Module 3 Platelets
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Platelets
cell fragments derived from Megakaryocytes
What are the functions of Platelets
sticky, adhere to site of damage blood vessels
forms platelet plugs that seal ruptured area
5 chemicals in platelet clotting process
serotonin
ADP
Calcium
enzymes
platelet dervied growth factors
thrombopoietin
platelet formation regulation
what 2 things makes platelets inactive
nitric oxide and prostacyclin
Platelets formed in where
myeloid cell line. Megakaryoblast
Hemostasis
series of fast reaction to stop bleeding
3 steps of Hematosis
vascular spasm
platelet plug formation
coagulation (blood clotting)
step 1 of hematosis
vascular spasms trigger by
direct injury to vascular smooth muscle
chemicals released by endothethial cells and platlets
pain reflexes
step 2 of hematosis
platelet plug formation
platelets stick to collagen fibers, when exposed to damage
step 2 of hematosis
what is von willebrand factor
stabilize platelet collagen adhesion
Step 2 of hematosis
plates swell becoming spiky and sticky. what 2 chemicals messengers are released
ADP and serotonin
what type of feedback if platelet formation
positive feedback.
remember positive escalating to fix the body
negative feedback, a loop to restore balance
hemostasis step 3
coagulation
blood clotting
Hematosis step 3 coagulation:
what is phase 1 of coagulation:
2 pathways of thrombin activators
triggered by intrinsic and extrinsic pathways (usually both)
Hematosis step 3 coagulation
2 pathways: what is the intrinsic pathway
triggered by?
Called “intrinsic” because clotting factors are present within the blood
triggers: collagen exposure
Hematosis step 3 coagulation
2 pathways: what is the extrinsic pathway?
triggered by?
Called “extrinsic” because factors needed for clotting are located outside blood
trigger: eposure to tissue factor (TF) comes contact with blood
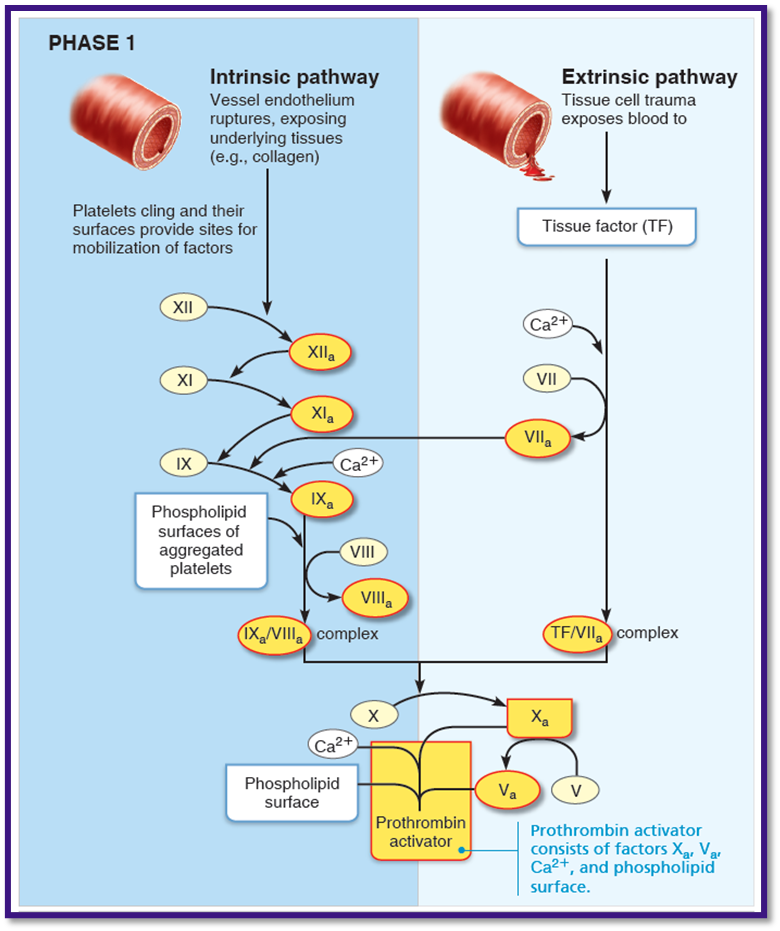
Hemostatis step 3: Coagulattion
what is phase 2?
pathway to thrombin
Hemostatis step 3: Coagulattion
what is phase 3?
common pathway to the fibrin mesh