Serious offending: Arson
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
What is arson?
criminal damage act of 1971- an act of attempting to destroy or damage property, and/or in doing so, to endanger life.
deliberate fires: where the motive was ‘thought to be’ or ‘suspect to be’ deliberate.
deliberate fires include arson; deliberate fores are not the same as arson
fire-setting refers to the acts of juveniles below the age of criminal responsibility who deliberately set fires.
what is the prevalence of arson?
fire and rescue calls out- 69,000 cases of arson.
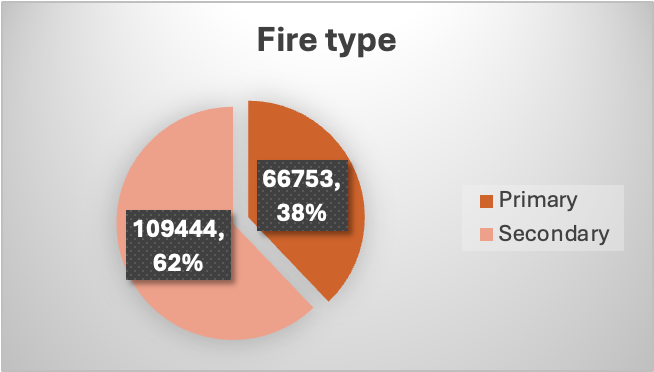
primary fire
takes place in (non-derelict_ building or a vehicle
it involves fatalities, casualties or rescues.
the fire is attended by five or more pumping appliances.
secondary fires
all others
in march 2023 246 fatal fires and men more likley than women to die and be injured in a fire
What are adult firesetters?
research indicates that they are likely to be males- but there is a rise of female arsonists
generally young- but age is rising, men that set fires are younger than women.
45-55% tend to have previous than women
violence
criminal damage
theft
arson
What are juvenile fire setters?
research indicates that they are likely to be:
male
a fascination with fire from an early age
a range of problem bheaviours
a range of psychological factors
disrupted education
disrupted family life
MacDonald (1963) Triad- predicted of violent behaviour in adulthood.
Do arsonists reoffend?
they are likley to commits less arson offences with less than 5% of arsonist being reconvicted for arson offences, but this is increasing in more recent years to 10.7%
however, arsonists around 50% do receive reconnections for other offences,
increasing to around 70% in recent years.
What is the association between intellectual functioning and arson?
long standing associations between arson and low intellectual functioning- e.g.,Dickens et al 2008: firesetters referred for psychiatric assessment 43% had an IQ < 85 lower iq more likley to set fires- rubbish and smaller kinda fires
often co-morbid with other mental disorders/ communication difficulties
Autism- systematic revire- additional personal and social issues.
What is the association of mental illness and arson?
10% forensic psychiatric patients have committed arson.
compared to forensic psychiatric patients who hadn’t committed arson, fire setters are:
- Younger
- More likely to have:
- a history of unusual interest in fire
- a history of violence
- spent time in an institution
Repeat forensic psychiatric firesetters (compared to those set one fire):
- Younger by 4 years (mean = 26 years)
- Greater history of violent and other criminal behaviour
What is the DSM-V diagnostic criteria?
Deliberate and purposeful fire-setting on more than one occasion.
Tension or affective arousal before the act.
Fascination with, interest in, curiosity about, or attraction to fire and its situational contexts (e.g., paraphernalia, uses, consequences).
Pleasure, gratification, or relief when setting fires, or when witnessing or participating in their aftermath.
The fire setting is not done for monetary gain, as an expression of socio-political ideology, to conceal criminal activity, to express anger or vengeance, to improve one’s living circumstances, in response to a delusion or hallucination, or as a result of impaired judgment (e.g., in dementia, mental retardation, substance intoxication)
The fire setting is not better accounted for by conduct disorder, a manic episode, or anti-social personality disorder
What is the Finnish study say about DSM5 crietria?
- 401 arsonists referred for psychiatric assessment
- Of these, 90 repeat arsonists
- Of these, only 3 met DSM-IV-TR criteria
Less than 1% of original sample = “pure arsonists”
What did Prin’s 1995 say the typology of arsonists?
They grouped types of arsonists according to interred motibations
Mental illness
crime concealment
revenge
proft-motivated
political
attention-seeking
What is mental illness?
description- sever mental illness, maybe influenced by symptoms
motivation- internal factors
characteristics- irrational or bizarre act with no clear goal.
What is criminal concealment?
description- set fires to destroy evidence of another crime
motivation- avoid detection or prosecution
characteristic- planned, serves a secondary purpose.
What is revenge?
Description- retaliation against a person, group or institution
motivation- anger desire for vengeance
characteristicts- specific target
What is profit- motivated?
description0 set fires for financial gain
motivation- financial benefit
characteristics- often planned and trgets high value property
What is political?
Description- set in the name of a cause
motivation- create disruption, gain attention of media.
characteristics- often extermists, terrorists or demonstrators.
What is attention-seeking?
description- to grain attention, sympathy or recognition from others
motivation- needs for validation, outlet for feelings of neglect or inadequacy
characteristics- visible locations/ times when arson can interact with witnesses.
What is action system model (Canter & Fritzon’s 1998)
Alternative to motivational classification
Focus on the arsonist’s behaviours
Uses a technique called smallest space analysis
plots associations between crime scene variables
Identified two dichotomies in the data which create four groupings:

What is a serial arsonists?
A proportion of arsonists set more than one fire
Kocsis and Cooksey (2002) – three or more fires
High degree of planning
Wachi et al. (2007) – solved cases
6% committed five or more offences of arson
6% of these were women
66% = expressive – close to home, brief period of time, stayed close
33% = instrumental – targeted buildings away from home, revenge or to conceal a crime
What are theories of Arson?
Very few theoretical models of arson
Early psychodynamic theorical accounts:
an association between fire, enuresis, and sexual desire (Freud, 1932)
instinctual drives such as aggression and anxiety explain firesetting (Kaufman, Heims, & Reiser, 1961; Macht & Mack, 1968)
Very little evidence to support these proposals
What is the learning theory of arson?
Body of research examined the use of fire images in advertising to children
Curri et al (2003): survey of toy packaging in national store
- 404 toys portraying fire
- 97% aimed at boys
Greenhalgh & Palmieri (2003): TV and printed media accounts of fire, burn injuries and burn prevention
- Media depicting fire mainly aimed at boys
- Largely ignores/makes fun of fire e.g. adverts with people on fire/taking risks with fire
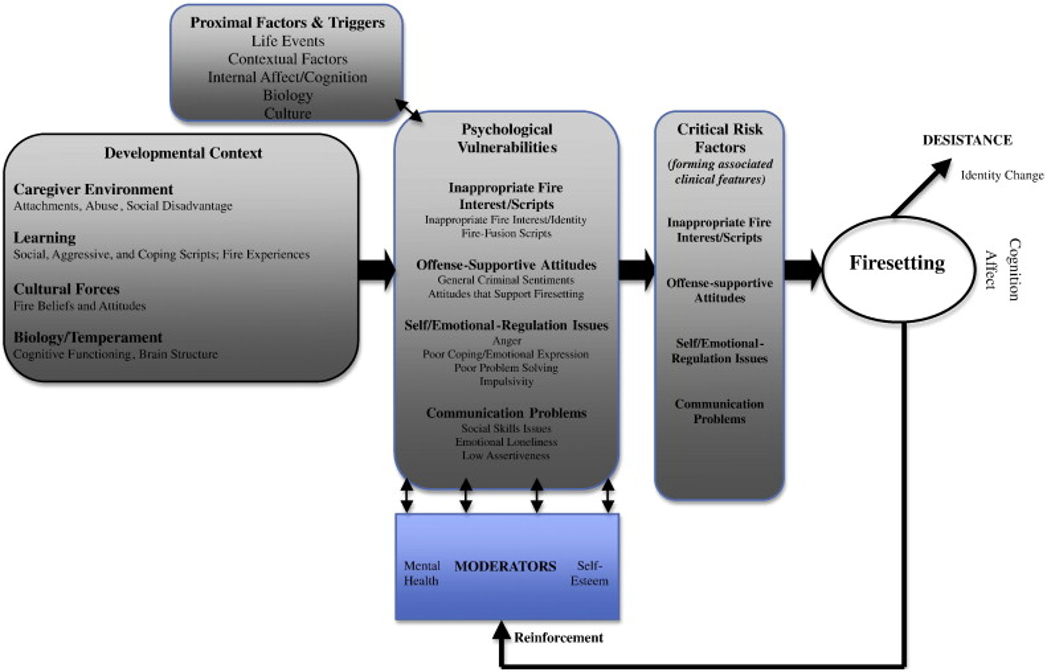
What is Gannon et al., 2012 multi-factor theory?
Proposed the Multi-Trajectory Theory of Adult Firesetting (M-TTAF)
Integration of theory, typologies and research findings
Describes aetiology of fire-setting
But also maintenance and desistence
Four key psychological issues likely to be associated with fire-setting:
Inappropriate fire interest/scripts
Offense-supportive cognition
Self/emotional regulation issues, and
Communication problems
What is two-tier theory?
First tier presents the overall theoretical framework
- Outlines the factors involved and how they may interact
Second tier of the theory proposes five prototypical trajectories
- Incorporates typological knowledge
- Useful for clinicians to consult
what is the fire-setting intervention programme for prisoners (FIPP; Gannon,2012)?
28 weekly 2-hour group sessions
weekly individual support session up to one hour in length
Four components:
Fire-related factors
Offence supportive cognition
Emotional regulation, and
Social competence
What is fire setters’ integrated responsive educational programme (Fire-P, Pearson et al., 20220)?
- for adults with convictions for deliberate firesetting
- specialist fire safety awareness programme
- developed by Forensic Psychologist at University of Portsmouth
- delivered by Fire and Rescue Service
- preliminary evaluation showing potential for positive results