GEO Midterm 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:54 PM on 2/24/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
1
New cards
Heat, Oxygen, and Hydrocarbons
**What three things are required for a fire to start?**
2
New cards
Oxygen
**In the photosynthesis reaction in plants, ________ is given off as a by-product of the reaction.**
3
New cards
Returned to the atmosphere
In effect, the solar energy stored by plants during their growth is _________________ during fire.
4
New cards
False
T/F: **Forests and woody shrubs can burn generating hot and intense wildfires, but grasslands never burn.**
5
New cards
Human Causes
**Most wildfires occur due to _________ NOT Natural Causes.**
6
New cards
Types of fuel, weather and topography
**The spread of fire depends on behavior within the fire itself and on __________________.**
7
New cards
(Fire) Up a slope
(Fire) **Fire burns faster ________________.**
8
New cards
All of these (wildfire)
**What are some construction and landscaping design methods to wildfire-proof your home?**
Do not use wooden roof shingles
Do not build a wooden deck that extends over a hillslope
Do not plant shrubs close to the building
Do not use wooden roof shingles
Do not build a wooden deck that extends over a hillslope
Do not plant shrubs close to the building
9
New cards
True
T/F: **Regional and local wind behaviors strongly influence the behavior of fires.**
10
New cards
True
T/F: **Many of the worst fires in history were accompanied by strong winds.**
11
New cards
Tornadoes
**The highest wind speeds of any weather phenomenon occur in ________________.**
12
New cards
**Thunderstorms cause damage**
Thunderstorms cause damage through: heavy rains, hail, and sometimes flash floods, lightning strikes, high-speed winds.
13
New cards
Florida
**Which state has the most lightning-related deaths?**
14
New cards
All of these (hail)
**Important requirements for hail to form are**
Strong updrafts to keep hailstones suspended while adding coatings of ice onto ever-growing cores
Upper-level cold air creating maximum temperature contrasts
None of these are correct.
Large thunderstorms with buoyant hot air rising from heated ground
Strong updrafts to keep hailstones suspended while adding coatings of ice onto ever-growing cores
Upper-level cold air creating maximum temperature contrasts
None of these are correct.
Large thunderstorms with buoyant hot air rising from heated ground
15
New cards
**Hail storms** (which type)
(which type) **_________________ most frequently occur during late spring and summer in Texas, Oklahoma, Kansas, and Missouri.**
16
New cards
Tornadoes (which type)
(which type) **__________________ most frequently occur from April - July in Texas, Oklahoma, Kansas, Arkansas** .
17
New cards
**The Enhanced-Fujita scale**
**_____________** quantifies tornado magnitude, based on maximum wind speed and damage
18
New cards
Hurricane
**Rank the following in order of** ***increasing*** **strength:**
Tropical disturbance, tropical depression, tropical storm, hurricane.
Tropical disturbance, tropical depression, tropical storm, hurricane.
19
New cards
In the eye wall
**The strongest winds in a hurricane are _____________.**
20
New cards
**Hurricanes (which type)**
(which type) **Most frequently occur from August - October in Florida, Texas, Louisiana, North Carolina, South Carolina, Alabama, Georgia, Mississippi, New York, Massachusetts, and Virginia.**
21
New cards
Sun
**Energy from the __________ drives the Earth’s climate and weather processes.**
22
New cards
True
T/F: **Air moves from high pressure areas to low pressure areas.**
23
New cards
Left
**An air mass moving south in the Southern Hemisphere bends to the ____.**
24
New cards
**El Niñ**o
Warmer than normal surface water temperatures along the west coast of the Americas contribute to ___________ conditions and bring about higher-than-average levels of rainfall. **Characterized by heavy rainstorms in the western United States.**
25
New cards
**Differential Heating (fill in the blank)**
**Due to the tilt of the Earth on its axis, _____________ occurs resulting in the equatorial regions of Earth receiving more solar energy than the polar regions. (fill in the blank)**
26
New cards
Evaporation
**The process of changing from a liquid to a gas.**
27
New cards
True
T/F: **Jet streams are relatively narrow bands of high-velocity winds that flow from west to east at high altitudes.**
28
New cards
True
T/F: **The energy released by condensing a given mass of water is the same as that absorbed by evaporating the same mass of water.**
29
New cards
**La Niña**
**A typical ________ winter brings cold air with high rainfall to the northwestern United States and western Canada, but causes warming and below average rainfall in most of North America.**
30
New cards
Foreshock
A smaller magnitude earthquake that precedes the mainshock.
31
New cards
Mainshock
The largest magnitude earthquake during an earthquake sequence.
32
New cards
Aftershocks
Smaller earthquakes occurring after a large earthquake as the fault adjusts to the new state of stress.
33
New cards
Climate
The average pattern of weather in a region over a
long period of time. ex) Ice ages, multiyear droughts
Rising CO2
long period of time. ex) Ice ages, multiyear droughts
Rising CO2
34
New cards
Weather
Pattern of weather variable over short time scales, day to day. ex) Rain, thunderstorms, Hurricanes, Tornadoes Sunshine or floods.
35
New cards
True
T/F: Climate helps to determine the type of weather in a given location at a given time of year.
36
New cards
What Drives Climate
Similar to plate tectonics, driving weather and climate requires a source of energy.
Unlike plate tectonics, the driver in weather and climate is an external source of energy.
Unlike plate tectonics, the driver in weather and climate is an external source of energy.
37
New cards
Solar Energy
Earth’s climate is powered primarily from the Sun.
Arrives as:
• Visible light
• Infrared (heat)
• Ultraviolet (UV)
Arrives as:
• Visible light
• Infrared (heat)
• Ultraviolet (UV)
38
New cards
Albedo
Reflectivity is referred to this and typically accounts for 30% of solar energy.
39
New cards
Terrestrial Radiation
Earth radiates longer wavelength (infrared) radiation back into space.
40
New cards
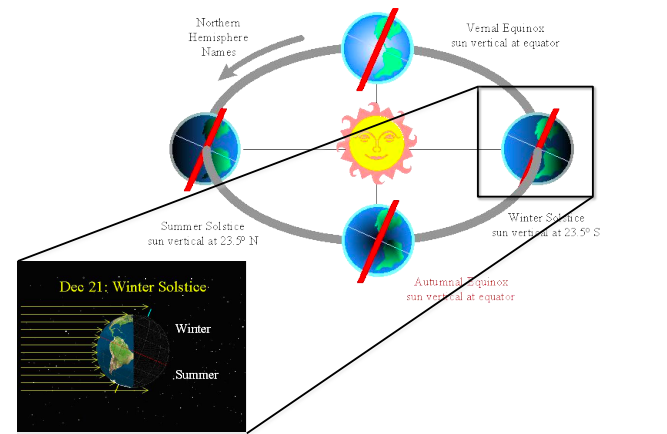
Differential Heating
The difference in how land and water surfaces absorb heat. Less heating at poles because of: Lower density of rays
Steeper angle = more reflection.
Steeper angle = more reflection.
41
New cards
Radiation
Energy that is transferred as electromagnetic waves, such as visible light and infrared waves.
42
New cards
Conduction
The direct transfer of heat from one substance to another substance that it is touching. Direct contact.
43
New cards
Convection
The transfer of thermal energy by the circulation or movement of a liquid or gas. Energy is transferred by the mass movement of molecules.
44
New cards
The role of water
71% of Earth is covered by water, 97.2% is found in Oceans. Regulating heat on earth by evaporation.
45
New cards
Hydrologic Cycle
The cycle through which water in the hydrosphere moves; includes such processes as evaporation. 24% of solar radiation received by Earth is used to evaporate water and begin.
46
New cards
True
T/F: Water has a very high heat capacity
47
New cards
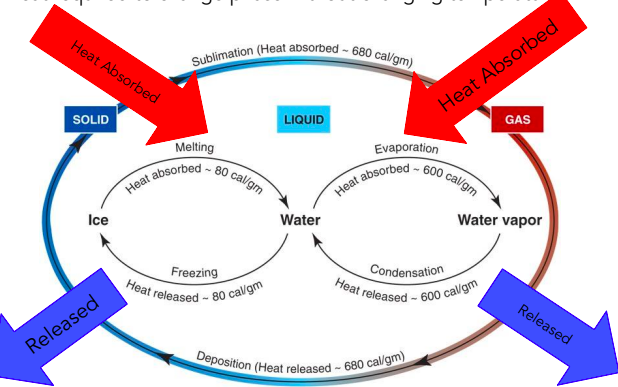
Latent Heat
Heat required to change phase without changing temperature
48
New cards
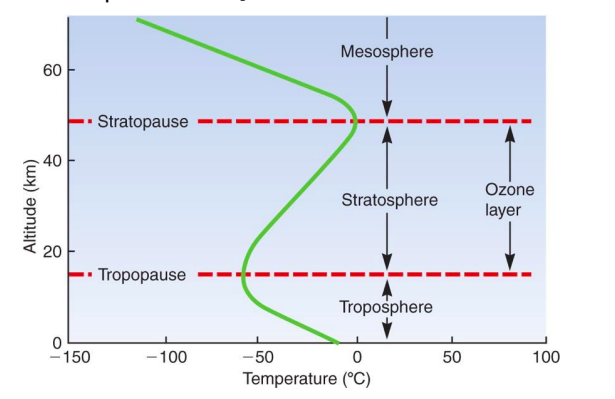
Atmospheric Layers
Troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere
49
New cards
Global air circulation
Polar, Ferrel, Hadley. Affected by the uneven heating of the earth's surface by solar energy, and the properties of air, water, and land. Easterlies and Westerlies.
50
New cards
Coriolis effect
Earth's rotation creates an apparent force. Deflects the paths of large, moving bodies to the right in the Northern Hemisphere, and two the left in the Southern Hemisphere.
51
New cards
Easterlies
Winds coming from the east and headed west.
52
New cards
Westerlies
Winds coming from the west and headed east.
53
New cards
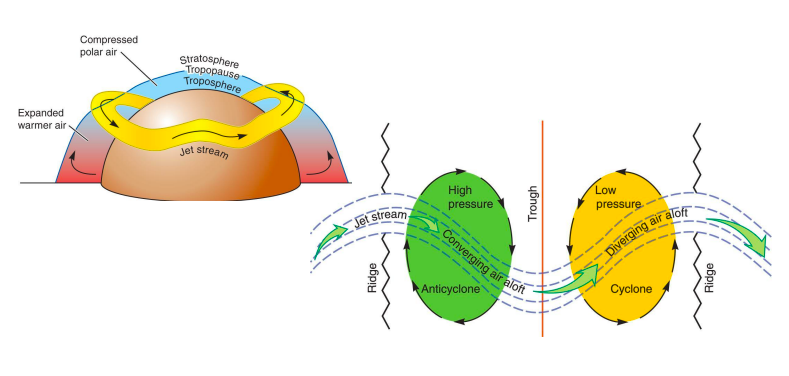
Jet streams
High-energy, elongated flows that travel in narrow, elongated bands. Can reach speeds of \~250mph. Meandering path can bend and travel in all directions.
54
New cards
Anticyclones
Air sinks downward and spreads out
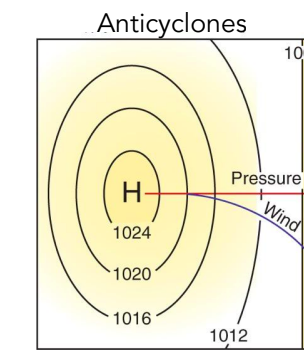
55
New cards
Cyclones
Air rises, cools and condenses, possible rainy weather.
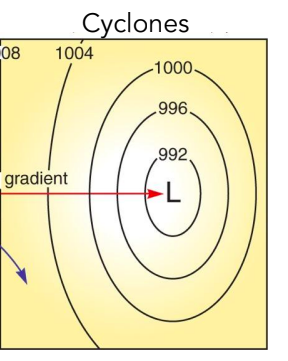
56
New cards
Air masses
Large bodies of air that have relatively uniform temperature and moisture content at a given altitude. Tend to build in the Pacific and move eastward as a result of the prevailing winds, Coriolis effect.
57
New cards
Fronts
A boundary between two masses of air. Many weather events
(rain, etc) are associated with fronts at midlatitudes.
(rain, etc) are associated with fronts at midlatitudes.
58
New cards
Orographic lifting
Cloud formation that occurs when warm moist air is forced to rise up the side of a mountain.
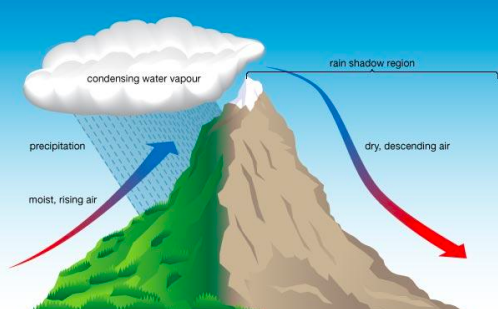
59
New cards
Surface circulation
Ocean Circulation is wind driven.
60
New cards
Deep ocean circulation
Ocean Circulation is density driven.
61
New cards
Moving air & weather
Northern hemisphere moves counter clockwise. Southern hemisphere moves clockwise.
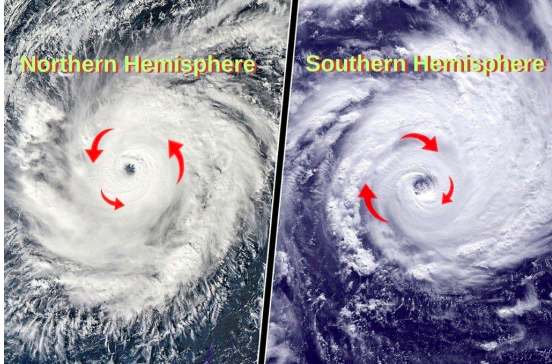
62
New cards
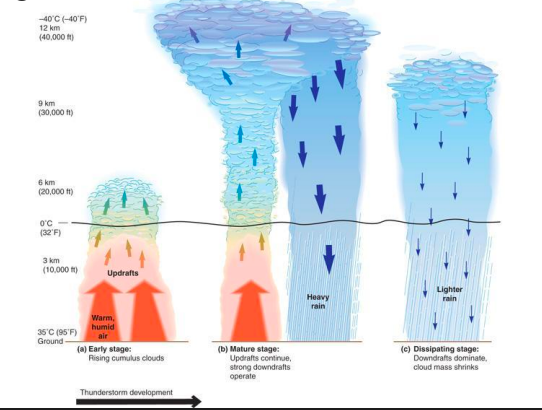
Stages of a Thunderstorm
Early stage: rising cumulonimbus clouds.
Mature stage: Updrafts continue strong downdrafts operate.
Dissipating stage: Downdrafts dominate, cloud drafts sink.
Mature stage: Updrafts continue strong downdrafts operate.
Dissipating stage: Downdrafts dominate, cloud drafts sink.
63
New cards
Types of precipitation in downdraft
Rain, freezing rain, sleet, snow, hail are all \_____________.
64
New cards
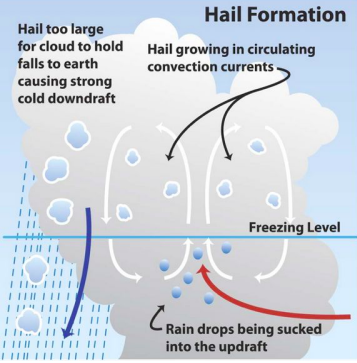
Hail formation
Rain freezes and falls to a warmer part of air, condenses and refreezes to ice balls. Hail too large for cloud to hold falls to earth causing strong cold downdraft.
65
New cards
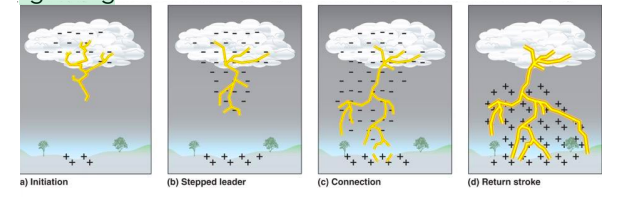
Lightning
Lightening is concentrated over land. Land heats up more quickly, leading to more convecting, upwelling. Abrupt electric discharge from cloud to cloud or from cloud to earth accompanied by the emission of light.
66
New cards
Recipe for a tornado
1) Low altitude, warm, moist tropical air from the Gulf of Mexico.
2) Cold, dry, fast moving air mass moving from Canada or Rockies, at mid
2) Cold, dry, fast moving air mass moving from Canada or Rockies, at mid
67
New cards
Single cell
Cool downdraft blocks upward flow of warm updraft.
68
New cards
Supercell
Shearing allows warm air to continue to rise into the central portion of the cell, while precipitation falls in the front.
69
New cards
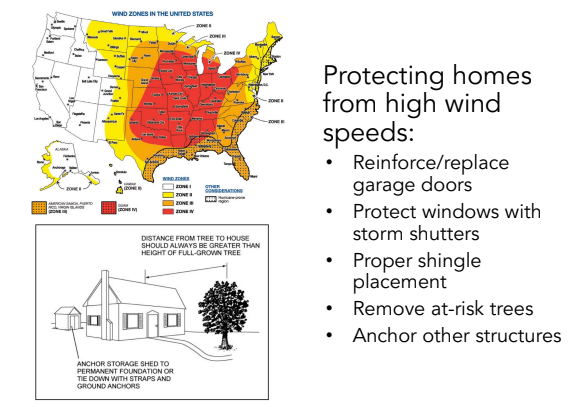
Tornado Damage Mitigation
Protecting homes from high wind speeds: Reinforce/replace garage doors. Protect windows with storm shutters. Proper shingle placement. Remove at
70
New cards
Influence of El Niño
Fewer Atlantic Hurricanes, El nino present cool sea surface, drier summer. Correlation with increased wildfire activity in Australia.
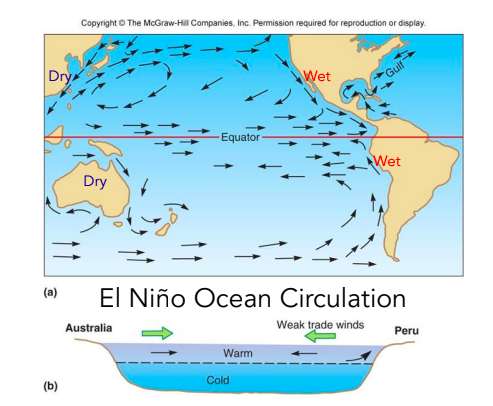
71
New cards
Influence of La Nina
More Atlantic Hurricanes, El Nino absent, warmer sea surface, wetter summer. Correlation with increased wildfire activity in southwestern U.S.
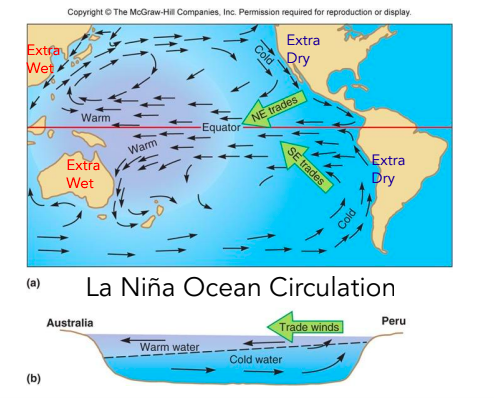
72
New cards
Perfect recipe for Wildfire
Triple-digit temperatures, Extremely low humidity, Dense Vegetation.
73
New cards
Wildfire
Requires 3 things:
• Material to burn (Fuel)
• Oxygen
• Source ignition (Heat)
• Material to burn (Fuel)
• Oxygen
• Source ignition (Heat)
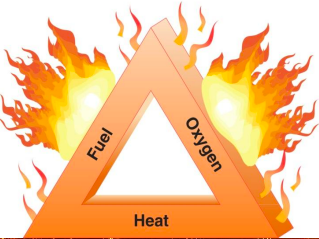
74
New cards
True
T/F: Combustion is the reverse of photosynthesis
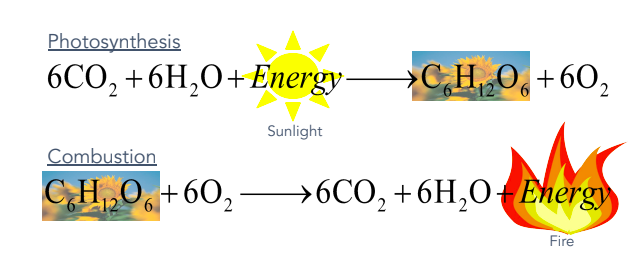
75
New cards
Tropical rain forest
Very high productivity, Very rapid decomposition.

76
New cards
Temperate deciduous forest
High productivity, Rapid decomposition in summer.

77
New cards
Chaparral
High productivity, Low decomposition.

78
New cards
Desert Scrub
Low productivity, Low decomposition.

79
New cards
Ignition
The act of setting on fire or catching fire. Lightning Strike Density, correlation between lightning & wildfires.
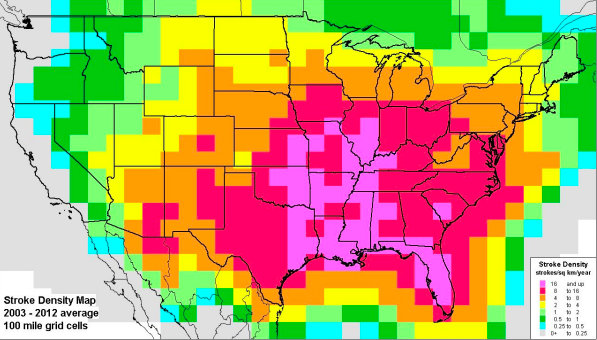
80
New cards
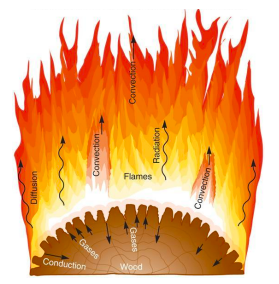
Heat
Heat is carried via:
• Convection (air flow)
• Radiation (electromagnetic)
• Conduction/Diffusion
• Convection (air flow)
• Radiation (electromagnetic)
• Conduction/Diffusion
81
New cards
Tropical wave
Low pressure spawns showers and storms
82
New cards
Tropical depression
Sustained surface winds less than 39 mph
83
New cards
Tropical storm
Sustained surface winds 39+ mph
84
New cards
Hurricanes
Sustained surface winds 74+ mph
85
New cards
Saffir Simpson scale
Classifies hurricanes according to wind speed, air pressure in the center, and potential for property damage.
86
New cards
Hurricanes vs. Typhoons vs. Cyclones
Hurricanes: atlantic
Typhoons: hurricanes in PACIFIC
Cyclones: hurricanes in Indian ocean
Typhoons: hurricanes in PACIFIC
Cyclones: hurricanes in Indian ocean
87
New cards
Preheating
Water is removed from plants, wood, etc. Drying can occur due to nearby flames, drought.
88
New cards
Pyrolysis
Wood/Material breaks down to produce
flammable gases. Occurs at 615°F in wood. If oxygen is present, gases can ignite and combustion can begin.
flammable gases. Occurs at 615°F in wood. If oxygen is present, gases can ignite and combustion can begin.
89
New cards
Flaming combustion
Surface burns hot and fast. Greatest amount of energy release.

90
New cards
Glowing combustion
Solid wood burns, Lower temperature and more slowly than in flaming combustion. Combustion on the surface of a solid fuel in the absence of heat high enough to pyrolyze the fuel.

91
New cards
Spreading Fire
Wildfire can spread in different ways:
• Slowly along the ground (glowing combustion)
• Advance as a wall of fire (flaming combustion)
• Along the tree tops (crown fire)
Depends on Fuel, Wind/Weather, Topography and Behavior within the fire.
• Slowly along the ground (glowing combustion)
• Advance as a wall of fire (flaming combustion)
• Along the tree tops (crown fire)
Depends on Fuel, Wind/Weather, Topography and Behavior within the fire.
92
New cards
Fuel type common to California
Common to California: Evergreen shrubs, Highly flammable due to leaves coated in aromatic oils. Respond to fire in different ways such as sprouters, seeders, and germination.

93
New cards
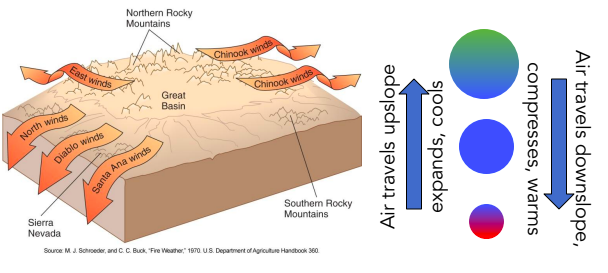
True
T/F :Air masses descend to lower elevation regions. As air descends, it compresses and warms.
94
New cards
Fire suppression
Fire retardant Retardant: smothers fuels, reduces flammability.

95
New cards
True
T/F: Natural ~50 year fire cycle in So. California.

96
New cards
Wildfire Management
Open forests \= small wildfires. Growth of understory \= large wildfires.

97
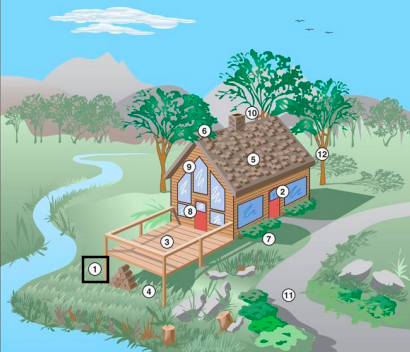
New cards
Reasons Why Houses Burn
Location, Design, topography, and fire travels uphill.
98
New cards
Bad Design for fireproof house
Wooden porch overhanging slope, Dry grasses, woody shrubs, and trees.

99
New cards
Good Design for fireproof house
Concrete barrier, poor conductor, Succulent plants,
high water storage.
high water storage.

100
New cards
Dry
Chaparral, Juniper, and Scrub grow in relatively ______ environments where wildfires are the primary mechanism of plant decomposition.