chemistry - biomolecules, fuel,
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
12.1 - synthesis of proteins - proteins
12.2 - synthesis of carbs, lipids - carbohydrates
12.2 - synthesis of carbs, lipids - lipids
12.3 - hydrolosis of biomolecules
2.1 - Exothermic and endothermic reactions - energy + fuels
all chemicals contain stored energy + any chemical reaction will produce an energy change
fuels - substances that can easily release stored chemical energy by undergoing exothermic combustion reactions
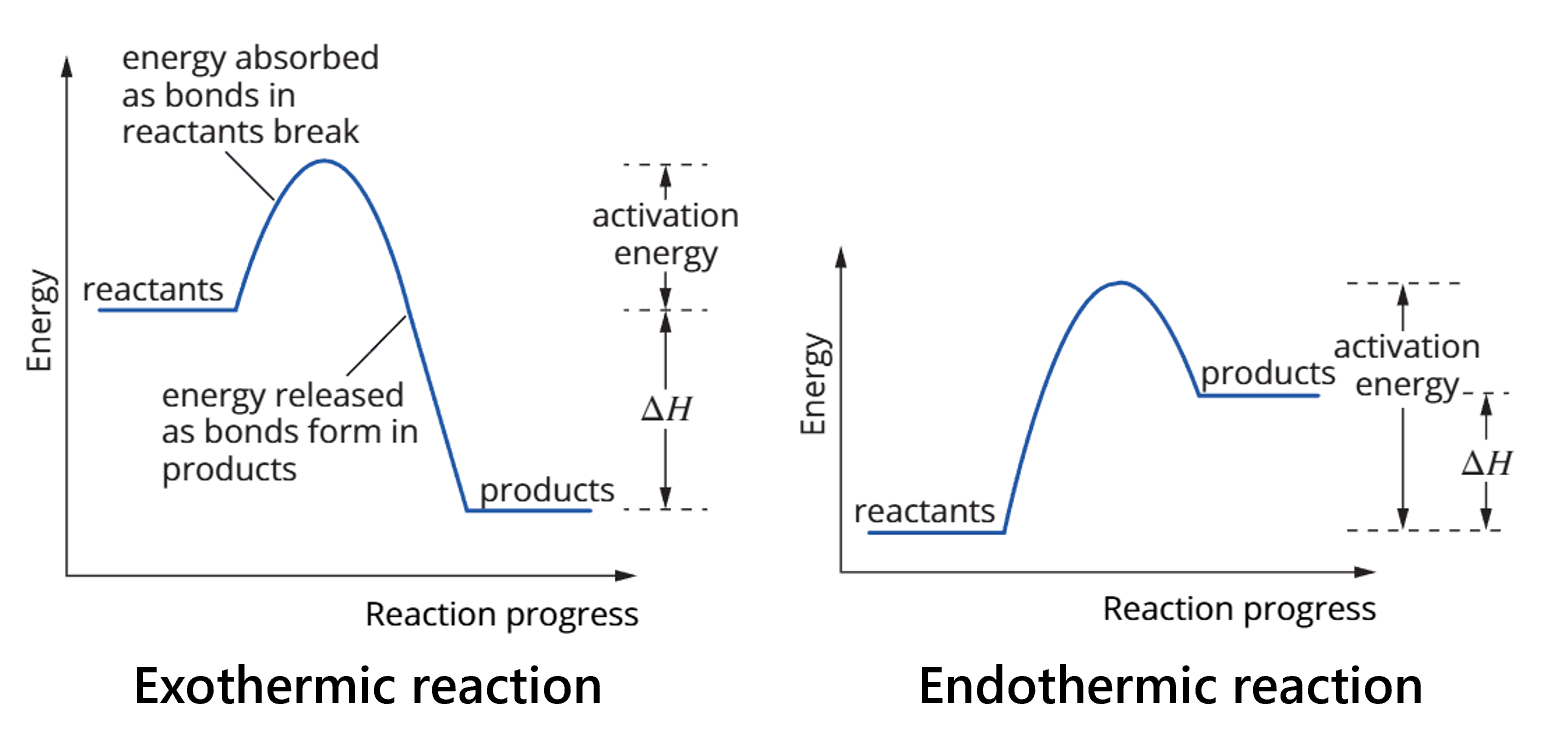
2.1 - Exothermic and endothermic reactions - exothermic reactions
exothermic reactions - release energy to the environment
2.1 - Exothermic and endothermic reactions - endothermic reactions
endothermic reactions - absorb energy
2.1 - Exothermic and endothermic reactions - enthalpy
enthalpy (H) - the chemical energy or heat content of a substance
Hr - enthalpy of reactants
Hp - enthalpy of products
∆H - enthalpy change - the exchange of heat energy between the system + its surroundings under constant pressure (SLC?). ∆H = Hp - Hr
2.2 - Types of fuels
2.3 - Fuel sources for the body
2.4 - Bioethanol
2.5 - Energy from the combustion of fuels
3.1 - Stoichiometry involving combustion of fuels
3.2 - Determination of limiting reactants or reagents
3.3 - Calculating heat energy released
3.4 - Solution calorimetry
3.5 - Energy from fuels and food
combustion reactions
exothermic reaction (releases heat)
ex. burning fuels
incomplete combustion - oxygen is a limiting reagant
complete combustion -
always assume complete combustion
equations
carbon oxidation reactions
combustion reactions in the body
fermentation reactions
equation - C6H12O6(aq) → 2C2H5OH(aq) + 2CO2(g)
plants → (using yeast) bioethanol
photosynthesis reactions
opposite of x equation
equation - 6CO2(g) + 6H2O(l) → C6H12O6(aq) + 6O2(g)
plants → (using light) glucose
exothermic reactions
reactant energy > products energy
releases heat as a byproduct
fuels
substance with high amount of energy stored in its bonds that can be readily accessed
fossil fuels
3 main - coal, crude oil/petrol, natural gas
advantages
higher energy content than biofuel → reduces cost
easier to transport + we already have infrastructure for obtaining, transport, processing → reduces cost
lots of jobs involved → good for economy
disadvantages
non-renewable
finite resource
production + combustion releases CO2 into atmosphere → adds to net CO2 emmissions → enhanced greenhouse effect → extreme weather events + climate change
release more pollutants - ex. photochemical smog such as NO2, SO2
biofuels
3 main - biogas, biodiesel, bioethanol
come from plant materials
advantages
renewable - uses natural processes + made quickly
do not add to net CO2 emmissions
disadvantages
lower energy content than fossil fuels
less investment in infrastructure → more expensive
coal
brown coal energy content -
black coal energy content -
crude oil
fractional distillation
fractions (different sized hydrocarbons) are seperated according to their boiling poit using a heat source
recondense
natural gas
biogas
low energy content - 26 kJ/g
biodiesel
bioethanol
non-renewable
produced at a rate faster tgan
CO2 emmissions
excess release of CO2 into atmosphere → adds to net CO2 emmissions → enhanced greenhouse effect → extreme weather events + climate change