Magnetism and Magnetic Materials
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Non-Comprehensive flashcards with all the important formulae you need for JEE Mains and IAT (and also NCERT). Use only Answer with Definition. Question mode: only flashcards. I may add to this deck to make it more comprehensive with all necessary concepts in the future!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
What is the key difference between electric field lines and magnetic field lines?
Magnetic field lines are continue closed curves, while electric field lines are not closed curves and are discontinuous.
What is the formula for force experienced by a magnetic dipole in an external magnetic field?
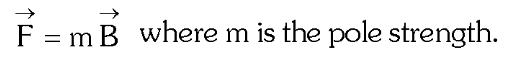
What is the formula for force of attraction between two magnetic poles of strength m_1 and m_2?
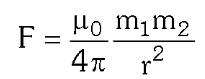
What is the formula for the magnetic field strength produced by a magnetic pole of strength m?
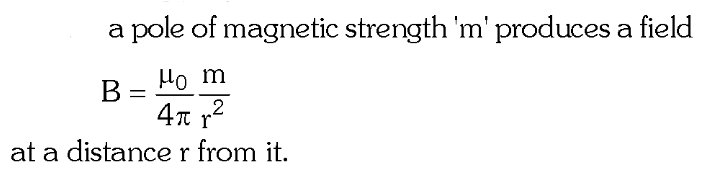
What is the SI unit of magnetic pole strength?
A-m (ampere-metre)
The axis of a dipole is the line joining the ____ pole to the ____ pole of the dipole.
(north, south)
The axis of a dipole is the line joining the south pole to the north pole of the dipole.
A point lying on the axis of a dipole is called ____-on position or tangent ____ position.
A point lying on the axis of a dipole is called end-on position or tangent A position.
A point lying on the perpendicular bisector of a dipole is called ____-on position or tangent ____ position.
A point lying on the perpendicular bisector of a dipole is called broadside-on position or tangent B position.
A current-carrying loop of area A with number of turns N can be represented with a magnetic dipole with dipole moment = ?
M=NiA=md
where
i is the current flowing through it
m is pole strength
d is distance between poles
How can a solenoid be represented by a bar magnet with north and south poles only at its ends?
Each coil is considered as a loop, and the north and south poles of each successive loop cancel each other out, so the solenoid can be considered as a bar magnet with north and south poles at its ends
What is the relation between the edge-to-edge dimension (geometric length) and the pole-to-pole dimension (magnetic length) in a bar magnet?
\dfrac{l_p}{l_e}\approx 0.84
where l_p is the pole-to-pole dimension (magnetic length) and l_e is the edge-to-edge dimension (geometric length)
Why is Gauss’ Law for a bar magnet always 0?
\oint \overrightarrow{B}\cdot\overrightarrow{ds}=0
This is because monopoles cannot exist in bar magnets
If the magnetic length of a bar magnet =2l, then what is the magnetic moment of the bar magnet?
M=2ml where m is the magnetic strength of the bar magnet
Magnetic field outside a bar magnet goes from _____ to _____, and magnetic field inside a bar magnet goes from _____ to _____.
(north, south)
Magnetic field outside a bar magnet goes from north to south, and magnetic field inside a bar magnet goes from south to north.
What is the formula for torque on a bar magnet? (both scalar and vector forms)
\tau = 2mBl\sin\theta = MB\sin\theta
\tau=\overrightarrow{M}\times\overrightarrow{B}
where \overrightarrow{M} is the magnetic moment of the bar magnet
What is the formula for work done in rotating a bar magnet from angle \theta_1 to \theta_2 in a magnetic field B?
W=MB\cos (\theta_1 -\theta_2)
where M is the value of magnetic moment of the bar magnet.
What is the formula for potential energy stored in a bar magnet at any angle \theta if potential energy at 90^{\circ}=0? (scalar and vector forms)
(\theta is the angle between the direction of magnetic field and the axis of the bar magnet)
U(\theta)=-MB\cos\theta=-\overrightarrow{M}\cdot\overrightarrow{B}
What is the SI unit of magnetic moment? How many ways can it be represented?
A\cdot m² = N\cdot m/T = J/T
where
A is ampere
m is metre
N is newton
T is tesla
J is joule
How would you approach questions where you need to find the magnetic field at any point due to a bar magnet?
By taking vector sum of fields created by the two poles of the bar magnet.
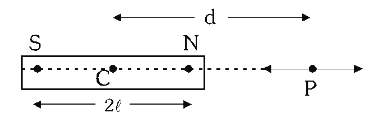
What is the formula for finding the magnitude of magnetic field at a point along the longitudinal axis of a bar magnet?
B=\dfrac{\mu_0}{4\pi}\dfrac{2M}{d³} or B=\dfrac{2kM}{d³)
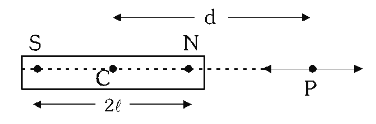
What is the formula for finding the magnetic potential at a point along the longitudinal axis of a bar magnet?
B=\dfrac{2kM}{d²}
What is the direction of the magnetic field at a point along the longitudinal axis of a bar magnet, with respect to the direction of magnetic dipole moment?
They are in the same direciton
(south to north)
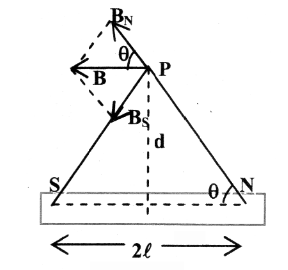
What is the formula for finding the magnitude of the magnetic field at a point on the perpendicular bisector of a bar magnet?
B=\dfrac{kM}{d³}
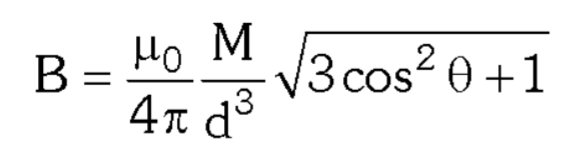
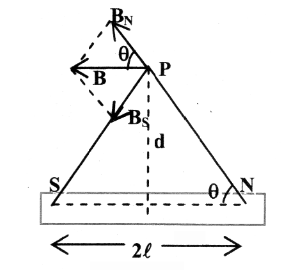
What is the direction of magnetic field at a point along the perpendicular bisector of a bar magnet, with respect to the direction of magnetic dipole moment?
They are in opposite directions
magnetic field: north to south
magnetic dipole moment: south to north
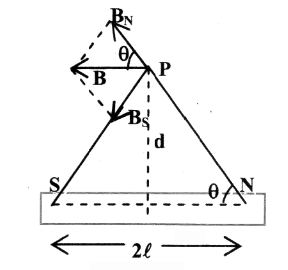
What is the magnetic potential at a point on the perpendicular bisector of a bar magnet?
0
What is the formula for finding the magnitude of magnetic field at any point in the vicinity of a bar magnet?
B=\dfrac{\mu_0}{4\pi}\dfrac{M}{d^3}\sqrt{3\cos^2\theta+1}=\dfrac{kM}{d^3}\sqrt{3\cos^2\theta+1}
What is the formula for finding the magnetic potential at any point in the vicinity of a bar magnet?
B=\dfrac{\mu_0}{4\pi}\dfrac{2M\cos\theta}{d²} where \theta is the angle between the magnetic dipole moment and the position vector of that point.
What is Magnetising Field, or Magnetic Intensity? What is the formula? What is the unit?
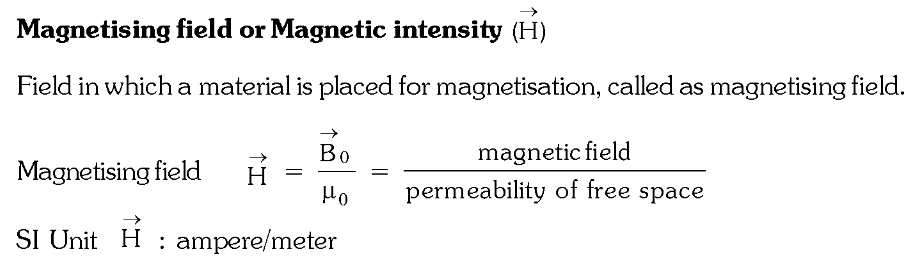
What is Intensity of Magnetisation? What is the formula? What is the unit?
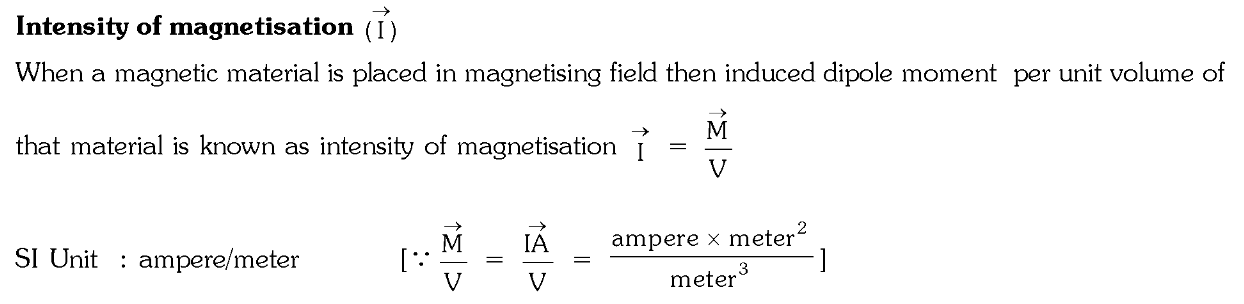
What are the two types of magnetic moments present in atoms?
Magnetic moment due to revolution of electrons
Magnetic moment due to spin of electrons
What is the total magnetic moment in an atom?
\overrightarrow{M_{\text{atom}}}=\overrightarrow{M_R}+\overrightarrow{M_S}
where \overrightarrow{M_R} is the magnetic moment due to revolution and \overrightarrow{M_S} is the magnetic moment due to spin of electrons
What is the cause of magnetism in Diamagnetic Materials?
only orbital motion of electrons
What is the cause of magnetism in Paramagnetic Materials?
only spin motion of electrons
What is the cause of magnetism in Ferromagnetic Materials?
formation of domains
What are domains in Ferromagnetic Materials?
A domain is a small volume in which a large number of atoms are aligned in the same direction.
What is the behaviour of a Diamagnetic Material in an external magnetic field?
poor magnetisation in the opposite direction
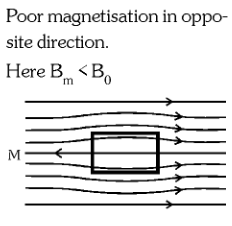
What is the behaviour of a Paramagnetic Material in an external magnetic field?
poor magnetisation in the same direction
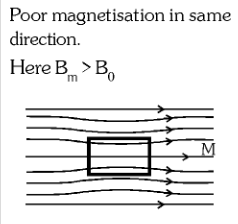
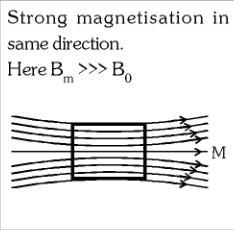
What is the behaviour of a Ferromagnetic Material in an external magnetic field?
strong magnetisation in the same direction.
Match the following with Diamagnetic, Paramagnetic, and Ferromagnetic materials:
Atoms have a permanent magnetic moment which are randomly oriented
Atoms have permanent magnetic moment which are organised in domains
Atoms do not have any permanent magnetic moment.
Atoms have a permanent magnetic moment which are randomly oriented — Paramagnetic
Atoms have permanent magnetic moment which are organised in domains — Ferromagnetic
Atoms do not have any permanent magnetic moment. — Diamagnetic.
Which out of Diamagnetic, Paramagnetic, and Ferromagnetic materials show hysteresis?
Ferromagnetic materials
What is magnetic susceptibility? Is it scalar or vector? What is the formula?
Magnetic Susceptibility is the ease with which a magnetic material can be magnetised. It is a scalar.
\chi_m=\frac1H
What is the relationship between magnetic permeability and magnetic susceptibility?
\mu_r=1+\chi_m
What is the relationship between magnetic susceptibility and absolute temperature of a material?
\chi_m \propto \frac{1}{T}
What is the significance of Curie temperature?
At Curie temperature, ferromagnetic substances turn into paramagnetic substances
What is Hysteresis, actually?
The lagging of intensity of magnetisation (I) or magnetic field (also called magnetic induction (B) behind magnetising field (H) , when a specimen of a magnetic substance is taken through a complete cycle of magnetisation is called hysteresis.
What is hysteresis loss?
The area of a hysteresis loop is equal to the energy loss per cycle of magnetisation-and-demagnetisation per unit volume of that material (usually ferromagnetic material).