anatomy lab exam 4 yay
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
131 Terms
what type of skeletal muscles function under involuntary control?
smooth and cardiac
what type of muscles are under voluntary control?
skeletal
what feature do cardiac muscles have that skeletal muscles don’t?
intercalated discs
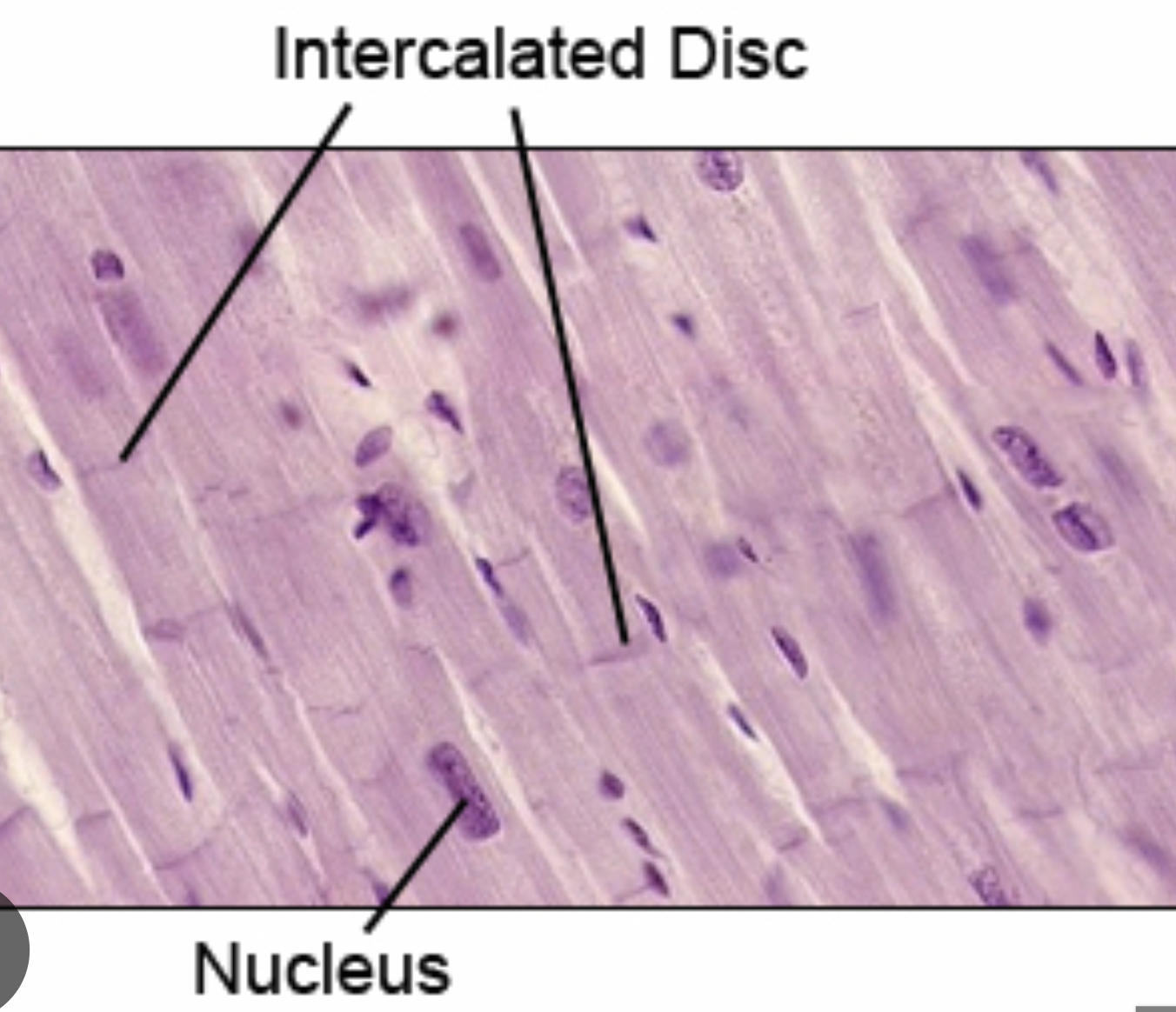
what do skeletal and cardiac muscles both have in common?
striations

what does the smooth muscle line?
internal organs like inside blood vessels, stomach, large intestine, trachea
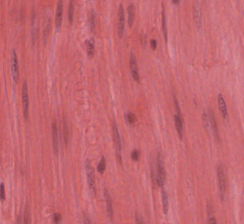
function of skeletal muscle
movement of skeleton
function of cardiac muscle
forms the heart
what do all muscle types do?
contract and cause movement
what components do muscle cells contain?
actin, myosin, and proteins
what nervous system stimulates skeletal muscles?
somatic nervous system
what nervous system stimulates cardiac and smooth muscles?
autonomic nervous system
what are skeletal muscle cells often referred to as? what are their function?
skeletal muscle fibers; extend from one end of a muscle cell all the way to the other end
what does multinucleated mean? what is an example of this?
containing many nuclei of the cells that fused together, skeletal muscle fibers are multinucleated
what are myofibrils?
bundles of actin and myosin
what gives skeletal muscle its striated appearance?
the orderly arrangement of actin and myosin in the myofibrils
use the terms striated or smooth and involuntary or voluntary to describe the three types of muscle tissue
skeletal: voluntary and striated
cardiac: involuntary and striated
smooth: involuntary and smooth
both axons and skeletal muscle cells are often referred to as fibers. what do both of these structures have in common that leads them to being called fibers?
both skeletal muscle cells and axons tend to be long and thin.
An enzyme called acetylcholinesterase is found in the neuromuscular junction. This enzyme breaks down acetylcholine. If the action of this enzyme, acetylcholinesterase , was blocked, then what would happen to the muscle? Would it be unable to properly contract or would it be unable to properly relax? explain your answer
acetylcholine would remain in the synapses longer that it should, stimulating the muscle to contract. the muscle would be unable to relax properly
Why is the surface of the motor end plate ruffled, rather than smooth?
increases the surface area at the neuromuscular junction
What is the strong sheet of tissue that acts as a tendon to attach muscles to bone
aponeurosis
What is the attachment of a muscle that remains relatively fixed during muscular contraction
origin
What is the attachment of a muscle tendon to a moveable bone or the end opposite the origin
insertion
skeletal muscle image
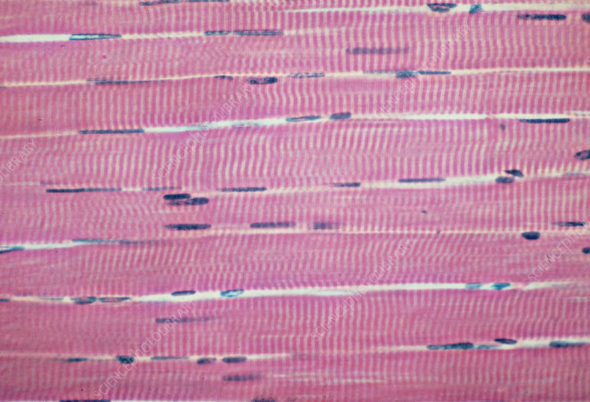
cardiac muscle image
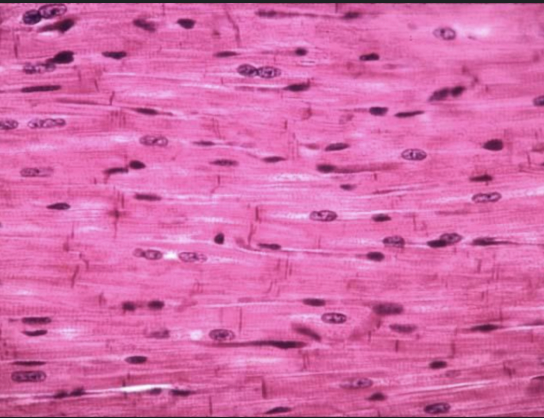
smooth muscle image
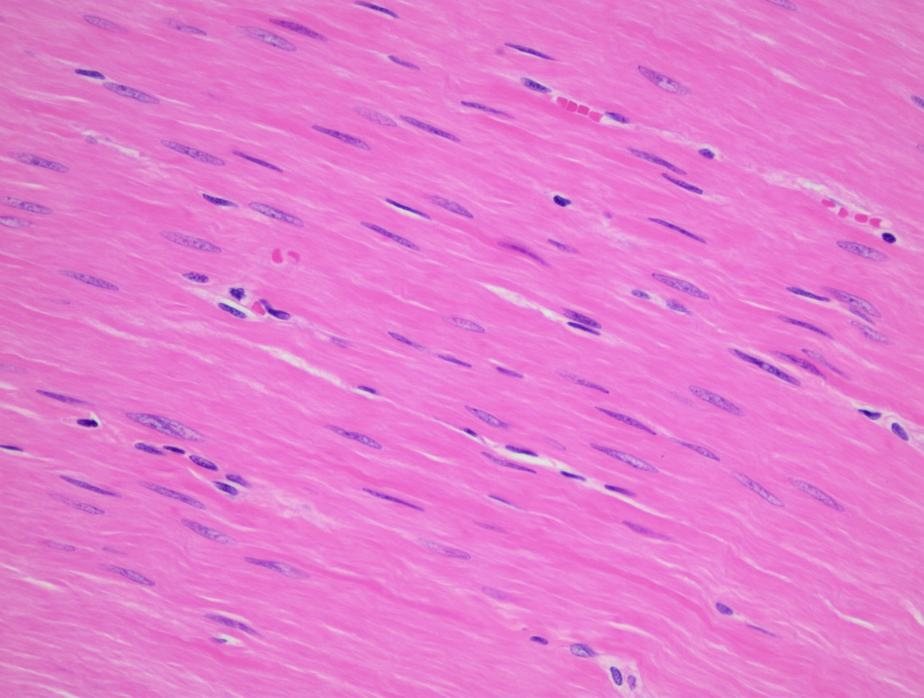
what do intercalated discs contain?
desmosomes and gap junctions
what do gap junctions allow?
allow action potentials to spread quickly from one cell to the next
how does the structure of a cardiac muscle cell help its function?
they are branched, allowing rapid spread of action potential across heart
what is the sarcolemma? what is it capable of?
plasma membrane of a muscle fiber; excitable and capable of conducting action potentials
what is the connective tissue that wraps around the muscle fiber called?
endomysium
what does a skeletal muscle fiber synapse with? what is this synapse called?
somatic motor neuron; neuromuscular junction (NMJ)
what happens when a somatic motor neuron fires an action potential?
the action potential propagates along the axon and causes the release of a neurotransmitter, acetylcholine, from the synaptic bulb.
what does acetylcholine do once it enters the synaptic cleft?
it binds to nicotinic receptors on the motor end plate, stimulating a muscle fiber to fire its own action potential, spreading it to the sarcolemma, causing contraction of the muscle.
belly
the thickest, fleshy part of a muscle, where most of the muscle fibers are located
tendon
muscle to bone
aponeurosis
connective tissue that connects muscle to muscle
origin
the attachment point of a muscle to a bone that doesn’t move during contraction
insertion
the attachment point where a muscle connects to a bone that moves during a muscle's action
synergist
muscle that assists the main muscle (agonist) performing a joint action
antagonist
one that opposes or resists the action of an agonist muscle
how many skeletal muscles does the human body contain?
over 600
what forms the neuromuscular junction (NMJ)?
synapse between motor neuron axon and skeletal muscle fiber
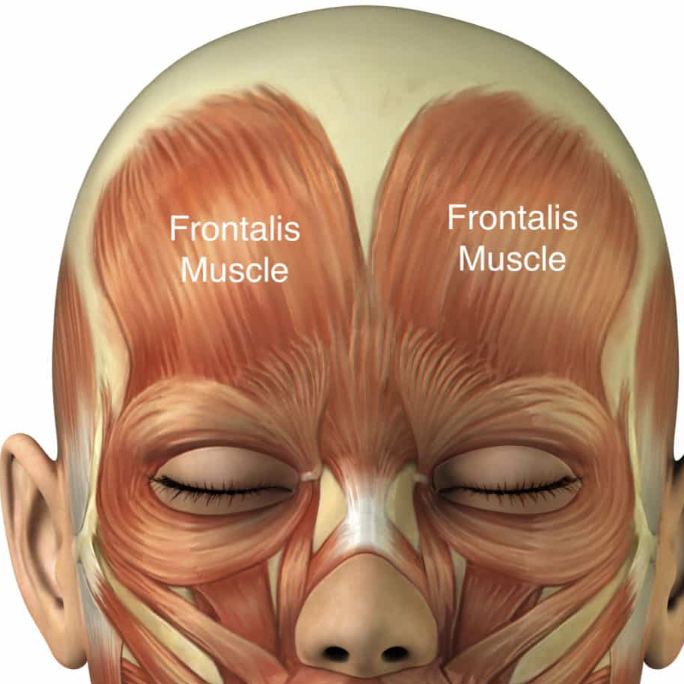
function of frontalis muscle
to raise eyebrows
function of orbicularis oculi
blinking and closing eyelids
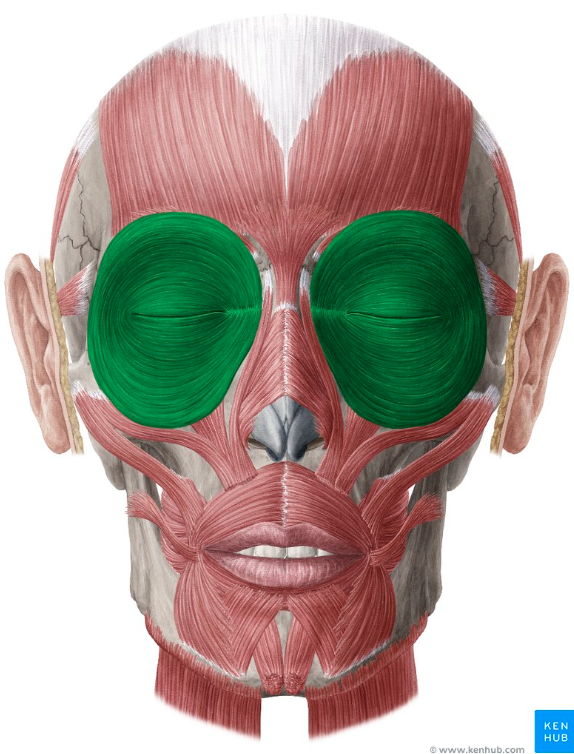
function of orbicularis oris
closes mouth area and does kissing
function of zygomatic major and minor
goes to corner of mouth and helps you smile
where does the zygomatic major originate from? where is its insertion?
originates on the zygomatic bone and inserts on the skin at superolateral region of mouth
function of masster
allows elevation of mandible
where does the masseter originate and where is its insertion?
originates on the zygomatic arch and maxilla and inserts on the angle and ramus of mandible
function of temporalis
to elevate the mandible
what is the origination and insertion of the temporalis
originates on the parietal bone and inserts on the coronoid process of mandible
function of platysma
depresses the mandible
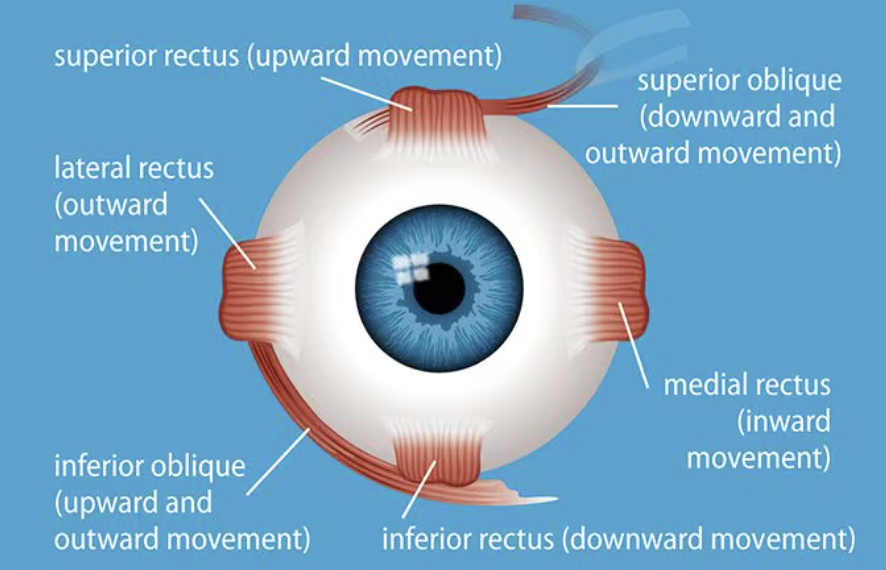
what is the function of the four eye muscles? what are their names
superior rectus: rotates eye superiorly, to look up
inferior rectus: rotates eyeball inferiorly, to look down
medial rectus: rotates eyeball medially, toward the nose
lateral rectus: rotates the eyeball laterally
name two synergist muscles on the face
temporalis and masseter
name three antagonistic pairs on the face
temporalis and platysma
masseter and platysma
lateral and medial rectus
if you are looking to your left, which muscle is responsible for getting your left eye into position? what about your right?
lateral rectus; medial rectus
function of sternocleidomastoid muscle
allows you to bend your neck and turn or tilt your head
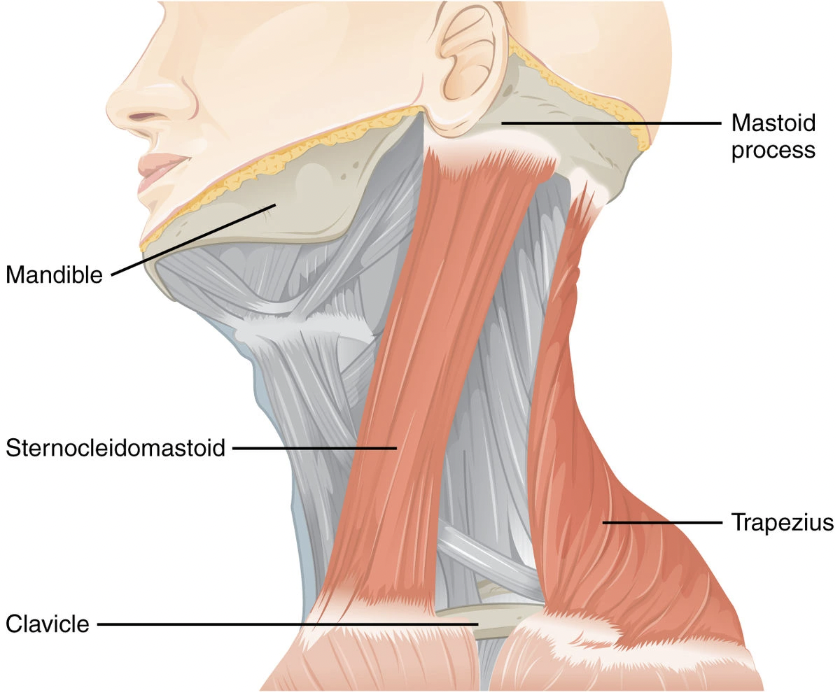
what is the origination and insertion of sternocleidomastoid muscle?
originates on the manubrium and the clavicle; inserts on the mastoid process
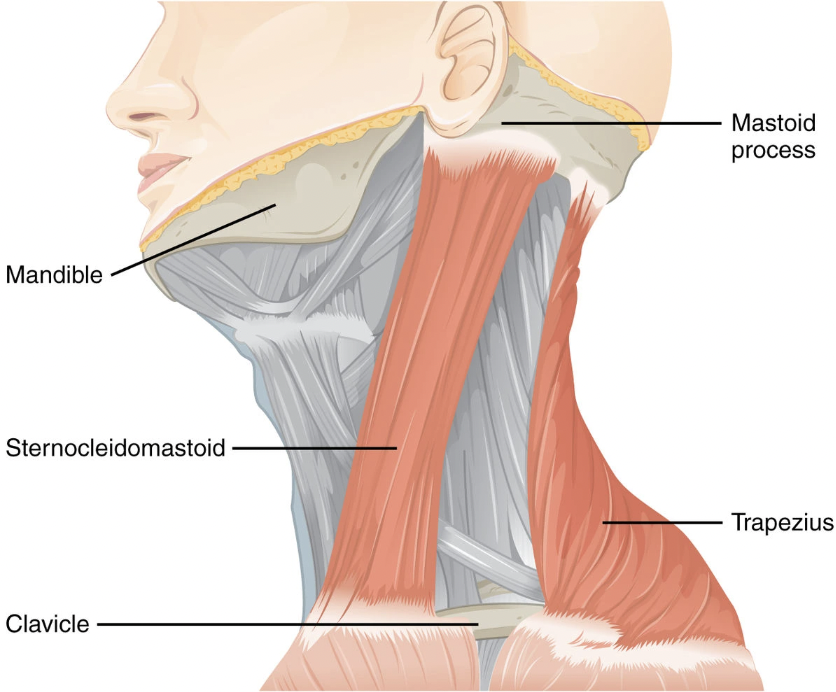
what happens if both splenius capitis muscles contract?
the head extends and works as antagonist of sternocleidomastoid muscle
what happens if ONE of the splenius capitis muscles contract?
head rotates ipsilaterally and muscle works as a synergist with one of sternocleidomastoid muscles
which muscles contract and which ones relax when you turn your head to the right?
contracted: left sternocleidomastoid and right splenius capitis
relaxed: right sternocleidomastoid and left splenius capitis
what are certain situations in which the abdominal muscles work together to compress the abdomen?
urination, defecation, vomiting, childbirth, and coughing
function of diaphragm
inhalation
function of external intercostals
elevate rib cage and aid inhalation
function of internal intercostals
depress the rib cage to aid exhalation
function of erector spinae
extend the vertebral column
function of rectus abdominis
flex vertebral column
what is the origin and insertion of the rectus abdominis?
origin is on the pubis, insertion is on the xiphoid process and some of the costal cartilages
function of external and internal oblique
rotate trunk of body
function of transverse abdominis
compress the abdomen
which muscle is antagonist to the rectus abdominis?
erector spinae
Place a finger on your right side, between your iliac crest and your rib cage. If you were to stick a needle into your abdominal cavity at this point, it would pass through three layers of skeletal muscle. What are they? List them in order from superficial to deep.
external oblique, internal oblique, transverse abdominis
function of pectoralis minor
protract and depress the scapula
what is the origin and insertion of the pectoralis minor?
originates on ribs 3-5, inserts on coracoid process of scapula
function of serratus anterior
protract the scapula and hold is close to the rib cage
function of the trapezius
superior fibers: elevates scapula
middle fibers: retract scapula
inferior fibers: depress scalpula
how did the trapezius get its name?
from its trapezoid shape
function of pectoralis major
flexes and adducts the arm, ex. bench press
function of latissimus dorsi
extends and adducts the arm, ex. rowing
function of deltoid
abducts the arm
what’s the origin and insertion of the deltoid muscle
originates on the clavicle, and the acormion and spine of the scapula; inserts on the deltoid tuberosity of humerus
function of tres major
adducts and extends the arm
function of subscalpularis
rotates arm medially
function of supraspinatus
abducts the arm
function of infraspinatus
adducts arm and laterally rotates arm
function of tres minor
adducts and laterally rotates arm
what are the two large superficial muscles visible on the back?
trapezius and latissimus dorsi
The military press is an exercise in which weights are lifted straight up and over the head. What is the main muscle acting to move the arm during exercise?
the deltoid
function of biceps brachii
flex the forearm
where is the origin and insertion of the biceps brachii?
origin is coracoid process of scapula and inserts into radial tuberosity
function of brachialis and brachioradialis
flex the forearm
function of triceps brachii
extend the forearm
what is the origination and insertion of the triceps brachii
originates on the scapula and posterior shaft of the humerus, inserts on the olecranon process
what two pair of muscles in the superior appendages are antagonistic?
biceps brachii and triceps brachii
deltoids and latissimus dorsi
why do muscles have “brachi” in their name?
indicates the location of the muscle
function of flexor carpi radialis
flex and abduct the hand
what is the origination and insertion of the flexor carpi radialis?
originates on the medial epicondyle of the humerus and inserts onto the second and third metacarpals
function of the flexor carpi ulnaris
flexes and abducts the hand
function of extensor carpi radialis longus? what does it work with to do?
extends the hand, works with flexor capri radialis to abduct the hand
extensor carpi ulnaris function? what does it work with?
extends the hand, works with flexor carpi ulnaris to abduct the hand