NC 101 Preliminary Exam
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Computer network topology
is the way various components of a network (like nodes, links, peripherals, etc.) are arranged.
Two Types of Topologies
physical and logical
Physical Topology
is the physical layout of nodes, workstations and cables in the network.
Logical topology
is the way information flows between different components.
Types of Physical Network Topologies
•Bus Topology
•Star Topology
•Ring Topology
•Mesh Topology
•Tree Topology
•Hybrid Topology
Bus Topology
the computers are connected through a common communication media. A special type of central wire is used as
communication media. This central wire is called Bus.
Advantages:
•Easy to install and configure
•Inexpensive
•Easily extended
Disadvantages:
•Performance decreases
•Weak signals
•Difficult troubleshooting
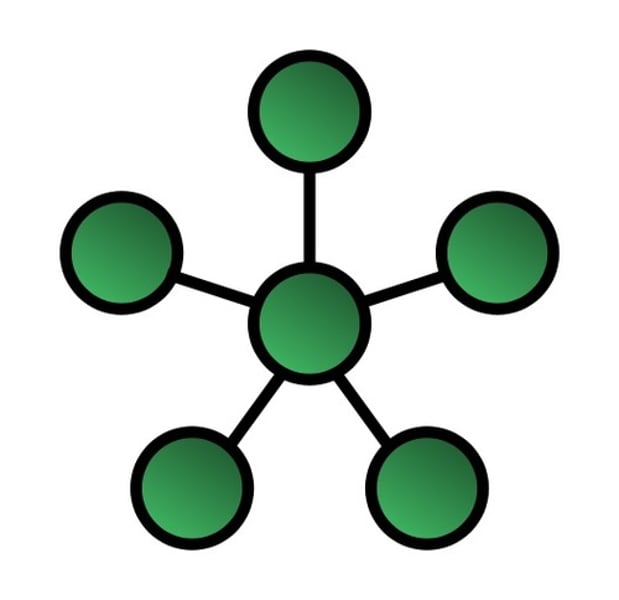
Star Topology
uses a separate cable for each workstation as shown in fig. The cable connects the workstation to a central device typically a HUB. The configuration provides a more reliable network that is easily expended.
Advantages:
•Easily expended and modified
•Easy to troubleshoot
•Multiple cable types supported by hub
Disadvantages:
•If hub fails then entire network will fail
•Require more cables
•May require a device to rebroadcast signals across the network
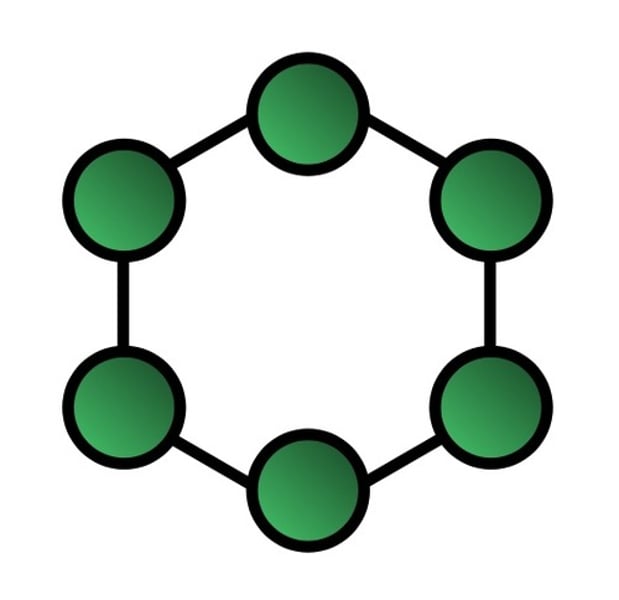
Ring Topology
•Every computer is connected to the next computer in the ring, and each transmits what it receives from the previous computer. The messages flow around the ring in one direction.
Advantages:
•It provides an orderly network in which every device has access to the token and can transmit.
•It performs well under a heavy load.
Disadvantages:
•Failure of one computer can effect the whole network .
•Difficult to troubleshoot.
•Change mode with adding or removing a device effect the entire network.
ring token passing
Some ring networks do ___________________. A short message called token (memory area) is passed around a ring until a computer wishes to send information to other computers. That computer modifies token, adds an electronic address and data and send it around the ring.
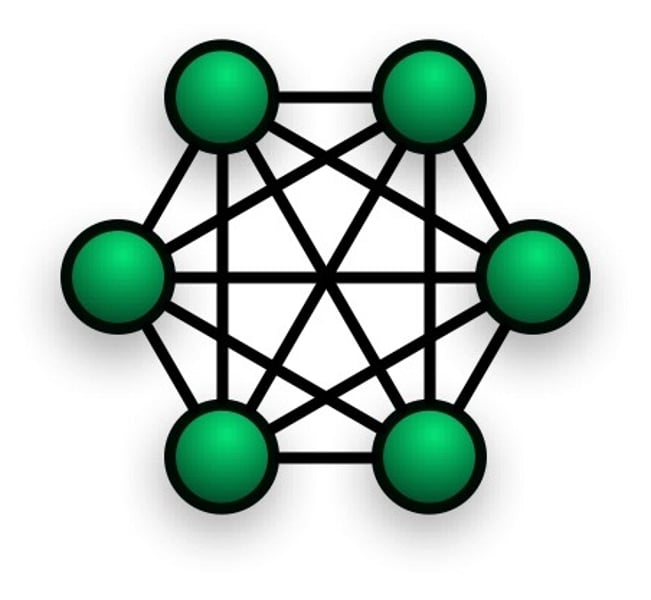
Mesh Topology
uses separate cable to connect each device to every other device on the network, providing a straight communication path. For sending messages, check the cable connected into two devices.
Advantages:
•Enhance for error tolerance provided by redundant links.
•Easy to troubleshoot.
Disadvantages:
•Difficult to install and maintain.
•Expensive.
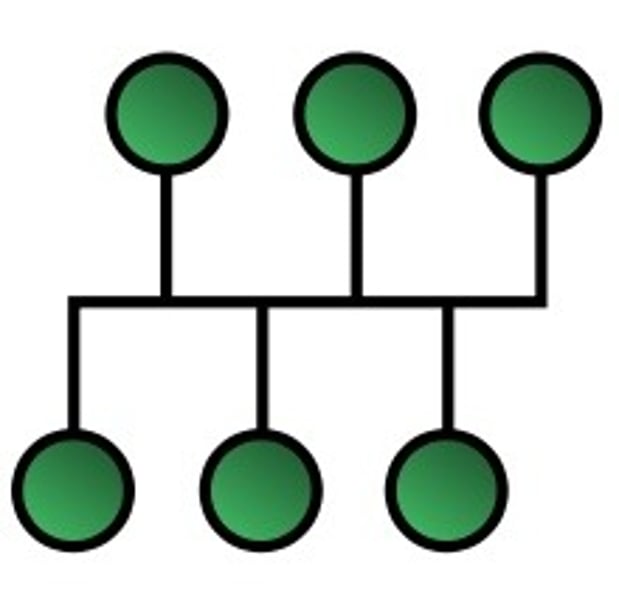
Tree Topology
The type of network topology in which a central 'root' node (the top level of the hierarchy) is connected to one or more other nodes that are one level lower in the hierarchy (i.e., the second level) with a point-to-point link between each of the second level nodes and the top level central 'root' node
Advantages:
•It is scalable.Secondary nodes allow more devices to be connected to a central node.
•Point to point connection of devices.
•Having different levels of the network makes it more manageable hence easier fault identification and isolation.
Disadvantages:
•Maintenance of the network may be an issue when the network spans a great area.
•Since it is a variation of bus topology, if the backbone fails, the entire network is crippled.
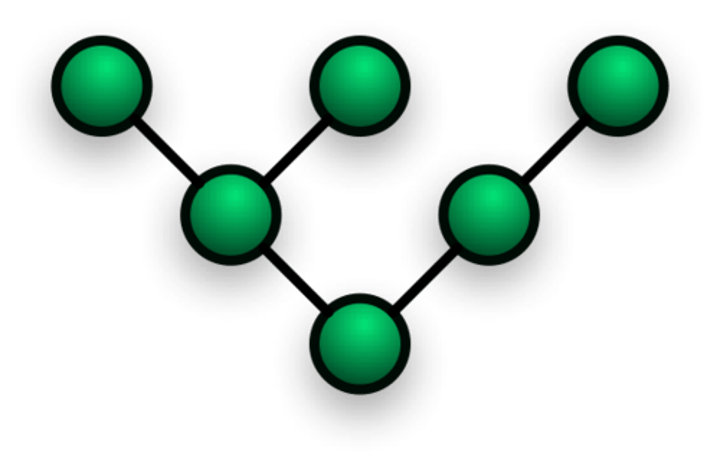
Hybrid Topology
use a combination of any two or more topologies in such a way that the resulting network does not exhibit one of the standard topologies (e.g., bus, star, ring, etc.).
Layered Protocols
a network communication approach where the communication process is organized into distinct layers, each handling specific tasks. This modularity allows for standardized protocols, interoperability, and easier troubleshooting in networking systems.
Standard Bodies
IEEE - Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
ITU - International Telecommunication Union
IETF - Internet Engineering Task Force
ISO - International Organization for Standardization
ETSI - European Telecommunications Standards Institute
IEEE - Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
develops standards for a wide range of technologies, including networking (e.g., Ethernet) and wireless communication (e.g., Wi-Fi).
ITU - International Telecommunication Union
is a United Nations specialized agency that focuses on information and communication technologies. It develops standards for telecommunications, including those related to networking and communication protocols.
IETF - Internet Engineering Task Force
is a community-driven organization that develops and promotes voluntary Internet standards. It plays a crucial role in the development of protocols like TCP/IP, HTTP, and others.
ISO - International Organization for Standardization
develops international standards for various industries, including networking and communication. ISO/IEC 7498-1 is an example of a standard defining the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model.
ETSI - European Telecommunications Standards Institute
is an independent organization that produces globally applicable standards for information and communication technologies, including 3G and 4G mobile communication standards.
The Seven OSI Models
Physical Layer
Data Link Layer
Network Layer
Transport Layer
Session Layer
Presentation Layer
Application Layer
Physical Layer
This layer specifies the physical media connecting hosts and networks, and the procedures used to transfer data between machines using a specified media. This layer is commonly referred to as the hardware layer of the model.
Data Link Layer
This layer manages the reliable delivery of data across the physical network. For example, it provides the abstraction of a reliable connection over the potentially unreliable physical layer.
Responsible for error detection and correction on the physical medium.
Network Layer
This layer is responsible for routing machine-to-machine communications. It determines the path a transmission must take, based upon the destination machine's address. This layer must also respond to network congestion problems.
Manages routing and forwarding of data between devices on different networks.
Transport Layer
This layer provides end-to-end sequenced delivery of data. It is the lowest layer that provides applications and higher layers with end-to-end service. This layer hides the topology and characteristics of the underlying network from users. It provides reliable end-to-end data delivery if the service characteristics require it.
Ensures end-to-end communication reliability and error recovery. TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and UDP (User Datagram Protocol) operate at this layer.
Session Layer
This layer manages sessions between cooperating applications.
Manages sessions or connections between applications. NetBIOS (Network Basic Input/Output System) and PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol) are examples.
Presentation Layer
This layer performs the translation between the data representation local to the computer and the processor-independent format that is sent across the network. It can also negotiate the transfer formats in some protocol suites. Typical examples include standard routines that compress text or convert graphic images into bit streams for transmission across a network.
Translates data between the application layer and the lower layers.
Application Layer
This layer consists of the user-level programs and network services. Some examples are telnet, ftp, and tftp.
Provides network services directly to end-users. Protocols like HTTP, SMTP, and FTP operate at this layer.
Hubs
are used in networks that use twisted-pair cabling to connect devices. Hubs can also be joined together to create larger networks.
are simple devices that direct data packets to all devices connected to the hub, regardless of whether the data package is destined for the device.
switches
are the connectivity points of an Ethernet network. Devices connect to switches via twisted-pair cabling, one cable for each device.
Bridges
are used to divide larger networks into smaller sections. They do this by sitting between two physical network segments and managing the flow of data between the two.
Routers
are used to create larger networks by joining two network segments.
Wireless access points
are a transmitter and receiver (transceiver) device used to create a wireless LAN (WLAN).
Modems
is a device that converts the digital signals generated by a computer into analog signals that can travel over conventional phone lines
Firewalls
l is a networking device, either hardware or software based, that controls access to your organization's network
MAC Addresses
s is a unique 6-byte address that is burned into each network interface or more specifically, directly into the PROM chip on the NIC