kin 216 general motion
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Angular movements give rise to ______
Shoulder _____ which makes arm go ______.
_______ ________ causes _____ displacement of arm
linear change
rotates, up
Angular rotation, linear
most examples of human movement are
motion general
we can separate motion into its individual components, including
rotation and translation
The further sth rotates..
eg..
the further it will translate
if you wanna throw a fastball, you have to put fast spin on it
the more the angular motion
the more the linear change occurs
The amount of rotation is related to …. BUT..
the amount of translation BUT they’re not the same!
When rotating shoulder joint, linear change is related to angular change for elbow and hand but..
but they’re not the same thing because the translation depends on how far the elbow/hand is away from axis of rot
Need to know how far the thing is from AOR
the further you are from axis of rotation,
the greater the translation
the amount of linear change will depend on
distance between axis of rotation and point of interest
The amount of rotation (phi, theta, sigma, omega)
radius of rotation (r)
UoM
distance between axis of rotation and point of interest
Rad of rot is a linear value
m
unit for radius of rotation
m
what happens if you increase radius of rotation at same angular input
increase linear distance
when system rotates about an axis, how far a point translates
l = rΦ
m = m x ____
when system rotates about an axis, how fast a point translates
v = rω
m/s
when system rotates about an axis, the size of dynamic change
a = rα
m x __/s²
why do we use distance (l) not displacement for general motion
When a system rotates about an axis, how a point on that system translates is found using distance not displacement because:
displacement underestimates how far a system has moved
if we used displacement, we would not go around the arc of the circle, we would go straight thru it
a radian is
a ratio between distance around the circle to the radius of the circle
the radius of rotation is
linear distance from axis of rotation to a point of interest on the system
what happens when you choke up (hold the bat up higher)
what happens when you choke down
you shrink the radius of rotation, so as a result, you sacrifice distance and velocity to gain more accuracy
l = r x phi & v = r x w
For the same angular velocity (w), you reduce r, so the linear speed of the bat reduces
For the same angular distance (phi), you reduce r, so the linear distance moved is also decreased
Increase radius of rotation so you get more distance and velocity but at the cost of accuracy
l = r x phi & v = r x w
For the same angular velocity (w), you increase r, so the linear speed of the bat increases
For the same angular distance (phi), you increase r, so the linear distance moved is also increased
How calculate linear and angular variables
All linear stuff is measured in meters (he will give in centimeters)
But if given deg/s or rev/s, convert that number into radians
Radian relates linear to angular concept
for angular motion, angles can be in
degree, radian, revolution
for relating linear and angular variables, the angle must be in
radians
a bottle, spinning clockwise is placed on the ground. which way does it move
If Ball spins clockwise, it translates to the right direction
When object hits surface, angular motion (rotation) , creates linear change.
Tangent line reflects linear change, based on angular movement. So tangent line tells me sth about performance
direction of linear movement is on a _______ to the rotating object
tangent.
Tangential acceleration
tangential acceleration is linear acceleration caused by rotation (change in number).
Centripetal acceleration
centripetal acceleration is change in direction caused by rotation (change in direction).
When does an object have both tang and centripetal accel?
an object can have both of these at the same time if it is speeding up or slowing down and going around a curve at the same time.
Key ideas for tangential:
If angular velocity is constant (alpha = 0), then tangential acceleration is zero
If ang vel is increasing or decreasing, tang acceleration is present
Tang acceleration only affects speed, NOT direction
direction controlled by centripetal acceleration
a t subscript means
tangential (linear movement caused by rotation)
is V a linear measure
yes
is Vt a linear measure
yes
if we say a bottle traveled with the velocity: V
the bottle slid across (no rotation)
if we say a bottle travelled with velocity: Vt
the bottle rolled
is tangential change the same as linear change
yes, the only difference is tangential remindsd you that angular movement gave rise to linear change
does an object moving around a curve at the the same speed be accelerating
Vectors are defined by a magnitude (number) and a direction (orientation). If either the number is changing or the direction is changing, then you have acceleration. And that acceleration was created by a force.
Linear or tangential acceleration refer to a change in the number – how fast or slow an object is travelling.
Radial or centripetal acceleration refer to a change in orientation – the direction.
Takeaway on why diff formula for linear and tang vel/acc
Linear and tangential values are the same thing. They are both linear concepts and deal with a change in position. Tangent lines are used to reflect the linear movement created by a rotating object.
Angular movements create linear movements. So the term tangential is used and it reminds us that an angular movement created the linear change.
So, linear velocity = tangential velocity. And, linear acceleration = tangential acceleration. The terms mean the same thing. We use tangential when we are using the angular concepts to calculate the linear variables.
Takeaway for linear vs radial acceleration
Vectors are defined by a magnitude (number) and a direction (orientation). If either the number is changing or the direction is changing, then you have
acceleration. And that acceleration was created by a force.
Linear or tangential acceleration refer to a change in the number – how fast or slow an object is travelling.
Radial or centripetal acceleration refer to a change in orientation – the direction.
a point spinning at a constant angular velocity is
constantly changing direction and is experiencing radial/centripetal (linear) acceleration
what acceleration is present when an object changes direction on circle
centripetal or radial acceleration.
the number is not changing (speed), but the orientation is changing so acceleration is present since we are changing direction as we go around a a curve/circle.
how is the force directed for radial accel?
the force that causes radial accel is directed towards the axis of rotation
radial/centripetal acceleration =
UoM
The linear acceleration directed toward the axis of rot
ar =v²/r
m/s²
Linear acceleratoin is directed towards what?
●As r decreases, what happens to ar? Explain why - To make a sharper turn, would you need more or less force?
●As v increases, what happens to ar? Explain why - To make a faster turn, would you need more or less force?
Ar = v²/r
Ar increases as radius of rotation decreases. More force would be required to make a sharper turn.
more force required to make sharper turn
Ar increases as velocity increases.
More force would be required to make faster turn
when competing in a 400m race, which path is more advantageous (outside lane or inside lane)
Outside lane because it has the longer radius of rot so less Ar (radial acceleration) and less force.
Radial force required to keep a runner on their curved path is lower
Why?
When you go around to turn, create two forces. One to propel you forward and another to keep you along the curve.
The more force required to push you inside, the less available to push you forward.
When running around outside curve, you’re making wider turn. Requires less force to turn so more force to propel you forward.
Runners on inside have less energy available to propel themselves forward bc Those runners in the inside lanes, closer to the field must make sharper turns.
●Stay on outside lane
○Pass on outside cuz forward force can be kept highest and radial force needs are lowest cuz wide, not sharp, turn
if we increase velocity, what happens to ar (rad accel)
decrease vel?
if ar = 0?
increases so more force
decreases, so less force
you are moving in a straight line
what is total acceleration
sum of tangential acceleration and centripetal acceleration
atotal =
sqrt (at^2 + ar^2)
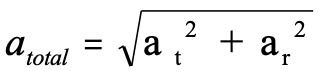
for the same movement input, will a ball travel farther with a short or long club
longer.
l = phi x r. if we increase r, l increases
If want to drive ball far, take longer club
If want to hit ball shorter, take a pitching wedge type of club. Decrease radius of rot so decrease impact that the linear change has.
the formulas of general motion say that there is a _____ relationship between linear and angular variables
if we increase linear variable, the angular variable
if we decrease linear variable, the angular variable
positive linear
increases
decreases
the formulas of general motion say that there is a positive linear relationship between linear and angular variables
this is not the case for
internal movement in human body
There is a non-linear relationship between angular and linear variables when it comes to movements inside the body
linear changes occur at which parts in humans?
a muscle
angular changes occur at
a joint
what happens to muscle length during flexion (bicep)
shortening
what happens to muscle length during extension ( bicep)
lengthening
what happens to angle of joint during flexion (elbow)
decreases
what happens to angle of joint during extension (elbow)
increases
angular kinematics is concerned with description of
angular motion
absolute angular vs relative angular position difference
Absolute angular position refers to the orientation of an object relative to a fixed reference line or plane
Relative angular position refers to the orientation of an object relative to another object or line
Q1: what are the units used when converting btwn linear and angular variables?
●Need to change deg or rev to radians. Because radians are a unitless ratio (arc length divided by radius), making them naturally compatible with linear measurements.
●Before we can relate linear and angular variables, the quantities need to be in the same form -> use RADIAN! (so always convert deg or rev to radians first !!)
Q2: define linear and tangential velocity and distinguish btwn the two?
Linear velocity = tangential velocity. They mean the same thing. Tangential is just used when we are using angular concepts to calculate linear variables.
Q3: what is happening to a system if it has centripetal acceleration?
A3: Centipetal or radial acceleration refers to a change in orientation – the direction.
Q4: what advantage does a longer-limbed athlete have in throwing and striking activities?
Longer limb = longer radius of rotation, thus, able to make a greater linear translation and throw/strike the object a farther distance.
What two conditions must be met to convert between linear and angular kinematics?
Rigid body + fixed axis of rotation
• Why is it important to study angular kinematics?
Understanding angular kinematics lets us convert between angular and linear motion which helps explain how rotations at joint allows linear movement of distal segments