micro final
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/104
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:38 PM on 5/4/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
1
New cards
diplococci
cocci growing in pairs
2
New cards
streptococci
chains
3
New cards
staphylococci
grape-like clusters
4
New cards
tetrads
4 cocci in a square
5
New cards
sarcinae
cubic configuration of 8 cocci
6
New cards
coccobacilli
very short rods
7
New cards
vibrios
resemble rods, comma shaped
8
New cards
spirilla
rigid helices
9
New cards
spirochetes
flexible helices
10
New cards
Robert Hooke
described fruiting structures of molds, named "cell" after cork
11
New cards
Antony van Leeuwenhoek
first person to observe and describe microorganisms accurately
12
New cards
Franceso Redi
discredited spontaneous generation for large animals, demonstrated microbe fermentation, discoveries led to development of microbial control methods, discovered attenuation, developed vaccines for anthrax, chicken cholera, rabies, solidified germ theory of disease
13
New cards
Ignaz Sammelweis
Demonstrated that hand washing could drastically reduce the number of women dying during childbirth. "childbed fever"
14
New cards
Joseph Lister
developed a system of surgery designed to prevent microbes from entering wounds
15
New cards
Robert Koch
established relationship between bacteria and diseases
16
New cards
Edward Jenner
Discovered the small pox vaccine from cowpox pus
17
New cards
Ferdinand Cohn
Discovered and described bacterial endospores, classified bacteria by shape, botanist: though bacteria were plants
18
New cards
Alexander Flemming
discovered penicillin
19
New cards
Martinus Beijerinck
\-pioneered the use of enrichment cultures and selective media
\-isolated the first pure cultures of many soil and aquatic bacteria
\-described the first virus
\-isolated the first pure cultures of many soil and aquatic bacteria
\-described the first virus
20
New cards
Sergei Winogradsky
\-proposed concept of chemolithotrophy
\-isolated an anaerobic N2-fixing bacterium
\-isolated an anaerobic N2-fixing bacterium
21
New cards
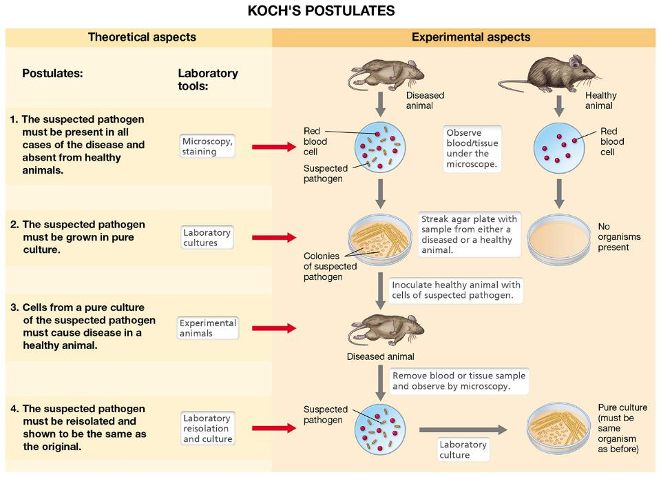
Koch's Postulates
1. The suspected pathogen must be present in all cases of the disease and absent from healthy animals. (microscopy, staining)
2. The suspected pathogen must be grown in pure culture. (laboratory cultures)
3. Cells from a pure culture of the suspected pathogen must cause disease in a healthy animal. (experimental animals)
4. The suspected pathogen must be reisolated and shown to be the same as the original. (laboratory reisolation and culture)
22
New cards
general purpose media
to grow as broad a spectrum of microbes as possible
23
New cards
enriched media
general purpose media supplemented by blood or other special nutrients
24
New cards
minimal media
contains the minimal necessities for growth of the wild-type; only contains inorganic salts, a simple carbon source, and water
25
New cards
selective media
favor the growth of one organism over another
26
New cards
differential media
Allow distinguishing of colonies of different microbes on the same plate
27
New cards
Tuberculosis
a. Mycobacterium tuberculosis
b. Small, rod-shaped, strictly aerobic, acid-fast bacillus
c. Transmitted through the air
d. Cough with blood
b. Small, rod-shaped, strictly aerobic, acid-fast bacillus
c. Transmitted through the air
d. Cough with blood
28
New cards
Bubonic Plague
a. Yersinia pestis
b. Gram-negative, non-motile, coccobacillus
c. Transmitted through bite of infected flea
d. Large lymph nodes, bleeding into skin and organs
b. Gram-negative, non-motile, coccobacillus
c. Transmitted through bite of infected flea
d. Large lymph nodes, bleeding into skin and organs
29
New cards
Tetanus
a. Clostridium tetani
b. Spore forming, gram-positive, bacillus
c. Transmitted from contaminated soil, dust, objects through cut
d. Locked muscles
b. Spore forming, gram-positive, bacillus
c. Transmitted from contaminated soil, dust, objects through cut
d. Locked muscles
30
New cards
Pertussis
a. Bordetella pertussis
b. Gram-negative, coccobacillus
c. Transmitted through air
d. Whooping cough
b. Gram-negative, coccobacillus
c. Transmitted through air
d. Whooping cough
31
New cards
Rabies
a. Rabies lyssavirus
b. RNA, bullet-shaped
c. Transmitted from saliva (or nervous system tissue) of infected to open would or mucous membrane
d. Confusion, agitation, hydrophobia
b. RNA, bullet-shaped
c. Transmitted from saliva (or nervous system tissue) of infected to open would or mucous membrane
d. Confusion, agitation, hydrophobia
32
New cards
Smallpox/Monkeypox
a. Orthopoxvirus, Variola virus
b. DNA, brick or oval shape
c. Transmitted through airborne saliva droplets
d. Progressive skin rash
b. DNA, brick or oval shape
c. Transmitted through airborne saliva droplets
d. Progressive skin rash
33
New cards
basic stain
positive charged, salt of colored base, used to stain cell
34
New cards
acidic stain
negatively charged, salt of colored acid, used to stain background
35
New cards
microbial species
a collection of __strains__ that share many stable properties and differ significantly from other groups of strains
36
New cards
microbial strain
a strain consists of the descendants of a single, __pure__ microbial culture (a single cell)
subset of a microbial species
subset of a microbial species
37
New cards
Koch’s Postulates
1. The suspected pathogen must be present in all cases of the disease and absent from healthy animals.
2. The suspected pathogen must be grown in pure culture.
3. Cells from a pure culture of the suspected pathogen must cause disease in a healthy animal.
4. The suspected pathogen must be reisolated and shown to be the same as the original.
38
New cards
refractive index
light is refracted when passing from one medium to another
39
New cards
total magnification =
mag. of ocular lens x mag. of objective lens
40
New cards
resolution (d) =
0\.5 λ/NA = 0.5 λ/(nsinθ)
41
New cards
ways to decrease d (better resolution)
shorter wavelength (λ), increase numerical aperture, increase θ (move objective closer), increase n (add oil)
42
New cards
gram stain
gram+ are purple, gram- are pink
43
New cards
defined media
exact composition is known, for growing a singular type of bacteria
44
New cards
complex media
contain some ingredients of unknown composition and/or concentration, general purpose to see what will grow
Common components
1\. Peptones
2\. Extracts
3\. Agar
Common components
1\. Peptones
2\. Extracts
3\. Agar
45
New cards
enriched media
general purpose media supplemented with highly nutritious substances such as blood, ex. Chocolate agar
46
New cards
minimal media
contains the minimal necessities for growth of the wild-type, only contains inorganic salts, a simple carbon source, and water
47
New cards
selective media
favor the growth of some microorganisms and inhibit the growth of others, ex. EMB agar selects for gram (-)
48
New cards
differential media
distinguish between different groups of microorganisms based on their biological characteristics, ex. Blood agar: hemolytic vs. nonhemolytic, MacConkey agar: lactose fermenters vs. nonfermenters
49
New cards
peptidoglycan functions
1\. provides shape to cell
2\. protects from __osmotic__ lysis
3\. may contribute to pathogenicity
4\. protects from __toxic__ substances
2\. protects from __osmotic__ lysis
3\. may contribute to pathogenicity
4\. protects from __toxic__ substances
50
New cards
What makes up peptidoglycan?
two alternating sugars form backbone with Beta (1,4) linkages
*N*-acetylglucosamine __(NAG)__
*N*- acetylmuramic acid __(NAM)__
*N*-acetylglucosamine __(NAG)__
*N*- acetylmuramic acid __(NAM)__
51
New cards
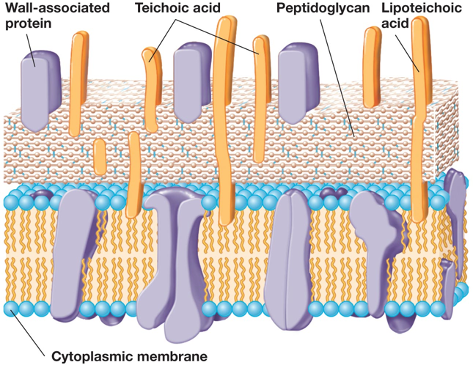
gram-positive cell wall
composed primarily of peptidoglycan (up to 90% of wall), may also contain teichoic acids (__negatively__ charged give bacteria negative charge)
1\. bind Ca2+ and Mg2+
2\. help maintain structure of cell wall
3\. protect from harmful substances
4\. role in __pathogenesis__
lipoteichoic acids - attached to membrane lipids
1\. bind Ca2+ and Mg2+
2\. help maintain structure of cell wall
3\. protect from harmful substances
4\. role in __pathogenesis__
lipoteichoic acids - attached to membrane lipids
52
New cards
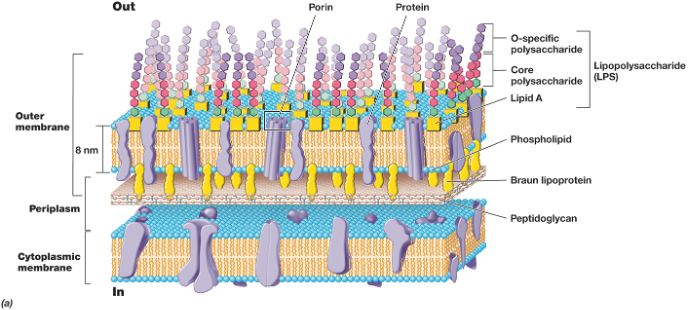
gram-negative cell wall
1. consist of a thin layer of peptidoglycan surrounded by an __outer membrane__
2. __outer membrane composed of lipids, lipoproteins, and lipopolysaccharide (LPS)__
1. __no teichoic acids__
2. peptidoglycan (up to 10% of cell wall)
3. periplasm (may constitute 20–40% of cell volume) (many enzymes present)
3. outer membrane - lies outside of the thin peptidoglycan layer
1. porins = channels through which small, hydrophilic molecules (like sugars) can pass
4. Braun’s lipoproteins - connect outer membrane to peptidoglycan
5. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
53
New cards
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
1\. Three parts: lipid A, core polysaccharide, O-specific polysaccharide (O antigen – immune system reacts)
2\. Lipid A embedded in outer membrane
3\. Core polysaccharide (- charge gives cell – charge) and O side chain extend out
4\. Importance:
a. contributes to __negative__ charge on cell surface (core polysaccharide)
b. helps stabilize outer membrane structure (lipid A)
c. may contribute to attachment to surfaces and __biofilm__ formation
d. creates a permeability barrier
e. may mutate to protect from host defenses (O antigen)
f. can act as an __endotoxin__ (lipid A)
2\. Lipid A embedded in outer membrane
3\. Core polysaccharide (- charge gives cell – charge) and O side chain extend out
4\. Importance:
a. contributes to __negative__ charge on cell surface (core polysaccharide)
b. helps stabilize outer membrane structure (lipid A)
c. may contribute to attachment to surfaces and __biofilm__ formation
d. creates a permeability barrier
e. may mutate to protect from host defenses (O antigen)
f. can act as an __endotoxin__ (lipid A)
54
New cards
what type of cells usually make endospores?
gram +
55
New cards
What makes endospores so resistant?
1. core
1. low water content
1. “frozen” state because of lack of water – dehydrated (1/4th)
2. calcium dipicolinate (Ca-DPA)
1. Ca-DPA important for dehydrating the core, gets between bases of DNA to protect
3. SASPs
4. small, acid-soluble, DNA-binding proteins
1. SASPs bind and compact DNA – to protect, can be used as a carbon source to start germinating
5. slightly lower pH
1. pH around 5.5 as opposed to normal 7
2. exosporium and spore coat
56
New cards
formation of vegetative cell
1. activation
1. prepares spores for germination.
2. often results from treatments like heating.
3. not the point of no return – start to wake up a little
2. germination
1. environmental nutrients are detected.
2. spore swelling and rupture of spore coat.
3. loss of resistance
4. increased metabolic activity.
5. detectors on inner membrane – point of no return when water starts to come in – loses resistance, very vulnerable if conditions change.
3. outgrowth – emergence of vegetative cell, sloughs off layers – exosporium, spore coat, outer membrane, cortex
57
New cards
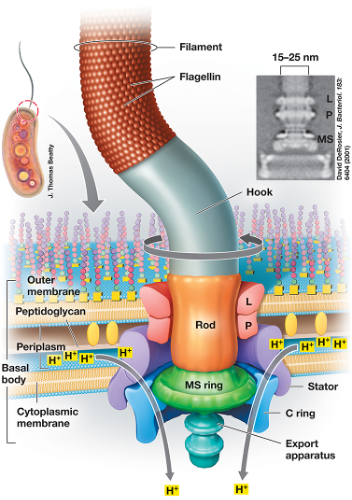
flagellum structure
1. Flagellin – one protein type stuck together – hollow tube.
2. Hook – single protein – attaches to motor (basal body) – hollow tube.
3. Motor –
1. L ring (in outer membrane – LPS layer), P ring (peptidoglycan ring): both don’t move and keep stability
2. MS ring (membrane supra = inner membrane, one on top), C ring (cytoplasm): both spin, like a revolving door (rotor) (interact with stator (Mot A and Mot B proteins)
4. Motor force – H protons to outside, charge separation, potential energy, H protons to inside (spin rings) transfer movement
58
New cards
flagellum in gram+ vs gram-
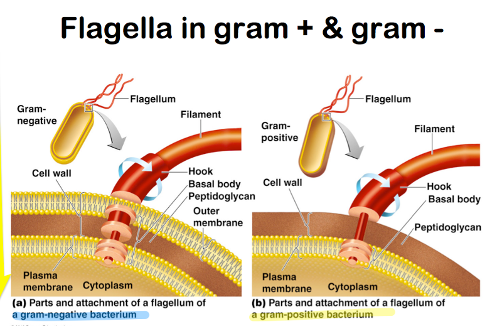
59
New cards
counterclockwise rotation of flagella
forward motion - run
60
New cards
clockwise rotation of flagella
disrupts run causing cell to stop and tumble
61
New cards
monotrichous
one flagellum
62
New cards
polar flagellum
flagellum at one end of cell
63
New cards
amphitrichous
one flagellum at each end of cell
64
New cards
lophotrichous
cluster of flagella at one or both endsp
65
New cards
peritrichous
spread over entire surface of cell
66
New cards
chemotaxis
movement toward a chemical attractant or away from a chemical repellant
67
New cards
spirochete movement
flagella twisted around each other (axial fibril) and then would around spirochete (aka endoflagella)- gives twisting, flexing movement
68
New cards
twitching
social
short, intermittent, jerky motions
type IV pili at ends of cell
move together towards something like food or light
short, intermittent, jerky motions
type IV pili at ends of cell
move together towards something like food or light
69
New cards
gliding
adventurous
smooth movements
helical track, gliding motors, and extracellular adhesion proteins
many times involves slime
smooth movements
helical track, gliding motors, and extracellular adhesion proteins
many times involves slime
70
New cards
phototrophs
use light as energy source
71
New cards
chemotrophs
obtain energy from oxidation of chemical compounds
72
New cards
lithotrophs
use reduced inorganic substances as electron source
73
New cards
organotrophs
obtain electrons from organic compounds
74
New cards
heterotrophs
use organic molecules as carbon sources
75
New cards
autotrophs
use carbon dioxide as their sole or principal carbon source
76
New cards
catabolism
fueling reactions
energy-conserving reactions
provide reducing power (electrons)
generate precursors for biosynthesis
energy-conserving reactions
provide reducing power (electrons)
generate precursors for biosynthesis
77
New cards
anabolism
the synthesis of complex organic molecules from simpler ones
78
New cards
free energy (G)
the amount of energy that is available to do useful work
79
New cards
standard free energy change (DGo’)
the change in free energy during a chemical reaction for standard conditions (pH 7, temperature of 25°C, 1 atmosphere, reactants and products at 1 M concentration)
80
New cards
exergonic reactions
release energy
A + B → C + D + energy
DGo’ is negative (rxn proceeds spontaneously)
A + B → C + D + energy
DGo’ is negative (rxn proceeds spontaneously)
81
New cards
endergonic reactions
require energy
A + B + energy → C + D
DGo’ is positive (rxn will not proceed spontaneously)
A + B + energy → C + D
DGo’ is positive (rxn will not proceed spontaneously)
82
New cards
oxidation
removal of an electron (or electrons) from a substance
83
New cards
reduction
addition of an electron (or electrons) to a substance
84
New cards
standard reduction potential (E’o)
equilibrium constant for an oxidation-reduction reaction
a measure of the tendency of the reducing agent to lose electrons.
more __negative__ E’o → better electron donor
more __positive__ E’o → better electron acceptor
the greater the difference between the E’o of the donor and the E’o of the acceptor → the more negative the DGo’
a measure of the tendency of the reducing agent to lose electrons.
more __negative__ E’o → better electron donor
more __positive__ E’o → better electron acceptor
the greater the difference between the E’o of the donor and the E’o of the acceptor → the more negative the DGo’
85
New cards
two classes of electron carriers
1. coenzymes
1. freely diffusible; can transfer electrons from one place to another in the cell (ex. NAD+)
2. prosthetic groups
1. firmly attached to enzymes in the plasma membrane (ex. cytochromes)
86
New cards
substrate-level phosphorylation
used in __fermentation__ and other pathways.
ATP is synthesized during steps in the catabolism of an organic compound.
The only way ATP can be made in fermentation.
ATP is synthesized during steps in the catabolism of an organic compound.
The only way ATP can be made in fermentation.
87
New cards
oxidative phosphorylation
used in respiration
ATP is produced by proton motive force
ATP is produced by proton motive force
88
New cards
Strep Throat (Streptococcal pharyngitis)
o *Streptococcus pyogenes*
o Gram +, cocci
o Direct contact with discharges of infected
o Red, sore throat; swollen tonsils
o Gram +, cocci
o Direct contact with discharges of infected
o Red, sore throat; swollen tonsils
89
New cards
Cholera
o *Vibrio cholerae*
o Gram -, vibrios
o Contaminated food/water
o Severe diarrhea
o Gram -, vibrios
o Contaminated food/water
o Severe diarrhea
90
New cards
Bacterial Meningitis (Meningococcal)
o *Neisseria meningitidis*
o Gram -, diplococci
o Water droplets
o Stiff neck, swelling of the head
o Gram -, diplococci
o Water droplets
o Stiff neck, swelling of the head
91
New cards
Lyme Disease
o *Borrelia burgdorferi*
o Gram -, spirochete
o Bite of infected tick
o Rash
o Gram -, spirochete
o Bite of infected tick
o Rash
92
New cards
Infectious Mononucleosis
o Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)
o Double-stranded DNA virus, toroid-shaped protein core wrapped with DNA and nucleocapsid with 162 capsomers and external spikes
o Saliva
o Fatigue; swollen lymph nodes
o Double-stranded DNA virus, toroid-shaped protein core wrapped with DNA and nucleocapsid with 162 capsomers and external spikes
o Saliva
o Fatigue; swollen lymph nodes
93
New cards
Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2)
o SARS-CoV-2
o Single-stranded RNA
o Respiratory fluids
o Single-stranded RNA
o Respiratory fluids
94
New cards
Influenza A (H1N1, Swine Flu)
\
1. RNA Virus
Roughly Spherical envelope virus
Has multiple proteins on the surface like spikes
3. Spreads through the air in droplets from an infected person’s sneezes or coughs
Can also spread after touching a contaminated surface and then touching your eyes, nose, or mouth
4. Fever (not always)
Achy muscles
Chills and sweats
Cough, Sore throat, runny/stuffy nose,
Headache
\
Other very basic symptoms that are common
1. RNA Virus
Roughly Spherical envelope virus
Has multiple proteins on the surface like spikes
3. Spreads through the air in droplets from an infected person’s sneezes or coughs
Can also spread after touching a contaminated surface and then touching your eyes, nose, or mouth
4. Fever (not always)
Achy muscles
Chills and sweats
Cough, Sore throat, runny/stuffy nose,
Headache
\
Other very basic symptoms that are common
95
New cards
Hepatitis A
1. Hepatitis A Virus (HAV)
2. RNA Virus
Spherical/icosahedral shape, has a protein shell
3. ingesting the virus through eating fecal/blood contaminated food or drink or close personal contact with an infected person
4. Yellowing of the skin and the whites of your eyes (**jaundice**)
Loss of appetite
Dark urine
Clay- or gray-colored stool
Sudden nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea
\
Pain near **liver** (upper right side below your ribs)
96
New cards
Polio
1. Poliovirus (Enterovirus C)
2. RNA Virus
Non Enveloped icosahedral with a protein shell
3. Person-to-person contact
Contact with the **feces** of an infected person or droplets from an infected person
4. Paralysis
Meningitis
Neck pain/stiffness
Tingling or pricking sensations
Muscle Spasms/Weakness
\
Less severe type only causes flu-like symptoms
97
New cards
Venereal Warts/Cervical Cancer
1. Human Papillomavirus
2. DNA Virus
Nonenveloped circular icosahedral symmetry
3. Sexually transmitted (vaginal, anal, or oral sex with an infected person)
Can also spread through close skin-to-skin contact
4. Various Types of Warts (Genital, Common, Plantar, Flat)
\
Cervical cancer (takes a while to develop
98
New cards
West Nile Virus
\
1. RNA Virus
icosahedral symmetry with protein shell
3. the bite of an infected mosquito (most common)
Mother to baby during pregnancy
Blood transfusion
4. Most people have no symptoms
Some get a fever, headache, body aches, rash, joint pains, fatigue, and weakness
Few people get a severe illness affecting the central nervous system
High fever
Neck stiffness
\
Disorientation, coma, tremors, convulsions, muscle weakness, vision loss, numbness, and paralysis.
1. RNA Virus
icosahedral symmetry with protein shell
3. the bite of an infected mosquito (most common)
Mother to baby during pregnancy
Blood transfusion
4. Most people have no symptoms
Some get a fever, headache, body aches, rash, joint pains, fatigue, and weakness
Few people get a severe illness affecting the central nervous system
High fever
Neck stiffness
\
Disorientation, coma, tremors, convulsions, muscle weakness, vision loss, numbness, and paralysis.
99
New cards
Zika Virus
\
1. RNA Virus
enveloped and icosahedral
3. through the bite of an infected *Aedes* species mosquito
Mother to baby during pregnancy
Sexually Transmitted
4. **Birth Defects for a fetus**
**Guillain-Barre Syndrome**
Mild to no symptoms
Fever
Rash
Headache
\
Red Eyes
1. RNA Virus
enveloped and icosahedral
3. through the bite of an infected *Aedes* species mosquito
Mother to baby during pregnancy
Sexually Transmitted
4. **Birth Defects for a fetus**
**Guillain-Barre Syndrome**
Mild to no symptoms
Fever
Rash
Headache
\
Red Eyes
100
New cards
Peptic Ulcer Disease
a. *Helicobacter* *pylori*
b. Gram-negative, spiral
c. Close contact, exposure to fecal matter or vomit
d. Stomach pain, uncomfortable fullness
b. Gram-negative, spiral
c. Close contact, exposure to fecal matter or vomit
d. Stomach pain, uncomfortable fullness