Concept 7.3: Passive transport is diffusion of a substance across a membrane with no energy investment
1/20
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
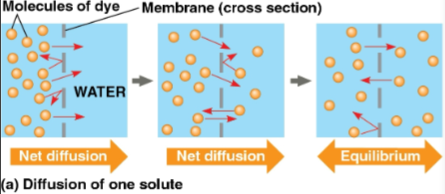
Diffusion
The movement of particles of any substance so that they spread out evenly into the available space
Generally directional until equilibrium is reached
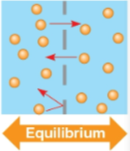
Dynamic equilibrium
State of diffusion where as many molecules cross the membrane in one direction as in the other
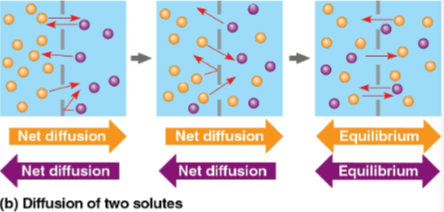
Concentration gradient
The region along which the density of a chemical substance increases or decreases
Substances diffuse down these, unaffected by the concentrations of other substances
Passive transport
Transport of substances that requires no cellular energy expidenture
Potential energy represented by concentration gradient
Rate of diffusion depends on membrane permeability
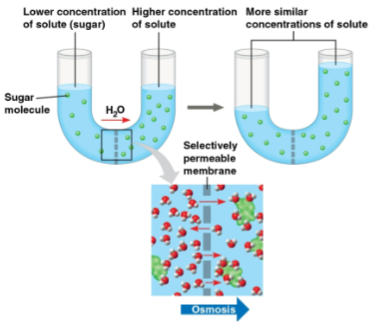
Osmosis
The diffusion of free water across a selectively permeable membrane
Water molecules diffuse to regions of lower to higher solute concentration until equilibrium is reached
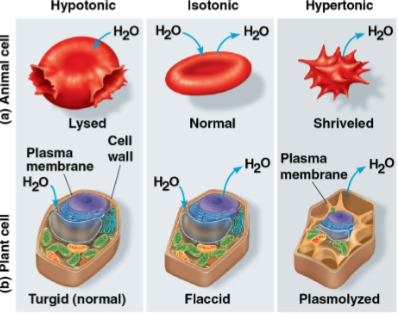
Tonicity
The ability of a surrounding solution to cause a cell to gain or lose water
Depends on the concentration of solutes that cannot cross the membrane relative to the inside of the cell
Water will be attracted to higher concentrations of solute, which can lead to water going in or out of each cell
Extreme hypo- or hypertonicity can cause problems for cells without walls
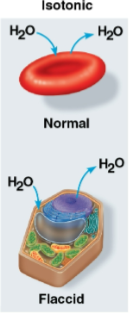
Isotonic
Solution where solute concnetration in a solution is the same as that inside the cell
No net water movement is done across the membrane
Volume remains stable in this solution
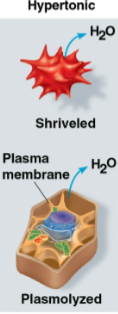
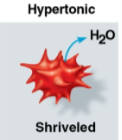
Hypertonic
Solution where the solute concentration is greater than that inside the cell
Net water movement goes outside of the cell to the solution
Cells may shrivel and die as they lose water
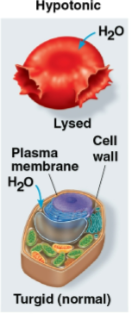
Hypotonic
Solution where the solute concentration is less than that inside the cell
Net water movement goes to the inside of the cell from the solution
Cells may swell and lyse (burst) as they gain water
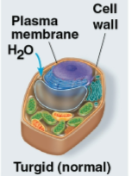
Turgid
Term for a normal plant cell in a hypotonic environment that contains more water
These cells swell until the inelastic wall exert a pressure on the cell, signaling a firm and healthy state
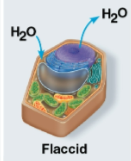
Flaccid
Term for a plant cell in an isotonic environment with less water
No net movement of water occurs, and plant cells will become limp causing wilting
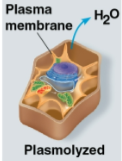
Plasmolyzed
Term for a plant cell in a hypertonic environment with low levels of water
Water moves out of the plant cell, causing the membrane to pull away from the cell wall causing potential death
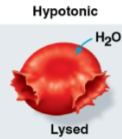
Lysed
Term for an animal cell in a hypotonic environment with too much water
Shriveled
Term for an animal cell in a hypertonic environment with too little water
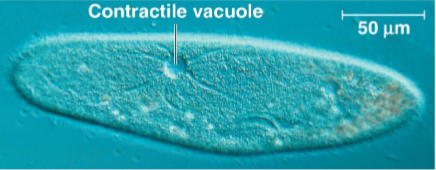
Osmoregulation
The control of solute concentration and water balance
Paramecium have a contractile vacuole to pump excess water out of the cell due to their hypotonic environment
Bacteria and archea in hypersaline environments have mechanisms to retain water
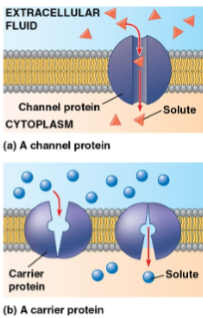
Facilitated diffusion
Diffusion where transport proteins speed up the passive movement of molecules across the plasma membrane
Does not require energy
Includes transport (channel, carrier) proteins
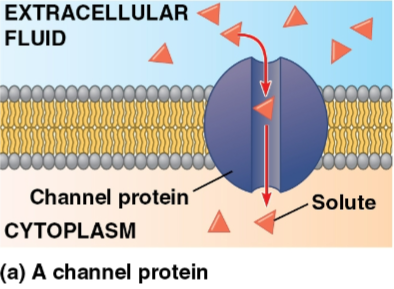
Channel proteins
Transport proteins that provide a corridor for a specific molecule or ion to cross the membrane
Aquaporin
Channel protein that facilitates the diffusion of water
Ion channel
Channel protein that facilitates the transport of ions
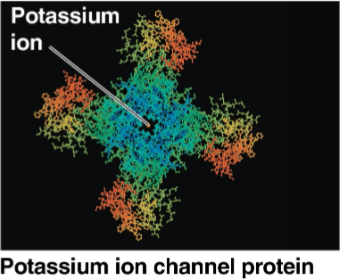
Gated channels
Ion channels that open or close in response to a stimulus
Potassium ion channels open in response to electrical stimulus in nerve cells
Others open in response to chemical stimulus, or the binding of a specific substance to the protein
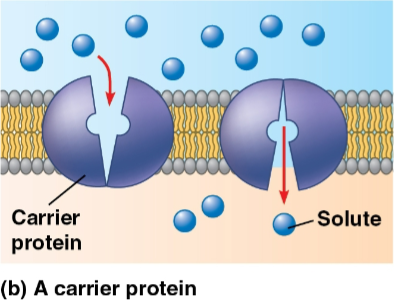
Carrier proteins
Proteins that undergo a substle shape change that moves the solute-binding site across the membrane
Can be triggered by the binding and release of the transported molecule
Substances are moved down the concentration gradient with no energy input required