Vocabulary Terms for Chapter 12
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocab terms to study for Exam #4 in Chapter 12.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Location
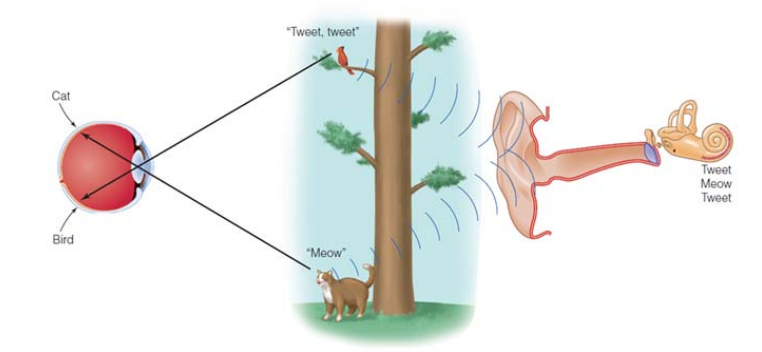
We consider the mechanisms that enable us to determine where sound is coming from & the mechanisms that enable us not to be confused by sound waves that are bouncing off the walls of a room. A single sound tends to come from one location & to move continuously.

Organization
We consider how we can separate individual sounds when many sounds are occurring simultaneously.
Auditory Space
Perception of where sounds are located in space. Surrounds a listener’s head in all directions, existing wherever there is sound.
Auditory Localization
The locating of sound sources in auditory space.
Binaural Cues
A location cue that depends on BOTH ears. Based on the comparison of the signals received by the left & right ears.
Monaural Cues
A location cue that depends on just ONE ear. Needed to locate sounds along the elevation coordinate. Primary monoaural cue for localization is called spectral cue.
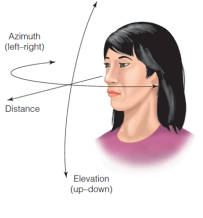
Azimuth Coordinates
Specifies locations that vary from left to right relative to the listener.
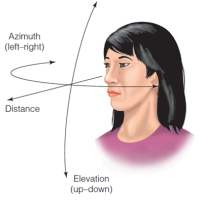
Elevation Coordinates
Sound locations that are up & down relative to the listener.
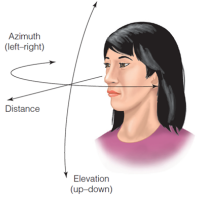
Distance Coordinates
How far the sound source is from the listener.
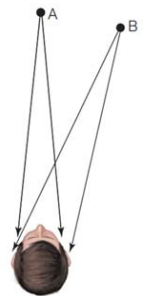
Interaural Level Difference (ILD)
The difference in sound pressure level reaching the two ears.
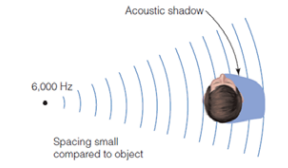
Acoustic Shadow
Shadow created by the head that decreases the level of high-frequency sounds on the opposite side of the head. This is the localization cue of interaural level difference.
Interaural Time Difference (ITD)
Difference between the times that sounds reach the two ears.

Cone of Confusion
A surface in the shape of a cone that extends out from the ear. Sounds originating from different locations on this surface all have the same interaural level difference & interaural time difference. So location information provided by these cues is ambiguous.
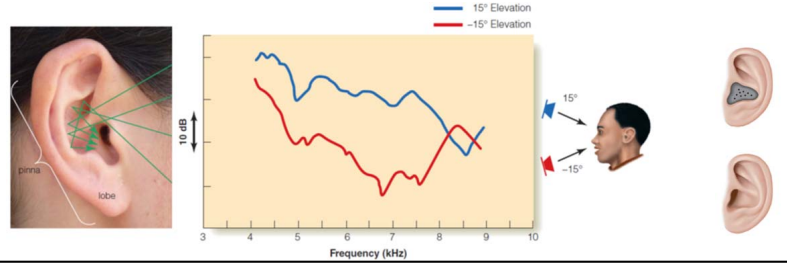
Spectral Cue
The distribution of frequencies reaching the ear that are associated with specific locations of a sound.
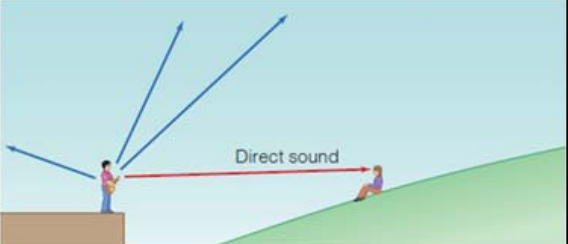
Direct Sound
Sound that reaches the listener’s ears straight from the source.
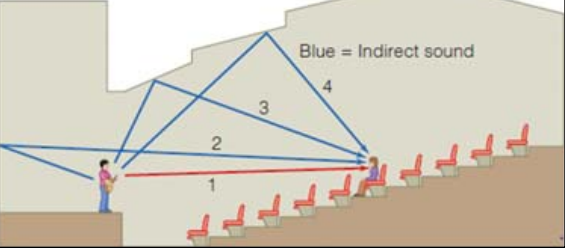
Indirect Sound
Sound that is reflected off of environmental surfaces & then to the listener.
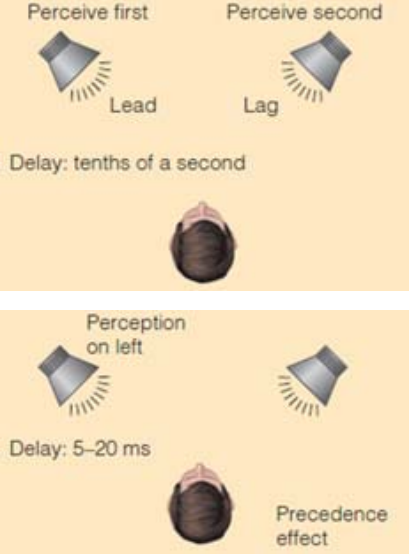
Precedence Effect
We perceive the sound as coming from the source that reaches our ears first. Governs most of our indoor listening experience.

Auditory Scene
The array of all sound sources at different locations in the environment.
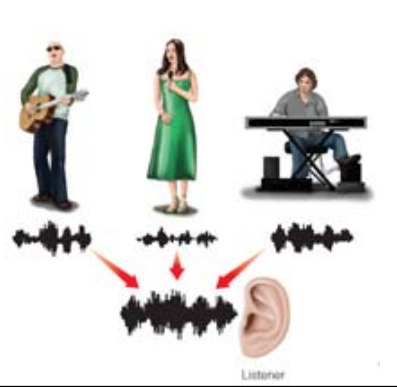
Auditory Scene Analysis
Process by which sound sources in the auditory scene are separated into individual perceptions.
Onset Time
Sounds that start at different times are likely to come from different sources.
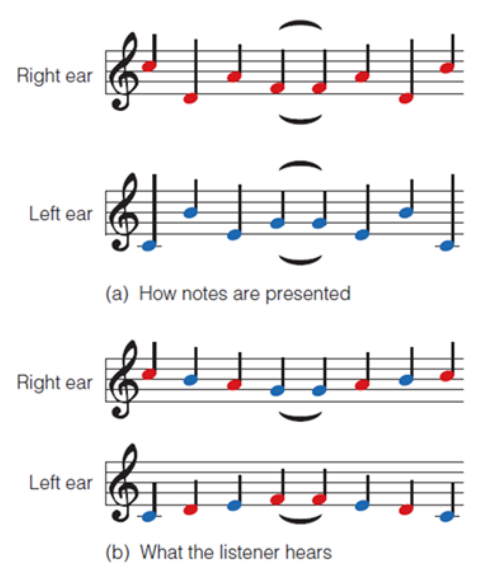
Similarity of Timbre & Pitch
Sounds that have the same timbre or pitch range are often produced by the same source.
Auditory Stream Segregation
The effect that occurs when a series of sounds that differ in pitch or timbre are played so that the tones become perceptually separated into simultaneously occurring independent streams of sound.
Proximity in Time
Sounds that occur in rapid succession usually come from the same source.
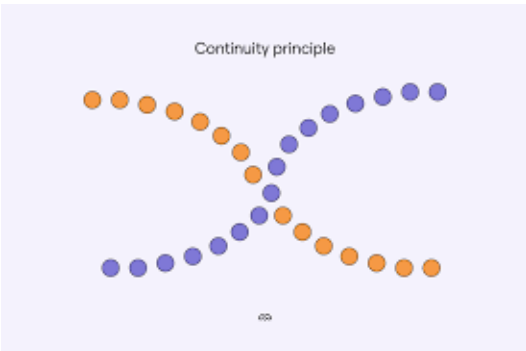
Auditory Continuity
Sounds that stay constant or change smoothly are usually from the same source.

Effect of Past Experience
An example demonstrating the effect of past experience is from an experiment by Dowling & Hardwood (1986).
The melody “Three Blind Mice” was played with notes alternating between octaves.
Listeners found it difficult to identify the song.
But after they heard the normal melody, they could hear it in the modified version using melody schema.
Multisensory Interactions
Use of a combination of senses. They usually complement each other.
Ventriloquism Effect (AKA, Visual Capture)
When sound is heard coming from a seen location, even though it is actually originating somewhere else.
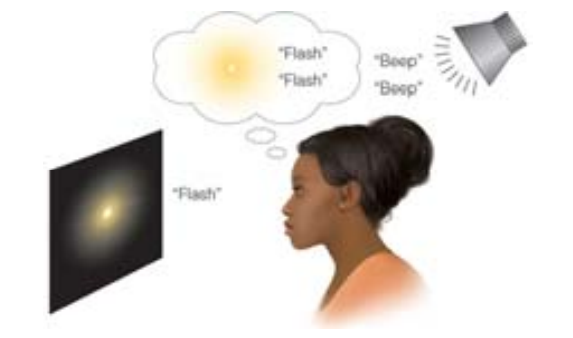
Two-Flash Illusion
An illusion that occurs when one flash of light is presented, accompanied by two rapidly presented tones. Presentation of the two tones causes the observer to perceive two flashes of light instead of one. S
Sound & Motion
They interact!
Echolocation
Locating objects by sending out high-frequency pulses & sensing the echo created when these pulses are reflected from objects in the environment. (EX: Echolocation is used by bats, dolphins, & some blind people too).