WBC Review
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
common progenitor with monocytes:
CFU-GM
which “pool” refers to self-renewal and differentiation?
stem cell pool
which “pool” refers to high proliferation (cell division) capacity?
mitotic pool
which “pool” refers to cells not being able to divide and just continue with maturation?
storage pool
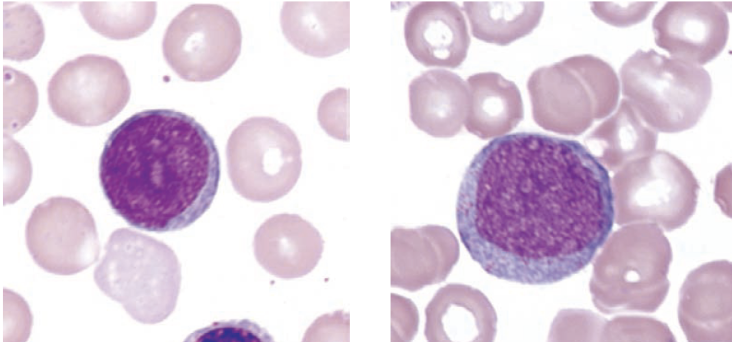
identify this cell:
myeloblast
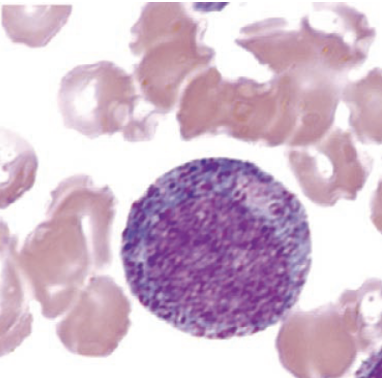
identify this cell:
promyelocyte
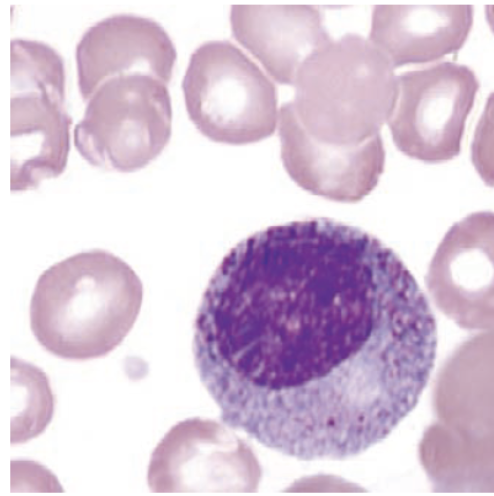
identify this cell:
myelocyte
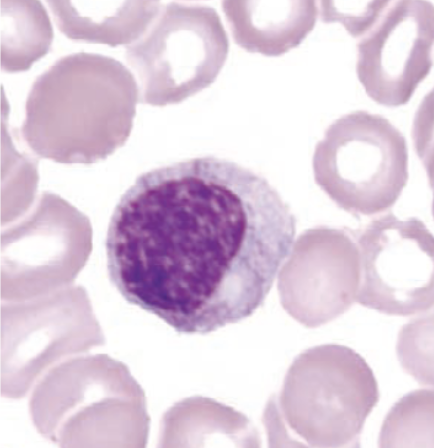
identify this cell:
myelocyte
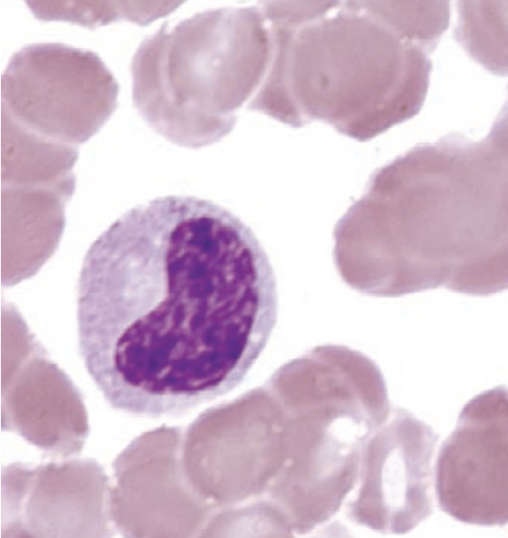
identify this cell:
metamyelocyte
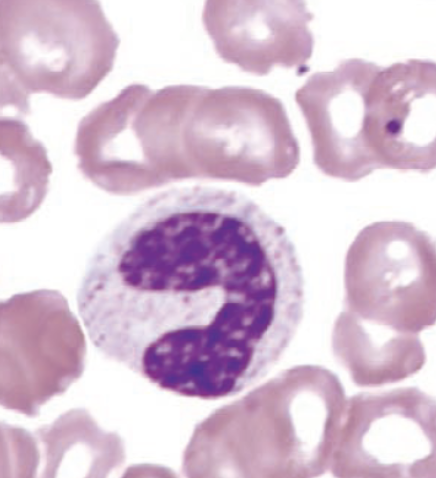
identify this cell:
band
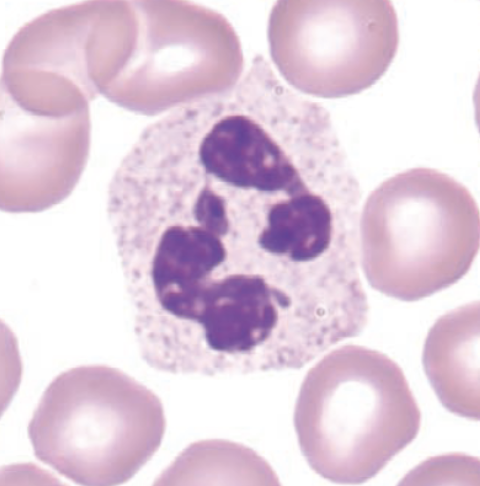
identify this cell:
segmented neutrophil
daily production of ____ is around one billion/kbw.
neutrophils
transit time from myeloblast through myelocyte is around ____.
6 days
transit time from myeloblast to maturation pool is around ____
4-6 days
the two pools in circulation for neutrophils: circulating neutrophil pool (CNP) and marginated neutrophil pool (MNP) has a ____ distribution.
50:50
what is the half life of a neutrophil?
7 hours
after the 7 hour half life of a neutrophil, it will leave circulation for tissues by ____ process (either involved in inflammation/infection or spontaneous apoptosis).
diapedesis
main function is phagocytosis (recognition and attachment; ingestion):
neutrophil
functions by killing and digesting (O2 dependent and O2 independent):
neutrophil
azurophilic granules refer to ____ granules.
primary
specific granules refer to ____ granules.
secondary
vesicles refer to ____ granules.
secretory
granules that develops at promyelocyte stage and contain MPO (most important type):
primary
granule formed during myelocyte and metamyelocyte stages that contain collagenase and lactoferrin:
secondary
granule formed during metamyelocyte and band stages that contains lysozymes:
tertiary
granule formed during band and segmented neutrophil stages that contain some complement components:
secretory
eosinophils separate from myeloid lines at the ____ stage.
promyelocyte
eosinophils can already be identified as eosinophilic at ____ stage.
myelocyte
eosinophilic promyelocytes can be identified by detection of ____ protein in their primary granules.
charcot leyden crystal
____ is the specific cytokine for eosinophils.
IL-5
what is the half life of eosinophils in circulation?
18 hours
functions in immune reactions (allergies):
eosinophil
functions by killing parasites (helminths) extracellularly by secreting major basic protein (MBP):
eosinophil
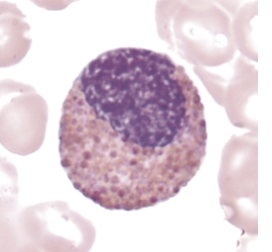
identify this cell:
eosinophilic myelocyte
similar to mast cells and probably has the same progenitor:
basophil
uses blood as a transit system but is a tissue-resident cell:
mast cell
what is the half life for basophils?
30 hours
functions as an inflammatory response and produces large amount of IL-4 and IL-13 (Th2 cytokines):
basophils
basophils synthesize ____ (most important cytokine in allergic reactions):
IgE
____ have receptors for IgE by cross-linking allergens triggering granular release of histamine (degranulation).
basophil
the main cytokine responsible for development of mononuclear cells:
M-CSF
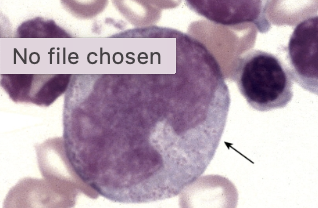
has the characteristic of light blue cytoplasm, delicate chromatin, 1-2 nucleoli, folded or indented nucleus and azurophilic granules (less than promyelocyte):
promonocyte
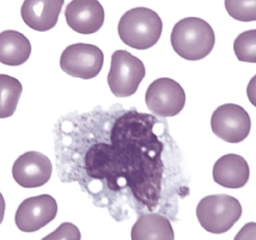
has the characteristic of mostly indented or folded nucleus, sometimes vacuoles, irregular in overall shape, fine (lacy) chromatin, few granules in cytoplasm (ground glass appearance):
monocyte
monocytes and macrophages have no storage pool in the BM (released immediately after maturation). true or false?
true
monocytes migrate to the tissues after ____.
3 days
term for monocytes/macrophages when in the liver:
kupffer cells
term for monocytes/macrophages when in the epidermis:
langerhans cells
term for monocytes/macrophages when in the CNS:
microglia
monocyte/macrophage functions for ____ immunity (NO production, expression of TLRs, FcyRs):
innate
monocyte/macrophage functions for ____ immunity (antigen presentation, activation of T and B cells):
adaptive
functions with housekeeping such as debris removal (dead cells at infection/inflammation site, old RBC destruction, production of many proteins (some coag factors), complement proteins, interleukins, growth factors, enzymes):
monocyte/macrophage
only mature cells that are able to proliferate/divide (blast transformation):
lymphocyte
of all lymphocytes, about ____% are B cells.
3-21%
of all lymphocytes, about ____% are T cells.
51-88%
of all lymphocytes, about ____% are NK cells.
4-29%
B cells develop in the ____ (pro-B, pre-B, immature B) and move to secondary lymphoid organs (as naive B cells).
bone marrow
T cells develop in the ____ (pro-T, pre-T, immature T) and move to secondary lymphoid organs (as naive T cells).
thymus
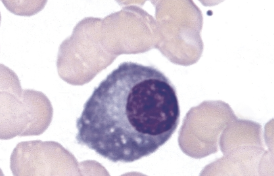
identify this cell:
plasma cell