Gametogenesis. Fertilization
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

65 Terms
Gametes are derived from
Primordial germ cells (PGCs)
primordial germ cells (PGCs)
Formed in epiblast and moves to wall of yolk sac at the end 3rd week
4th week: migrate to developing gonads
When do the primordial germ cells migrate from the yolk sac to the developing gonads?
4th week and arrive by the end of the 5th week
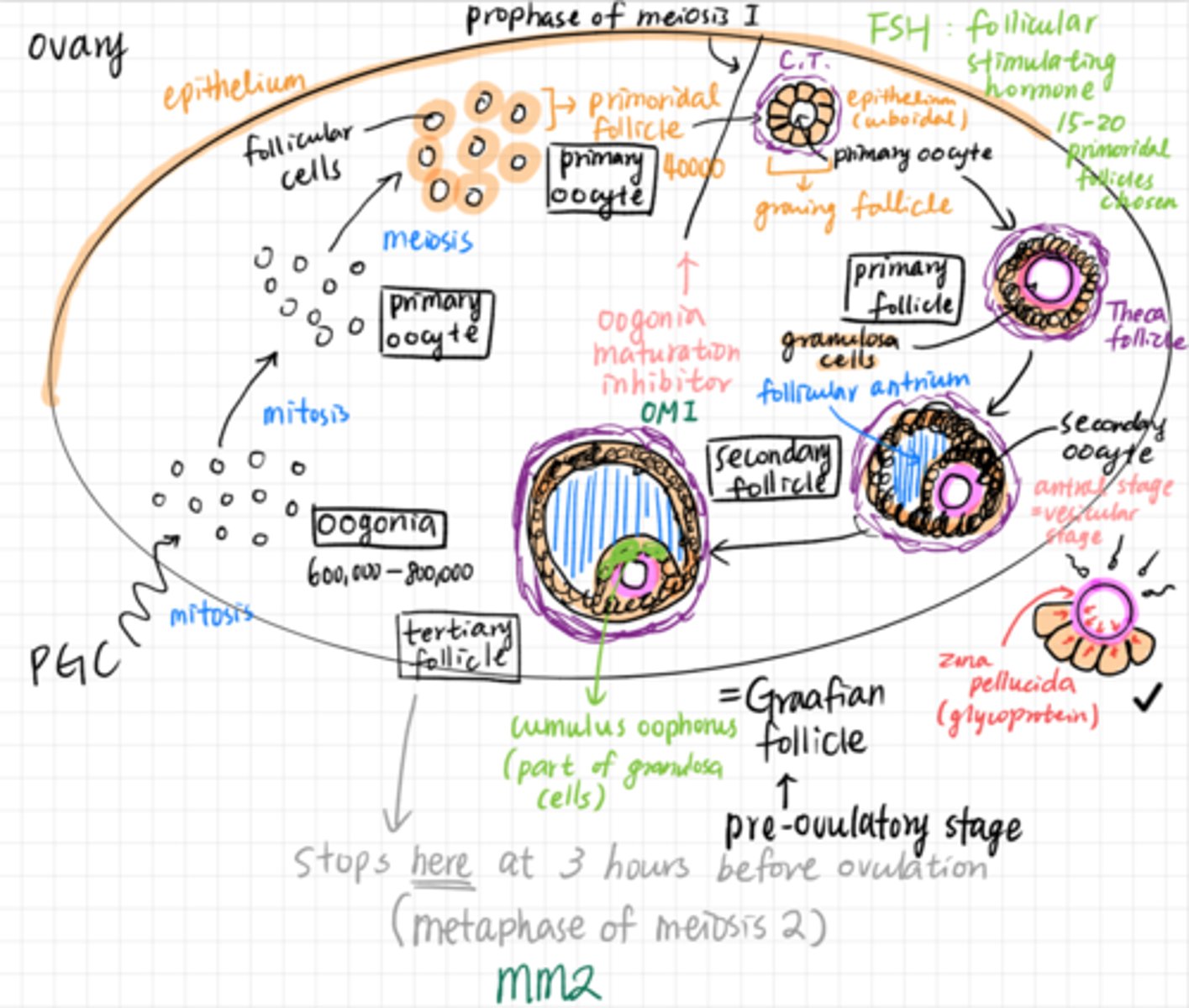
Oogenesis
the process in which PGCs differentiate into mature oocytes (ovum)
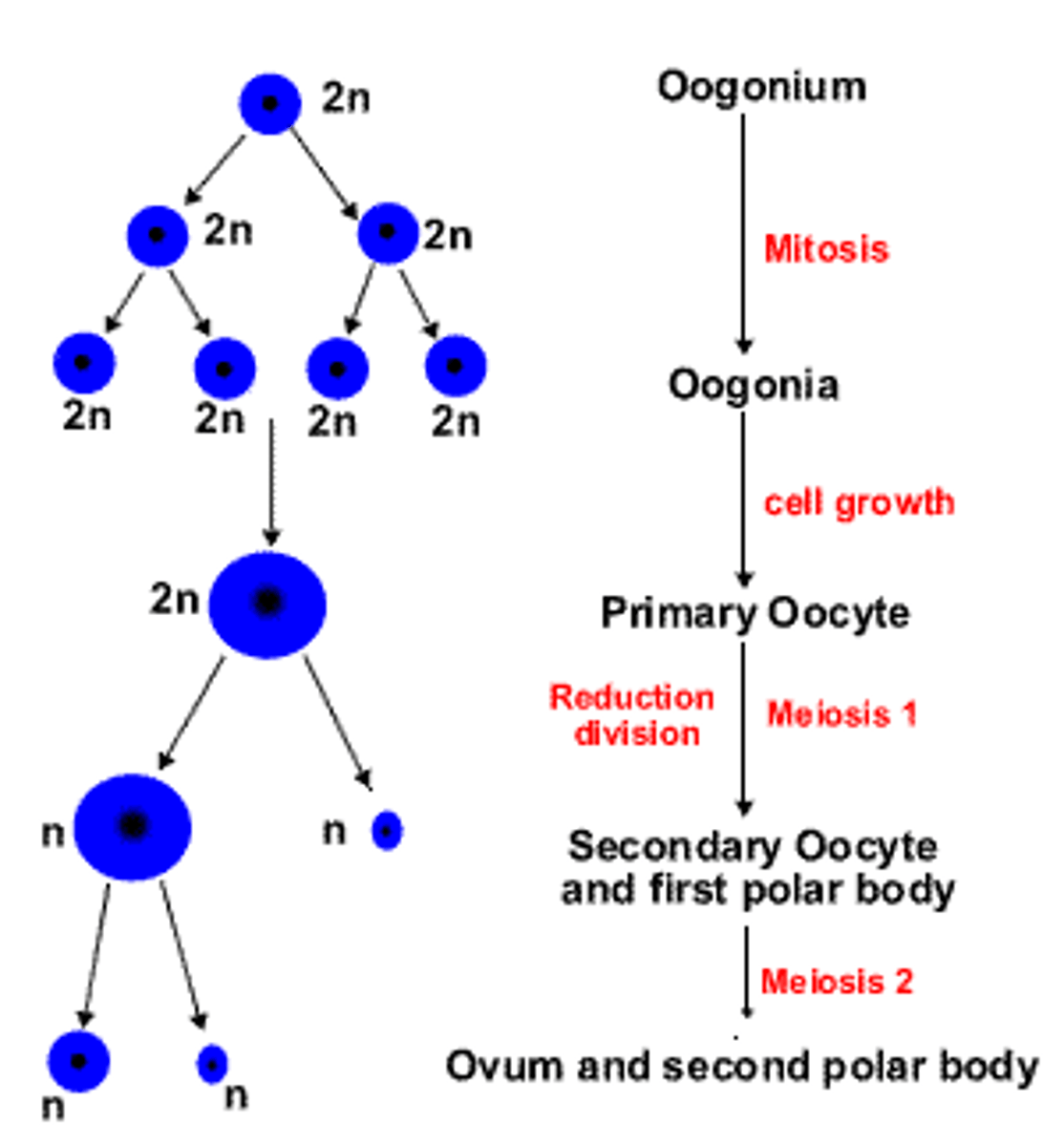
oogenesis location
cortex of ovary
When do PGCs differentiate into oogonia?
Before birth (embryo)
PGCs -> oogonium -> primary oocyte (arrested in prophase 1 of meiosis 1)
oogonia
When PGCs arrive at the developing gonads they differentiate into oogonia
Oogonia divide by mitosis to proliferate
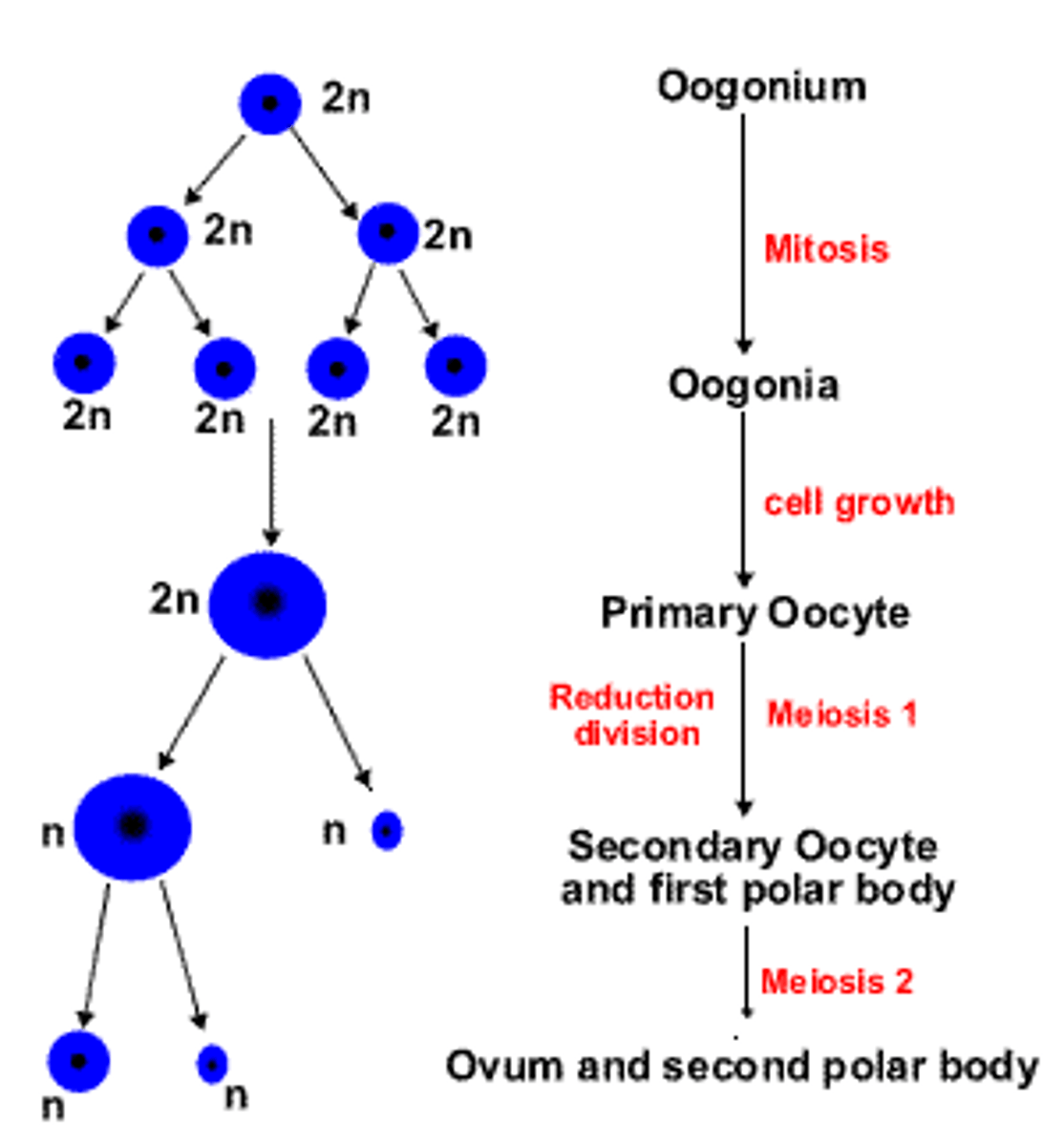
primary oocyte (2n)
Oogonia divides by meiosis to form primary oocyte (arrested in prophase 1 of meiosis 1)
diplotene stage
prolonged resting phase in oogenesis - primary oocytes are arrested in prophase 1 of meiosis 1 until puberty
atresia
Oocyte degeneration
5th month: 7 million PGCs
At birth: 600000 primary oocytes
At puberty: 40000 primary oocytes
Effect of atresia with increasing age
Primary oocytes are vulnerable as age increases -> Risk of having child with chromosomal abnormality
secondary oocyte
At puberty: primary oocyte completes meiosis 1 just 24 hours before ovulation -> secondary oocyte (arrested in metaphase of meiosis 2)
Cytokinesis of meiosis 1 gives the 1st polar body
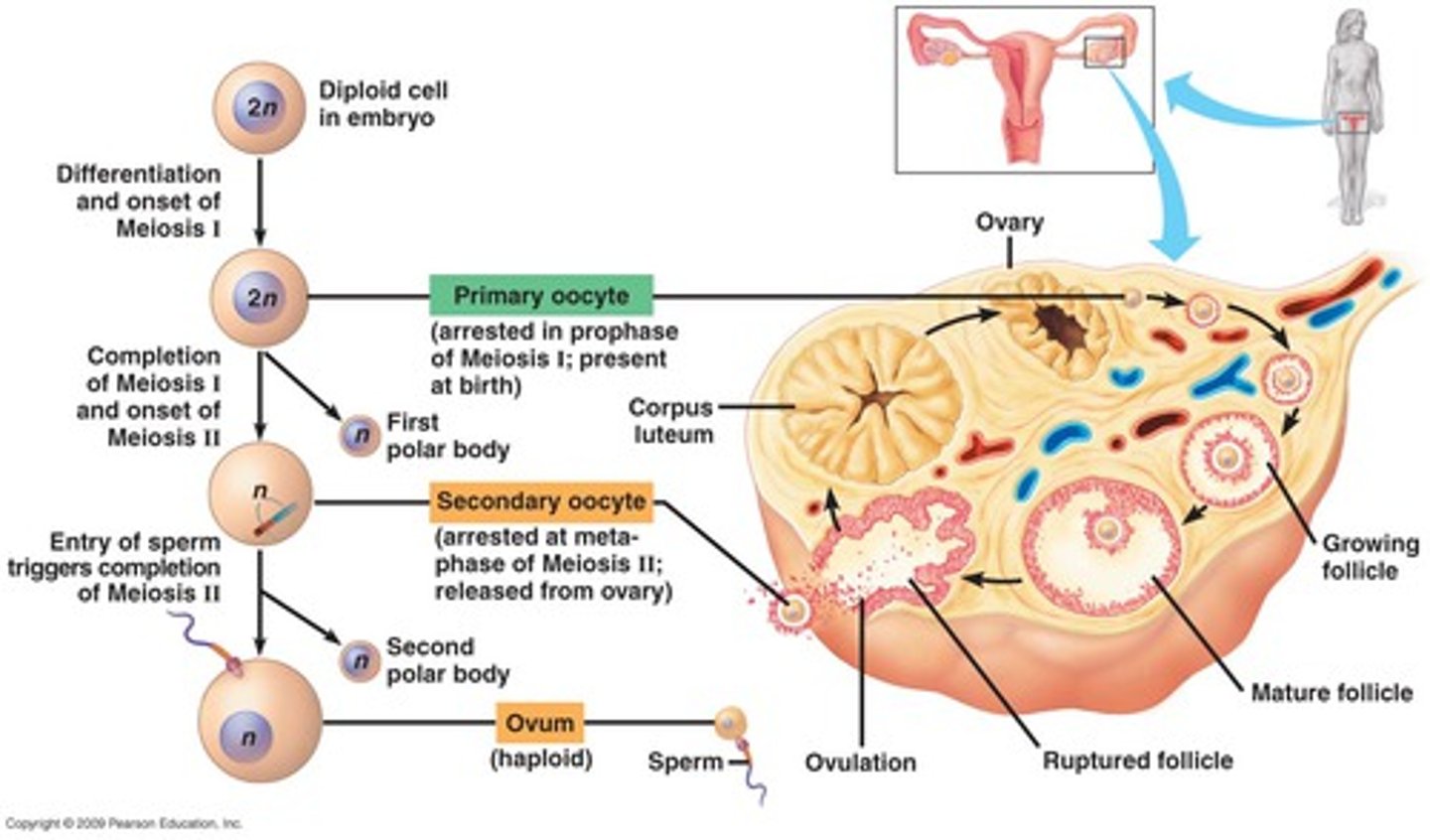
polar bodies
Receive little amount of cytoplasm and degenerate after
1 primary oocyte -> 4 daughter cells: 1 ovum + 3 polar bodies
Ovum (egg)
After fertilization: secondary oocyte finishes meiosis 2 -> ovum + 2nd polar body
No fertilization -> secondary oocyte degenerates
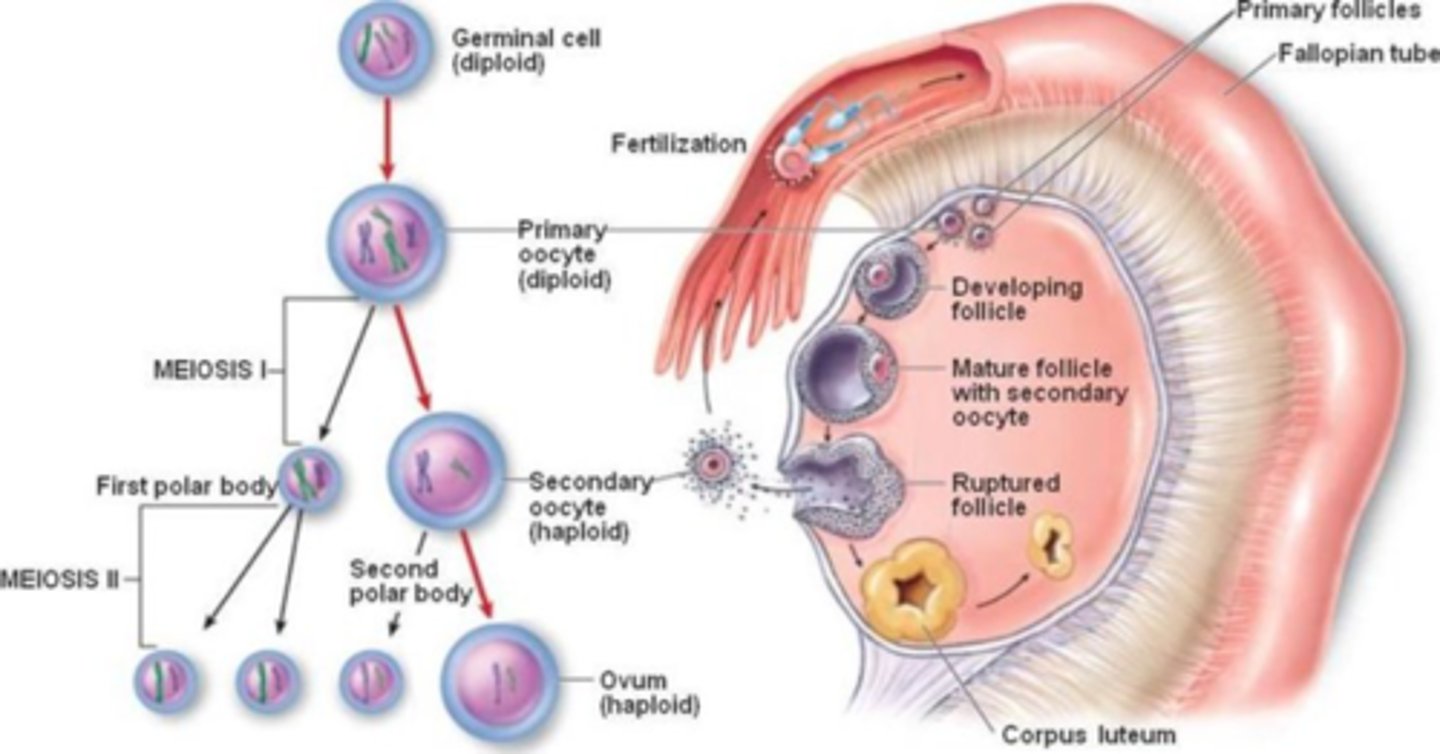
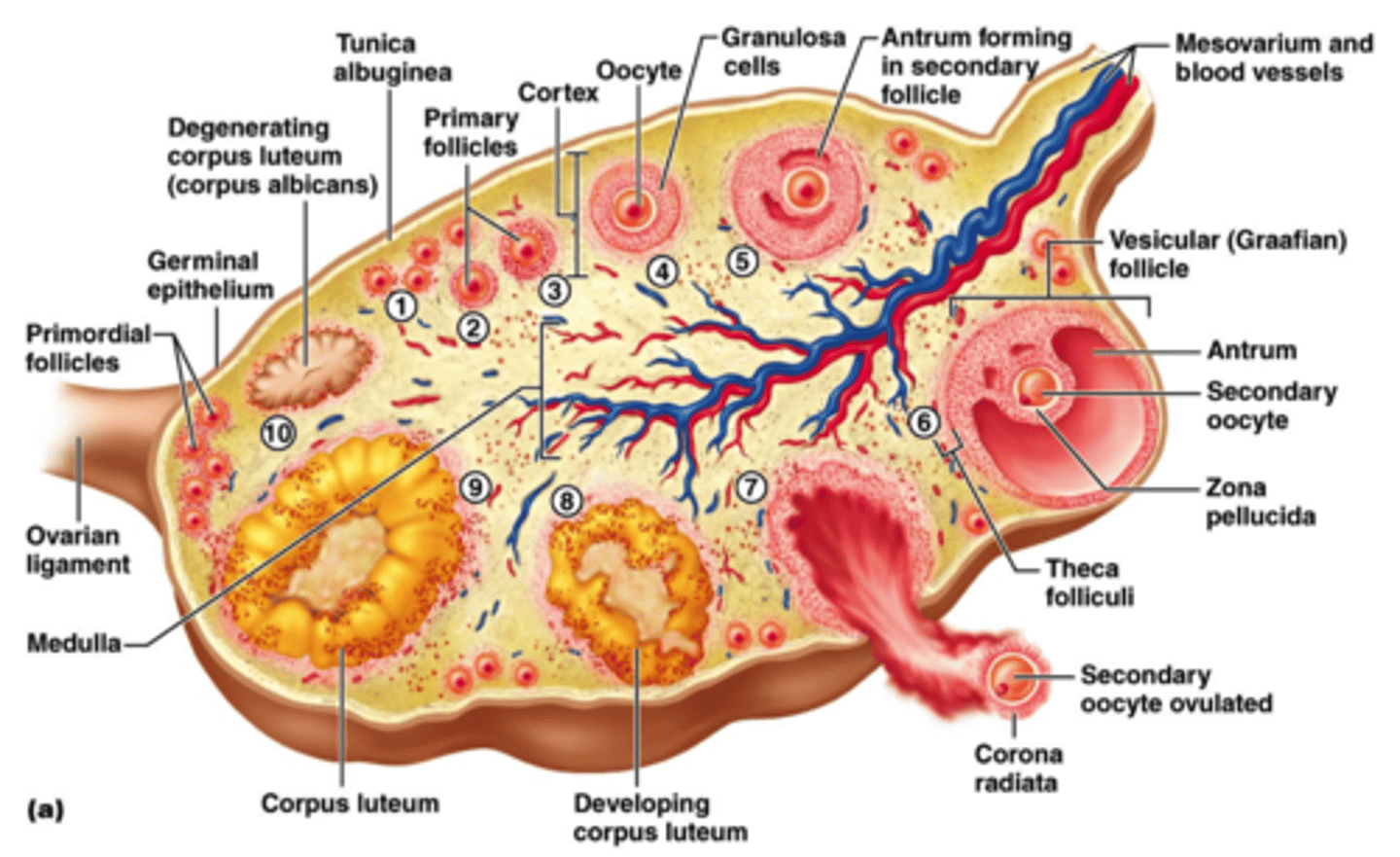
follicular development
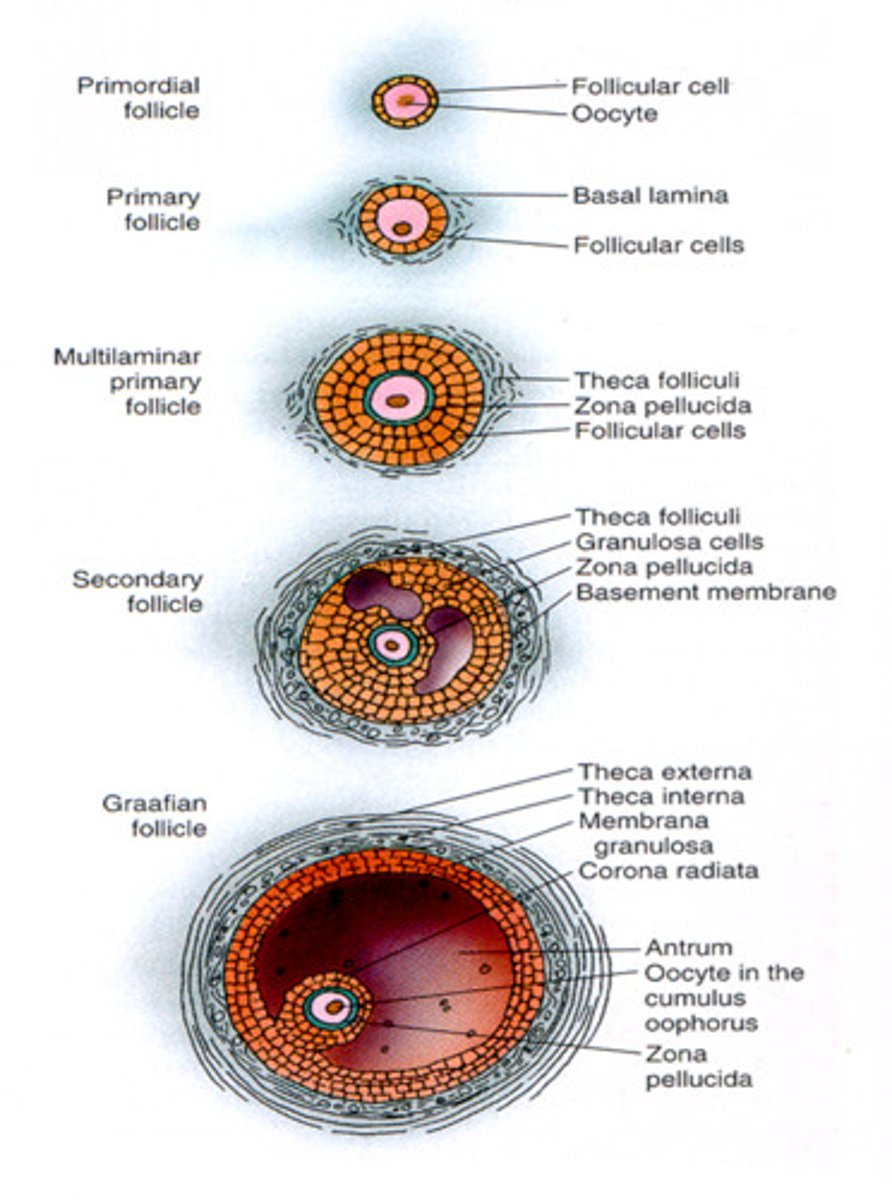
primordial follicle
Primary oocyte + single layer of squamous follicle cells
End of 3rd month
Arrested in this phase by OMI

primary follicle
Puberty, primary oocyte, 15-20 primary follicles begin to grow each month
Follicular cells: squamous -> cuboidal (granulosa cells); single layer -> stratified
Granulosa cells: produce zona pellucida
Theca folliculi: CNT surrounding ovarian
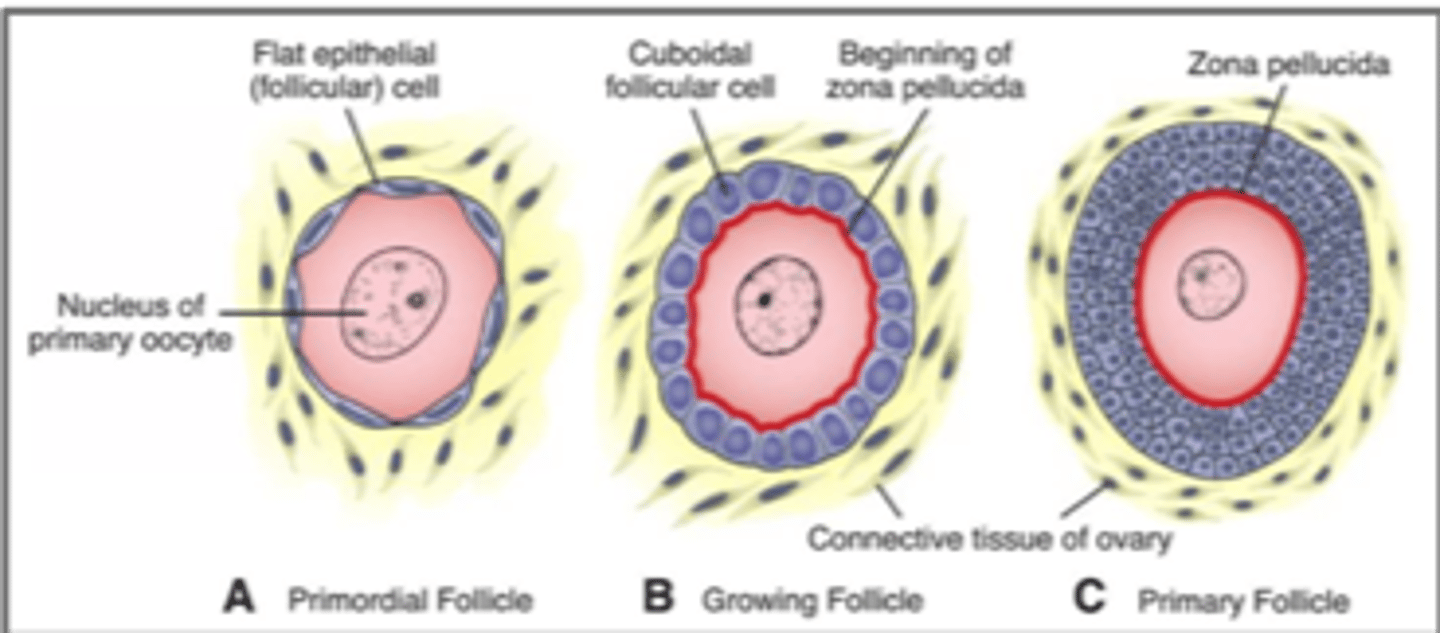
zona pellucida
Glycoprotein membrane surrounding the oocyte
Produced by granulosa cells
Provides support and nutrients to oocyte
How are materials transported to the oocytes?
cytoplasmic projections from granulosa cells to oocyte (across zona pellucida)
secondary follicle
Primary oocyte + layers of granulosa cells
Antrum
Theca folliculi: interna (estrogen production) + externa
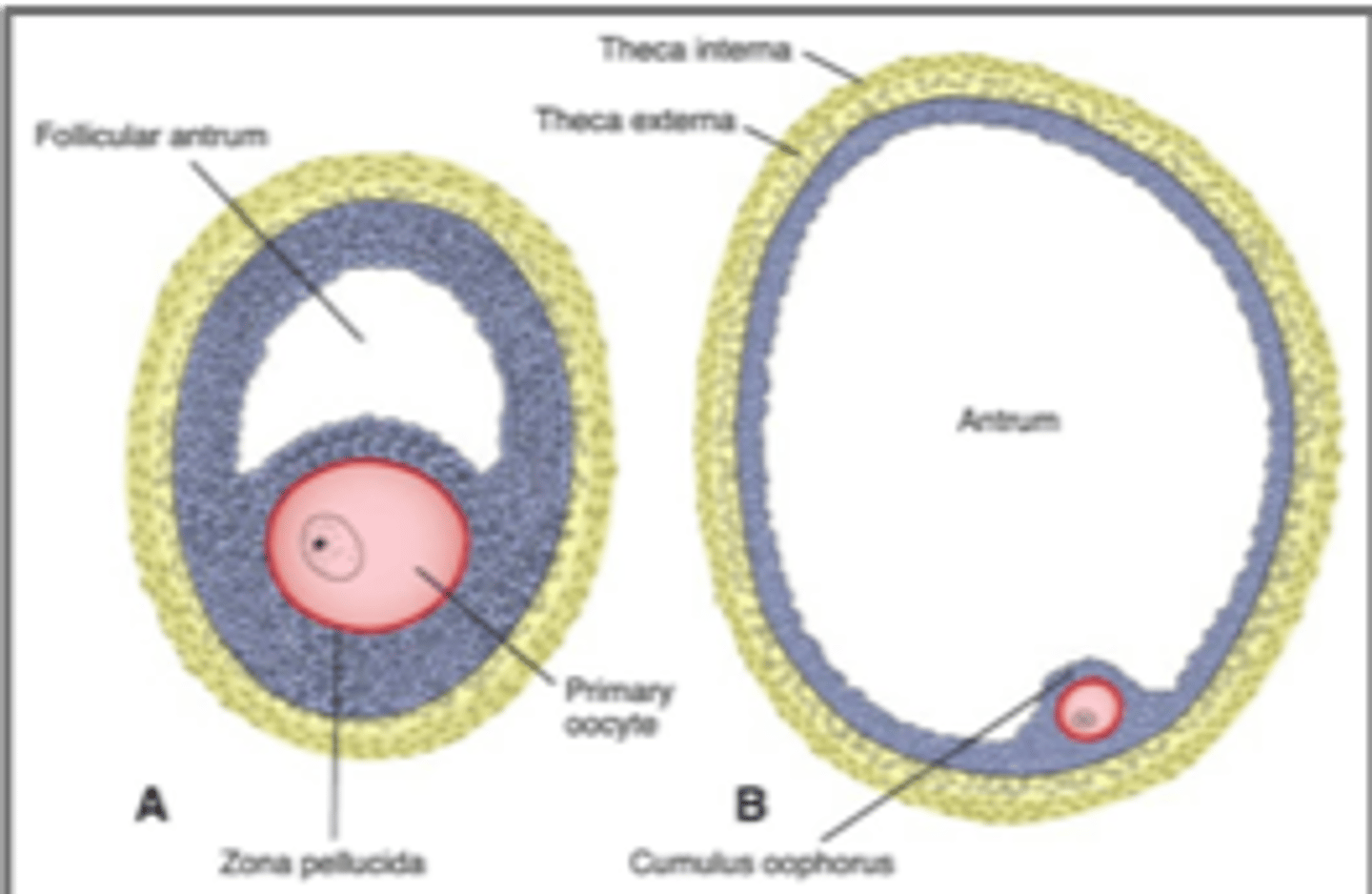
antral stage
Fluid accumulates between granulosa cells -> antrum
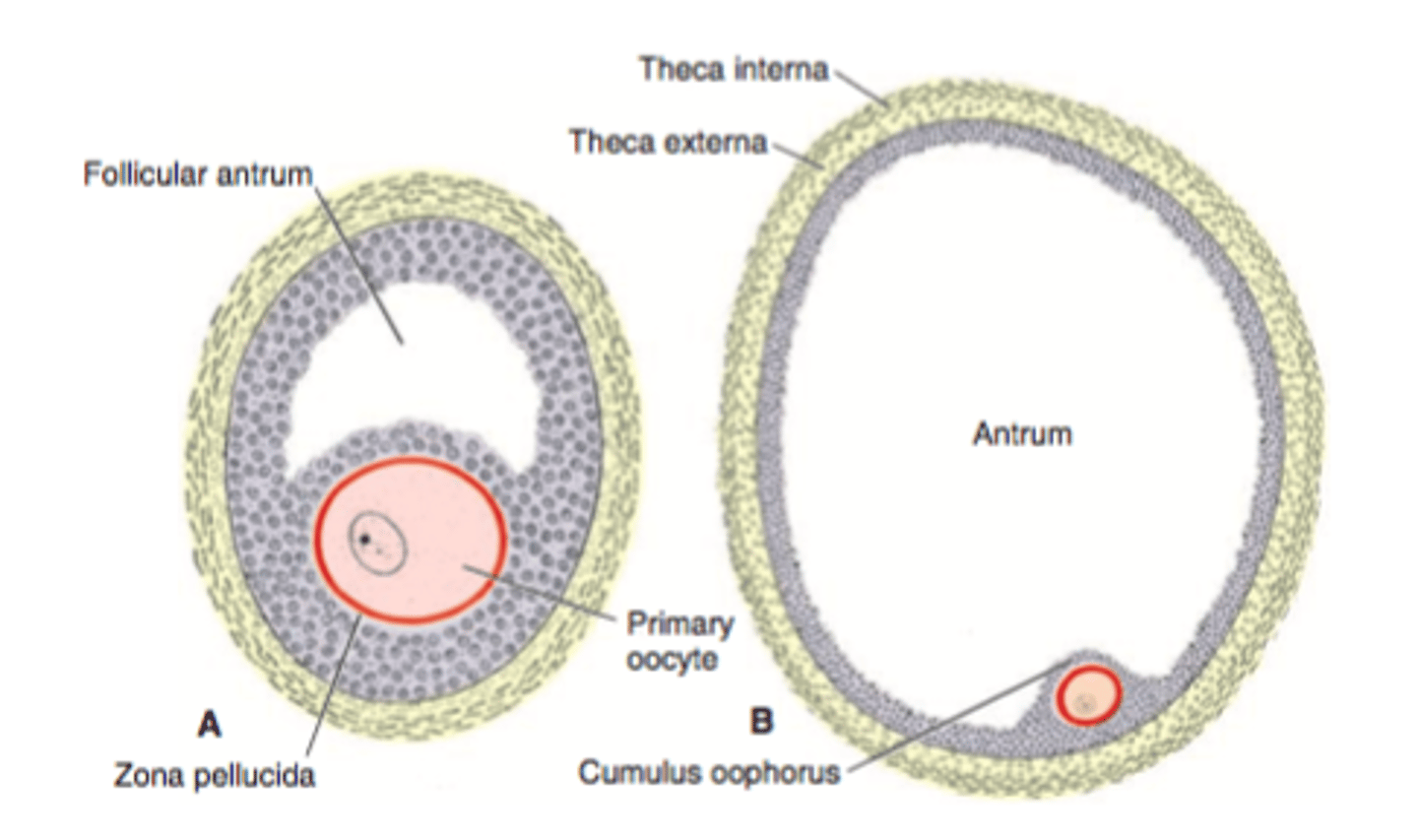
tertiary follicle (Graafian follicle)
Secondary oocyte
Cumulus oophorus
Corona radiata
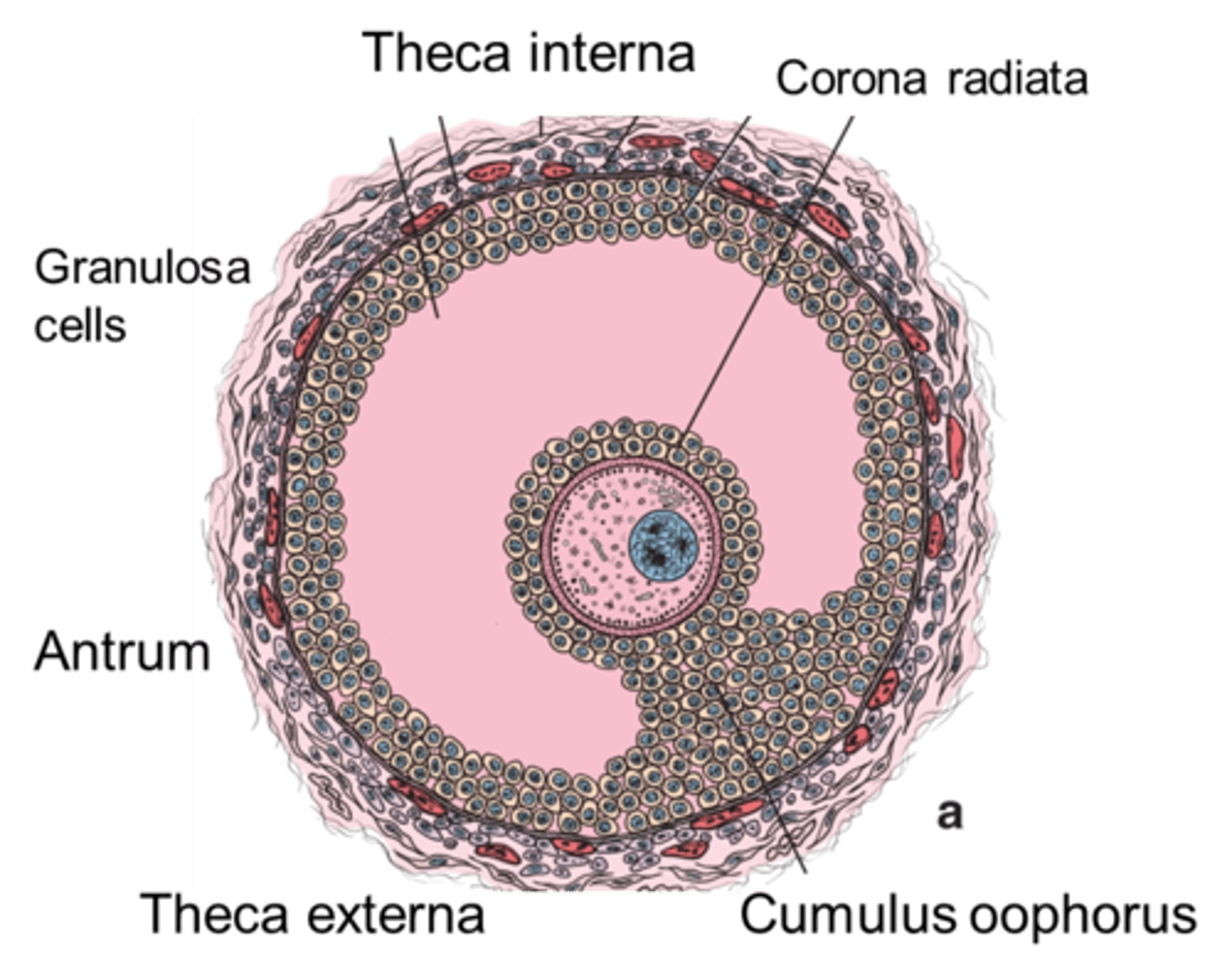
How many follicles mature each month?
1 from puberty to menopause
Overall oogenesis
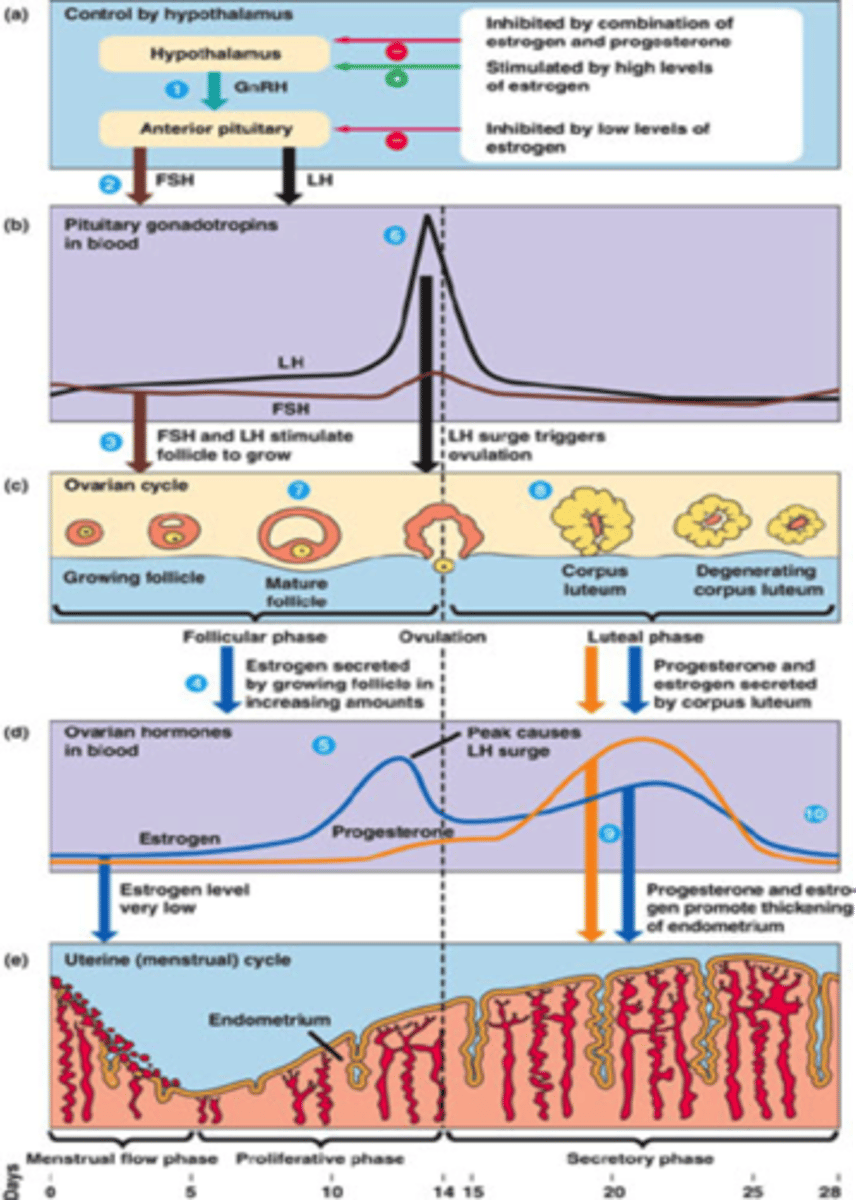
female reproductive cycle
Ovarian + uterine cycle (interconnected)
Average 28 days
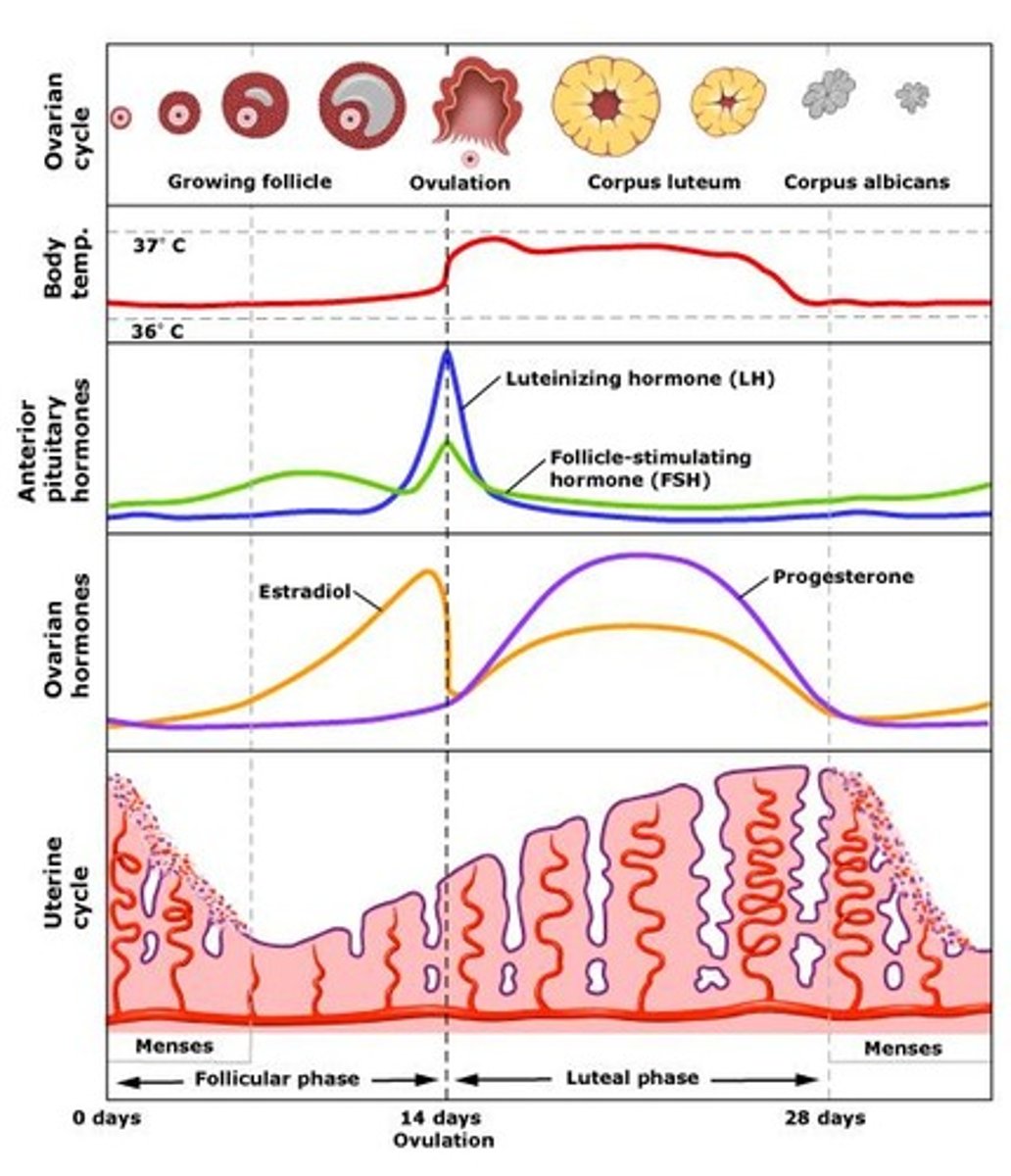
summary of ovarian cycle
ovarian cycle
Produce eggs and hormones
Follicular phase
Ovulation phase
Luteal phase
follicular phase of ovarian cycle
LH promotes development of theca folliculi -> secretes estrogen -> estrogen spike -> surge in LH -> ovulation around day 14
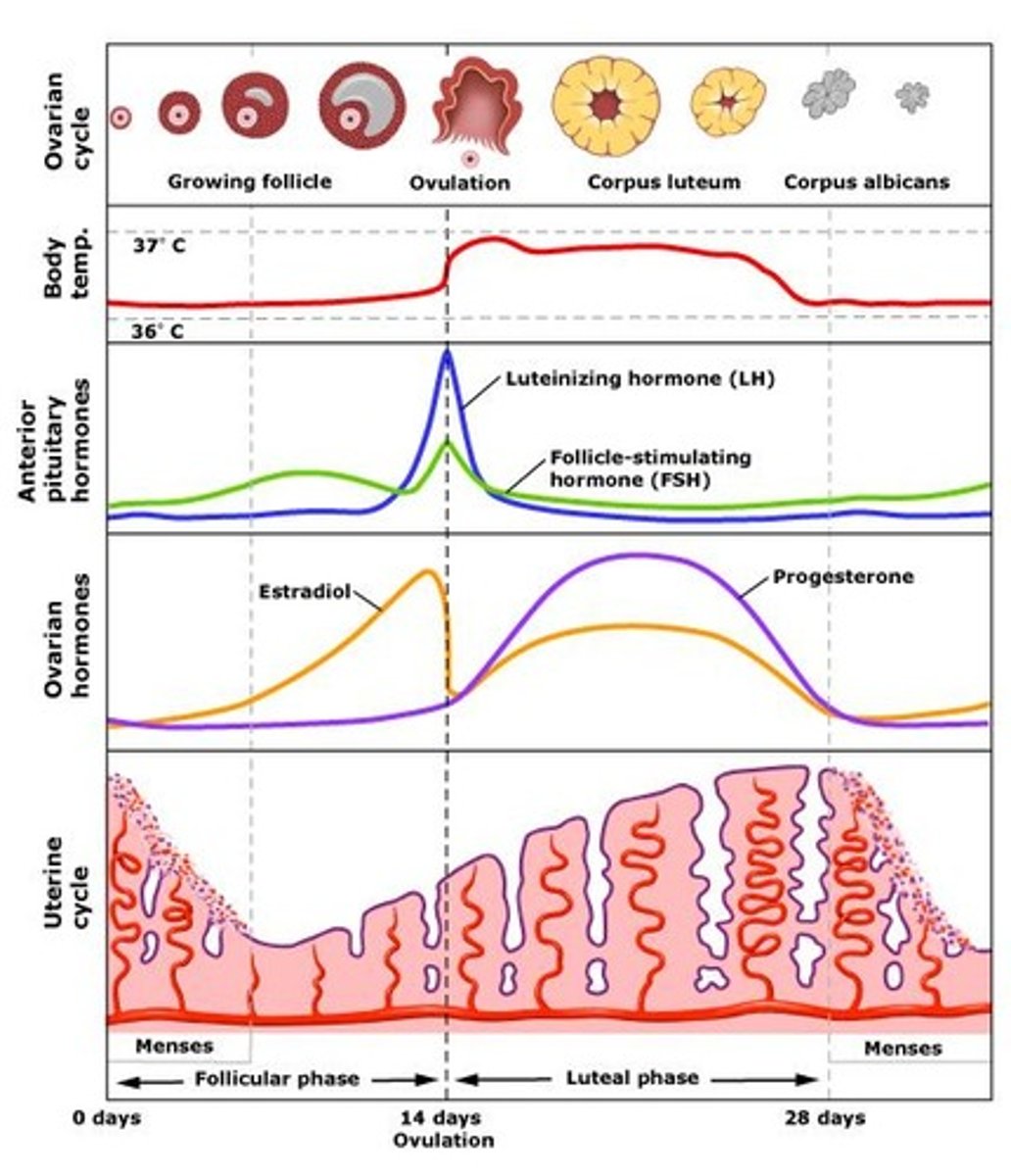
ovulation phase of ovarian cycle
Day 14
LH peak + FSH slight rise -> stimulates ovulation
(secondary oocyte release from mature follicle)
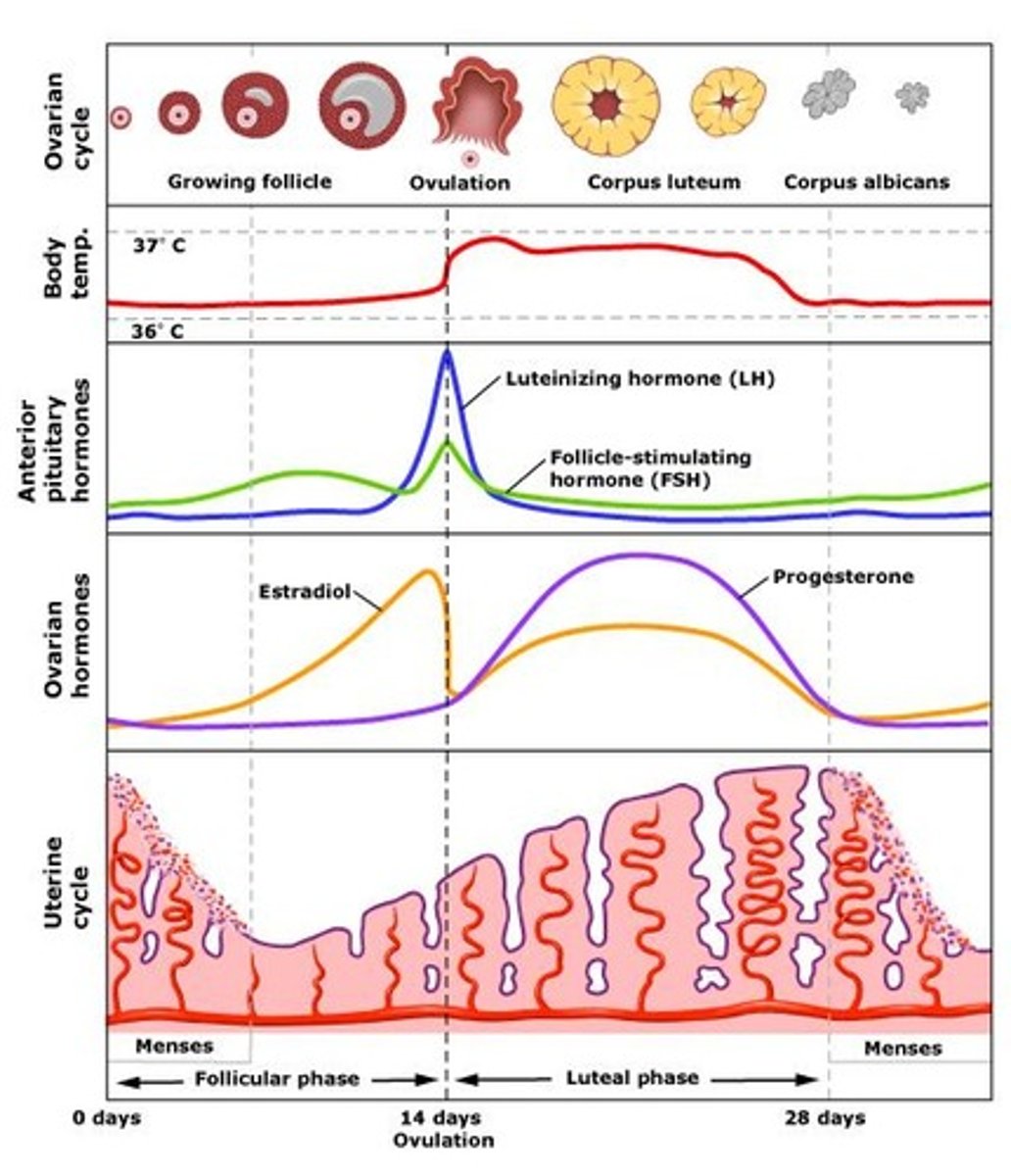
luteal phase of ovarian cycle
Days 15-28
LH stimulates secretion of progesterone by the corpus luteum -> promotes uterine lining growth
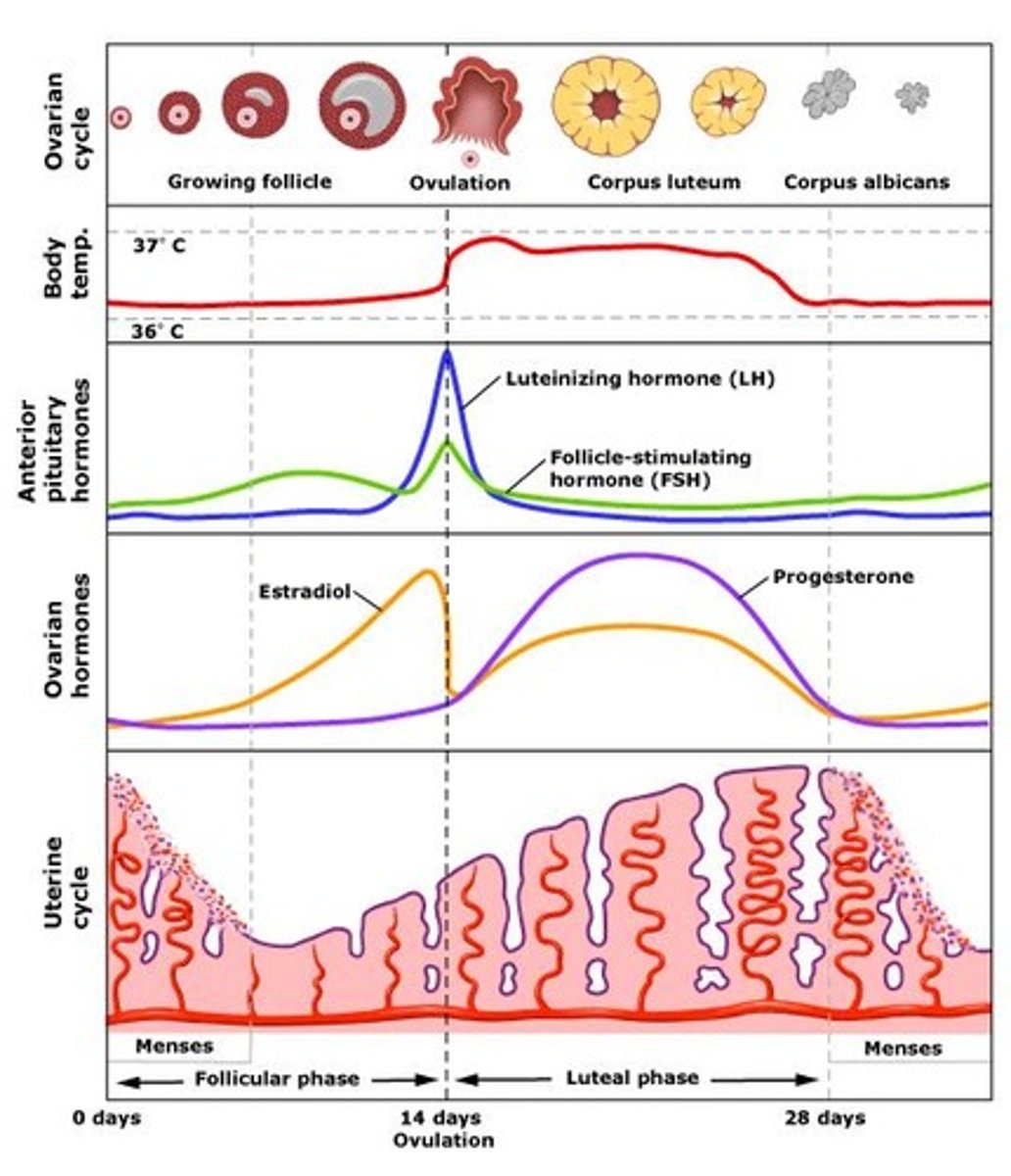
uterine cycle
Prepare lining of uterus (endometrium) for blastocyst
Endometrium remains 9 days after ovulation
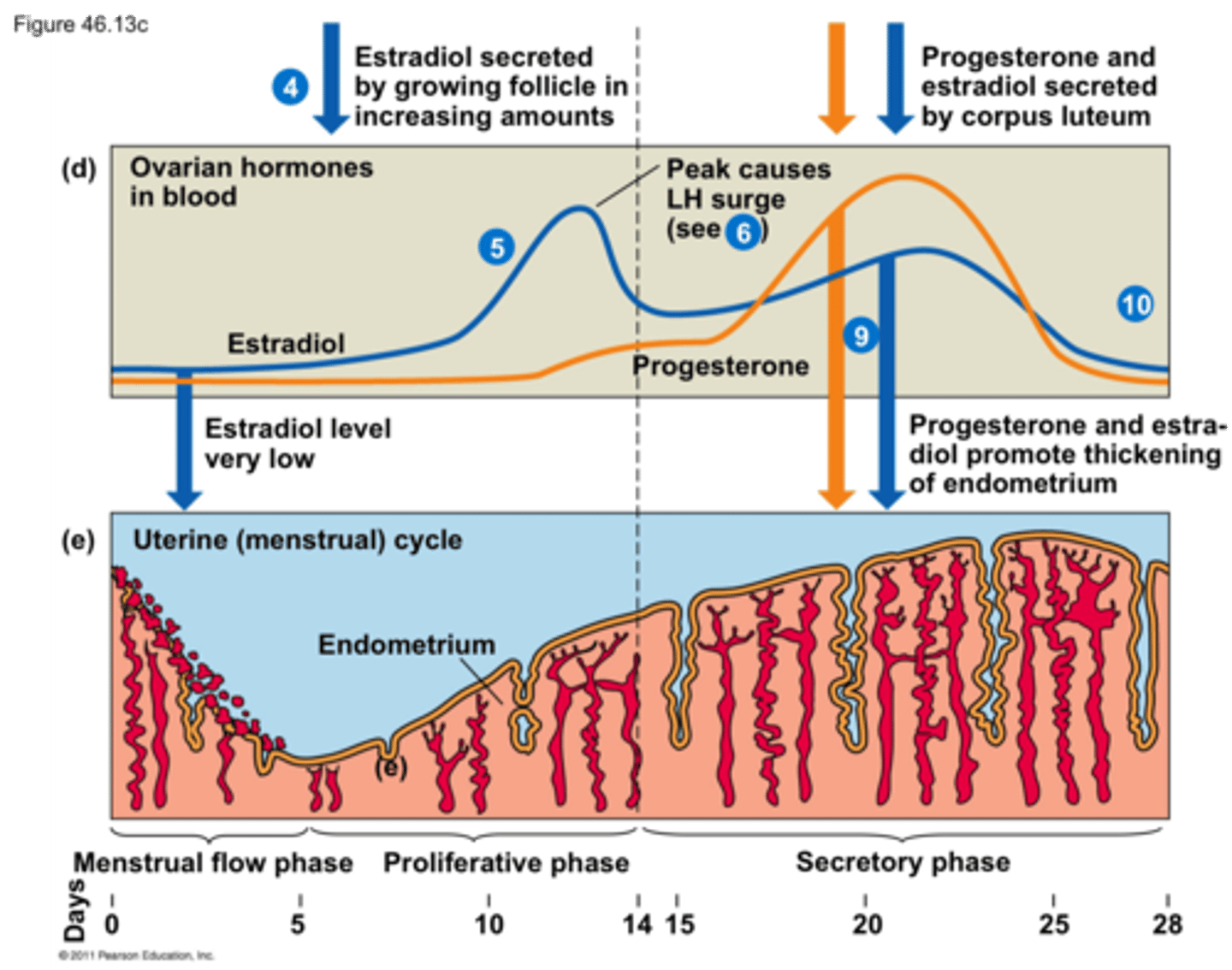
Menstruation
Shedding of the uterine lining without fertilization
GnRH, FSH, LH decrease
Progesterone
Produced by corpus luteum
Thickening of endometrium
Pregnancy: progesterone is produced until 3rd month of pregnancy (hCG)
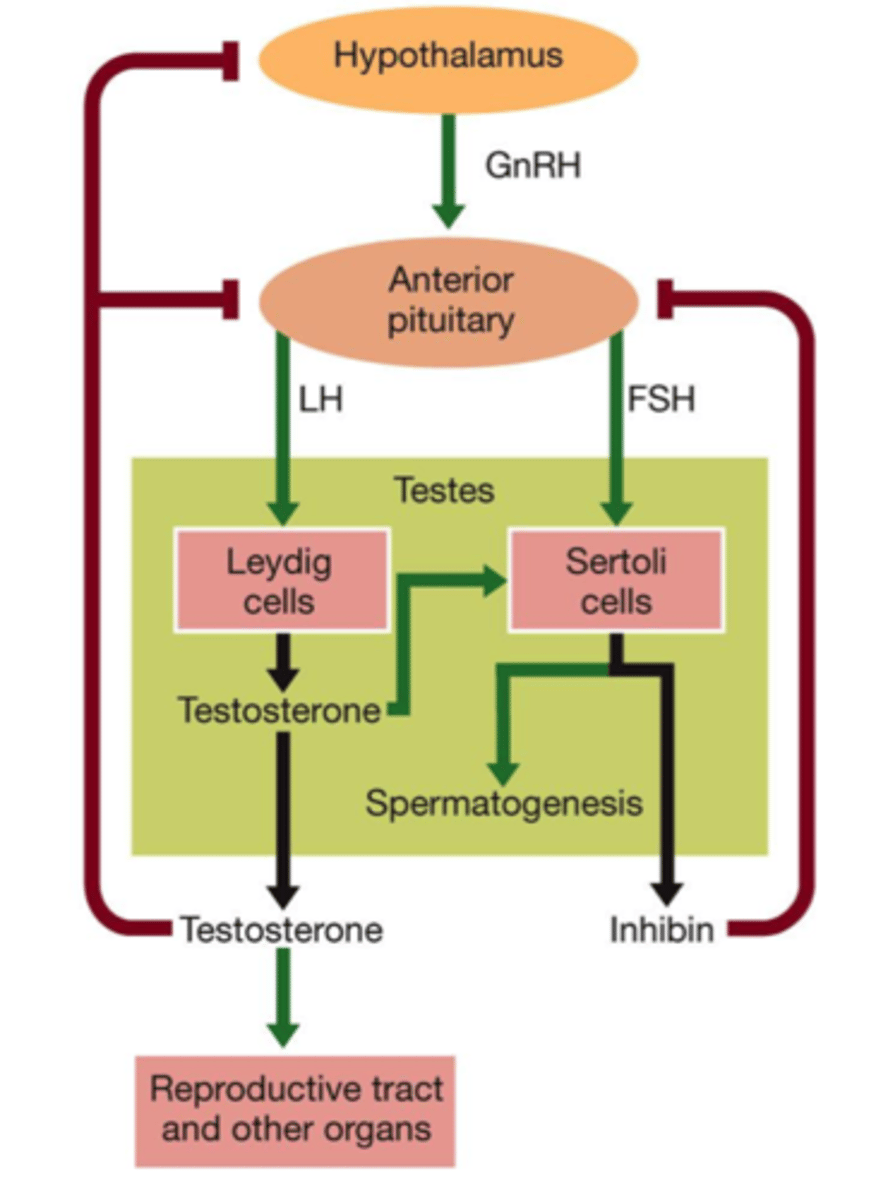
LH during oogenesis
LH surge causes primary oocytes to finish meiosis 1 -> secondary oocytes
maturation of secondary sex characteristics
caused by FSH and LH (GnRH)
LH during follicular phase
APG releases LH -> theca folliculi release androstenedione + testosterone
Granulosa cells convert them to estrogen
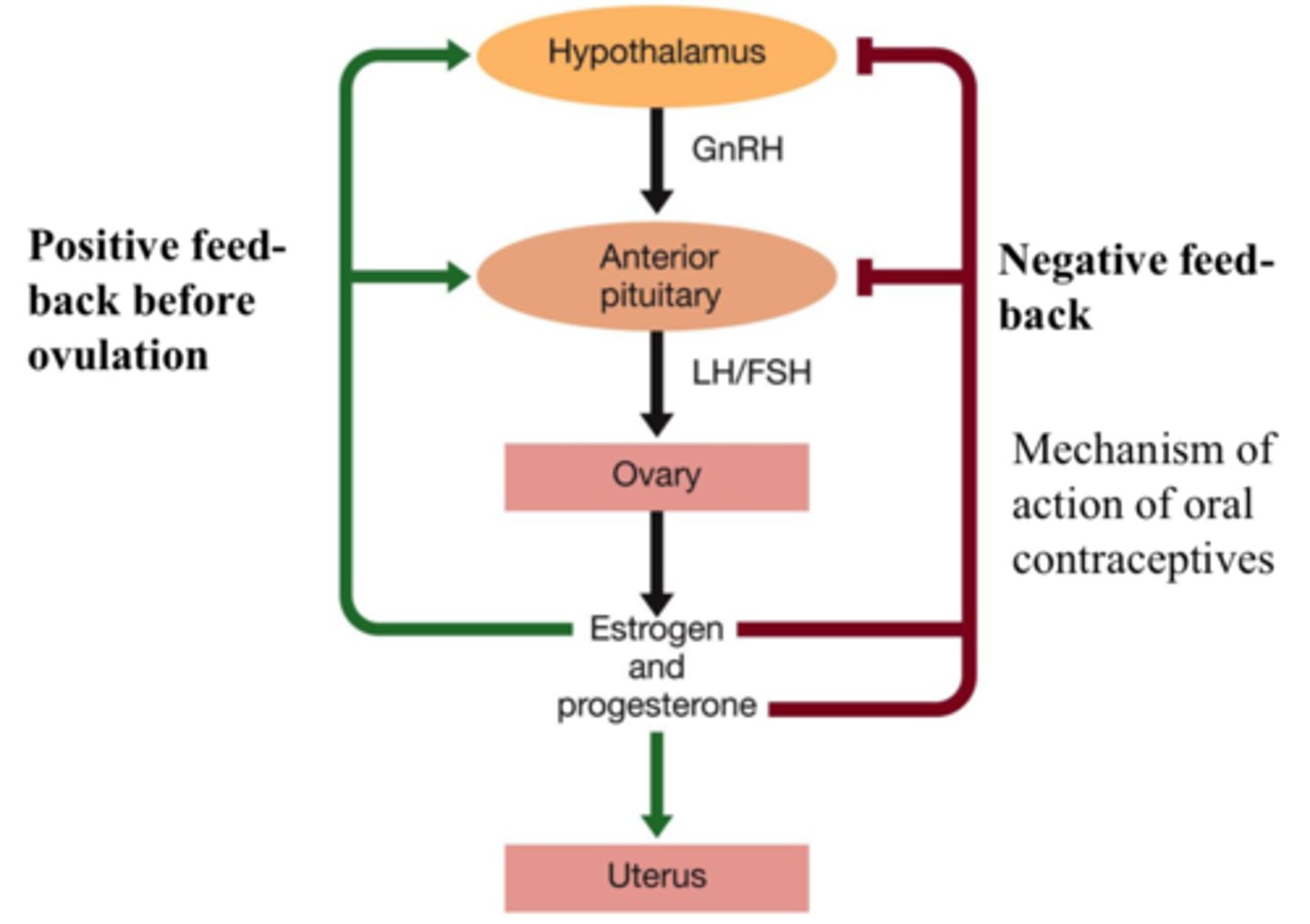
hormonal control of menstrual cycle
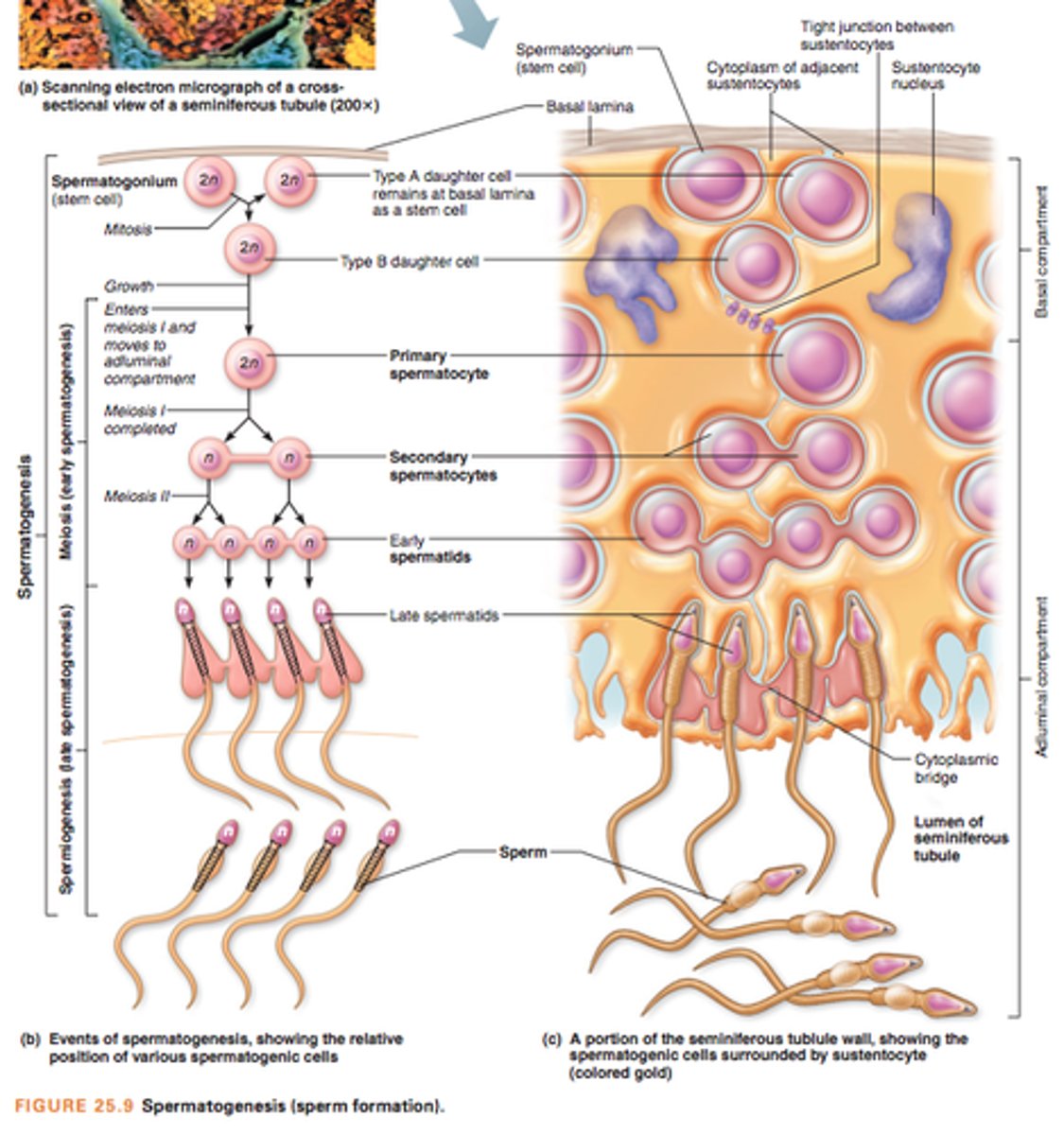
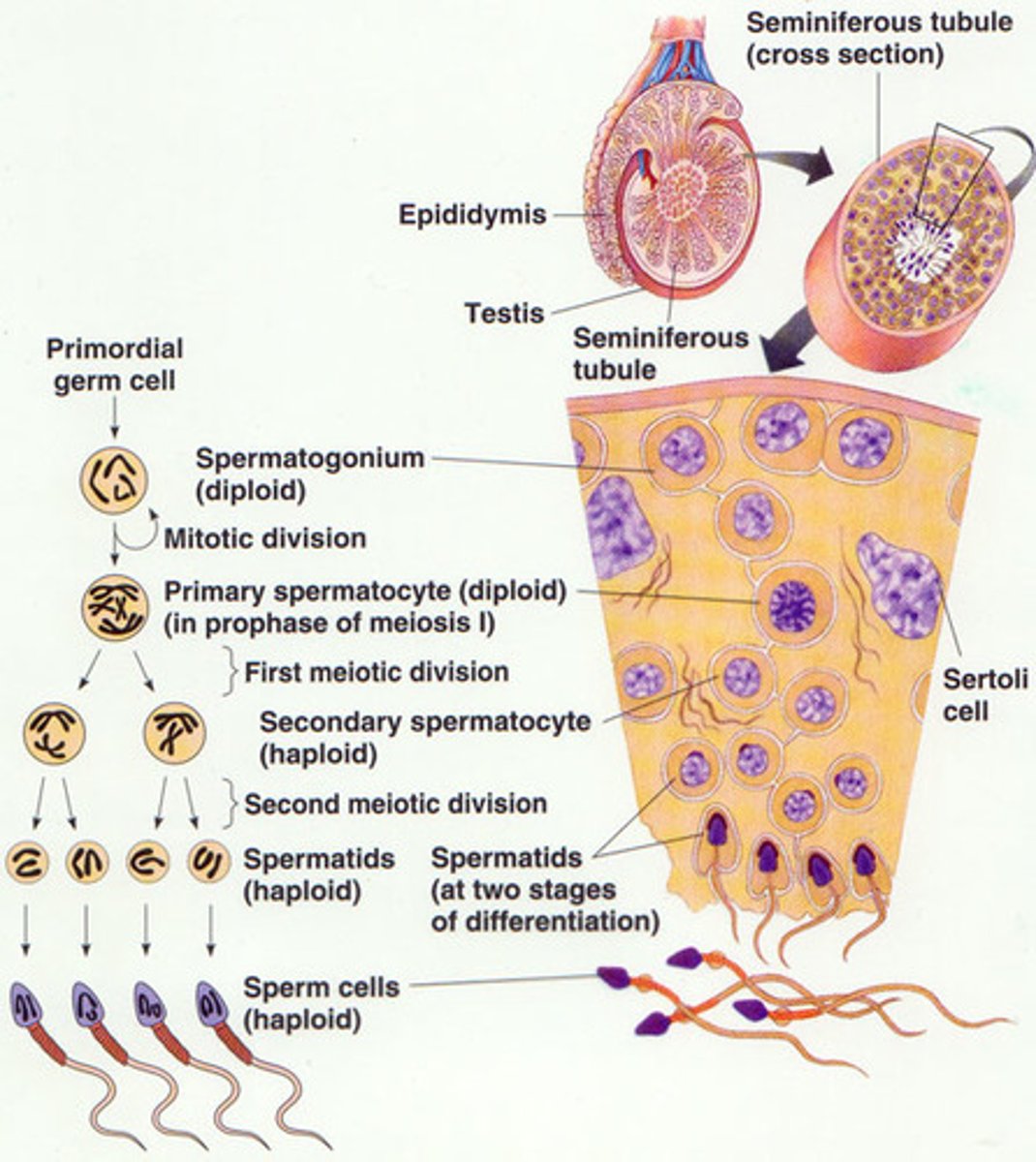
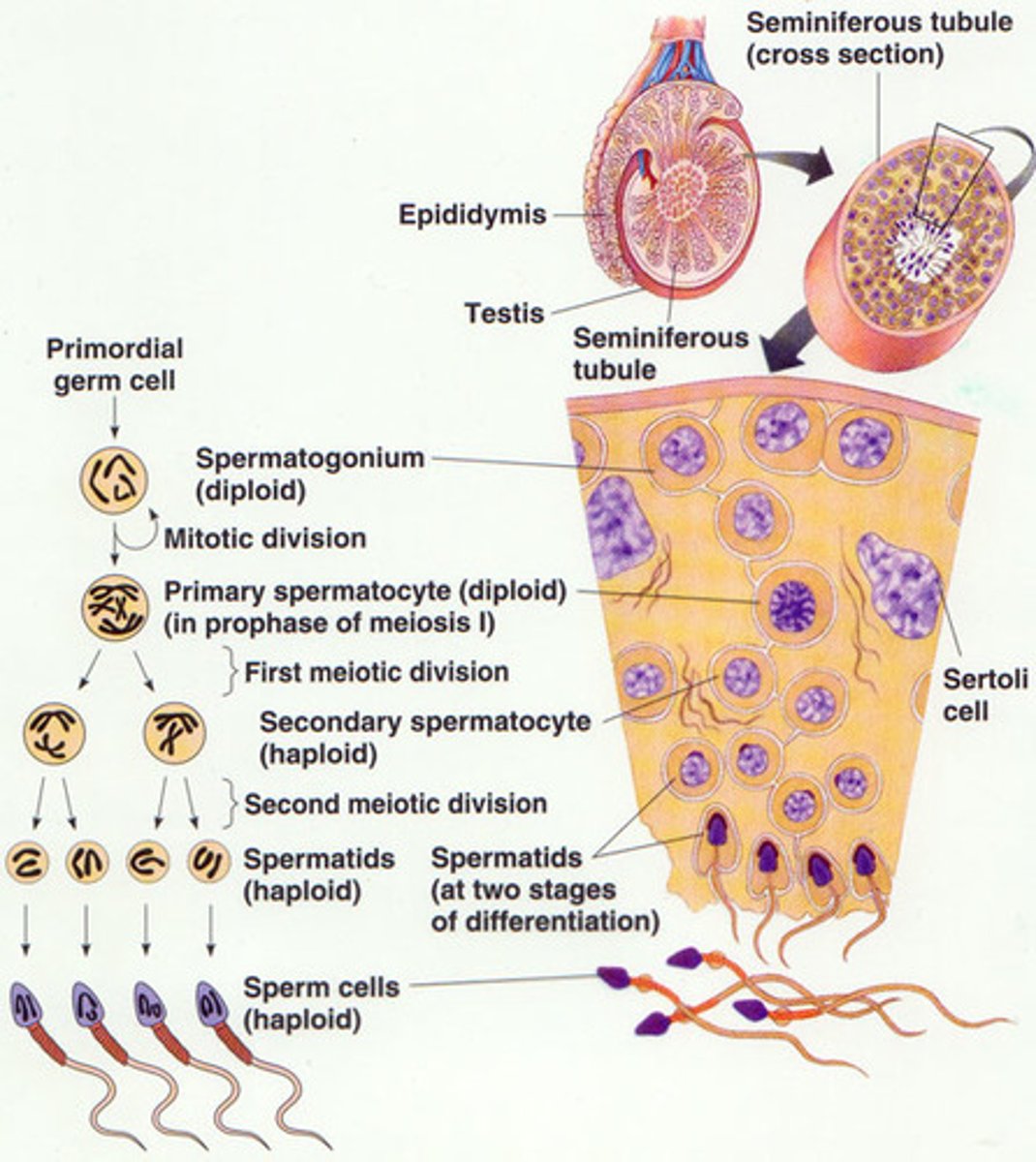
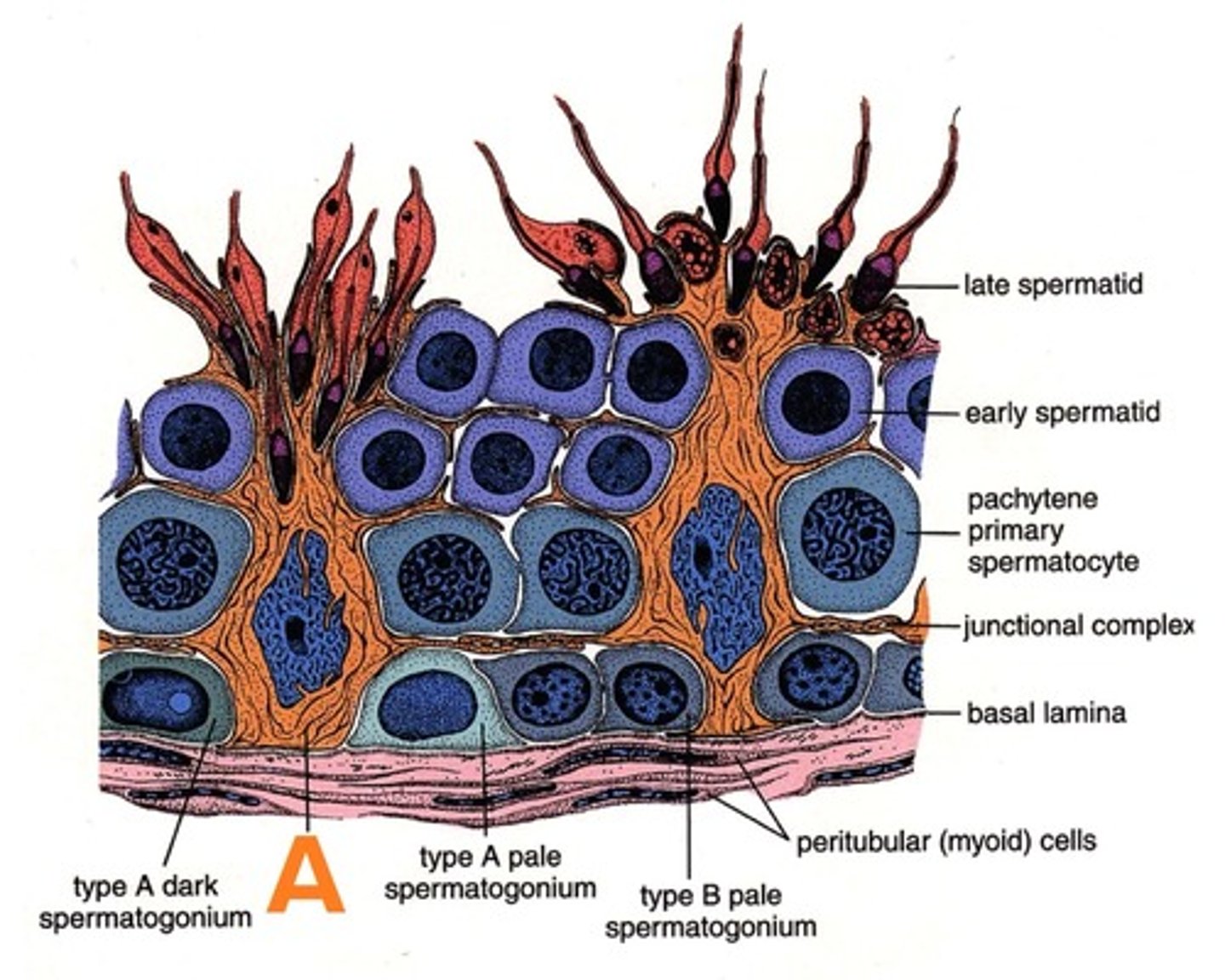
Spermatogenesis
Seminiferous tubules
Spermatogonia -> spermatozoa (mature sperm)
After puberty
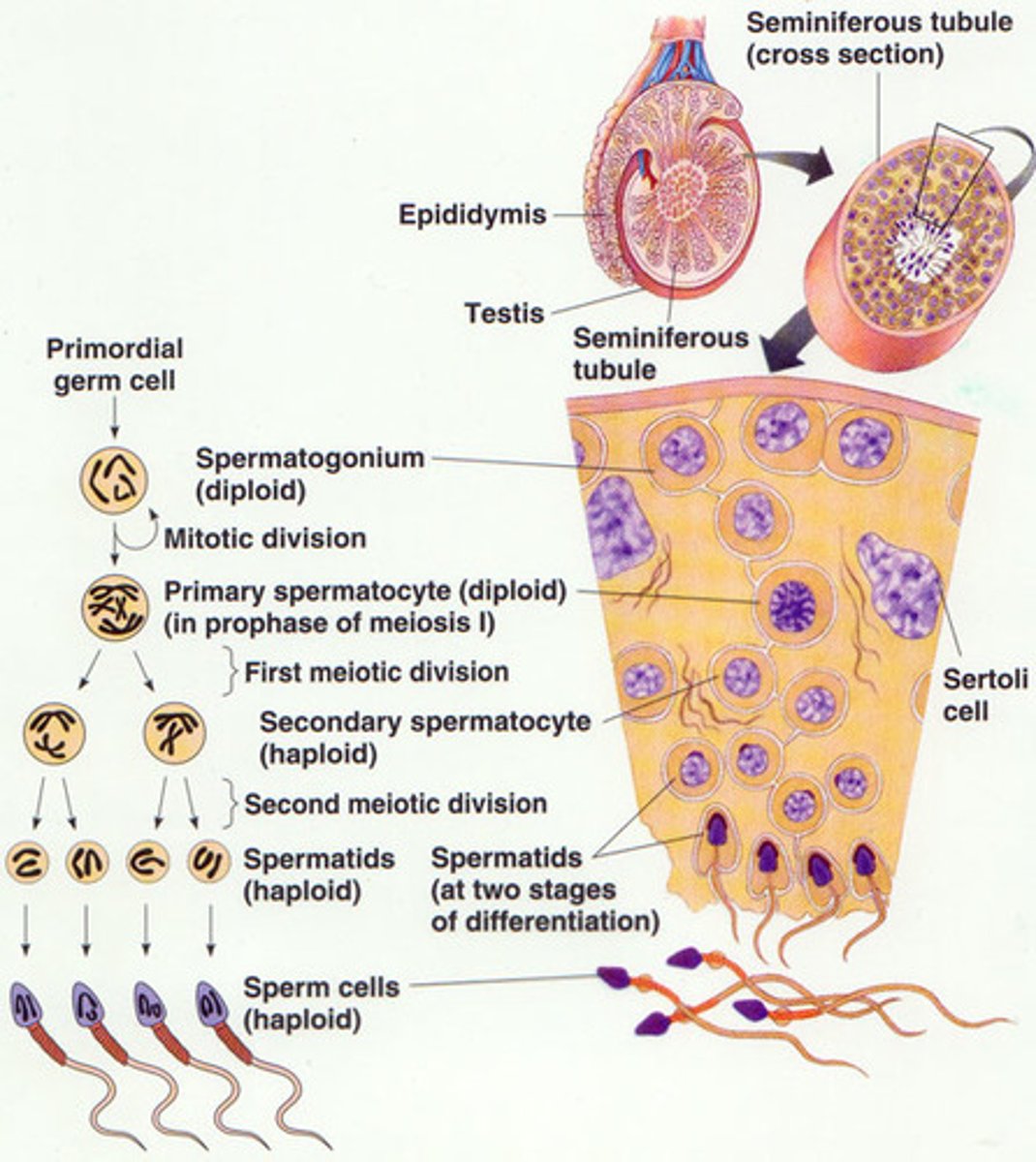
phases of spermatogenesis
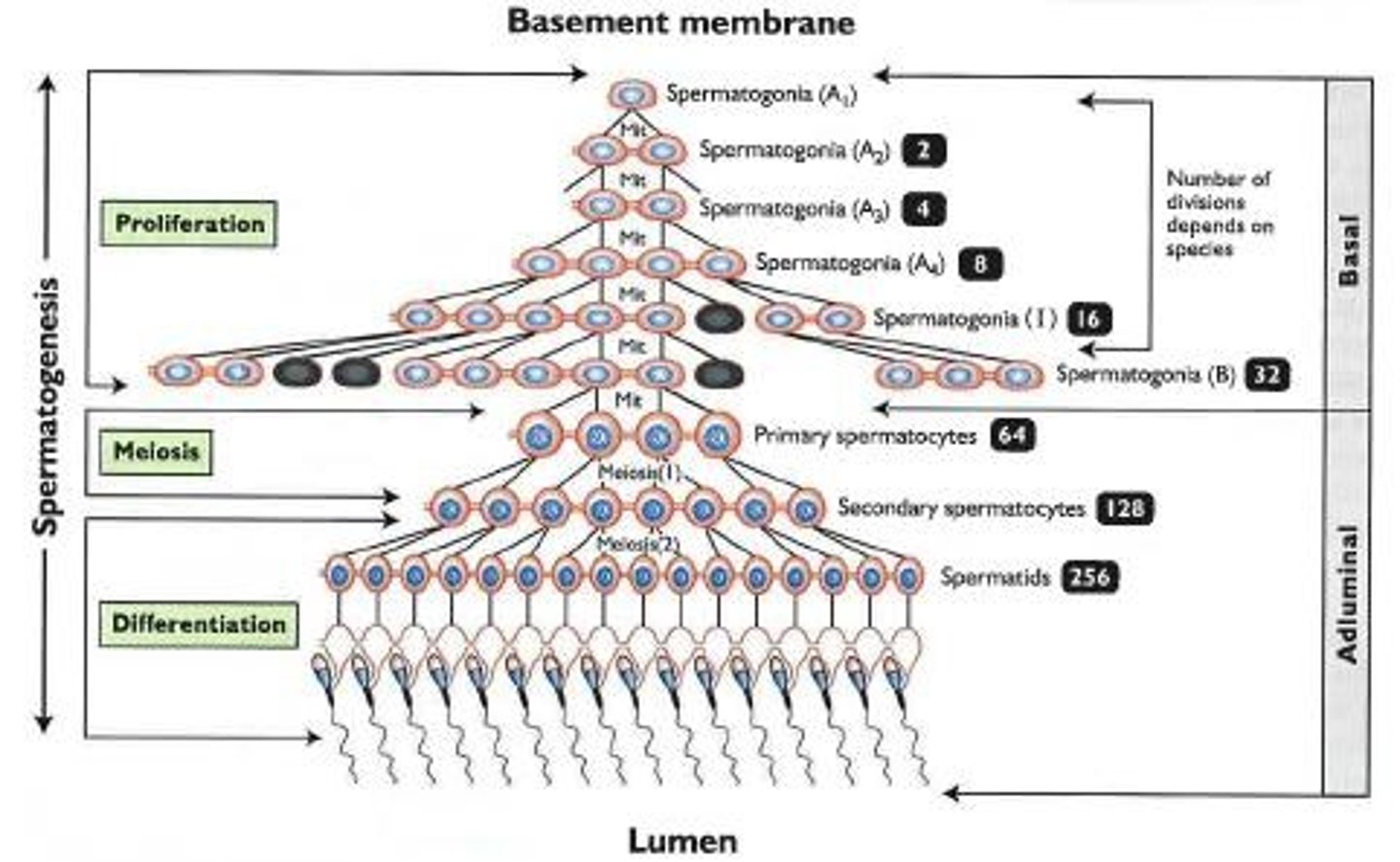
maturation phase of spermatogenesis
mitosis + meiosis 1 + meiosis 2
Type A spermatogonia
Undergo mitosis to produce type B spermatogonia
Type A dark spermatogonia
Type A pale spermatogonia
type B spermatogonia
divided by mitosis to form primary spermatocyte
Why is spermatogonia connected to each other?
Cytokinesis is incomplete -> connected by cytoplasmic bridges through out maturation
primary spermatocyte
Arrested at prophase 1 for 22 days
Complete meiosis 1 to produce secondary spermatocyte
secondary spermatocyte
Undergo meiosis 2 to produce spermatid
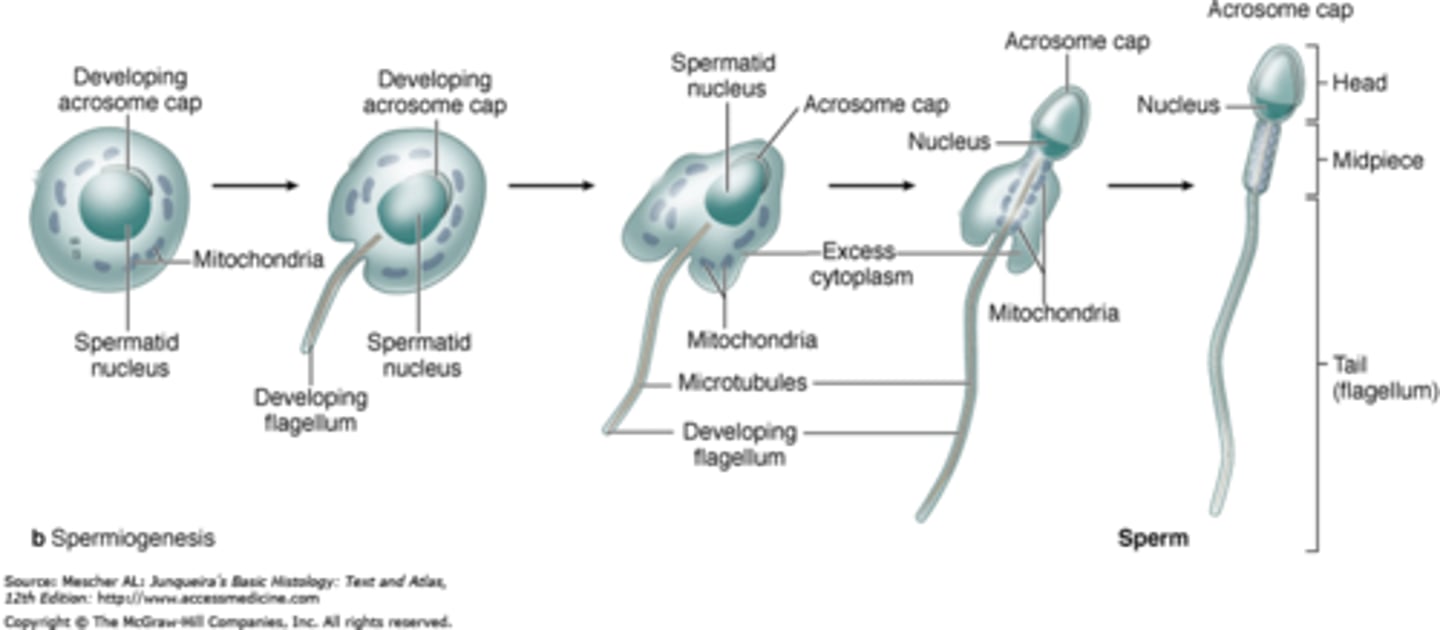
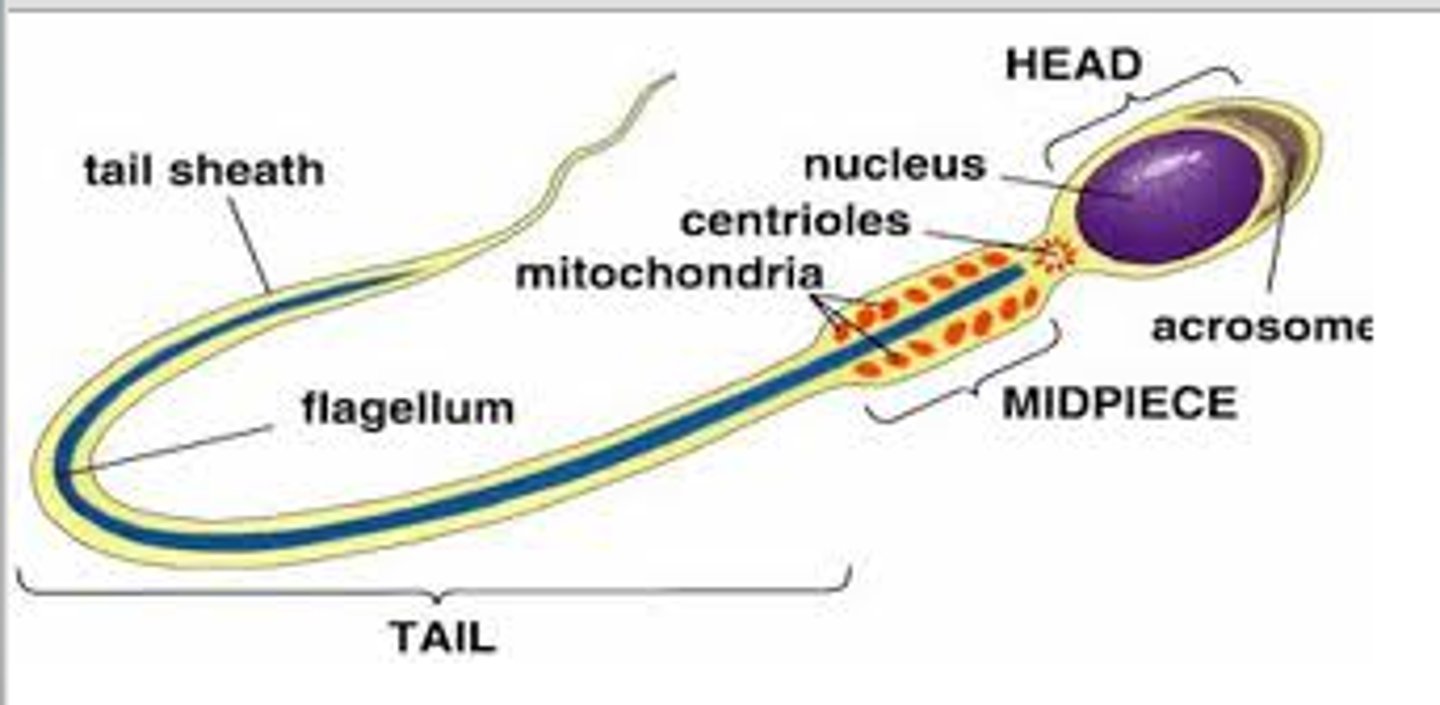
Spermiogenesis
Transformation of spermatids into spermatozoa
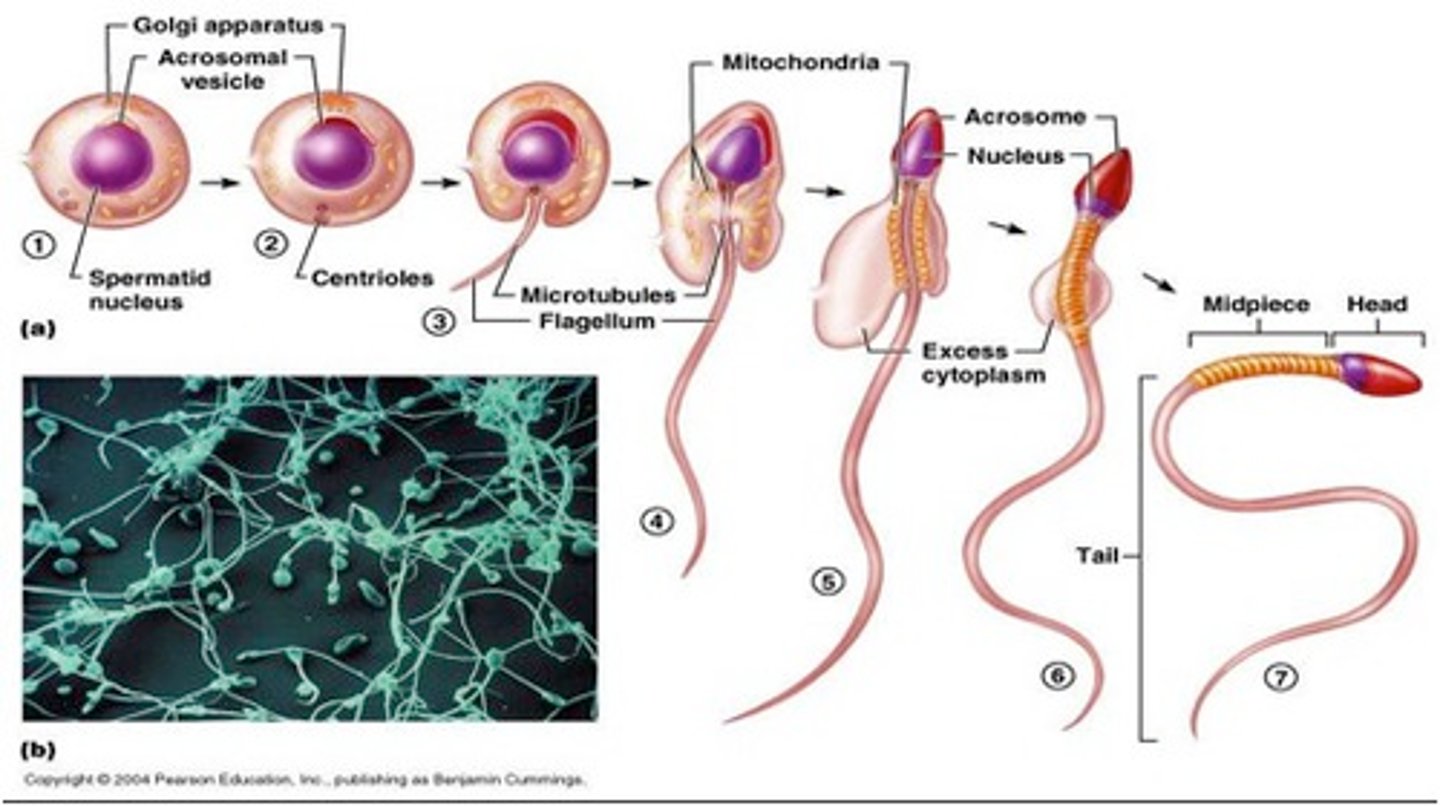
steps of spermiogenesis
Formation of acrosome
Condensation of the nucleus
Formation of the neck, middle piece, and tail
Shedding of most cytoplasm
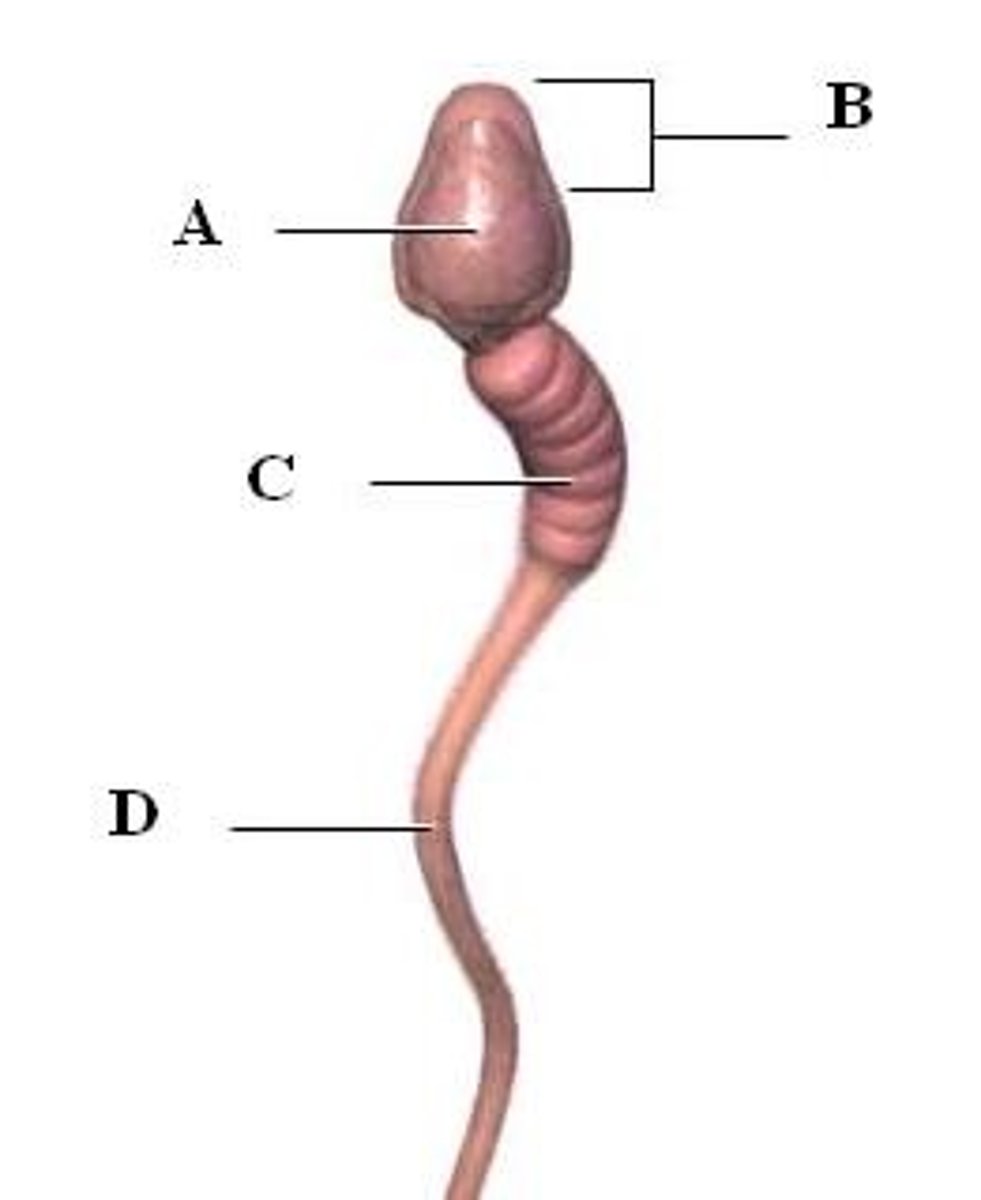
acrosome of sperm
contains hydrolytic enzymes to penetrate zona pellucida during fertilization
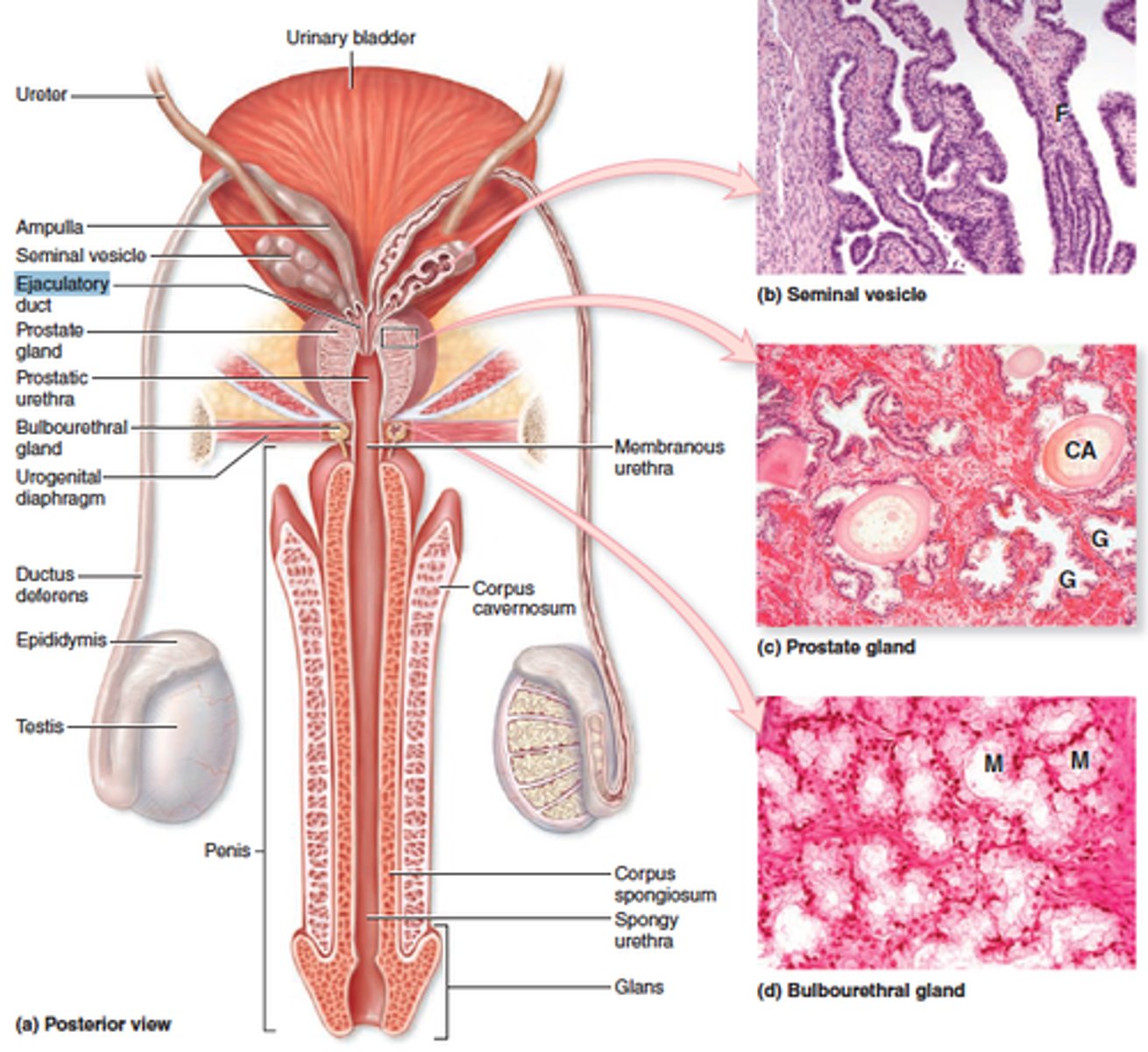
semen
Sperm cells and seminal fluid (secretion of prostate, seminal vesicle, bulbourethral glands)
Fructose
Alkaline pH (neutralize acidic pH of vagina)
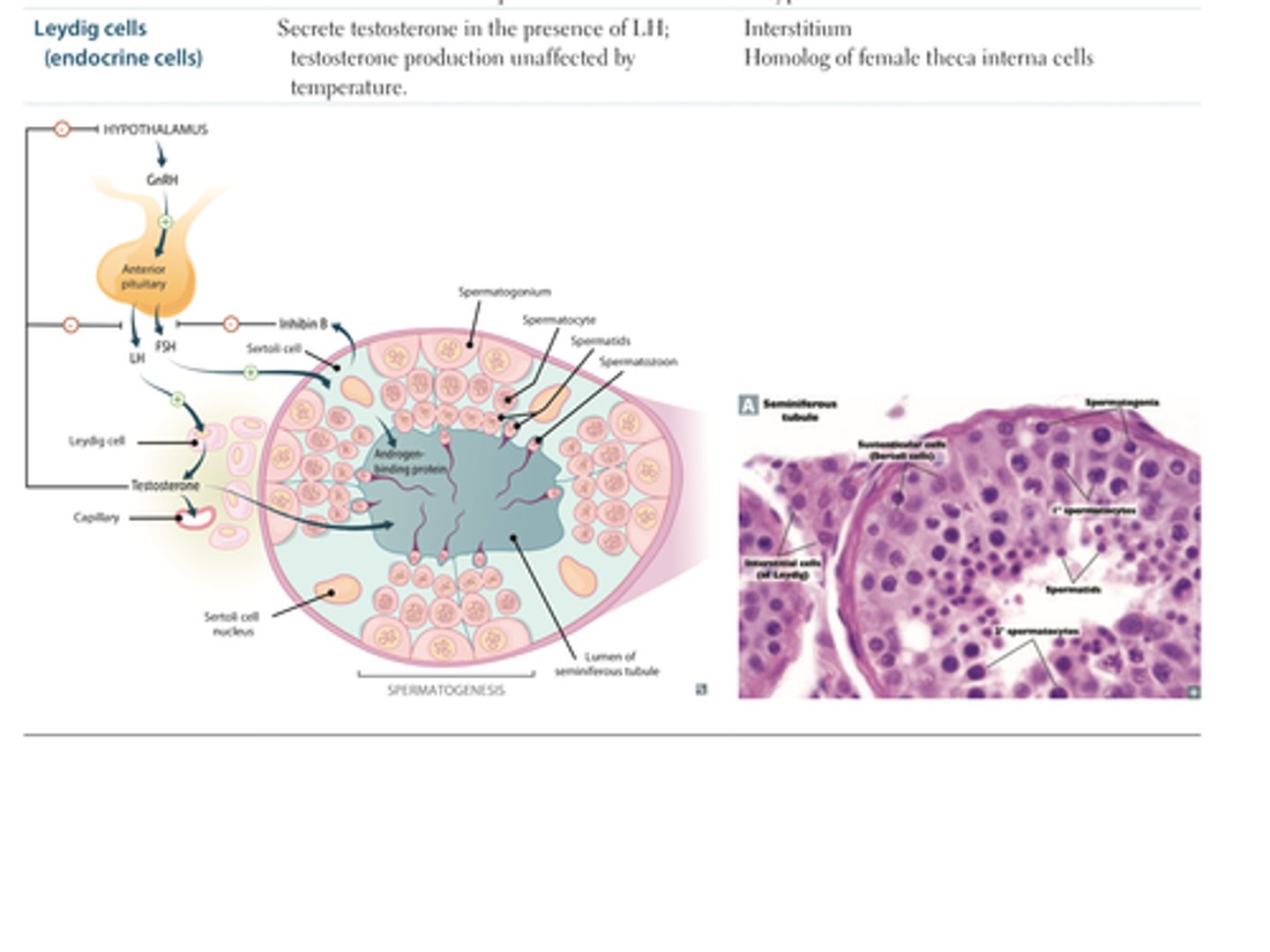
Sertoli cells
Within seminiferous tubules
Provide metabolic support for the spermatids
Leydig cells
Between the seminiferous tubules
Produce testosterone
sperm cell
Male Genital System
hormonal regulation of male reproductive cycle
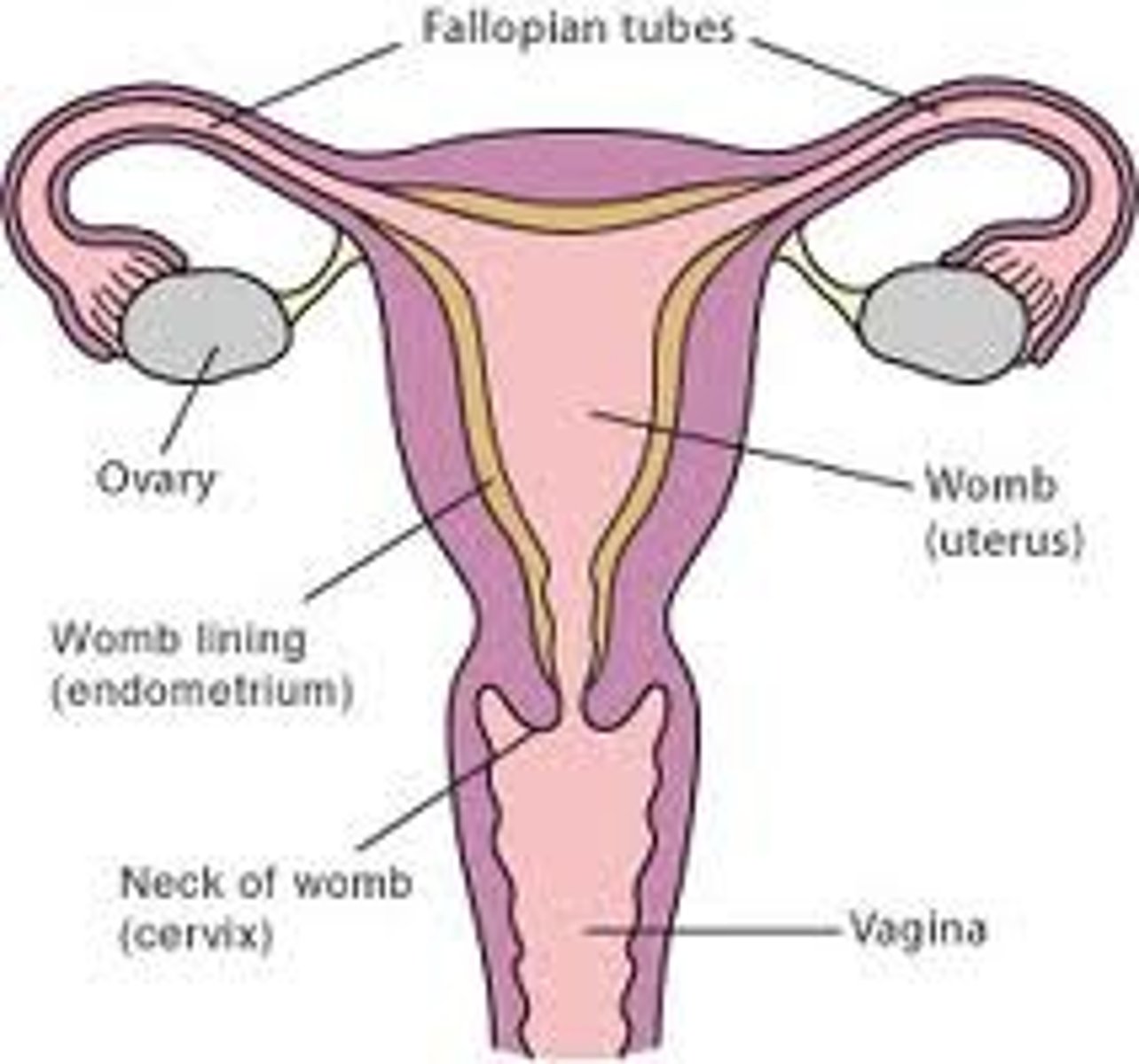
female genital system
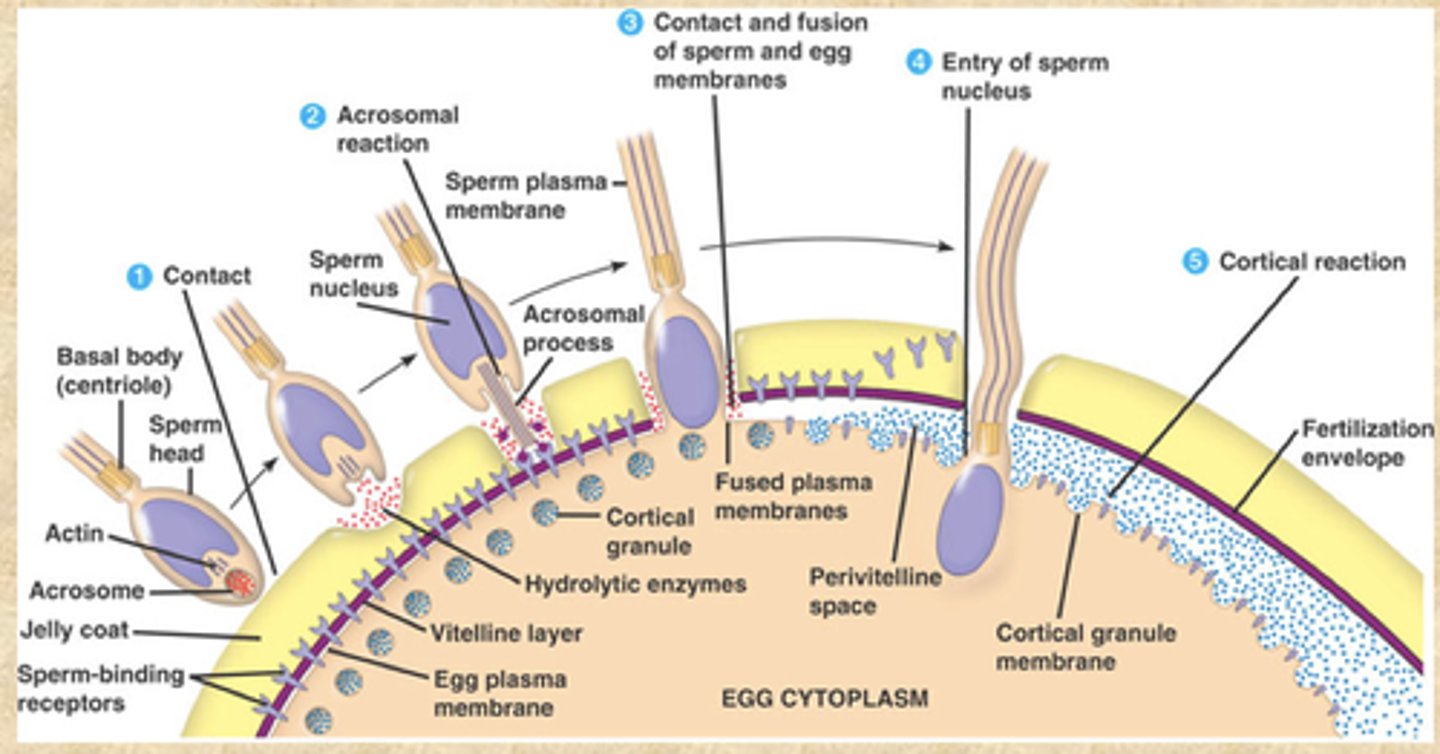
Fertilization
sperm enters the cytoplasm of the egg cell -> fusion of 2 nuclei -> diploid zygote -> embryo
steps of fertilization
Recognition of sperm and egg
Activation of sperm: capacitation, acrosome reaction
Plasma membrane fusion
Further entry of sperm is blocked
Activation of oocyte
Fusion of oocyte and sperm nucleus
Intercourse ___ before ovulation and ___ can result in fertilization
1-2 days; next day
At ejaculation, the semen is transferred to the ___
posterior vaginal vault
How long does it take for sperm to reach egg?
60-70 minutes
Where do sperm and egg meet?
fallopian tube
chemotactic
Substance that attract sperm
Produced by oocyte
Capacitation
Thinning of plasma membrane -> acrosomal cap
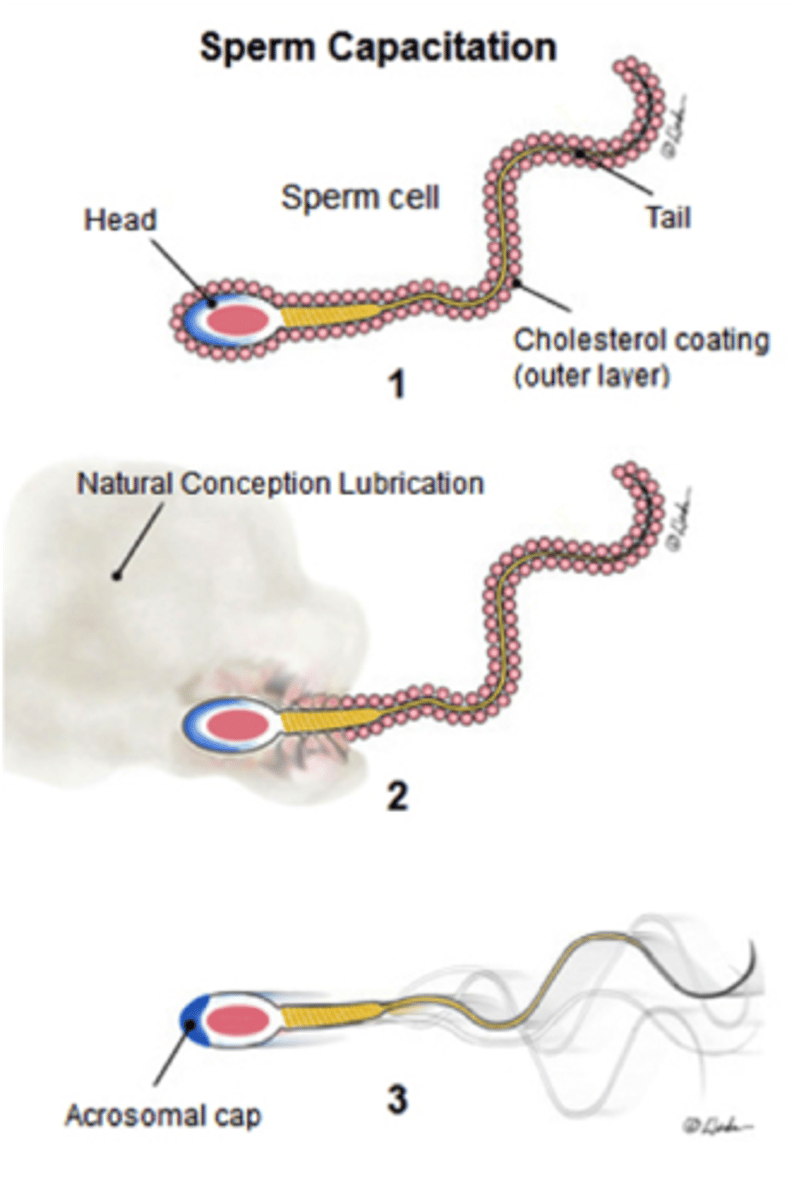
acrosome reaction
digest zona pellucida
Not studied (64)
You haven't studied these terms yet.