HBS 1.2.2 Makeup of a Muscle
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
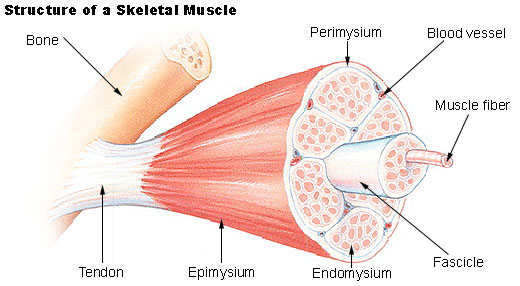
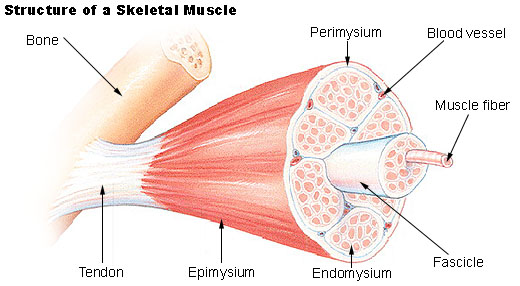
endomysium
The delicate connective tissue surrounding the individual muscular fibers within the smallest bundles.
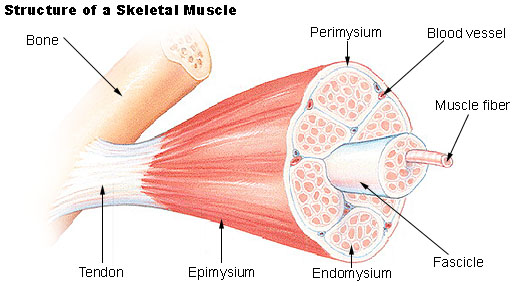
epimysium
The external connective-tissue sheath of a muscle.
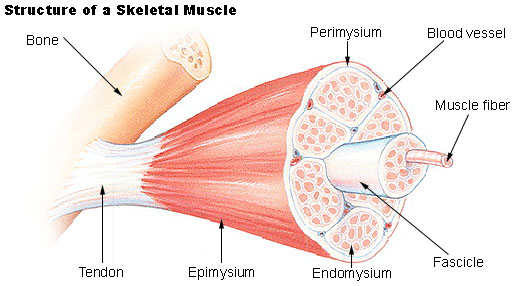
perimysium
The connective-tissue sheath that surrounds a muscle and forms sheaths for the bundles of muscle fibers.
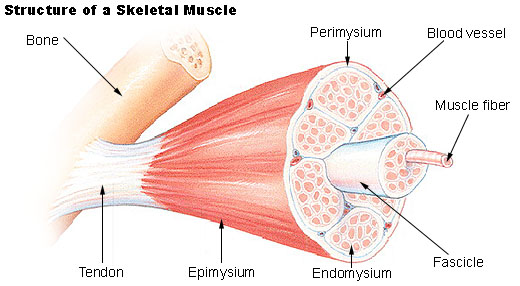
fascicle
A small bundle or cluster, especially of nerve or muscle fibers.
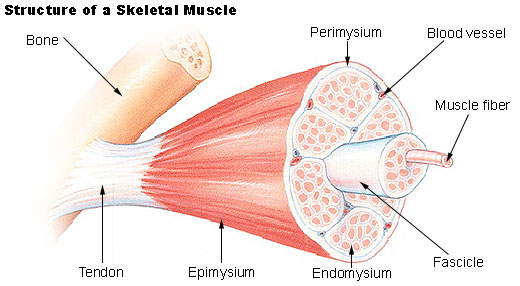
tendon
A flexible but inelastic cord of strong fibrous collagen tissue attaching a muscle to a bone.
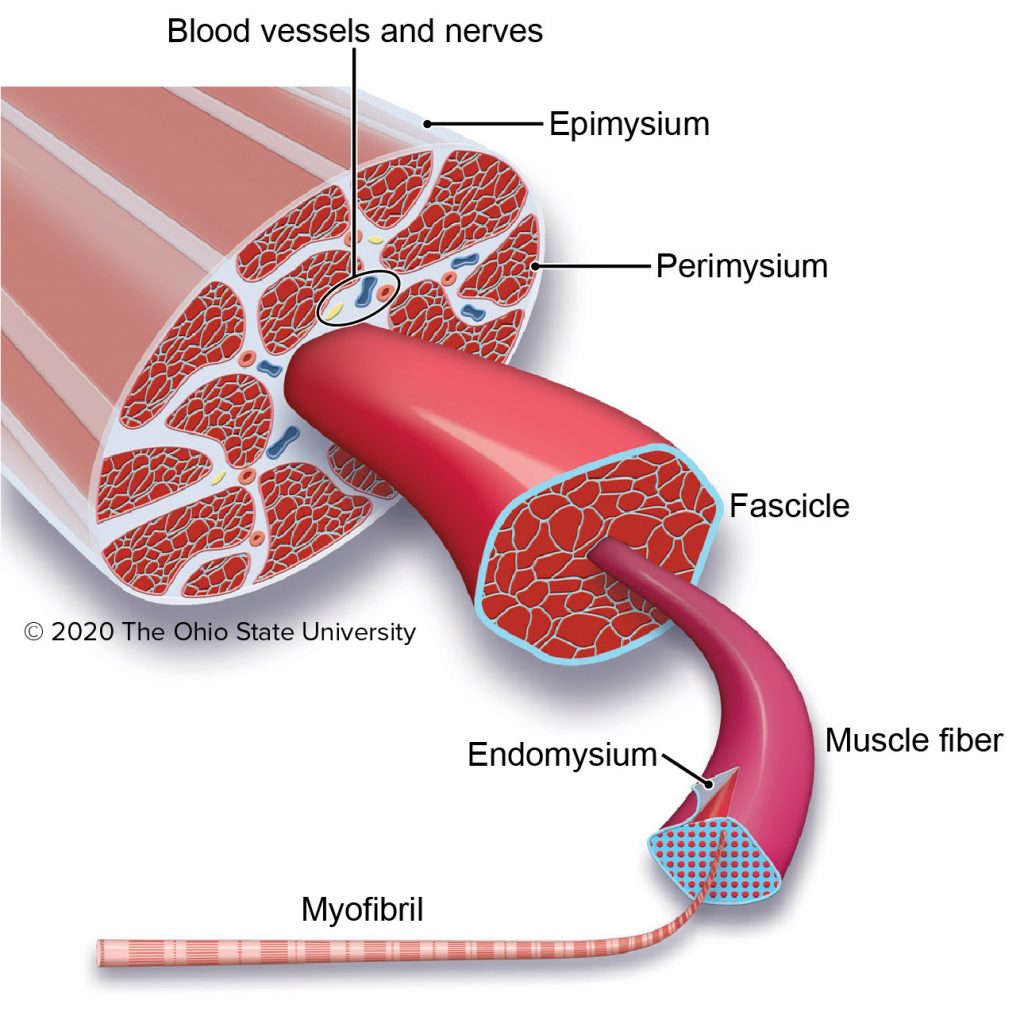
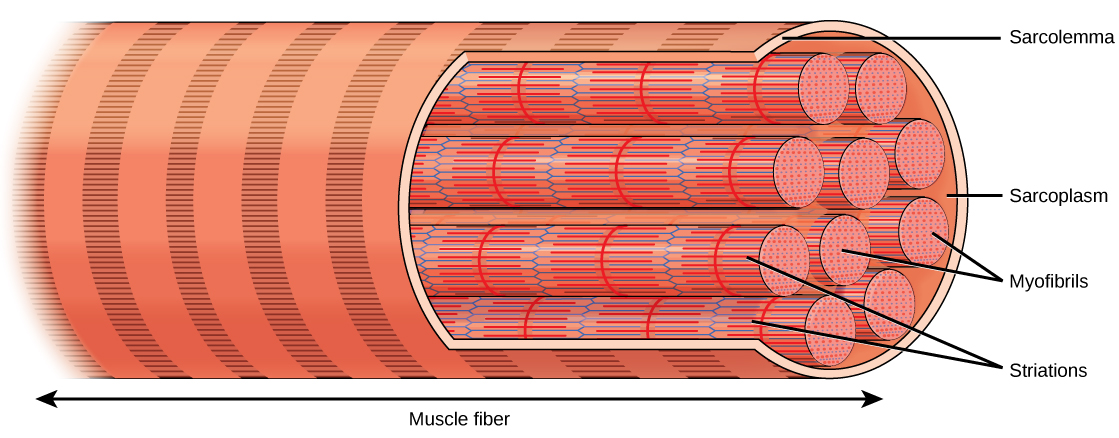
muscle cell/fiber
A specialized, elongated cell in muscle tissue responsible for generating force through contraction; it contains multiple myofibrils and plays a crucial role in body movement, stability, and various physiological processes.
myofibril
A threadlike structure, extending longitudinally through a muscle fiber (cell) consisting mainly of thick filaments (myosin) and thin filaments (actin, troponin, and tropomyosin).
sarcoplasmic reticulum
A specialized network of membrane-bound tubules within muscle cells (muscle fibers) that stores and regulates calcium ions (Ca2+), crucial for muscle contraction.
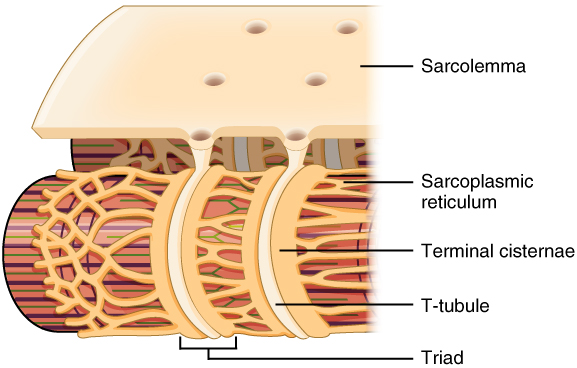
sarcoplasm
The cytoplasm of a muscle cell (muscle fiber) that surrounds myofibrils and contains various organelles, including the sarcoplasmic reticulum, and provides essential nutrients and energy for muscle function.
physiatrist
Medical specialist in non-surgical treatment of musculoskeletal and neurological conditions.
not a physician and cannot prescribe medications; they manage exercise programs aimed at relieving symptoms and improving function

physical therapist
Healthcare professional aiding physical function through exercises and therapy.
conducts treatment protocols that are prescribed by physiatrists and other physicians

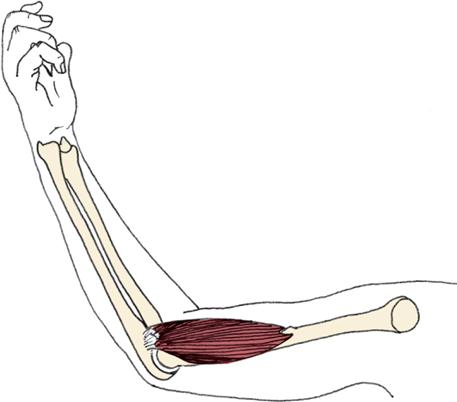
Muscle Rule #1
Muscles must have at least two attachments and must cross at least one joint.
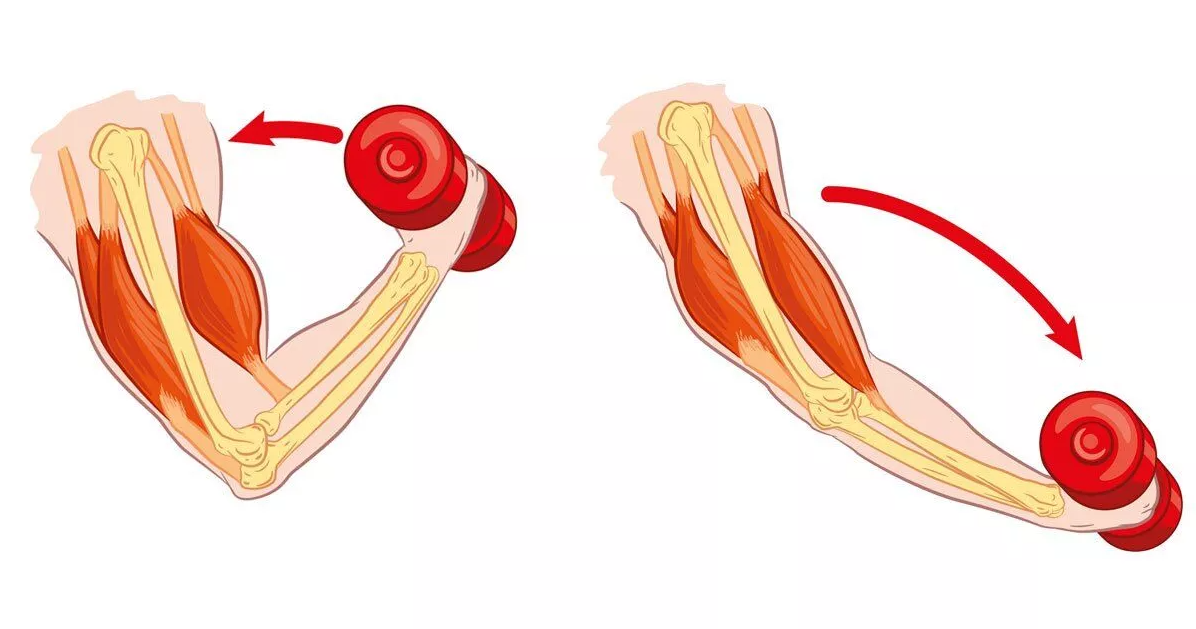
Muscle Rule #2
Muscles always “pull” and get shorter.
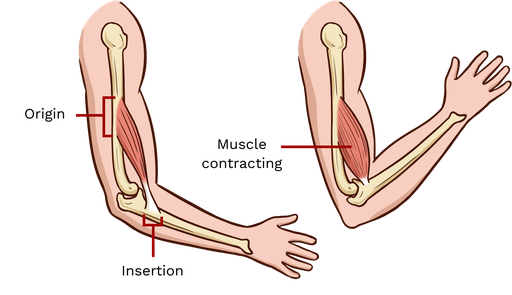
Muscle Rule #3
The attachment that moves is known as the insertion and the attachment that remains stationary is known as the origin.
Muscle Rule #4
Muscles that decrease the angle between ventral surfaces of the body are known as flexors. Muscles that increase the angle between ventral surfaces of the body are known as extensors.
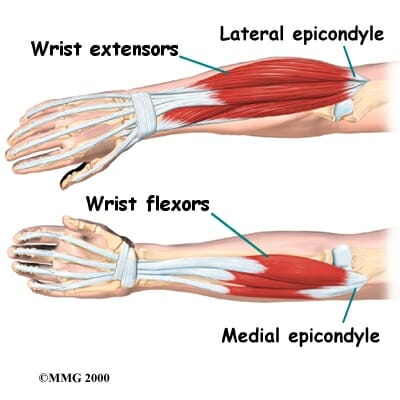
Muscle Rule #5
Muscles work in opposing pairs.
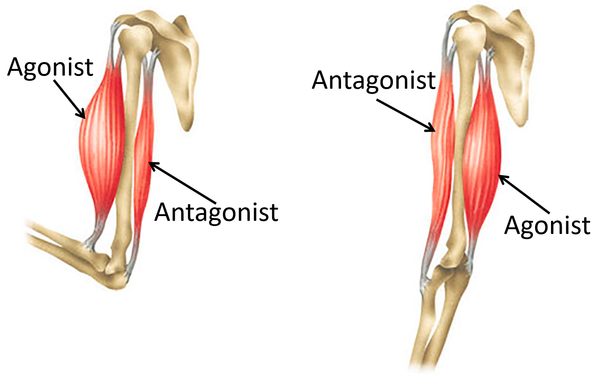
Muscle Rule #6
Muscle striations point to the attachments and show the direction of pull.
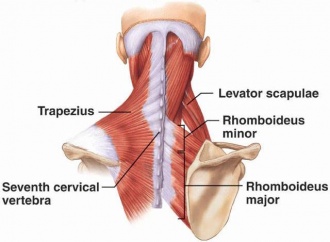
Trapezius and Rhomboid Minor
Named after shapes (trapezoid and rhombus) due to their shapes.
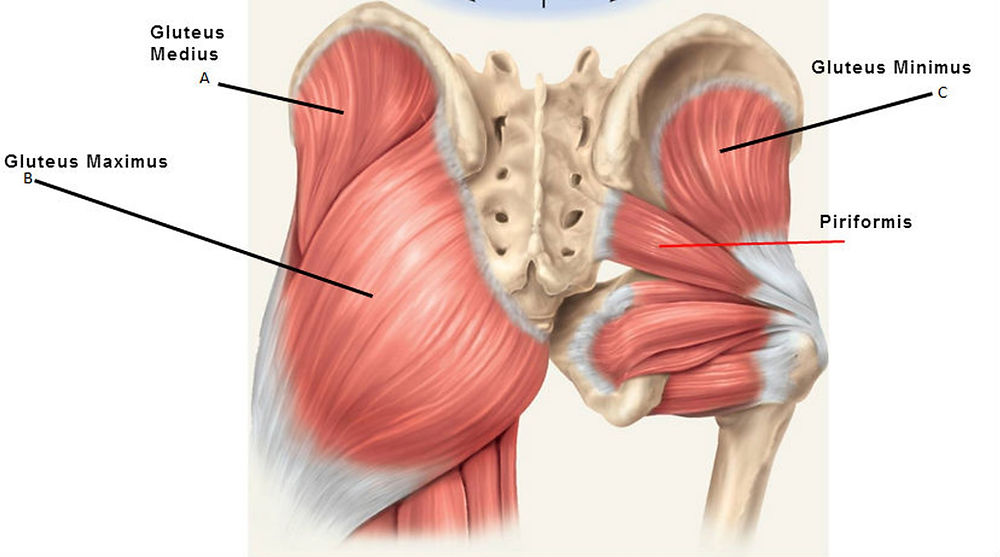
Gluteus Maximus and Gluteus Minimus
Named for their relative sizes within the gluteal muscles group (maximus being the largest, minimus being the smallest).
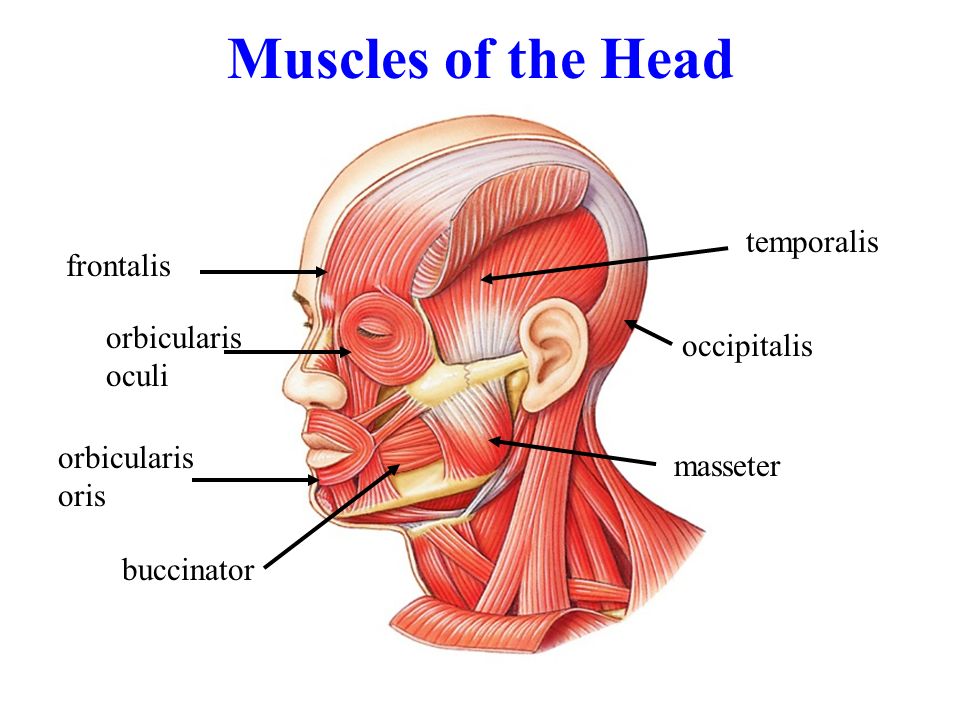
Frontalis and Temporalis
Named for their locations in the face (frontalis is in the forehead, temporalis is in the temporal region of the skull).
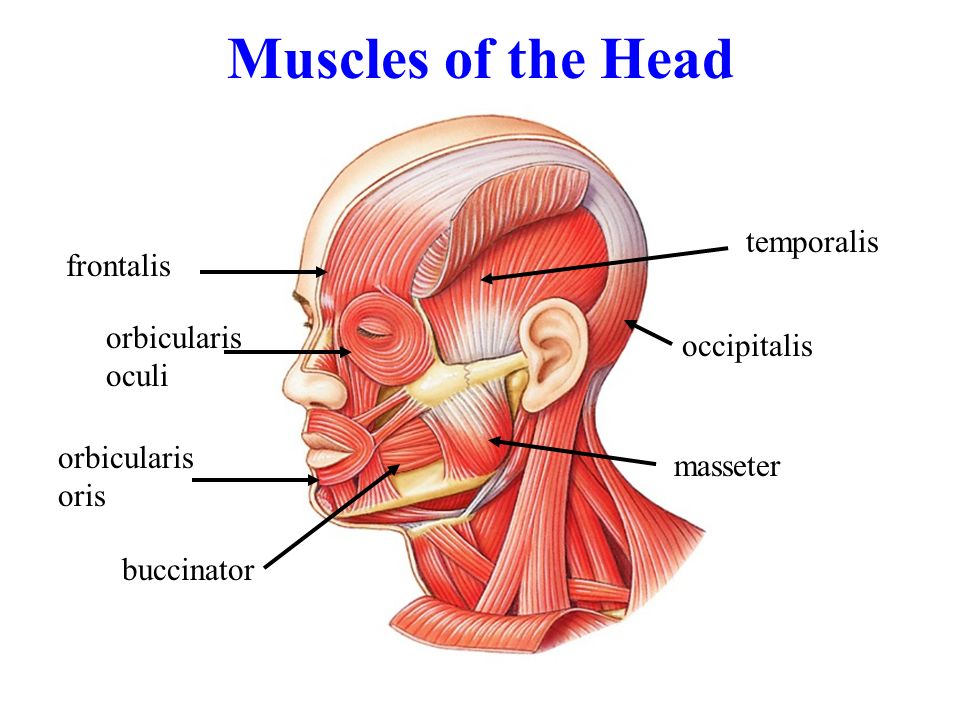
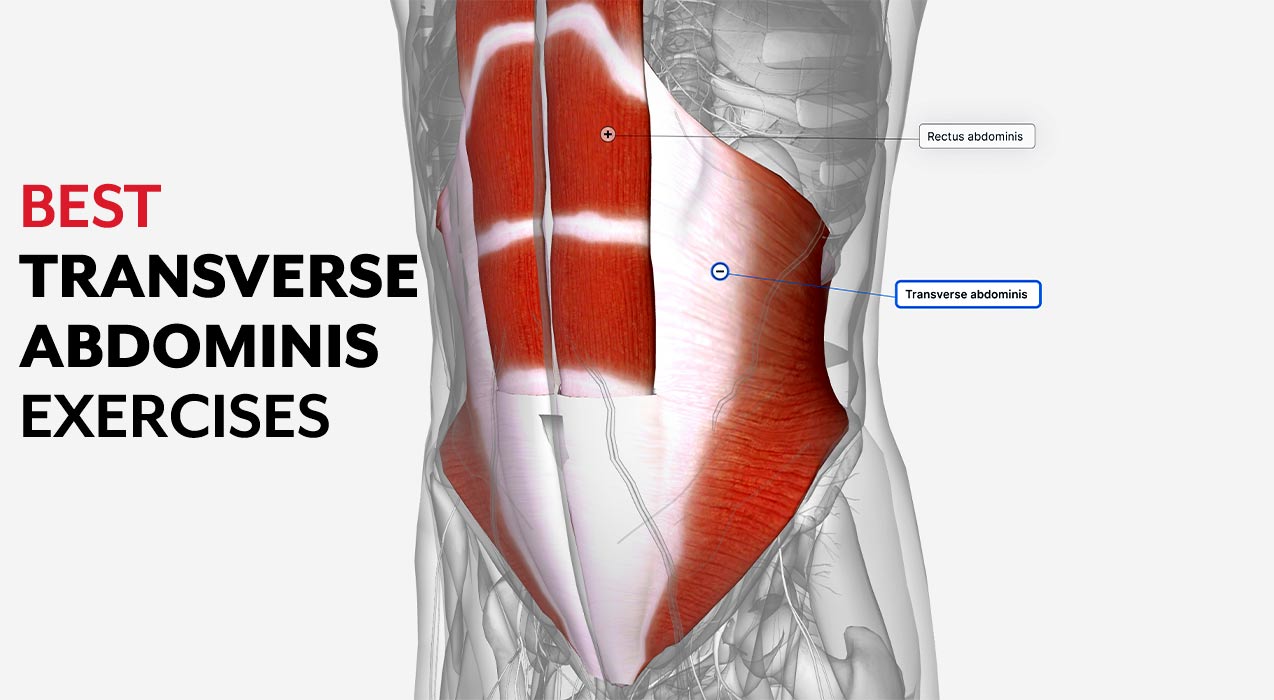
Orbicularis Oculi and Transverse Abdominis
Named for their shapes and locations (orbicularis oculi is circular and around the eye, while transverse abdominis runs transversely across the abdomen).
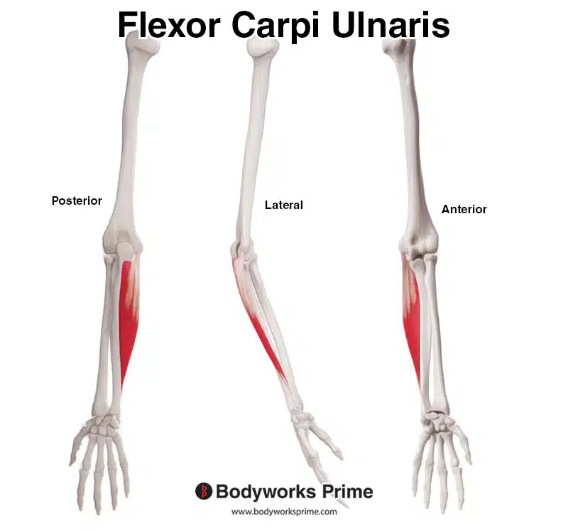
Flexor Carpi Ulnaris and Extensor Digitorum Longus
Named for their actions and locations (flexor carpi ulnaris flexes the wrist toward the ulna, extensor digitorum longus extends the digits/toes).
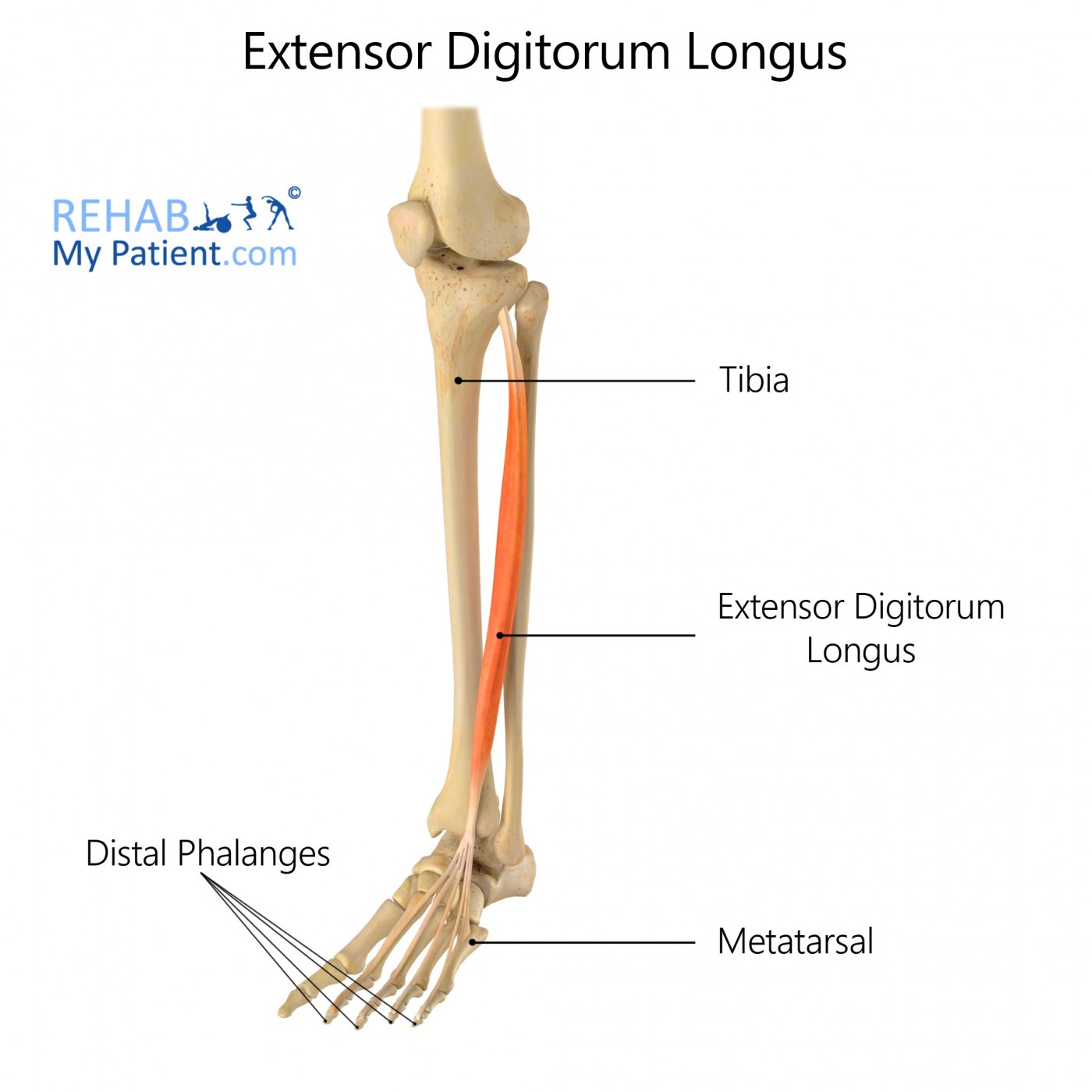
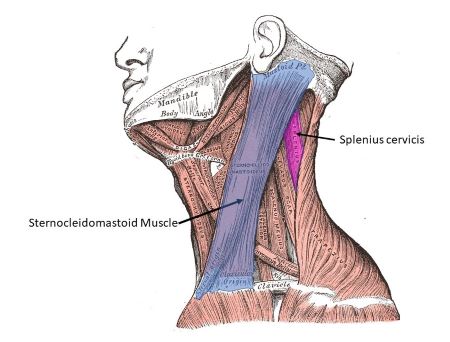
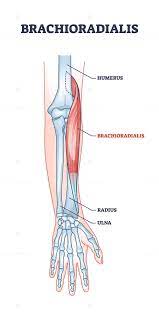
Sternocleidomastoid and Brachioradialis
Named for their locations and attachments (sternocleidomastoid attaches to the sternum, clavicle, and mastoid process of the temporal bone, brachioradialis attaches to the brachium and radius).
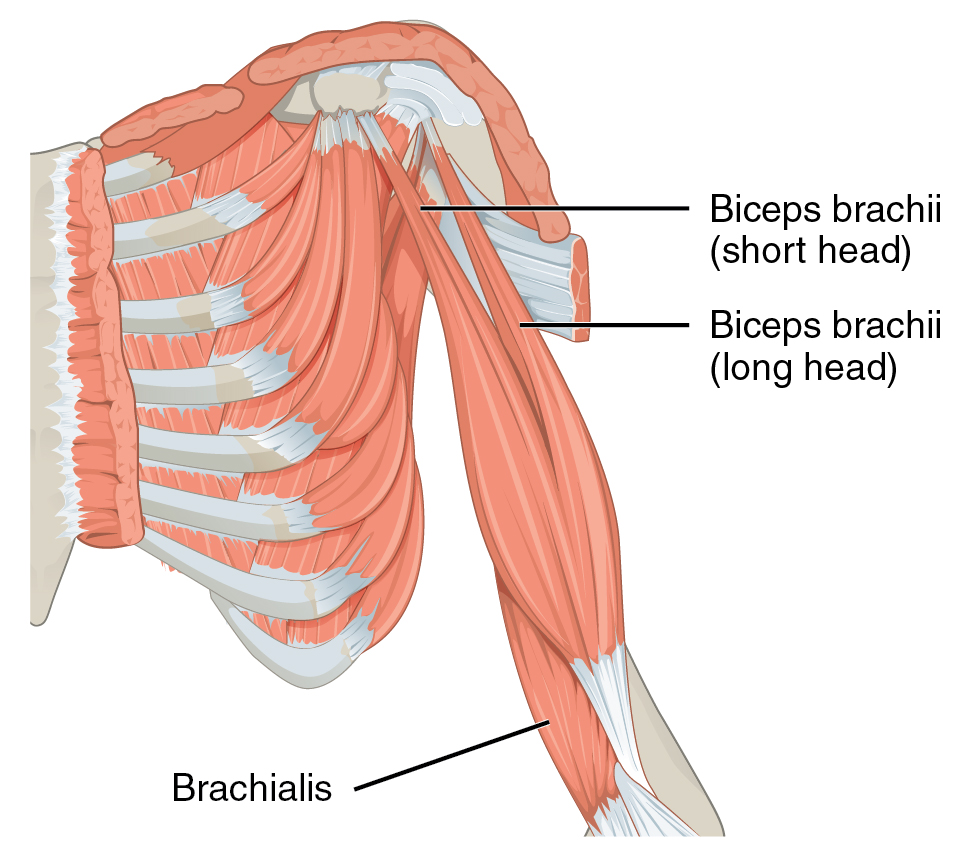
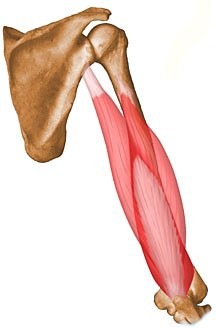
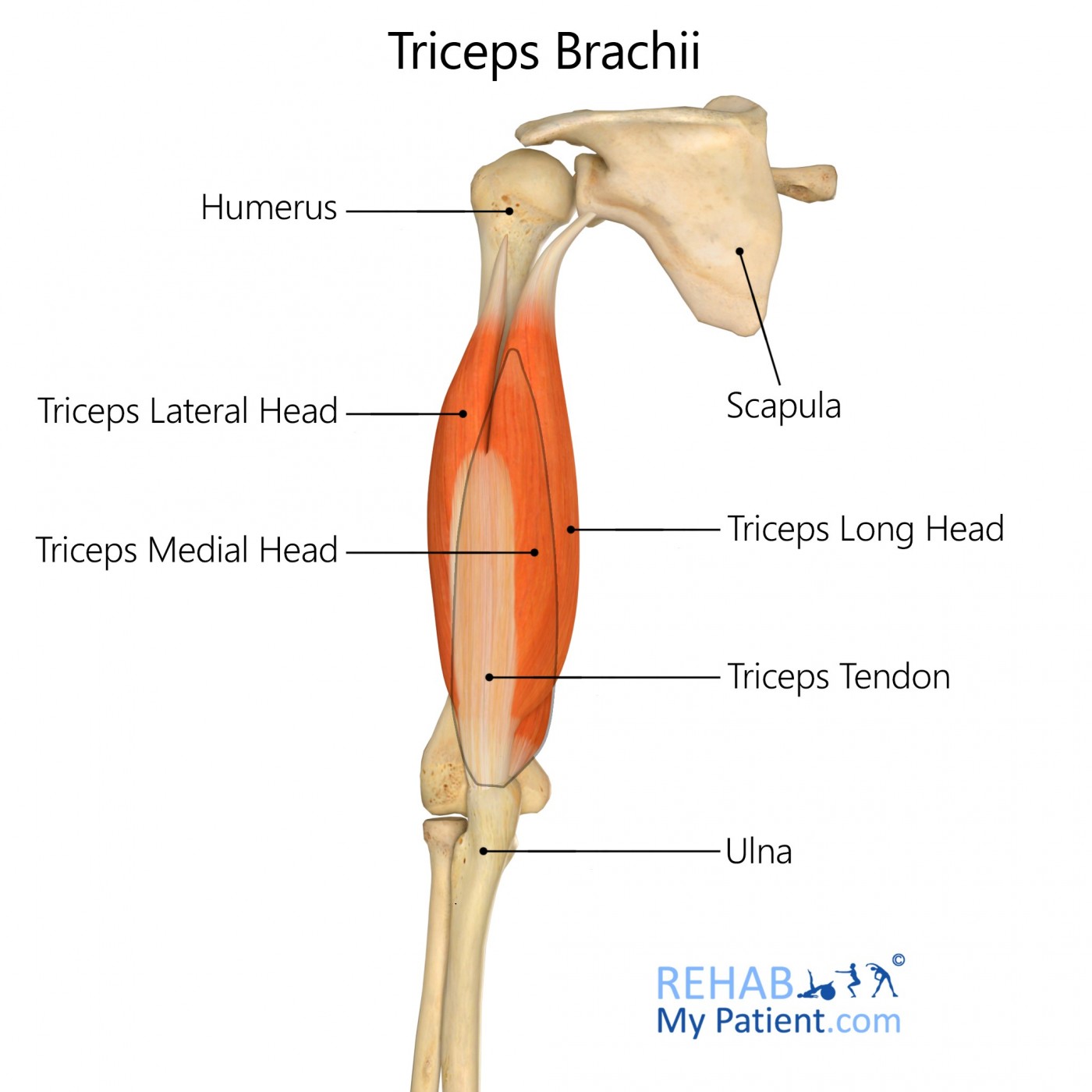
Biceps Brachii and Triceps Brachii
Named for the number of heads (biceps brachii has two heads, while triceps brachii has three heads).
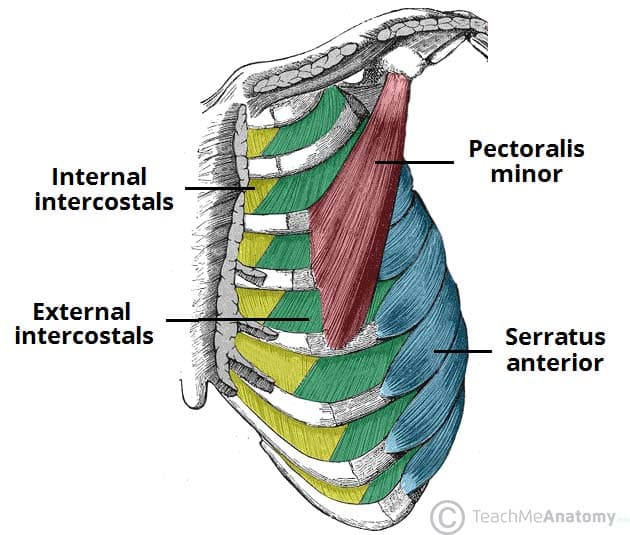
Intercostals
Origin: Between the ribs (intercostal spaces).
Insertion: Adjacent to and below the rib above.
Action: Contraction of intercostal muscles aids in the expansion and compression of the ribcage during breathing, facilitating inhalation and exhalation.
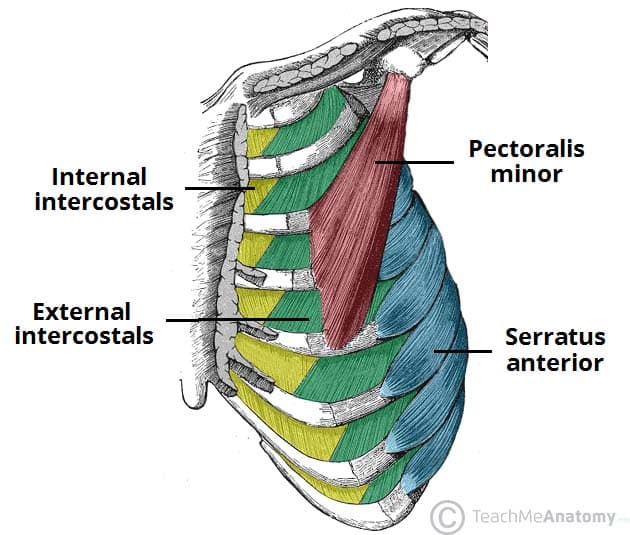
Pectoralis Minor
Origin: Third, fourth, and fifth ribs near their cartilages.
Insertion: Coracoid process of the scapula.
Action: Pulls the scapula forward and downward, contributing to movements like shoulder depression and protraction (forward movement).
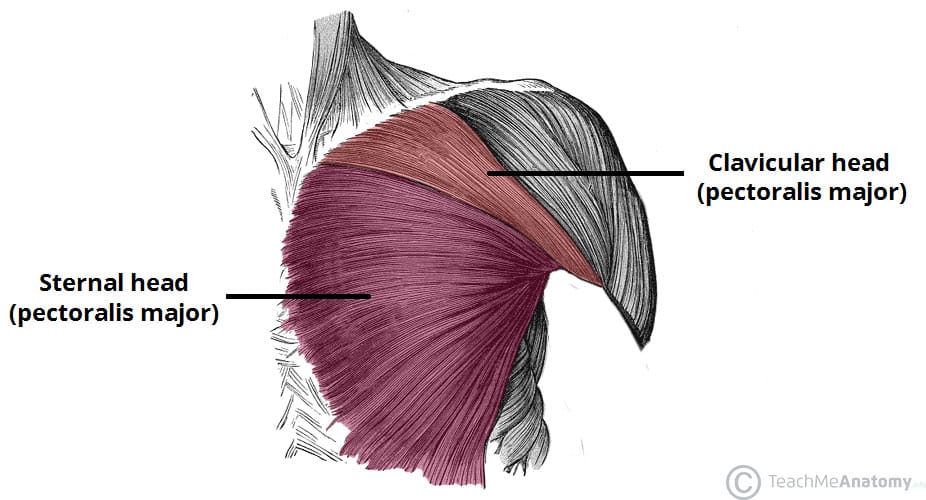
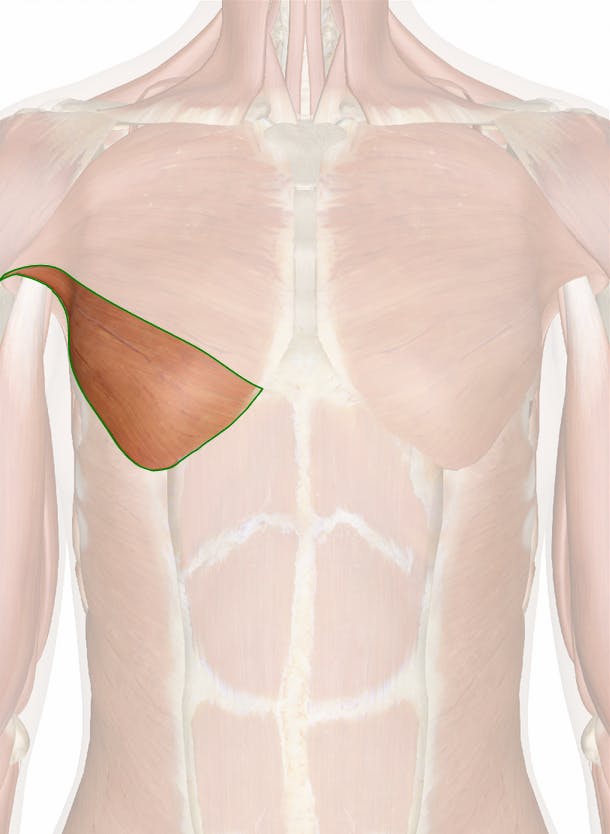
Pectoralis Major
sternal head
clavicular head
abdominal head
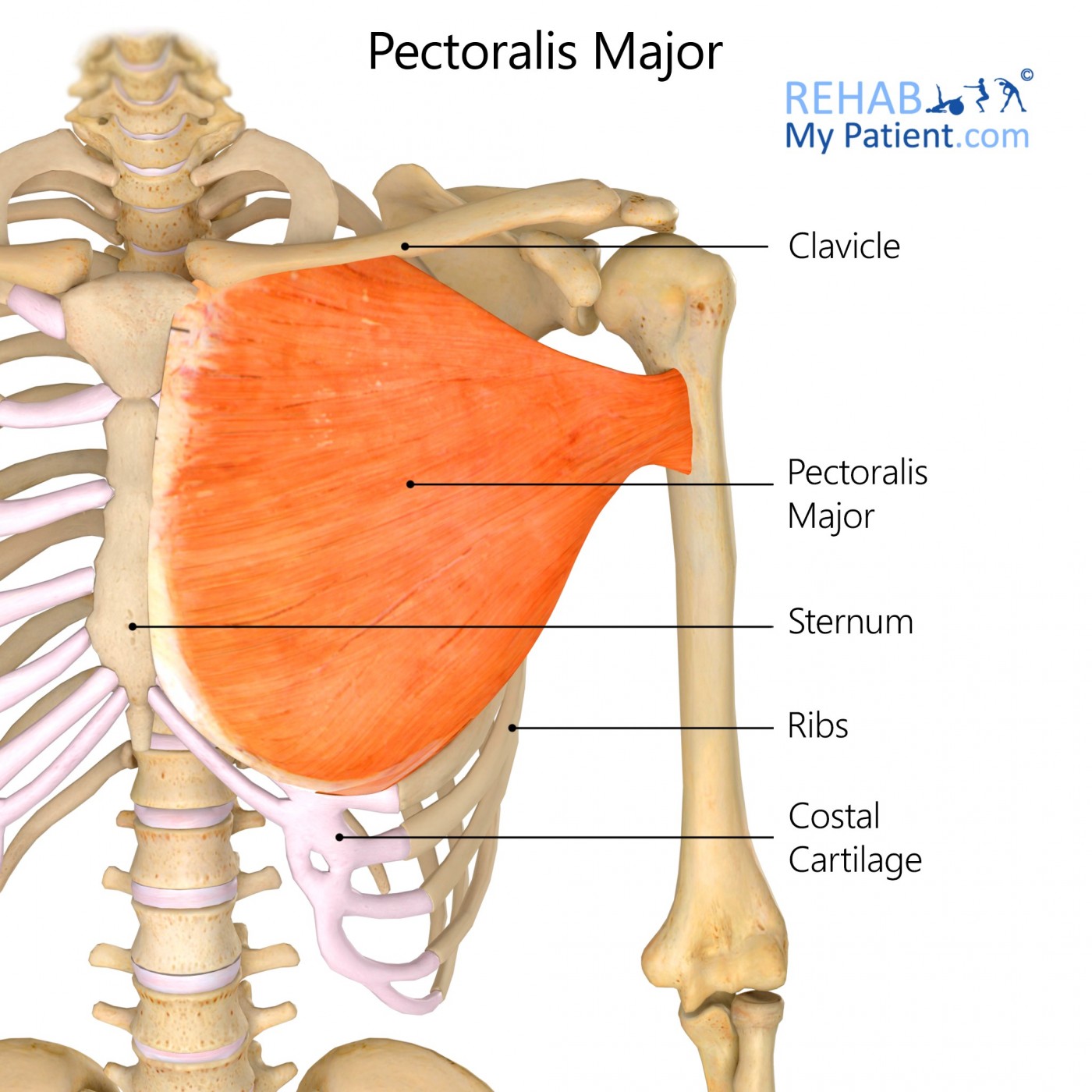
Sternal Head
Origin: Sternum (sternal part).
Insertion: Humerus (greater tubercle).
Action: Contraction of the sternal head contributes to arm flexion and medial rotation at the shoulder joint.
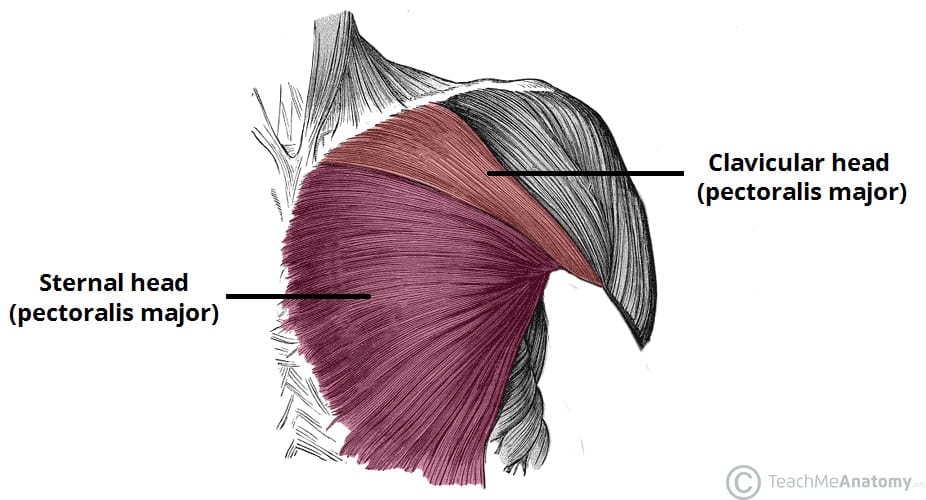
Clavicular Head
Origin: Clavicle (clavicular part).
Insertion: Humerus (greater tubercle).
Action: Contraction of the clavicular head also contributes to arm flexion and medial rotation at the shoulder joint.
Abdominal Head
Origin: External oblique muscle's aponeurosis.
Insertion: Humerus (greater tubercle).
Action: The abdominal head of the pectoralis major assists in arm flexion and medial rotation, especially when the arm is in a position of adduction (close to the body).
Common Types of Chest Muscle Injuries
Strain:
Cause: Overstretching or tearing of chest muscles due to sudden or excessive force, often during lifting or athletic activities.
Muscle Tear or Rupture
Cause: A severe strain or trauma, like a fall or lifting a heavy object, can lead to a partial or complete tear of chest muscle fibers.
Pectoral Tendonitis
Cause: Overuse or repetitive motions, such as excessive weightlifting, can lead to inflammation of the tendons connecting the pectoral muscles to the bones.