wildfires
5.0(4)
Card Sorting
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:25 AM on 4/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
1
New cards
what are wildfires?
* self-sustaining fires that start and spread out of control; often move into populated or agricultural areas
2
New cards
what are the diff causes of fires?
* number 1 natural cause → lightning
* arson
* campfires, smoking, playing
* transport
* elec power
* machinery
* debris burning
* unknown
* other anthropogenic causes
* 90% forest firest in US caused by human activity
* arson
* campfires, smoking, playing
* transport
* elec power
* machinery
* debris burning
* unknown
* other anthropogenic causes
* 90% forest firest in US caused by human activity
3
New cards
what is at risk with fires?
* humans
* ecosystem
* ecosystem
4
New cards
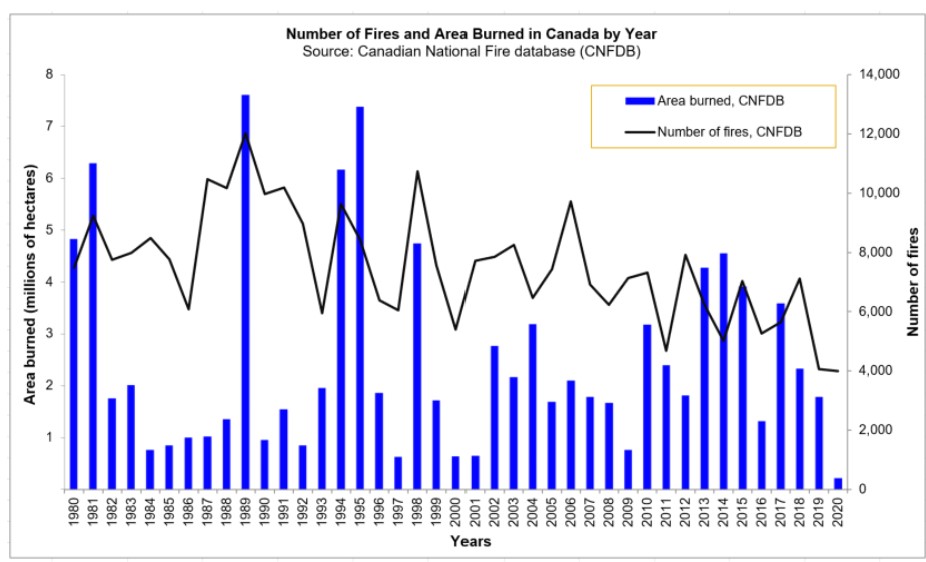
fires in Canada
* numb of fires each yr in Canada n total burned
* there is no correlation between the total area and the num of fires, as a few individual large fires account for most of the area
* there r many small fires
* less big ones
* there is no correlation between the total area and the num of fires, as a few individual large fires account for most of the area
* there r many small fires
* less big ones
5
New cards
what is fire?
* when gases react w/ oxygen to produce heat and light
6
New cards
what are flames?
* superheated gases (carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, nitrogen, oxygen, water vapour and organic chemicals)
7
New cards
what produces gases which fuel the fore?
* breakdown of cellulose, fats, oils and sugar in plant walls and cells produces gases which fuel the fire
8
New cards
what burns at relatively low temp?
* cellulose and hemicellulose
9
New cards
when does lignin burn?
* burn at higher temperature than cellulose
* tree species high in lignin (e.g., oak) will not burn as readily
* tree species high in lignin (e.g., oak) will not burn as readily
10
New cards
when does extractable burn?
* flame suddenly when exposed to heat
* contribute to the violence of wildfire in many conifer forest
* ex. resins, fats, oils
* unpredictable
* contribute to the violence of wildfire in many conifer forest
* ex. resins, fats, oils
* unpredictable
11
New cards
what is necessary to keep fire burning?
* oxygen
* heat
* fuel
* known as the fire triangle
* heat
* fuel
* known as the fire triangle
12
New cards
what is the preheating stage?
* heat source raises a fuel’s temperature; water evaporates
13
New cards
what is the pyrolysis stage?
* molecs in fuel decompose to produce gases that rise in the air
14
New cards
what is the combustion stage?
* gases ignite and react with oxygen → produce fire
15
New cards
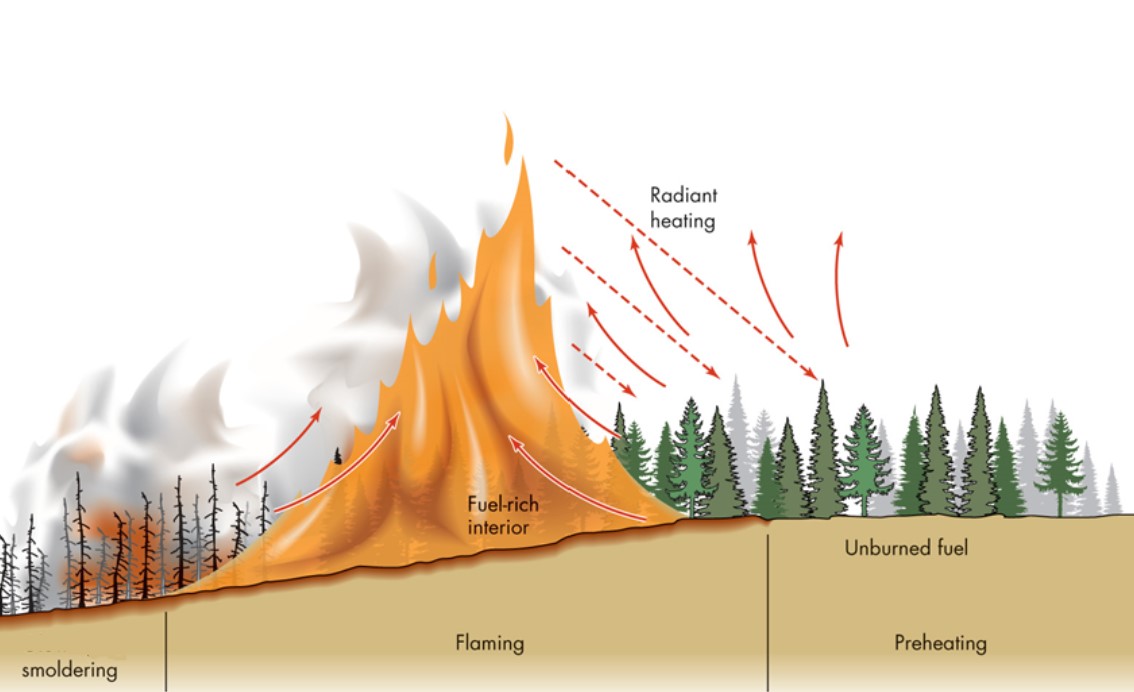
what is flaming combustion?
* dominates early fire
* produces large flames and little smoke
* initiated by ignition of volatile gases at 260ºC -450ºC
* temperatures can rise to 1,500ºC; high enough to melt metal and glass
* produces large flames and little smoke
* initiated by ignition of volatile gases at 260ºC -450ºC
* temperatures can rise to 1,500ºC; high enough to melt metal and glass
16
New cards
what is smoldering combustion?
* produces the most smoke
* lack flames - associated w/ conditions where oxygen is lim
* lack flames - associated w/ conditions where oxygen is lim
17
New cards
combustion
18
New cards
where do ground fires occur?
* within roots and buried organic matter
* creep along under ground surface
* little flaming, more smoldering; limited oxygen
* creep along under ground surface
* little flaming, more smoldering; limited oxygen
19
New cards
where do surface fires occur?
* burn low-lying vegetation (undergrowth and forest litter ex. grasses and dead leaves)
* burn slowly with smoldering, limited flaming
* burn slowly with smoldering, limited flaming
20
New cards
what do ladder fires burn?
* undergrowth and medium-sized trees (below the forest crown)
21
New cards
crown fires?
* flaming is carried via tree canopies
* driven by strong winds and steep slopes
* can jump from crown to crown without burning undergrowth
* driven by strong winds and steep slopes
* can jump from crown to crown without burning undergrowth
22
New cards
what is fire severity?
* percent biomass that burns during a fire
23
New cards
what is fire intensity?
* measure of energy released during burning
24
New cards
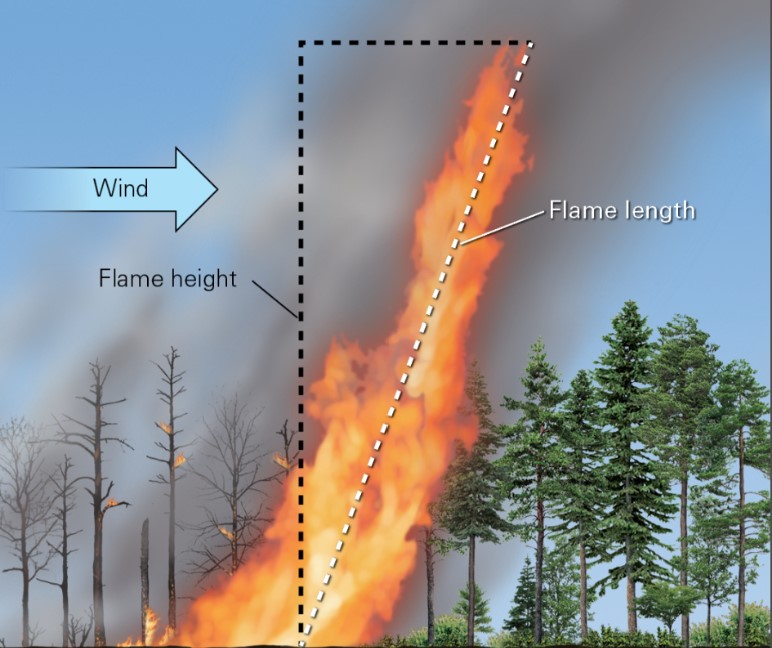
what is flame length?
* distance from the base to the end of the flame
* more intense fire = longer flame length
* more intense fire = longer flame length
25
New cards
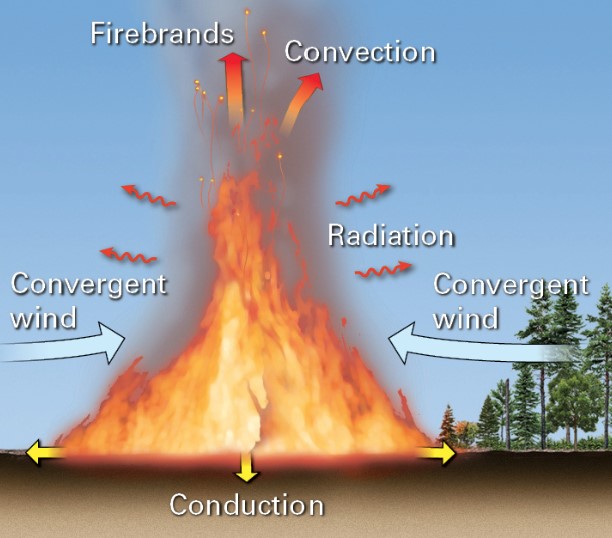
what is conduction?
* transfer of heart directly from molec to molec
26
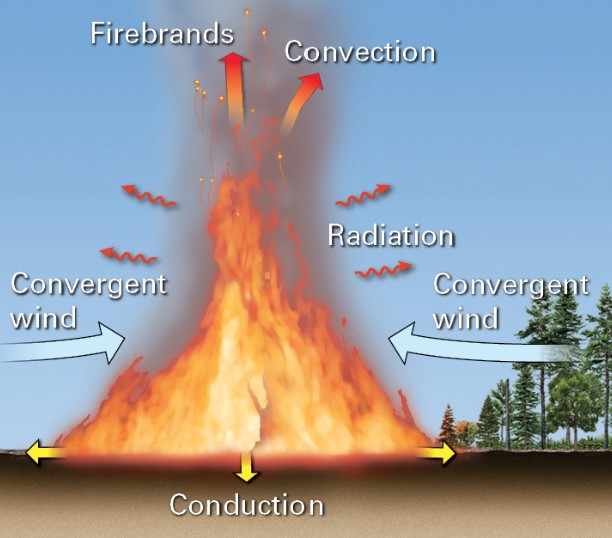
New cards
what is convection?
* transfer of heat by the movement of heated air
* hot gases are less dense and rise; pulls in fresh air to sustain combustion
* hot gases are less dense and rise; pulls in fresh air to sustain combustion
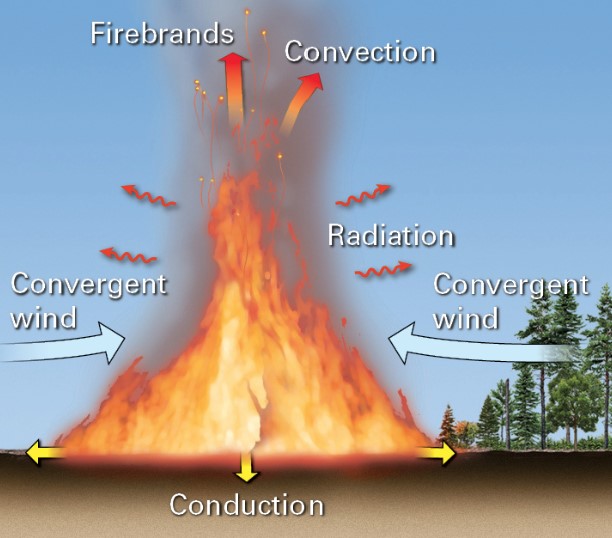
27
New cards
what is radiation?
* radiant energy heats fuel within 10-35m of a wildfire
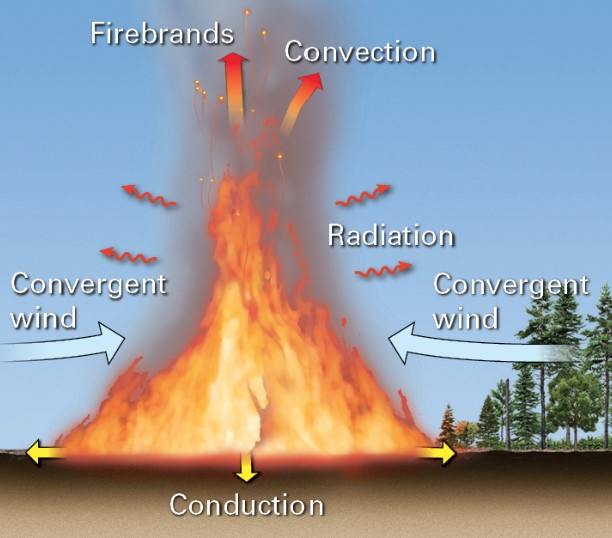
28
New cards
what are firebrands?
* sparks and embers can land on fresh fuel beyond the wildlife; start new fires
29
New cards
how do wildfires spread?
* start most often when a small heat source (spark from campfire, cigarette) comes into contact with dry grasses, leaves, small sticks
* heat from this small fire pre-heats surrounding fuel
* heat from this small fire pre-heats surrounding fuel

30
New cards
what does spread depend on?
* fuel
* weather (wind)
* terrain
* weather (wind)
* terrain
31
New cards
what do sparse or wet fuels result in?
* less intense wildfires
* seasonal changes dictate moisture lvls in fuel
* seasonal changes dictate moisture lvls in fuel
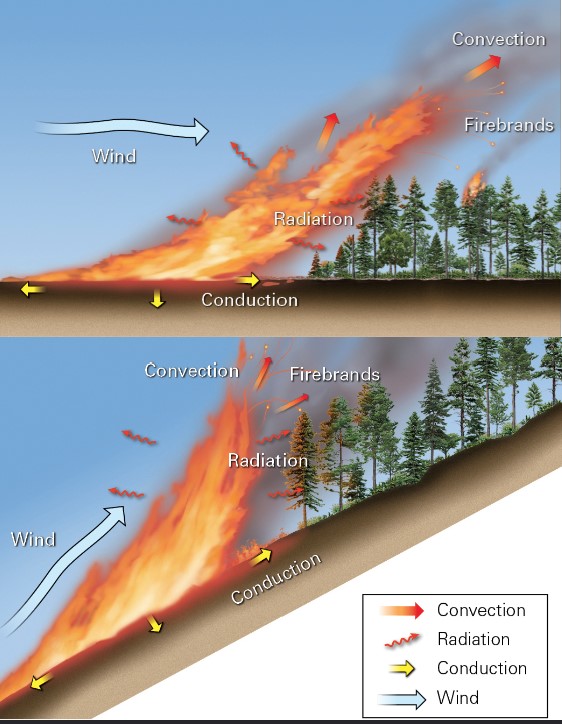
32
New cards
what does wind replace during burning?
* oxygen consumption
* also tilts flames causing preheating and spreading firebrands
* also tilts flames causing preheating and spreading firebrands
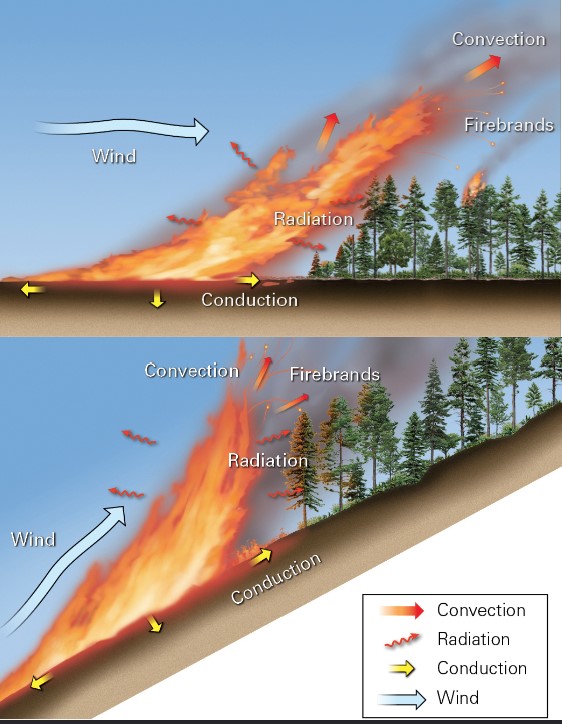
33
New cards
what do flaming gases and hot rise via?
* convection
* allows for fires migrate faster up slopes than down slopes
* allows for fires migrate faster up slopes than down slopes
34
New cards
what are ways enviro has adapted to fire?
* trees like cork oak have adapted to fire
* their sponge bark does not burn
* Jack pine are well adapted to fire, as the heat of the fire opens their cones liberating the seeds
* their sponge bark does not burn
* Jack pine are well adapted to fire, as the heat of the fire opens their cones liberating the seeds
35
New cards
what are primary disaster of wildfires?
* injury and death
* property, agricultural, and forest losses
* property, agricultural, and forest losses
36
New cards
what are secondary disaster of wildfires?
* health effects from smoke inhalation
* increased soil erosion
* destabilizes slopes - can lead to landslides
* longer impact
* increased soil erosion
* destabilizes slopes - can lead to landslides
* longer impact
37
New cards
Australia Bushfires 2020
* known as the “black summer”
* 5,900 buildings destroyed
* 34 deaths
* affected \~3 billion animals
* some endangered species believed to have been driven to extinction
* air quality hazardous in all southern and eastern states of Australia
* estimated to cost upwards of $100B
* Australia costliest natural disaster to date
* biggest concern was wildlife
* millions animals killed
* no ele, water, phone service in some areas
* not much govern help
* strong winds
* 5,900 buildings destroyed
* 34 deaths
* affected \~3 billion animals
* some endangered species believed to have been driven to extinction
* air quality hazardous in all southern and eastern states of Australia
* estimated to cost upwards of $100B
* Australia costliest natural disaster to date
* biggest concern was wildlife
* millions animals killed
* no ele, water, phone service in some areas
* not much govern help
* strong winds
38
New cards
fire suppression methods
* firebreak construction
* plane dropping retardant
* create break + start new fire
* plane dropping retardant
* create break + start new fire
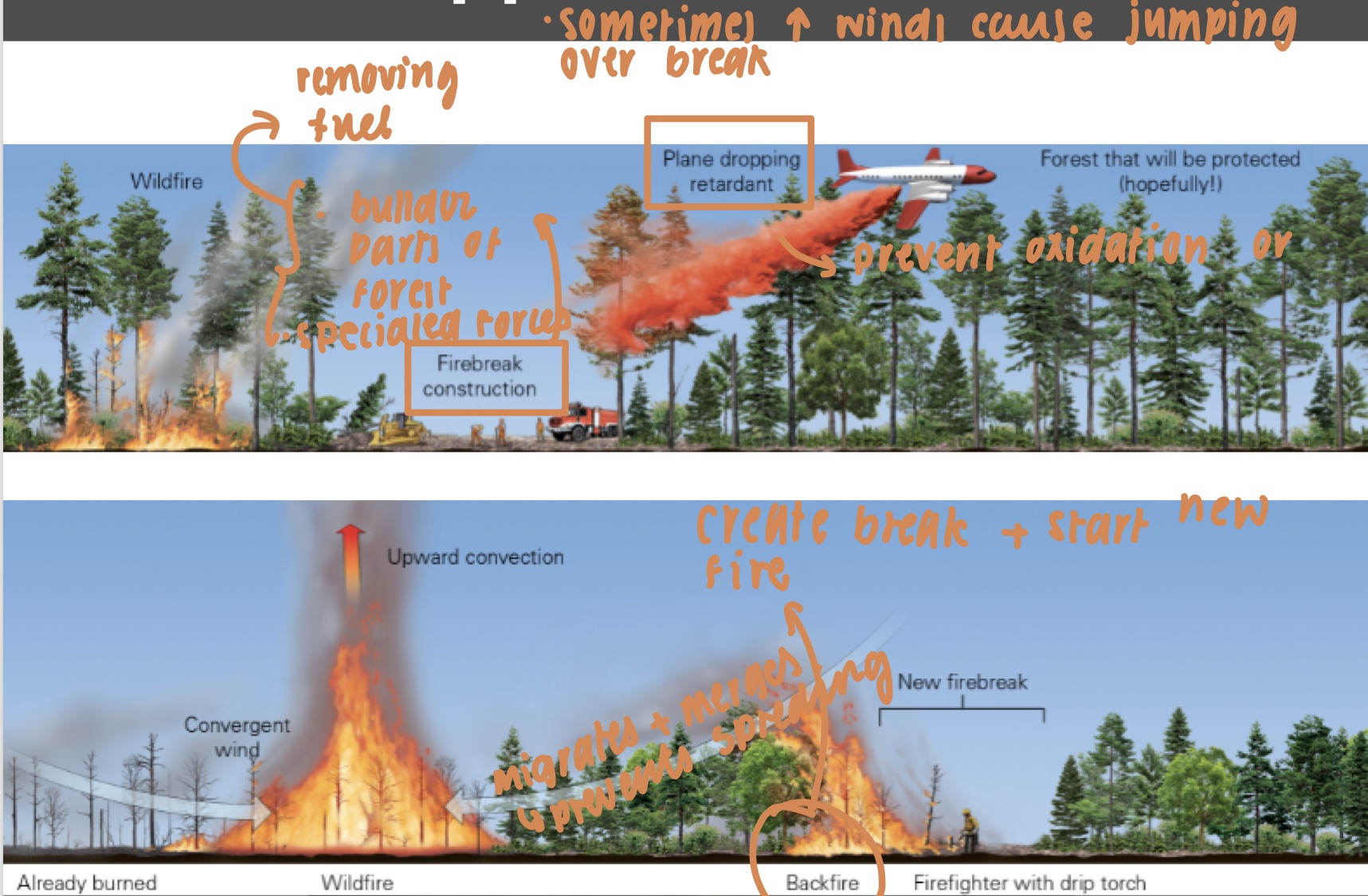
39
New cards
forest management
* total fire suppression (1940’s-1980s) results in large fuel accumulations and larger fires
* increased knowledge in forest ecology demonstrated the importance of fire for forest renewal
* policy has shifted toward prescribed burns in some areas to reduce large fuel accumulations
* natural lightning-caused fires were allowed to burn unless they posed threats to people, commercial timber lands or scenic attractions
* increased knowledge in forest ecology demonstrated the importance of fire for forest renewal
* policy has shifted toward prescribed burns in some areas to reduce large fuel accumulations
* natural lightning-caused fires were allowed to burn unless they posed threats to people, commercial timber lands or scenic attractions

40
New cards
there is a growing num of ____________ ______________________ bringing humans closer to fire risk
* interface communities
41
New cards
how to reduce risk?
* homes should be constructed from flame resistant material
* area around homes should be clear of brush
* a clear emergency plan and response should be in place
* area around homes should be clear of brush
* a clear emergency plan and response should be in place