ch 3: biology and behavior
1/88
Earn XP
Description and Tags
my head hurts
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
nervous system
system that regulates the body’s responses to internal and external stimuli
central nervous and peripheral nervous
the nervous system consists of what
central nervous system
the brain and the spinal cord
peripheral nervous system
sensory and motor nerves that connect the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body
neurons
nerve cells that provide communication through the body (the building blocks)
receive info, carry info, and pass info to next neuron
the three basic tasks neurons perform
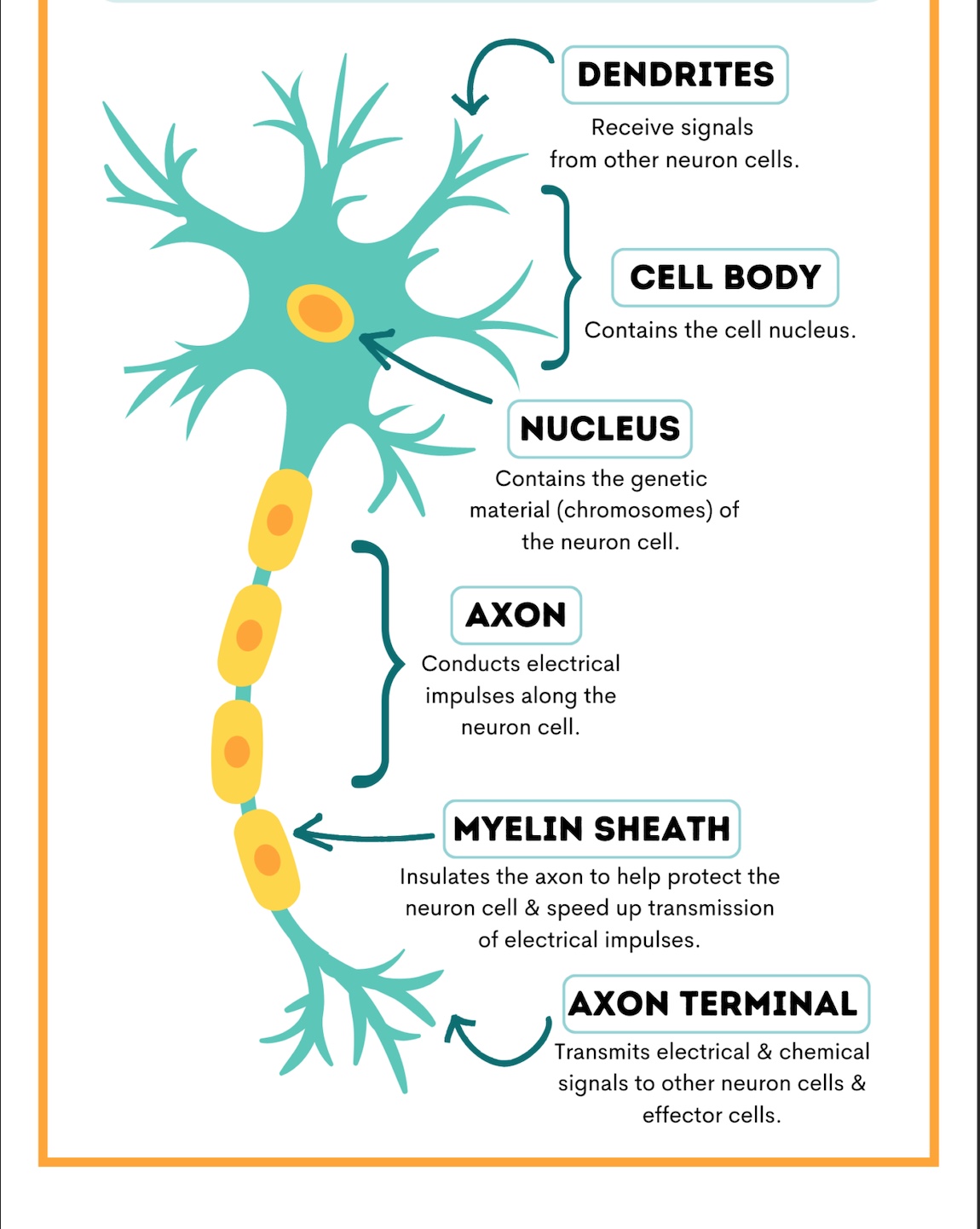
cell body, dendrites, axon, myelin
components of a neuron
cell body
produces energy for the cell
dendrites
receives impulses and conducts them to the cell body
axon
carries the messages away from the cell body
myelin
insulates and protects the axon
synapse, neurotransmitter
the communication process
synapse
junction between the axon terminals of one neuron and the dendrites of another neuron
neurotransmitter
chemical messenger that carries impulses across the synaptic gap across transmitters
action potential
electrical charge that travels down its axon
reuptake
the sending neuron reabsorbs the excess neurotransmitters form the synapse
somatic nervous and autonomic nervous
the peripheral nervous consists of two systems
somatic nervous system
communicate between central nervous system and all parts of the body; controls body’s skeletal muscles
autonomic nervous system
regulates body’s vital functions, controls glands and muscles of internal organs (heartbeat, breathing, digestion, blood pressure)
sympathetic nervous system
division of autonomic nervous that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations (fight or flight)
parasympathetic nervous system
division of ANS that calms the body, conserving its energy, bring body back to a relaxed state
endocrine system
one of the body’s two communication systems; a set of glands that produces hormones, chemical messengers that circulate the blood
hormones
chemical messengers produced by the endocrine glands and circulated in the blood; affects brain and other tissues of body
pituitary gland
called “master gland”; regulates growth and controls other endocrine glands
thyroid gland
regulates body’s metabolism by producing thyroxin
testes and ovaries
produce testosterone, estrogen, progesterone
adrenal gland
secretes hormones (epinephrine and norepinephrine) that arouse the body in times of stress
hindbrain, midbrain, and forebrain
three main sections of the brain
hindbrain
lower portion, controls vital functions, heart rate, respiration, balance, and most of brainstem
medulla, pons, cerebellum
three parts of the hindbrain
medulla
vital functions
pons
body movements, attention, sleep
cerebellum
balance and coordination; “the little brain”
midbrain
involved with vision and hearing
reticular activating system
attention, sleep, arousal
forebrain
forward most part of the brain that houses the following
limbic system
donut-shaped system of neural structures at border of brainstem and cerebrum, associated with emotions like fear, aggression, hunger; includes hippocampus
thalamus, hypothalamus, amygdala, hippocampus
four parts of the limbic system
thalamus
relay station for sensory information
hypothalamus
part of limbic system that lies below the thalamus; directs several maintenance activities like eating/cravings, body temperature, and control of emotion; works with the pituitary gland
amygdala
consists of two lima-bean sized neural clusters linked to fear and anger emotions; control center for fight, flight, and freeze
hippocampus
part of the brain shaped like a sea horse and part of limbic system; has central role in memory processes and learning
cerebrum
large part of the brain (70%), in charge of voluntary movement and activity in body
corpus callosum
largest white matter, below the cerebral cortex, connects two hemispheres, allows sides to communicate
cerebral cortex
wrinkled part of the brain; controls mental processes such as thought; body’s ultimate control center and information processing center
frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal
the four lobes of the cerebral cortex
frontal lobe
lobe that is in charge of movement and thinking (forehead area)
parietal lobe
lobe that is responsible for touch sensation and spatial relationships (top to rear head)
occipital lobe
lobe responsible for visual cortex (back of head)
temporal lobe
lobe that processes sounds, including speech (located at the side of the head)
motor cortex
area found behind the frontal lobe that controls voluntary movement
sensory cortex
strip of brain tissue at the front of the parietal lobe that registers and processes body sensations
Broca’s area
brain area of the left frontal lobe that directs the muscle movements involving speech
Broca’s aphasia
damage to Broca’s area where person can form ideas but cannot express them in speech
Wernicke’s area
brain area of the left temporal lobe involved in language comprehension and expression; the ability to understand what is being said
parts of a neuron
genes
building blocks of heredity, that make up chromosomes
chromosomes
threadlike structure in the nucleus of every living cell; contains genes
DNA
contains genetic information that makes up chromosomes
memory
system that encodes, stores. and retrieves information
encodes, storage, retrieval
the three steps in information processing model
encoding
modification of information to fit the preferred format for the memory system
automatic processing
unconscious encoding of incidental information
effortful processing
requires effort and attention to encode (rehearsal)
mnemonic device
memory aid that often rely on both acoustic and visual codes
chunking device
putting things into clusters or “chunks” so that items learned are in groups
storage
the retention of encoded material over time
sensory, working, long-term
the three types of memory
sensory memory
shortest of our memories and holds sights, sounds, smells, and textures, and other sensory information for a fraction of a second; holds the largest amount of information and constantly is in use
working memory
place where we sort and encode information before transferring it to long-term memory or forgetting it; we can hold 7 pieces of information
short-term memory
another name for working memory
limited capacity and short duration
working memory is subject to two limitations, what two limitiations
rehearsal
method or way that helps move memories from working to long-term
long-term memory
all you knowledge of yourself and the world around you; unless injury or illness, long term is limitless
procedural and declarative
two forms of longterm memory
procedural memory
(implicit); memory of how things are done; muscle memory/motor memory
declarative memory
(explicit); memory of specific information such as knowledge or personal memories
flashbulb memories
memories that are very clear and very vivid; typically high emotion events
retrieval
locating and recovering of information from memory
recall and recognition
two types of memory retrieval
recall
retrieval method where one must reproduce previously presented material
recognition
retrieval method where one must identify information that is produced, which has previously been presented
the two types of retrieval clues
encoding specificity principle and mood-congruent memory are what?
encoding specificity principle
more closely the retrieval clues match way the information was encoded, the better the info will be remembered
mood congruent memory
a theory which says we tend to selectively remember memories that match (are congruent with) our current mood
retrograde amnesia
the inability to remember information previously stored in memory.
anterograde amnesia
the inability to form memories from new material
encoding failure
what we don’t encode, we don’t remember; some info processing is automatic but some require more attention
storage decay
even if someone is able to encode well, they can still forget