Honors Biology Unit 5 - Vocab
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
alveoli
tiny air sacs surrounded by thin-walled capillaries
where gas exchange occurs
150 million/lung
arterioles
a small branch of an artery leading into capillaries
blood pressure
the pressure of the blood in the circulatory system
systolic over diastolic
capillaries
the smallest blood vessels
circulatory system
the system that circulates blood through the body
consists of the heart, blood vessels, blood, lymph, and lymphatic vessels and glands
gas exchange
oxygen in the alveoli diffuses across the alveoli wall into the capillaries which contain blood
carbon dioxide does the opposite, it diffuses from the blood across the alveoli wall and into the alveoli. from here co2 is exhaled
hypertension
high blood pressure
140/90 and above
lungs
2 of them
help with gas exchange
pharynx
aka the throat
helps you to breathe and digest food
pulmonary artery
there are two
they carry oxygen poor blood from the right side of your heart to your lungs
pulse
a rythmical throbbing of the arteries as blood is propelled through them
systolic pressure
pressure exerted when blood is ejected into arteries
veins
carry oxygen poor blood/carbon dioxide rich blood
body to heart
thinner because less pressure exerted on your veins
valves
white blood cells
involved in immunity
protect/fight infection
thousands
anemia
not enough red blood cells
can’t preform gas exchange properly
atria/atrium
each of the two upper cavities of the heart from which blood is passed to the ventricles
the right atrium receives oxygen poor blood
the left atrium receives oxygen rich blood
bronchus/bronchi
series of air passage tubes which diverge from the windpipe
cardiac cycle
the flow of blood through the heart coordinated by electrochemical signals that cause the heart muscle to contract and relax.
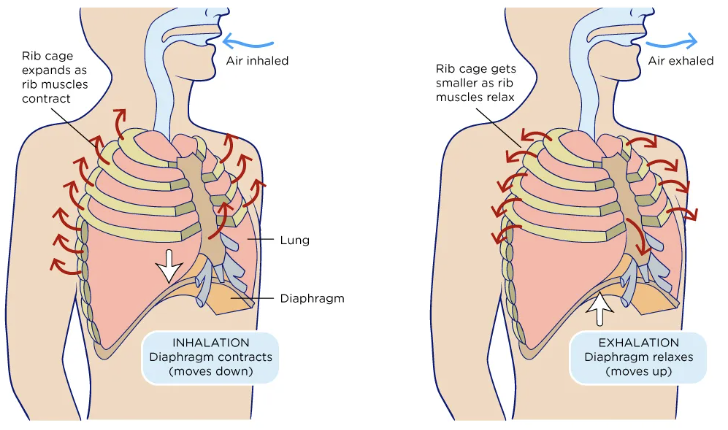
diaphragm
a thin dome shaped partition that seperates the thorax from the abdomen
plays a major role in breathing bc inflates the lungs
heart
pumps blood and oxygen through body
interstitial fluid
the body fluid between blood vessels and cells
negative pressure breathing
mechanical ventilation in which negative pressure is generated on the outside of the chest and transmitted to the interior to expand the lungs and allow air to flow in
plasma
fluid inside the blood vessels that house blood cells and many other substances
responsible for pH
55% of blood
pulmonary circuit
moves blood between the heart and the lungs
red blood cells
carrier of co2 and o2
created in bone marrow
eject nuclei when entering the blood stream
don’t intend to reproduce outside of bone marrow
want more space for hemoglobin
millions
trachea
aka windpipe
cartilage tube extending from larynx to bronchial tubes
moves air to and from the lungs
venule
a very small vein that collects blood from the capillaries
arteries
carry oxygen rich blood
heart to body
more pressure exerted on arteries so thicker vessels
blood
Plasma:
The fluid portion of the blood that surrounds/carries the blood cells. Also carries other molecules and ions.
pH of the plasma changes in different locations in the body
55% of blood
Red Blood Cells:
Made in bone marrow
ejects nuclei upon entering the bloodstream for the first time to make room for more hemoglobin
90% hemoglobin by weight
function: carries O2 and CO2
millions
White blood cells:
have a nucleus
responsible for fighting infections and protecting the body
thousands
Platelets:
fragments of cells that are used to create clots and prevent bleeding
100s - thousands
red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets make up 45% of blood
bronchioles
one of the smaller branches that diverge from the bronchi
carbon dioxide
made of one carbon and two oxygen
diastolic pressure
pressure blood exerts within arteries between heartbeats
heart attack
cardiac arrest
a sudden, sometimes fatal, occurence of coronary thrombosis - local clotting of the blood, typically results in the death of part of a heart muscle
larynx
aka the voice box
protects respiratory tract from aspirating food into the trachea
hollow tube above trachea behind esophagus
oxygen pacemaker
small group of cells found in the right atrium
sets the pace for the heart rate
the signal makes the atria contract then sends the signal to the ventricles which contracts second
platelets
fragments of cells that are used to create clots and prevent bleeding
100s - thousands
pulmonary veins
function is to transport oxygen rich blood to left atrium
lungs to heart
respiratory system
a group of organs and tissues that work together to help you breathe
vena cava
the largest vein in your body
carries oxygen poor blood to your heart
ventricle
a hollow cavity in an organ
each of the main chambers of the heart (left and right)
Positive pressure breathing
Frog gulps in the air (inhalation)
When the jaw is raised, the pressure of the air inside the mouth cavity increases
Close mouth and nares (nostrils)
Air moves from the mouth cavity (high pressure) to the lungs (low pressure)
Raises jaw and tongue to make cavity small
Force air down
tracheal breathing
Air exchange through tubes (trachea) in the air, takes air in without breathing/taking a breath
Cutaneous respiration(skin breathing)
Capillaries on the surface allow for gas exchange on the cover/at the skin
gill breathing
Like lungs that have been turned inside out
Do diffusion on the inside of the body, gas exchange with water on the outside
hemoglobin
most efficient gas transport
need proper iron levels for it to work
90% of weight of red blood cells