Genetics PPT
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
Large bundled lengths of DNA that’s wrapped around proteins, that contain many genes.
What is a pedigree
A pedigree chart is a diagram that shows the occurrence of certain traits through different generations of a family, most commonly for humans, show dogs, and race horses.
What does it mean when a gene is recessive?
It’s being masked by a dominant gene.
If a dog is white (recessive), what will its genes be?
ww
If someone had a brown haired mother (D) and blonde haired dad (d) , what would their kids genes be?
DD or Dd
If two parents have an autosomal dominant trait, what can you say about the parents?
When a trait is autosomal dominant, only one parent needs to have an altered gene to pass it on. Half of the children of a parent with an autosomal trait will get that trait. Only changes that occur in the DNA of the sperm or egg can be passed on to children from their parents.
If two parents do NOT have an autosomal recessive trait, what can you say about their children?
If both parents do not have the autosomal recessive trait, their children may or may not carry the gene for it, depending on whether one or both parents are carriers. However, none of the children will express the trait unless both parents are carriers and pass on the recessive allele (aa).
If two parents have an autosomal recessive trait, what can you say about their children?
If you are born to parents who both carry the same autosomal recessive gene, you have a 25% (1 in 4) chance of inheriting the variant gene from both parents and developing the disease.
Can autosomal recessive traits skip generations?
Autosomal recessive diseases typically affect both females and males equally. Autosomal recessive patterns manifest by skipping generations as the affected are usually children of unaffected carriers.
Where are chromosomes found?
The nucleus of the cell.
Where is DNA located?
Packed tightly within each chromosome.
What are homologous chromosomes?
Pairs of chromosomes which share similar size, centromere location, banding pattern etc
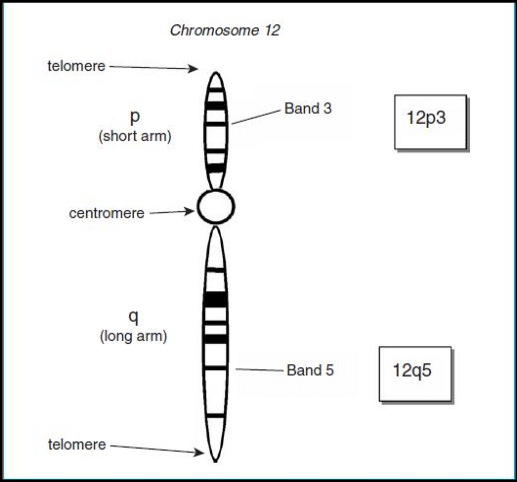
What does the structure of a chromosome look like?
What is a karyotype?
A “picture” of the complete set of chromosomes in a nucleus (they usually use white blood cells), which are arranged from largest to smallest, usually in homologous pairs.
Whats the function of a karyotype?
Can be used to determine sex by presence of X or Y chromosomes. Or, Missing, extra or malformed chromosomes can indicate genetic issues (you will need to know the issues we covered: Down, Klinefelter, XYY, Edwards and Turner syndromes)
How many pairs of chromosomes do humans have?
In humans there are 22 pairs of autosomes and one pair of sex chromosomes (a total of 46 chromosomes or 23 pairs).
What is DNA?
DNA is a nucleic acid, consisting of nucleotides
What is a nucleotide made up of?
Each nucleotide is made up of three parts: a 5-carbon sugar called deoxyribose, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
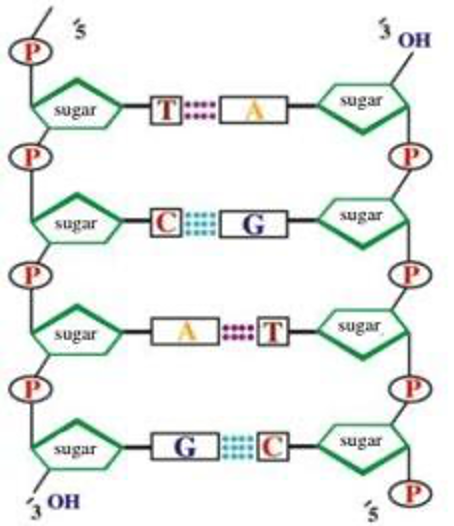
What makes up DNA structure?
The phosphate and sugar make up the sides of the ladder and the nitrogenous bases make up the rungs of the ladder.
What pairs up in the DNA?
T (Thymine) always pairs with A (Adenine) and G (Guanine) always pairs with C (Cytosine)
What makes up protiens?
Amino acids are what make up proteins (think of a long strand of beads being a protein and each bead is a different amino acid)
How many body chromosomes do humans contain?
46
There are 4 different bases in DNA called:
•Guanine (G)
•Cytosine (C)
•Adenine (A)
•Thymine (T)
Complementary base pairing: + What pairs together
When 2 strands of DNA combine, C & G join together and A & T join together.
Mitosis
this is when 1 body cell divides to make 2 identical copies of itself. Occurs every day and is needed for repair and growth.
Meiosis
when cells divide to form sex cells (sperm/egg cells). The copies made are not identical to the original cells.
Why is it important to duplicate the DNA before division?
the daughter cells would have disrupted normal cellular function, potentially causing diseases or cell death.
diploid cell
containing two complete sets of chromosomes/ 2 sets of each gene
Haploid cell
contains a single set of chromosomes, half the amount of DNA compared to a diploid cell, and is typically found in gametes (sex cells) like sperm and egg cells
centromere
a constricted region on a chromosome that holds sister chromatids together during cell division
Why are you not genetically identical to your siblings
random genetic combinations during the formation of sperm and egg cells,
gametes
reproductive cell of a male and female. sperm and egg cells.
There are 2 major types of mutations
•Point mutations
•Chromosomal mutations
A factor that triggers mutations in cells is called
a mutagen
Things that trigger a mutagen
Radiation, such as ultraviolet radiation, nuclear radiation and X-rays
Chemical substances, such as asbestos, tobacco and benzene (which used to be common in pesticides)
Infectious agents, such as human papillomavirus (HPV).
germline mutations.
Mutations in germline cells can be passed onto the next generations. EG Germline cells are cells that divide into sperm and egg cells in meiosis.
somatic mutations.
Mutations in body (somatic) cells are not passed onto offspring. These are called
Positive Consequence Of Mutations
•Variations that increase the chances of the organism surviving and reproducing, so therefore passing genetic information onto the next generation.

Negative Consequences Of Mutations
May cause death of the organism or issues that prevent it from passing on genetic information to the next generation
Neutral Consequences of Mutations
Do not kill the organism or increase the chances of the genetics being passed on to the next generation, but these variations accumulate in the gene pool and lead to genetic variation in a population.
Each point mutation
Occur when there is a change to one of the nitrogenous bases (A, T, C, G). This could then in-turn change the order of the amino acids in a protein.
•Each point mutation usually affects only 1 gene.
•There are 3 types:
•Substitution
•Insertion
Deletion
Substitution
•Occurs when one nucleotide is swapped for another ( a change of base) -for example, ATG becomes ACG.
Insertion
Occurs when an extra nucleotide (or more than one) is inserted into the DNA sequence (for example, ATG becomes ATCG).
Deletion
•Occurs when a nucleotide is deleted from the sequence (for example, ATG becomes AG).Occurs when a nucleotide is deleted from the sequence (for example, ATG becomes AG).
One chromosomal mutation affects
multiple genes. As chromosomes occur as homologous pairs, if one chromosome is abnormal the other is still likely to be normal (see diagram).
Four Types of Chromosomal Mutations
•Duplication - part of chromosome is copied, resulting in duplicate sections (potentially increases gene expression).
•Inversion - a segment of a chromosome is removed and then replaced within the chromosome in reverse order.
•Deletion - a portion of the chromosome is removed (along with any genes contained within this segment).
•Insertion – a portion of one chromosome is removed and then replaced in a second chromosome.
•Translocation - segments of two chromosomes are exchanged (may interrupt gene sequences).
What Pairs Of Chromosomes Do Humans Have
Humans have 1 pair of sex chromosomes (XX or XY) and 22 pairs of autosomes (chromosomes that are not sex chromosomes). Total = 46 chromosomes for humans.
Female chromosome pairs
two homologous paired X chromosomes (XX)
Male chromosome pairs

Males have a mismatched pair with a smaller Y chromosome (XY)
Different species have
different chromosome numbers
non-disjunction
If there is a failure to separate homologous chromosomes during sperm and egg formation, this can result in one too many or one too few chromosomes in the gamete.

Trisomy
scientific term for having an extra copy of a chromosome
Monosomy
1 copy
•Non-disjunctions on other chromosomes nearly always lead to
death of embryo or child before adulthood because too many genes are affected.