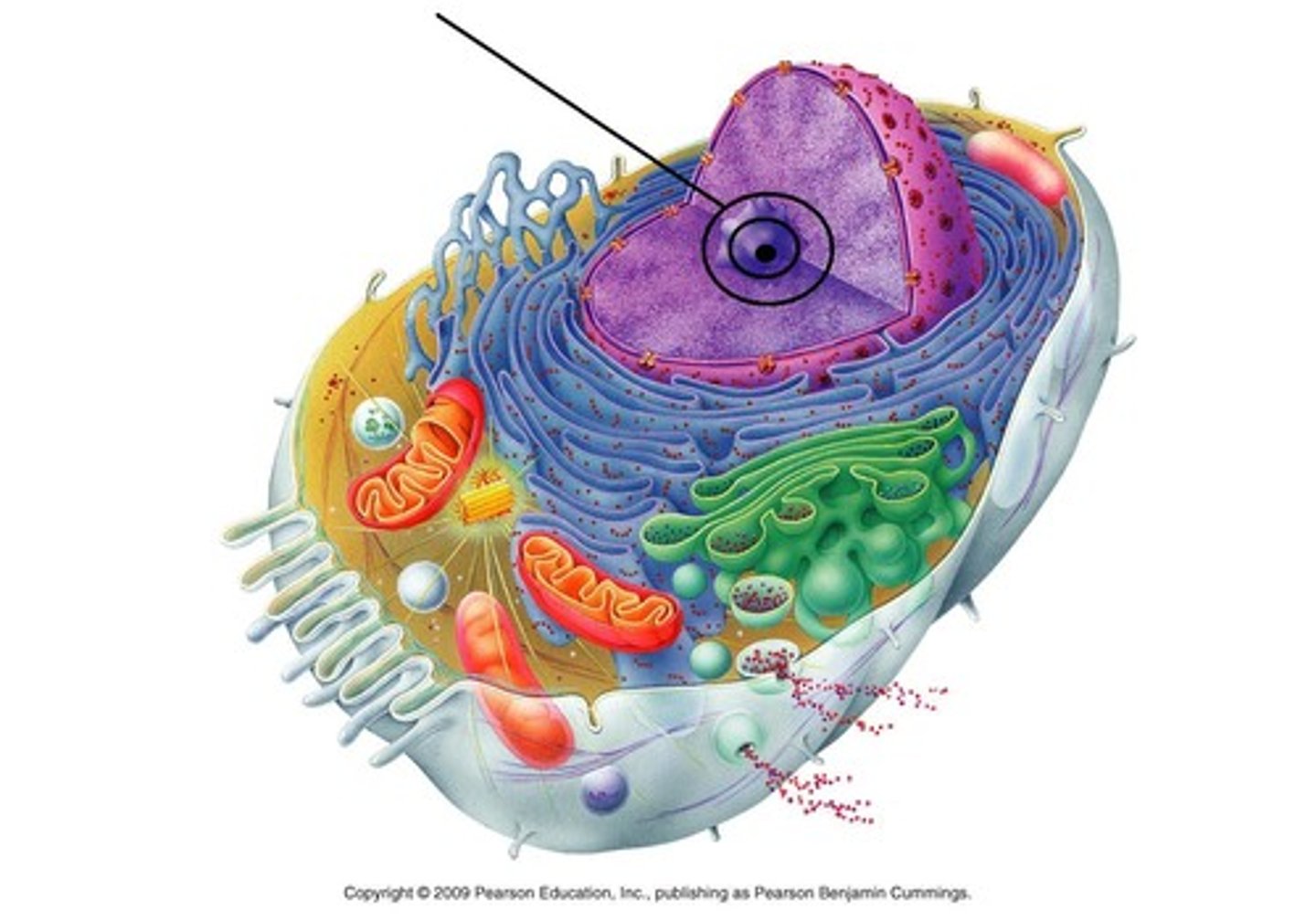
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Makes lipids; metabolizes carbohydrates; detoxifies drugs & poisons; Stores calcium
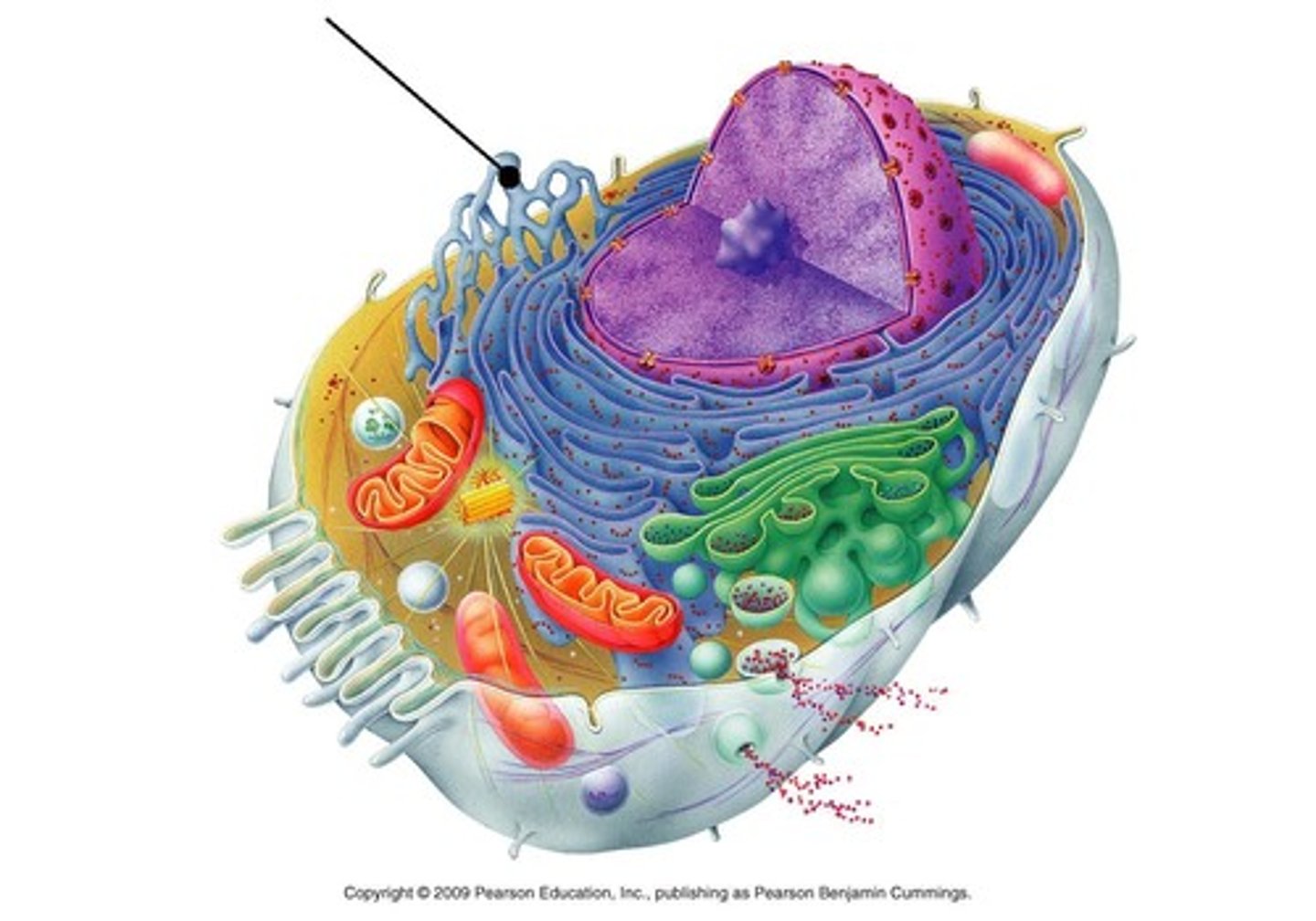
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Has ribosomes on surface that make proteins for export from cell; makes membranes
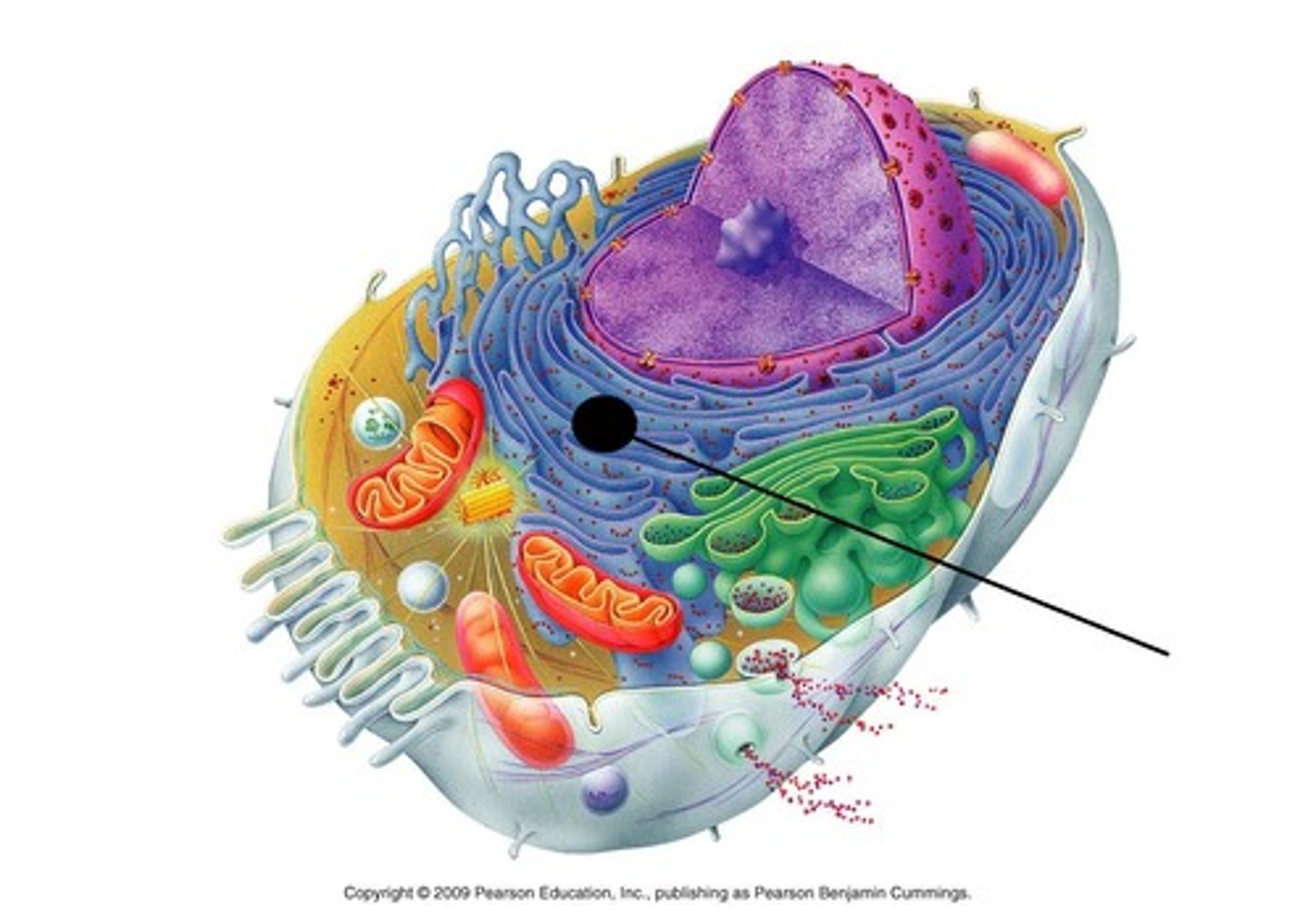
Golgi apparatus
stack of membranes in the cell that modifies, sorts, packages, and ships cell products
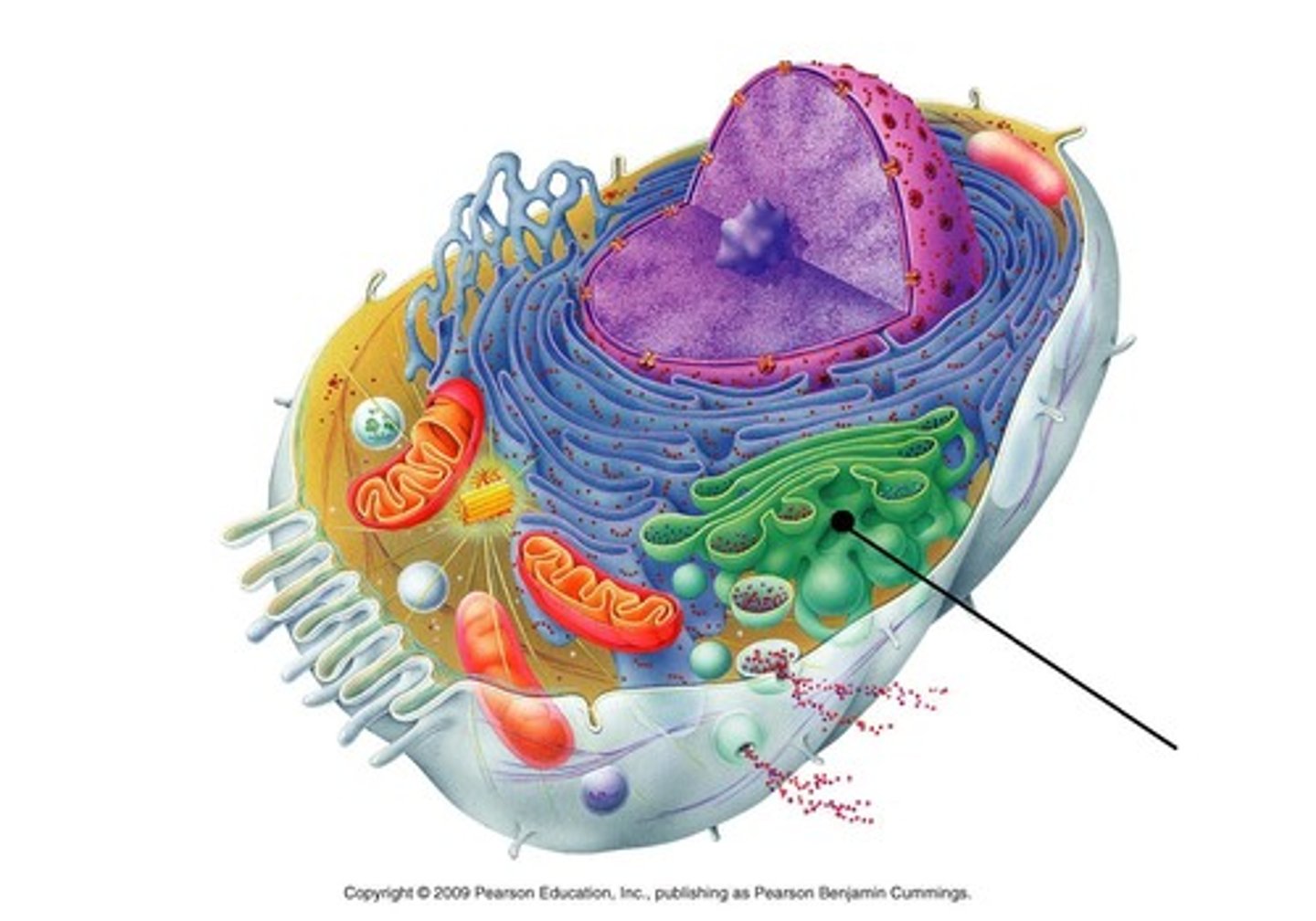
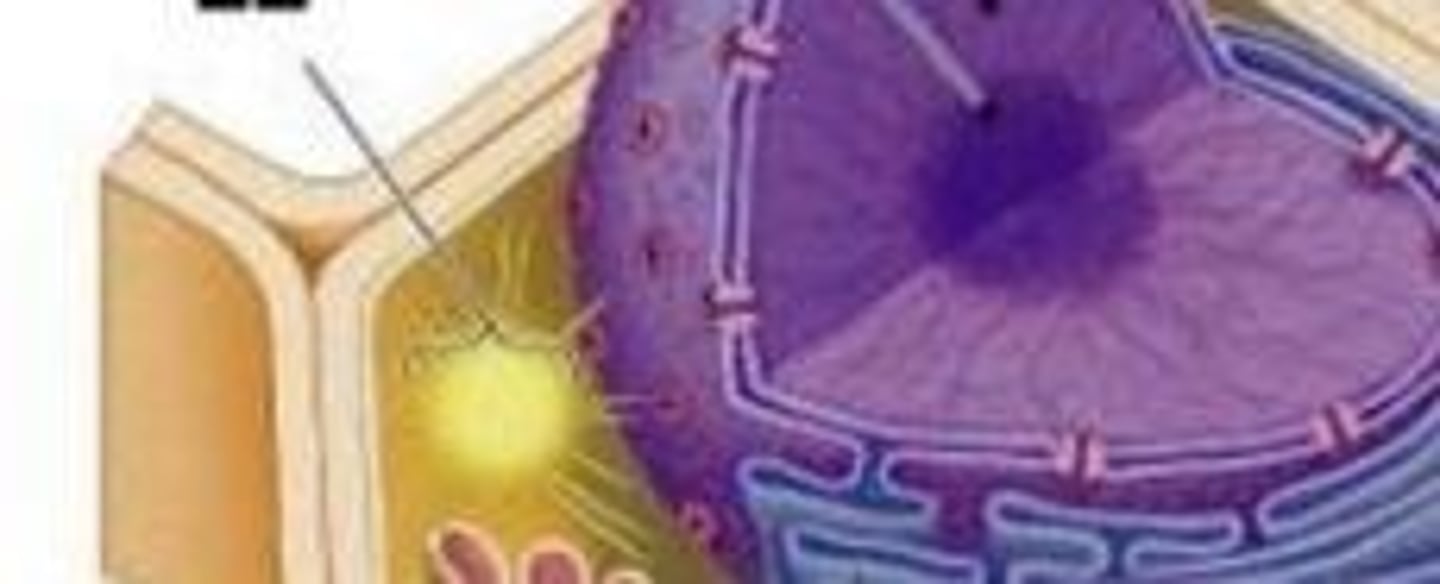
Centrosome
Involved in cell division in both plant & animal cells; microtubule organizing center (forms mitotic spindle)

Centrioles
Found in animal cells, stacks of microtubules that sit on top of centrosome, May play some role in cell division in animal cells.

Peroxisomes
Break down hydrogen peroxide to water, metabolize fatty acids, detoxify alcohol, convert fatty acids to sugar
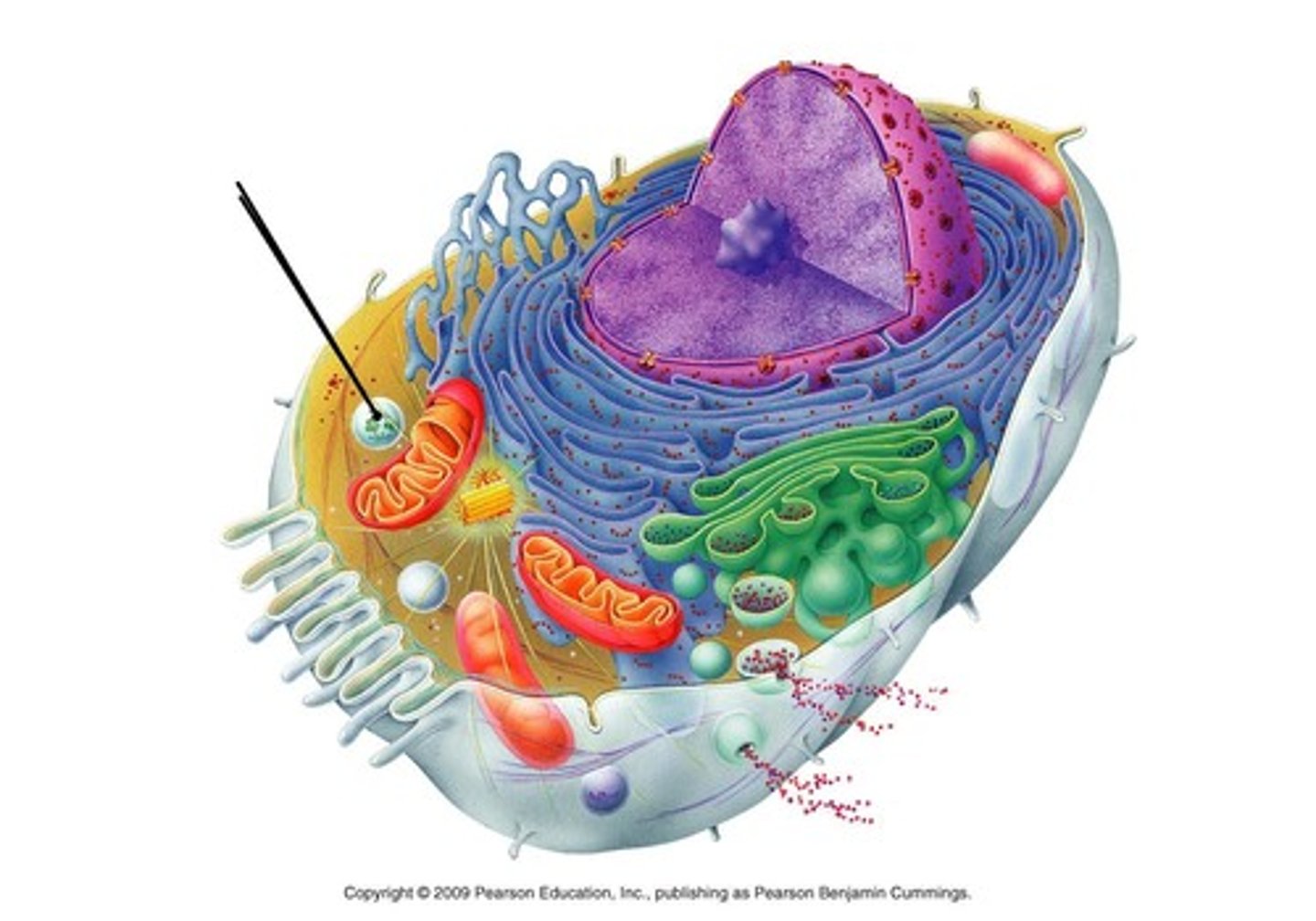
Cytoskeleton
A network of fibers that holds the cell together, helps the cell to keep its shape, provides support, and aids in movement. Fibers include microfilaments, microtubules, & intermediate filaments.
Cytoplasm
Fluid filled region between cell membrane & nucleus.
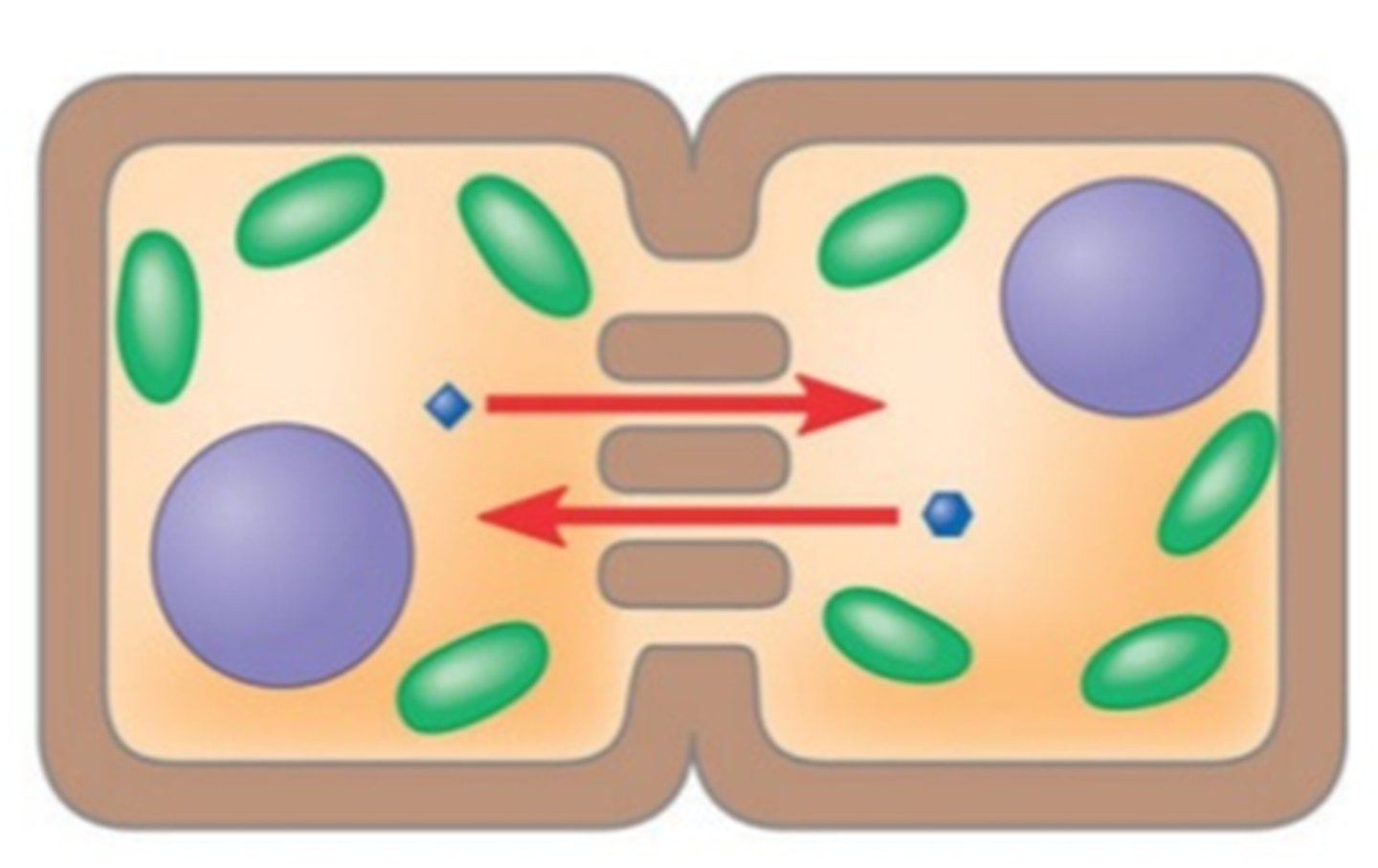
Plasmodesmata
channels through cell walls of plants that connect the cytoplasms of adjacent cells, allow water & solutes to move between cells
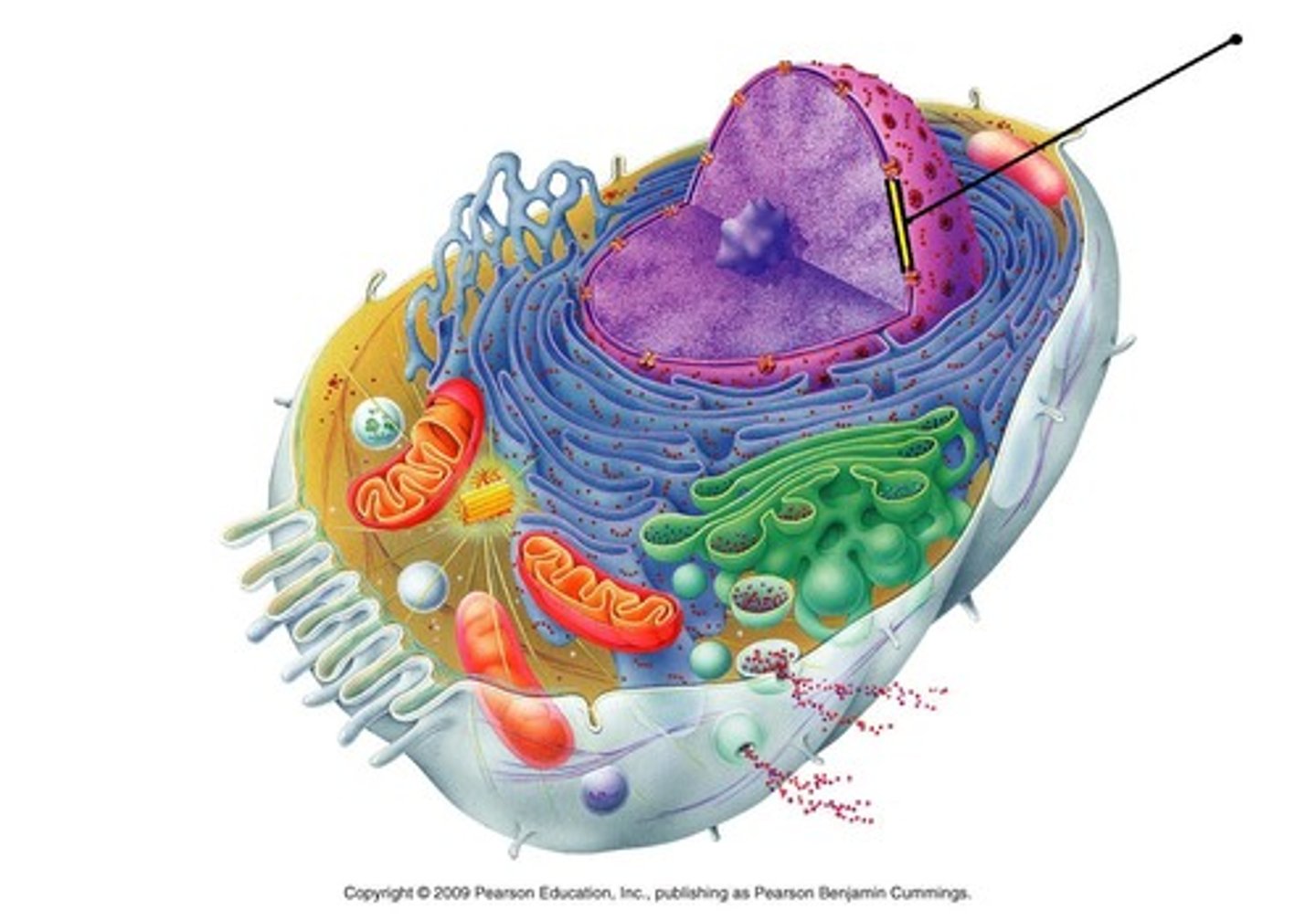
Nuclear membrane (envelope)
Surrounds the nucleolus and DNA. Controls what enters and leaves the nucleus.
Large central vacuole
the organelle that stores water in plants
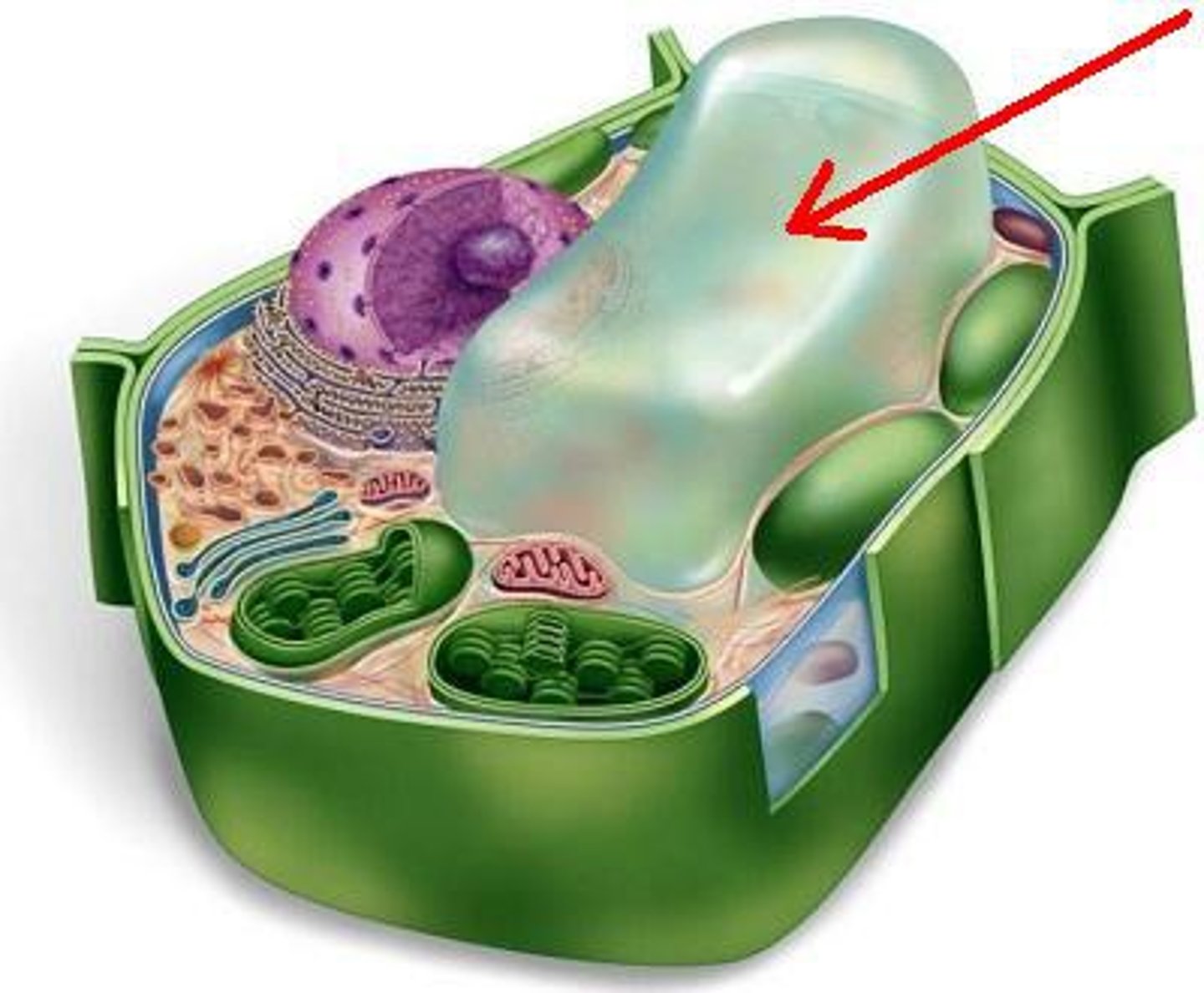
Tonoplast
membrane surrounding the large central vacuole
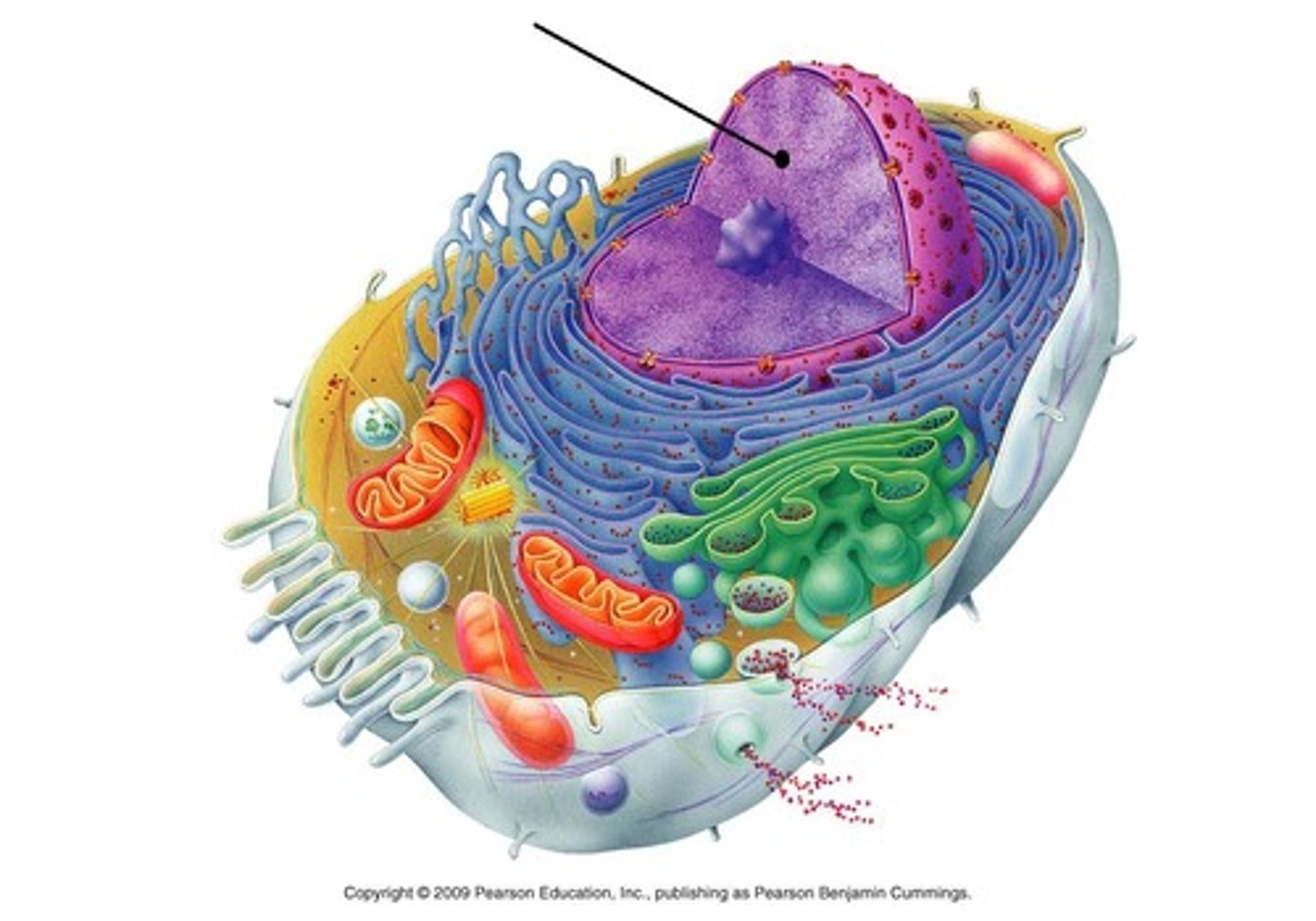
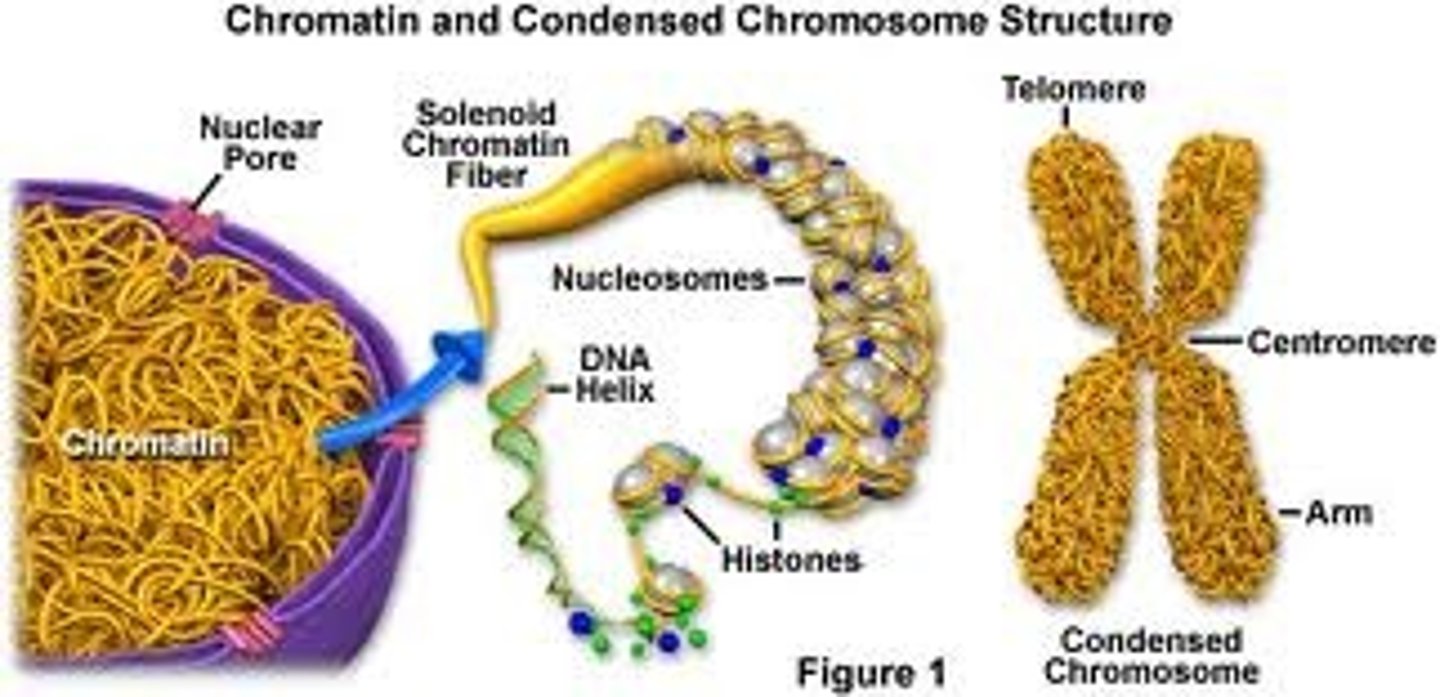
Chromatin
DNA & protein in nucleus (DNA is not visible)
Chromosome
DNA & protein, visible during cell division (condensed)
Prokaryote
unicellular organism lacking a nucleus; bacteria
Eukaryote
A cell that contains a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
plant vs animal cells (structures present)
Plant - Chloroplast, cell wall, large central vacuole, plasmodesmata Animal - lysosomes, centrioles
Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes
- Prokaryotes have no nucleus or membrane bound organelles
- Eukaryotes have a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
- Both can reproduce and respond to the environment
Structures found in all cells
cell membrane, cytoplasm, DNA, ribosomes
Factors that limit cell size
Surface area and volume
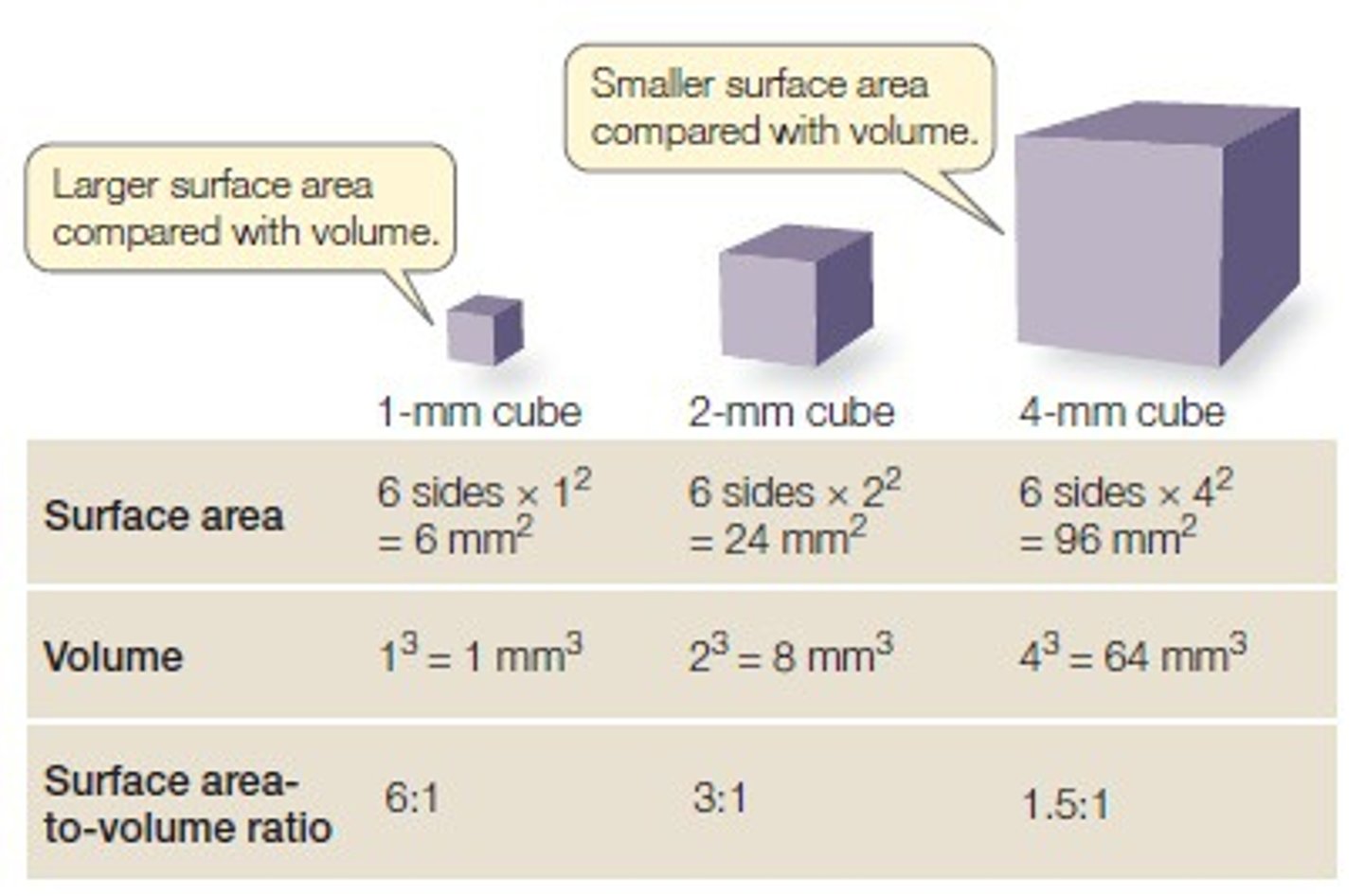
Surface Area to Volume Ratio
Affects diffusion of nutrients and wastes into and out of cells.
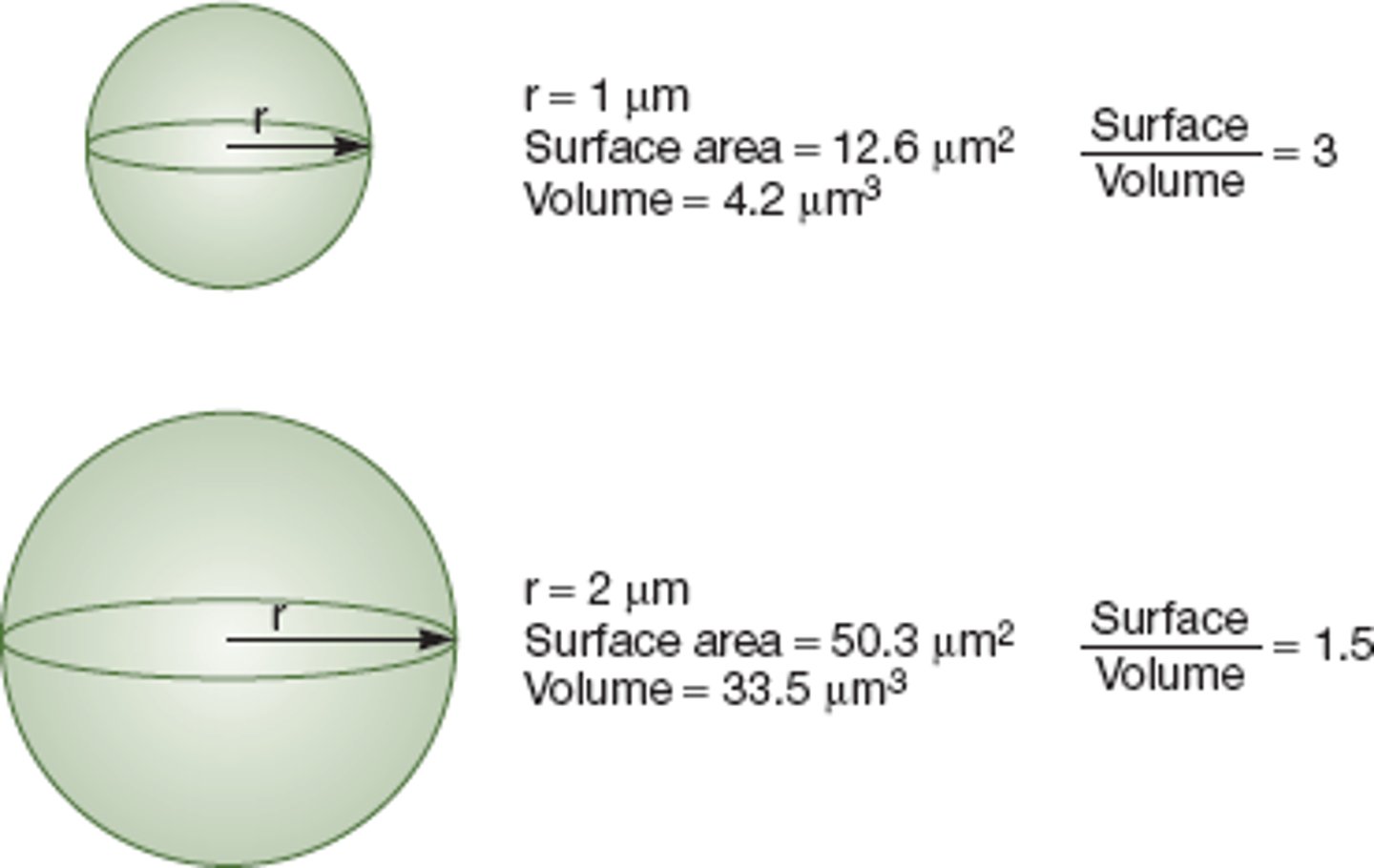
Large Surface Area to Volume Ratio
Most efficient for diffusion
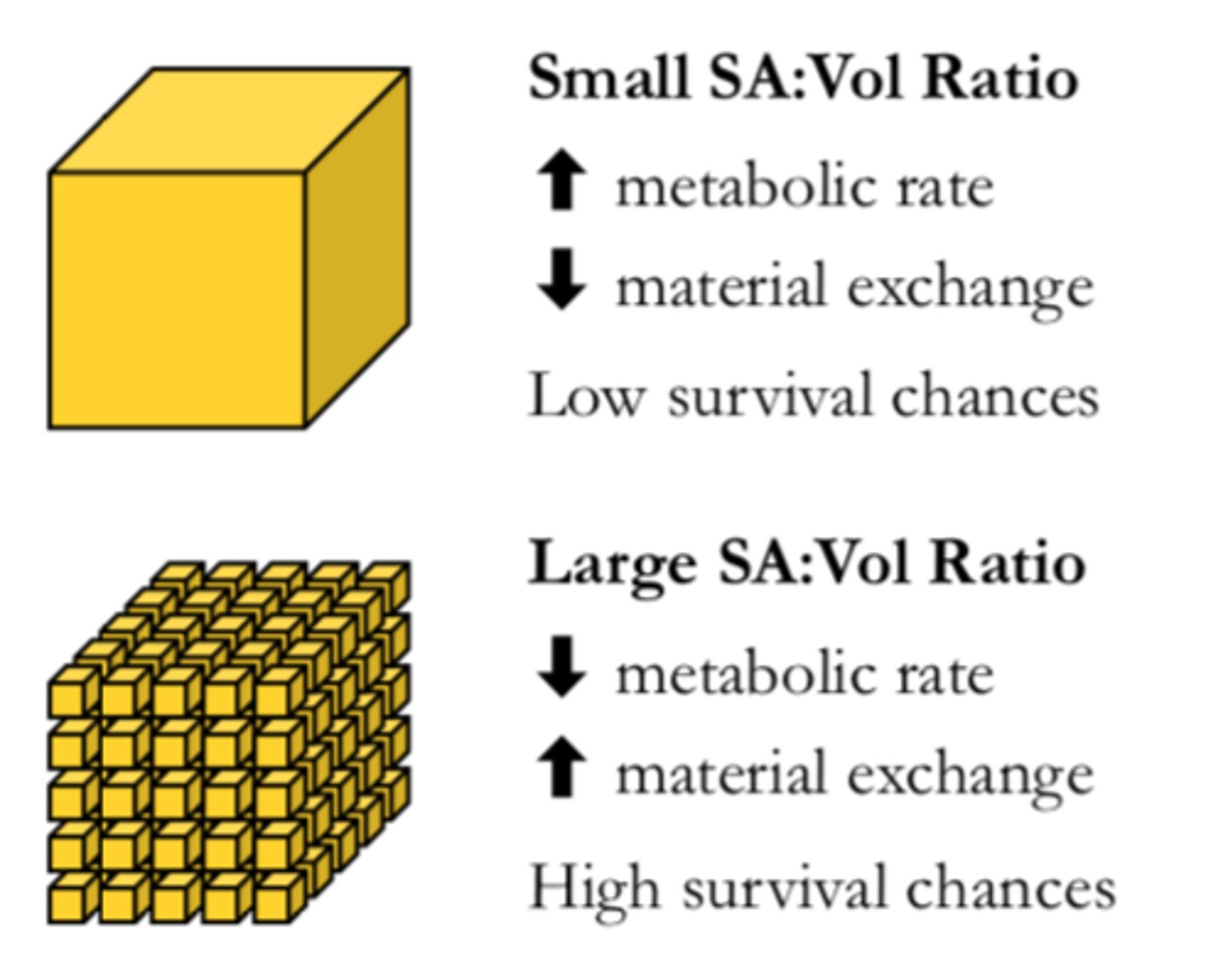
A cubed shape cell with a side length of 2 cm has a surface area to volume ratio of what?
3:1 (SA = 24 cm2 V= 8 cm3)
How do folded cell membranes benefit a cell?
Increase the surface area to allow more diffusion into or out of the cell.
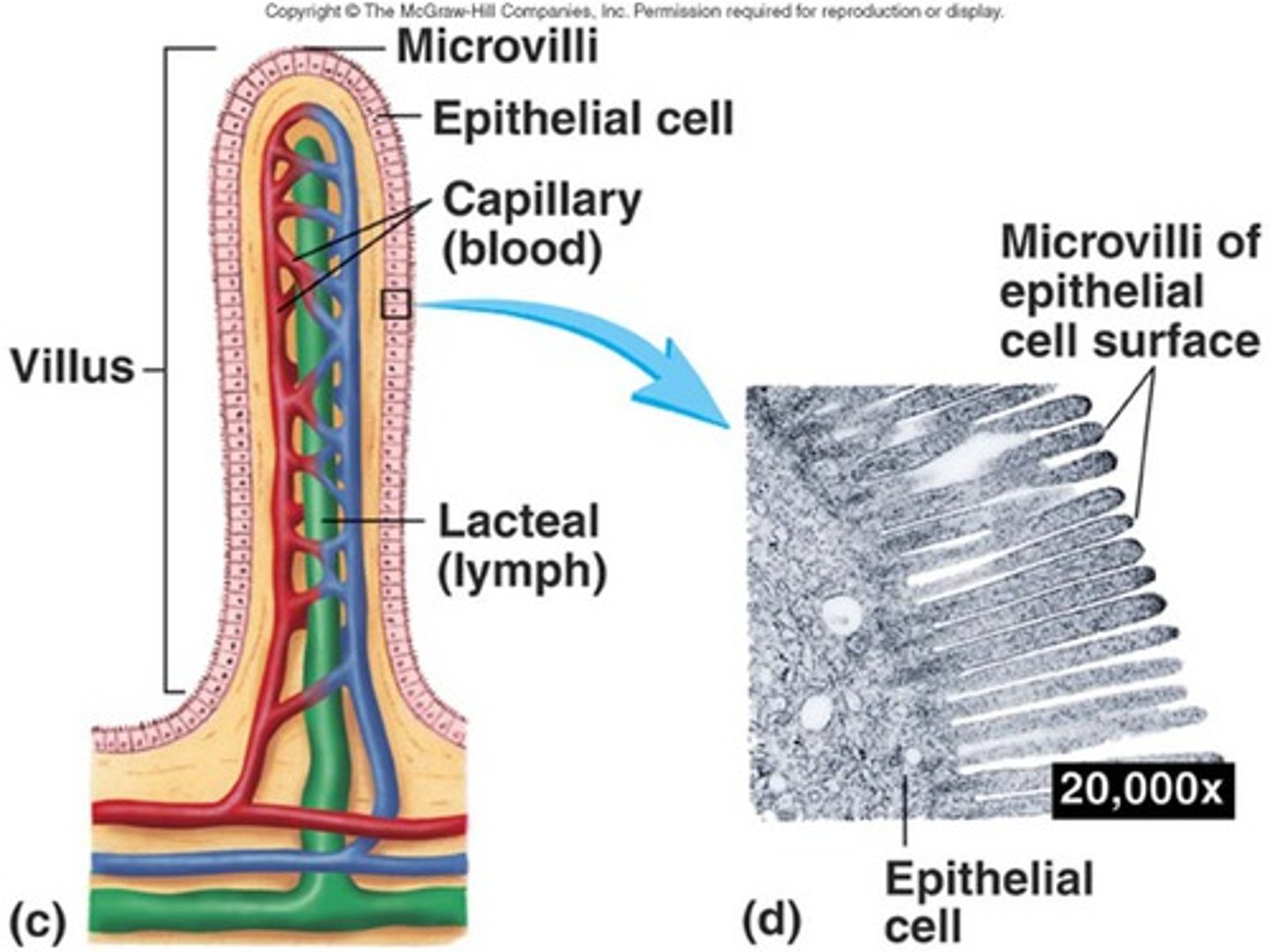
Why is a smaller volume better for the cell?
The diffusion inside the cell is faster. There is less distance between cell membrane and organelles. Substances can get from the cell membrane to an organelle faster when the cell has a smaller volume.