BIOL 220: CH. 12 - NERVOUS SYSTEM I
1/254
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
255 Terms
Which is a function of both the endocrine and nervous system?
maintaining internal coordination
Sensory (afferent) neurons do which of the following?
carry signals to spinal cord and brain
What are the two major anatomical subdivisions of the nervous system?
central and peripheral nervous systems
Taken together, the sensory and motor subdivisions make up which of the following?
peripheral nervous system
The autonomic nervous system is subdivided into the ______ division which tends to arouse the body for action and the ______ division which tends to have a calming effect.
sympathetic, parasympathetic
Which two organ systems are primarily responsible for coordinating the other bodily systems so as to maintain homeostasis?
endocrine system
nervous system
The release of a neurotransmitter is an example of which physiological property exhibited by a neuron?
secretion
Which structures carry out commands from the central nervous system?
muscles and glands
Afferent neurons are what type of neurons?
sensory
Ganglia are components of which division of the nervous system?
peripheral nervous system
The soma of a neuron gives rise to branch-like processes called what? They are the primary sites for receiving signals from other neurons.
dendrites
The somatic motor division carries information to which structure?
skeletal muscle
What are dendrites of neurons?
sites for receiving signals from other neurons
Which division inhibits digestion?
sympathetic
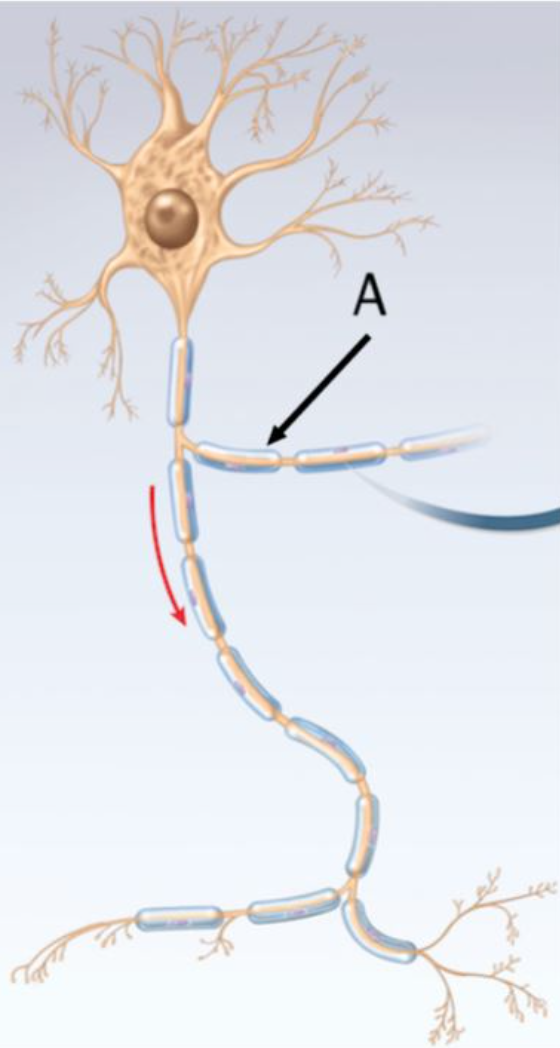
Name the outer covering of the neuron indicated by the arrow labeled A.
myelin sheath
List the fundamental physiological properties of neurons.
excitability, conductivity, secretion
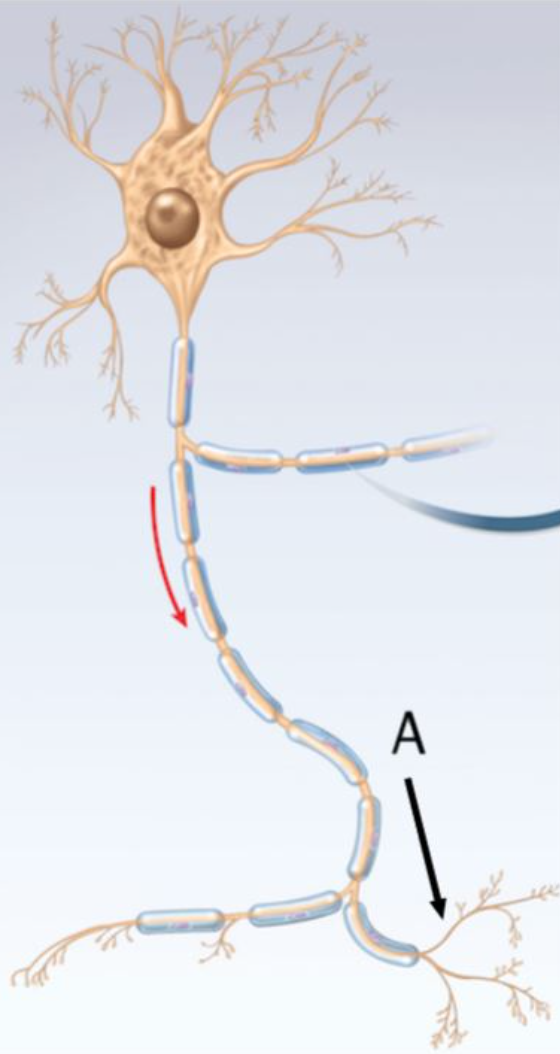
Which part of the neuron is indicated by the arrow labeled A?
terminal arborization
Choose the three functional classes of neurons.
motor neurons
interneurons
sensory neurons
Neurons are classified structurally according to the number of processes extending from the soma. Match each classification to its description.
multipolar neurons —> one axon; multiple dendrites
bipolar neurons —> one axon; one dendrite
unipolar neurons —> a single process
anaxonic neurons —> no axon; multiple dendrites
Choose all that are names for the cell body of a neuron.
neurosoma
soma
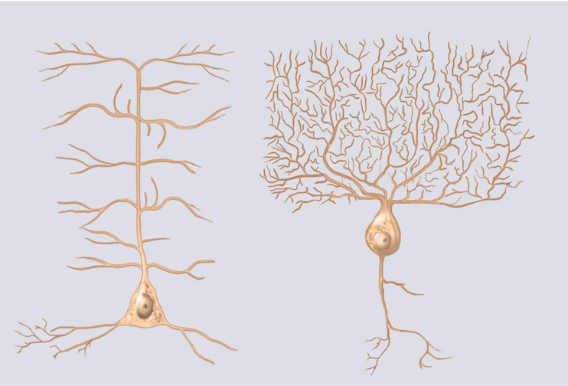
The picture shows the most common structural type of neuron. It contains one axon and multiple dendrites, and it is classified as what type of neuron.
multipolar
The processes of neurons that usually receive signals from other neurons are called ________.
dendrites
Match the following terms with their description.
axon hillock —>
axoplasm —>
axolemma —>
axon collateral —>
axon hillock —> a mound located on one side of the soma from which the axon originates
axoplasm —> cytoplasm of the axon
axolemma —> plasma membrane of the axon
axon collateral —> branch that originates from an axon
At its distal end, an axon has an extensive complex of fine branches called what?
terminal arborization
Neurons that have one axon and one dendrite, such as olfactory cells, certain neurons of the retina, and sensory neurons of the inner ear, are classified as which of the following?
bipolar
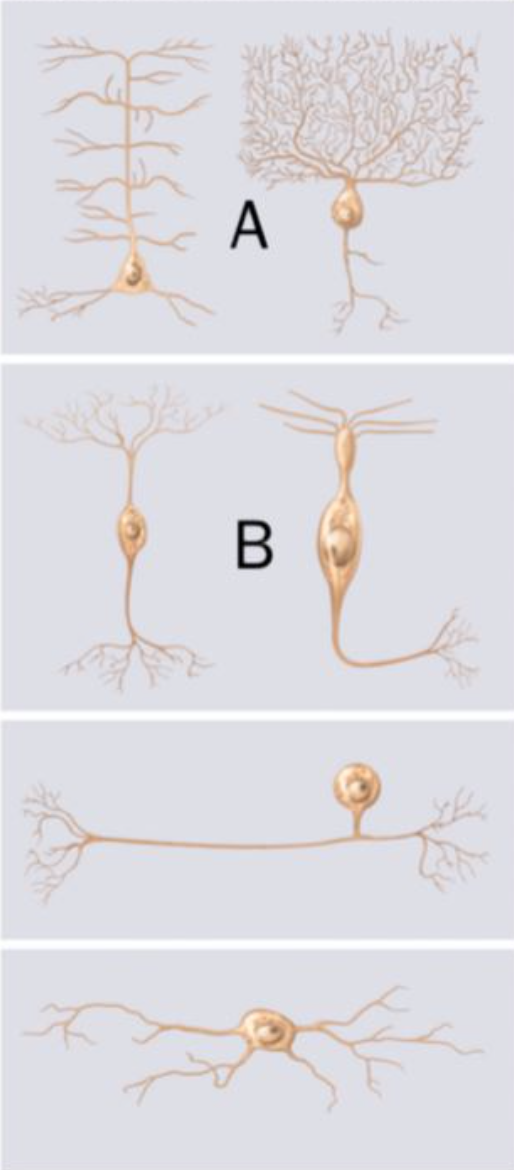
The neurons indicated by a letter "A" are structurally classified as ______ neurons. The neurons indicated by a letter "B" are structurally classified as ______ neurons.
multipolar, bipolar
Which type of neuron has one single process that branches like a T into a peripheral fiber and a central fiber?
unipolar
Neurons with numerous dendrites and a single axon are structurally classified as which of the following?
multipolar
Movement away from the neuron cell body toward an axon ending is called ______ transport.
anterograde
The processes that branch from the somas of most neurons are called __________.
dendrites
Choose all that are characteristics of neuroglia.
they bind neurons together and provide a supportive scaffold
they protect the neurons and help them function
Which process of a neuron is specialized for rapid conduction of nerve signals to structures relatively far away from the neuron cell body?
axon
Which types of glial cells are found in the central nervous system?
astrocytes
oligodendrocytes
microglia
ependymal cells
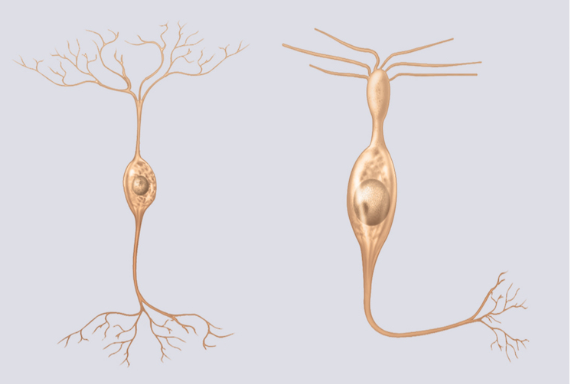
What type of neuron is shown in the given image?
bipolar
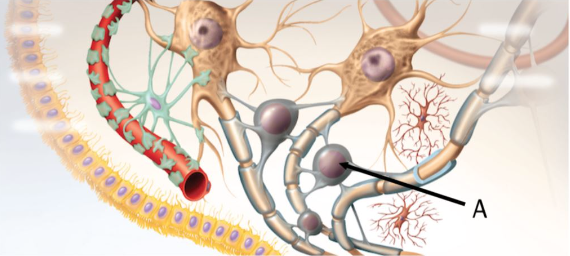
Which type of glial cell is indicated by the arrow labeled A?
oligodendrocytes
Neurons with a single process extending from the soma, such as the neurons that carry sensory signals to the spinal cord, are classified structurally as ______ neurons.
unipolar
Which glial cell type is indicated by the arrow labeled A?
ependymal
During axonal transport, motor proteins transport material as they crawl along microtubules. Match the type of axonal transport with its corresponding motor protein.
kinesin —>
dynein —>
kinesin —> anterograde transport
dynein —> retrograde transport
Neuroglial cells that act as macrophages within the CNS are ______.
microglia
What is the approximate ratio of glial cells to neurons?
1:1
Match each glial cell type with its location and function.
satellite cells —>
schwann cells —>
ependymal cells —>
microglia —>
satellite cells —> in the PNS; surround somas of neurons in ganglia, provide electrical insulation, and regulate the chemical environment of neurons
schwann cells —> in the PNS; form neurilemma around all PNS fibers and myelin around most of them; aid in regeneration of damaged nerve fibers
ependymal cells —> in the CNS; line cavities of the brain and spinal cord; secrete and circulate CSF
microglia —> in the CNS; phagocytize microorganisms, foreign matter, and dead nervous tissue
Which are functions of astrocytes?
secrete nerve growth factors
regulate chemical composition of tissue fluid
convert blood glucose to lactate for neurons to use for fuel
form blood-brain barrier
In the CNS, myelin is produced by glial cells called _______.
oligodendrocytes
Which glial cell produces and helps circulate cerebrospinal fluid?
ependymal cells
Choose all statements that are true about Schwann cells?
they assist in the regeneration of damaged nerve fibers
they form the myelin sheath in the PNS
Which type of glial cells in the central nervous system fight microorganisms and destroy foreign matter and dead nervous tissue?
microglia
The structure that consists of spiral layers of insulation around an axon is called a(n) _______ sheath.
myelin
Which cells protect the neurons and help them function?
neuroglia
Choose the name of the thin layer of fibrous connective tissue found around myelin in nerve fibers of the peripheral nervous system.
endoneurium
Which type of cell plays a role in the establishment of the blood-brain barrier?
astrocyte
Where are unmyelinated axons found?
in both the central and peripheral nervous systems
Which type of glial cell produces the myelin sheath in the PNS?
schwann cell
Which is true about a neuron with a large diameter, myelinated axon as compared to a neuron with a small diameter, unmyelinated axon?
signal conduction will be faster
The myelin sheath is a spiral layer of ______ around a nerve fiber.
insulation
Which term refers to the thick outermost coil of a Schwann cell?
neurilemma
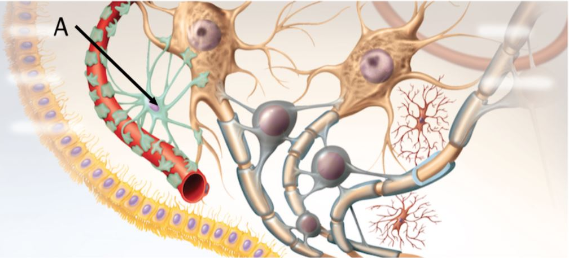
What type of glial cell is indicated by the arrow labeled A?
astrocytes
True or False?
Unmyelinated nerve fibers (axons) in the PNS are enveloped in Schwann cells.
true
Choose all the factors that influence the speed of nerve signal conduction.
diameter of axon
presence of myelin
What are the functional classes of neurons?
sensory (afferent)
interneurons
motor (efferent)
What is the role of sensory (afferent) neurons?
Sensory neurons carry information from sensory receptors (like skin, eyes, and ears) towards the CNS, allowing the body to perceive changes in the environment.
How do interneurons function in the nervous system?
Interneurons act as connectors or relays within the CNS, processing information between sensory and motor neurons, allowing for complex reflexes and higher-order processing.
What is the primary function of motor (efferent) neurons?
Motor neurons transmit signals from the central nervous system to muscles and glands, triggering actions like muscle contraction and gland secretion.
How do sensory and motor neurons differ in their direction of signal transmission?
Sensory neurons send signals towards the CNS, while motor neurons send signals away from the CNS towards muscles and glands.
What role do interneurons play in reflex actions?
Interneurons serve as intermediaries in reflex actions, allowing for quick communication between sensory and motor neurons, which results in rapid responses without involving higher brain centers.
What is the role of sensory input in the nervous system?
Sensory input involves the detection of external or internal stimuli through receptors, which then send signals to the brain or spinal cord.
How does integration function in the nervous system?
Integration refers to the processing and interpretation of sensory information in the brain, allowing for thoughts, memories, decision-making, and the sensation of the stimuli.
What is meant by the response aspect of the nervous system?
The response involves motor output, where the nervous system sends signals to muscles or glands, triggering an action or change in activity within effector organs.
What role do receptors play in the sensory input process?
Receptors detect changes in the environment (such as light, sound, or touch) and convert them into electrical signals that are transmitted to the central nervous system for processing.
How does the nervous system utilize thoughts, memories, and decisions in integration?
The nervous system processes sensory information alongside previously stored thoughts and memories, allowing it to make decisions and form responses that are appropriate to the situation.
What types of organs are considered effector organs in the response process?
Effector organs include muscles and glands, which carry out responses directed by the nervous system, such as muscle contraction or hormone release.
What is the relationship between sensory input, integration, and response?
Sensory input gathers information, integration processes this information to form a plan, and the response initiates action through motor output, resulting in changes in muscle or gland activity.
What are the main components of the nervous system?
The nervous system consists of the Central Nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
What are the two primary parts of the Central Nervous System (CNS)?
The brain and the spinal cord make up the Central Nervous System (CNS).
What role does the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) play in the body?
The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) connects the Central Nervous System (CNS) to the rest of the body, consisting of nerves outside the CNS.
What are nerves, and where are they found in the nervous system?
Nerves are bundles of axons found in the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS), including spinal nerves and cranial nerves.
What are spinal nerves?
Spinal nerves are nerves that emerge from the spinal cord and extend to different parts of the body.
What are cranial nerves?
Cranial nerves are nerves that originate directly from the brain and extend to various regions of the head and neck.
What are ganglia, and where are they found?
Ganglia are concentrations of nerve cell bodies that appear as knot-like swellings in the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
What are the two main divisions of the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)?
The two main divisions of the PNS are the Sensory (Afferent) Division and the Motor (Efferent) Division.
What is the role of the Sensory (Afferent) Division in the PNS?
The Sensory (Afferent) Division is responsible for transmitting sensory information from receptors to the Central Nervous System (CNS).
What types of information does the Somatic Sensory Division convey?
The Somatic Sensory Division conveys information from the skin, skeletal muscles, and joints to the CNS.
What is the function of the Visceral Sensory Division?
The Visceral Sensory Division transmits sensory information from the visceral organs (such as the stomach and intestines) to the CNS.
How do sensory receptors contribute to the function of the Sensory Division?
Sensory receptors detect changes or stimuli in the environment and send signals to the CNS through the Sensory Division.
What are the main divisions of the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)?
The main divisions of the PNS are the Motor (Efferent) Division and the Sensory (Afferent) Division.
What is the role of the Motor (Efferent) Division in the PNS?
The Motor (Efferent) Division carries signals from the CNS to muscles and glands to initiate a response.
What are the two components of the Motor (Efferent) Division
The two components are the Somatic Motor System and the Autonomic Motor System.
What is the function of the Somatic Motor System?
The Somatic Motor System involves motor nerve fibers that control skeletal muscles, allowing for voluntary movements and automatic reflexes.
What type of control does the Somatic Motor System have?
The Somatic Motor System has voluntary control over movements.
What does the Autonomic Motor System control?
The Autonomic Motor System controls involuntary functions like smooth muscle activity, heart rate, and glandular secretions.
How does the Autonomic Motor System influence bodily functions?
It manages involuntary processes through visceral reflexes, regulating functions such as digestion, heart rate, and respiration.
What is the difference between the Somatic and Autonomic Motor Systems?
The Somatic Motor System controls voluntary movements of skeletal muscles, while the Autonomic Motor System regulates involuntary activities in smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and glands.
What are the features of a neuron?
cell body (soma)
dendrites
axon
axon terminals
What is the function of the cell body in a neuron?
The cell body, or soma, contains the nucleus and is responsible for maintaining the cell's functions and health.
It integrates the signals received from dendrites.
What role do dendrites play in a neuron?
Dendrites are branching structures that receive signals from other neurons and transmit them toward the cell body.
How does the axon contribute to neuronal communication?
The axon transmits electrical impulses away from the cell body to other neurons, muscles, or glands.
What is the purpose of axon terminals in a neuron?
Axon terminals are the endpoints of an axon, where the neuron communicates with other neurons or cells through synapses, releasing neurotransmitters.
Do all neurons have the same axon length?
No, neurons can differ in axon length and size depending on their function and location in the nervous system.
How many neurons are estimated to be in the adult human brain?
The adult human brain contains approximately 86 billion neurons.
What are the components of a cell body?
metabolism
organelles
no centrioles
nuclei
ganglia
What is the function of the cell body in a neuron?
The cell body, or soma, contains the nucleus and is responsible for maintaining the cell's health and carrying out metabolic activities.