The First 20 Elements in the Periodic (Updated)
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
H
Hydrogen
He
Helium
Li
Lithium
Be
Beryllium
B
Boron
C
Carbon
N
Nitrogen
O
Oxygen
F
Fluorine
Ne
Neon
Na
Sodium
Mg
Magnesium
Al
Aluminum
Si
Silicon
P
Phosphorus
S
Sulfur
Cl
Chlorine
Ar
Argon
K
Potassium
Ca
Calcium
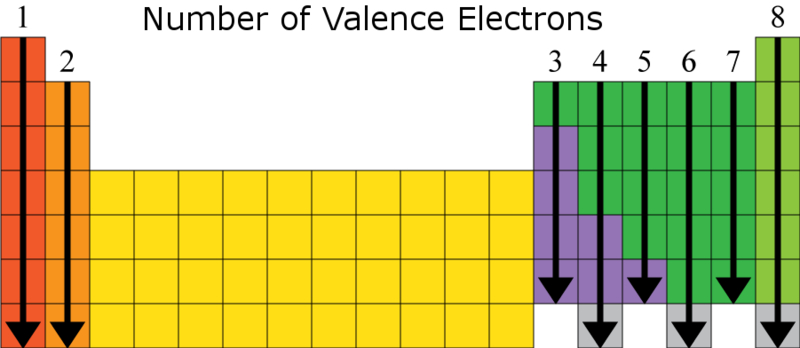
Valence Charges Based on Column
+1, +2, skip 10 columns, +3, +4/-4, -3, -2, -1, 0 (+ nums means that how many in valence shell, - is how many away from full valence) exception is helium but its inert
if valence charge is positive (+1, +2, +3)
electrons are usually lost
if valence charge is negative (-1, -2, -3)
electrons are usually gained
if valence charge is ±4
Electrons can be gained or lost
if valence charge is 0
valence shells are filled and the element is nonreactive/inert
iIf a metal and nonmetal element bond…
The metal loses electrons and the nonmetal gains electrons.
How many electrons are gained or lost in an ionic bond?
Enough to complete the shell of the nonmetal and empty the shell of the metal. If that isn’t possible more atoms may need to be added to the mix.
What happens in an ionic bond?
Electrons are lost or gained.
What happens in a covalent bond?
Electrons are shared between atoms to complete shells.
If electrons are lost…
The atom has a positive charge
if electrons are gained
The atom has a negative charge
Cations are...
Positively charged
Anions are…
Negatively charged
How do you find the amount of electrons in an atom?
Use the atomic number of the element from the periodic table.
How do you find the amount of protons in an atom?
The number of protons in an atom is equal to its atomic number.
How do you find the amount of neutrons in an atom?
To find neutrons in an atom, subtract the atomic number from the atomic mass.
What do covalent bonds form?
Molecules
What do ionic bonds form?
A crystal lattice
Characteristics of Alkali Metals
Physical:
Soft, low melting, shiny metals: conduct heat and electricity
Chemical:
React vigorously with acids, water, oxygen, and halogens. The reaction with water generates hydrogen gas and a base.
Valence Number:
1
Characteristics of Alkaline Earth Metals
Physical:
Harder, higher-melting metals: conduct heat and electricity
Chemical:
React with acids, water, oxygen, and halogens, but not as violently as alkali metals. Reaction with water generates hydrogen gas and a base, unlike alkali metal bases, these are not too soluble in water, just like mud or “earth”.
Valence Number:
2
Characteristics of Halogens
Physical:
Some are gases, others liquid, and others solids at room temp. No other family is found in all three states at room temperature. Poor conductors.
Chemical:
React with most metals, and form diatomic molecules. F2 is so reactive that it will attack gases that would not normally react.
Valence Number:
7
Characteristics of Noble or "Inert gases"
Physical:
All gases are at room temperature. Poor conductors.
Chemical:
Generally, not chemically active. None of the noble gases are flammable. They will only react with strong electron muggers
Valence Number:
8
Valence number by column
1, 2, skip 10, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8
What is the most electronegative element?
Fluorine, the closer you get to it (rows and columns) the more electronegative the element. Least electronegative goes in the center for a lewis structure except hydrogen.