Animal Science Exam 1 Study guide (Notes)
1/212
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
213 Terms
Diet consists of both plants and animal tissue
Define Omnivorous behavior
1. Omnivorous behavior
2. Fire Controlled
3. Glacial Exodus Ends
What were the building blocks towards domestication?
Created extinction, famine, and choice
What was the Glacial Exodus?
Provided the ability to cook meat, which then led to being able to prevent food borne illness.
What was the significance of fire control?
The settling of clans and the beginning of agriculture
What was the Neolithic Revolution?
The conscious production of biological products to meet human needs
Define Agriculture
A species of animal who has been purposefully genetically altered to meet human needs
Define Domesticated Species
In time health increased, labor became divided, cultures formed, and animals became part of the humanities
What were the results of domestication?
An increased dependency and and an intensified need to breed. This led to our relationships becoming symbiotic
As domestication expanded our relationships involved into what?
In order to live comfortable with domesticated animals, to increase productivity, reduce stress, and maximize human safety
Why do we study behavior and handling?
Being able to describe categories of innate and learning behavior, explaining principles of moving livestock with minimal stress, and being able to identify some common methods of "restraint" and control
What were the outcomes of studying behavior and handling?
The way an animal reacts to a stimulus
Define Behavior
Habituation, conditioning, extinction, and imprinted behavior
What are some learning behaviors?
Desensitization
What is habituation?
"cue, response, reward"- acquire new response by association with old one
What is conditioning?
Reinforcement not continued
What is extinction?
Phase/age sensitive learning (independent of consequences)
What is imprinted behavior?
Ingestive, eliminative, shelter seeking, investigative, agonistic, sexual, mother of offspring, and social organization/domestic hierarchy
What are the categories of innate animal behavior?
Lower stress handling
Innate behavior can be used to accomplish ___________.
For the animal to move itself with no force and minimal stress
What is the goal of 'working' livestock?
What are some common distractions when 'working' livestock?
puddle reflections, chain noise, shadows, high pitch noises, etc...
Skin rafts and oils/glands
How do dogs smell a person?
Orientation is on footprints, they will ignore fresher airborne rafts that are not on track, may need sent article and follows footsteps
Define a tracking dog.
A known PLS
Where does a tracking dog start?
An animal that uses scent detection, they follow rafts that have fallen to the ground or onto higher vegetation.
What is a Trailing Dog?
They follow human scent and not the ground disturbance, the wind moves the sent way form the path over time, so the dog will leave the tack to follow the fresher air-borne scent
How does a trailing dog work?
These dogs work in wind patters, they pick up airborne scent cone from missing person, and they may ignore ground scent
What is an area search/wilderness dog?
The handler works the dog based on terrain and conditions, the dog will then hit the sent cone and work in a zig-zag in order to find the person
How do search/wilderness dogs work?
Search, locate, report
What is the 3-step behavior to scent detection and location?
A natural behavior of the dog that occurs when the dog hots a source of scent
Define Alert/indication when concerning a service dog.
The trained behavior telling their handler they have made a find
Define Final response when concerning a service dog.
The animal that displays the highest likelihood of success and one that will train to deployable level in least amount of time
How do we select a canine candidate for search and rescue?
The dog is at least 12 months old, in good physical condition, and they performed in an unfamiliar area
What is the screening process?
Drive, nerve strength, sociability, and physical screening
When selecting an animal for search and rescues what are the selection process components?
Good appetite, content and comfortable, alert, productive, physical norms, and temperament
What is normal behavior in animals?
Body condition scores, consumption rate, feces score, biol tests, assays, and vial signs
How can normal be measured?
Any difference that an animal displays from their normal behavior or "a difference from normal"
Define Disease
Physiological, anatomical, or chemical changes, impairment to function, and inability to adapt to environment
What do some disease deviations include?
Infectious or non-infectious
How are "deviations from normal" acquired?
A disease that is infection and is transmitted from animal to animal
Define infectious disease
A genetic abnormality, environmental stress or injury, chemical toxicity or deficiency, and digestive disease
Define non-infectious disease
Selection, handling, facilities, training, conditioning, and control intake
How can we prevent/treat a non-infectious disease?
Viruses, bacteria, prions, protozoa, etc...
What are some examples of infectious diseases?
This is a protein capsule that lacks ribosomes (not a 'cell'), it is not antibiotic responsive, and it needs a host cell to survive and will destroy cells as they reproduce
What is a virus?
A one-celled prokaryote with a cell wall that is antibiotic sensitive
What is bacteria?
Abnormal protein that affects the nervous system. It has a long incubation period
What are prions?
Eukaryotic that form 2 infections, they produce toxins
What are fungi and molds?
Antifungals
How do we treat fungi and molds?
Worms, bots, and grubs
What are some examples of Endoparasites?
Flies, fleas, ticks, lice
What are some examples of ectoparasites?
Organisms that survive on the external surface of their host, they often transmit other diseases
Define Ectoparasites
Chemical insecticides (not vaccines)
How do you treat ectoparasites?
Organisms that survive on the internal surfaces of hosts, they have a complex life cycle with multiple hosts
Define endoparasites
How do you treat endoparasites?
Anthelmintics (not vaccines and not antibiotics)
An endoparasite that is single celled and known as eukaryotic (membrane bound nucleus)
What is a Protozoa?
Reservoir, venue of transmission, and susceptible animal
What are the "links" of transmission?
Stops movement, limits auctions and exhibition, and is on farm isolation areas (Quarantine)
Explain the reservoir link
Sanitation, anthelmintics insecticides, and pharmaceuticals
Explain the Transmission link.
Sanitation, vest assisted planning, records and analysis, following labels, and using good facilities
What are some examples of biosecurity?
91%
What percent of the US seafood supply is imported?
The farming of aquatic organisms, including fish, mollusks, crustaceans, and aquatic plants
Define Aquaculture
Norway
Who is the number one producer of farmed salmon?
60+ producers
How many aquaculture producers are there in Iowa?
A microorganism that can grow with or without oxygen, very salt tolerant, and is able to survive refrigeration. Is also a problem in ready to eat meat
What is Listeria Monocytogenes?
Young children, pregnant women, and people with a weakened immune system
Who are some at risk populations concerning Listeria Monocytogenes?
Microscopic forms of life that are widely dispersed in the environment
Define microorganisms
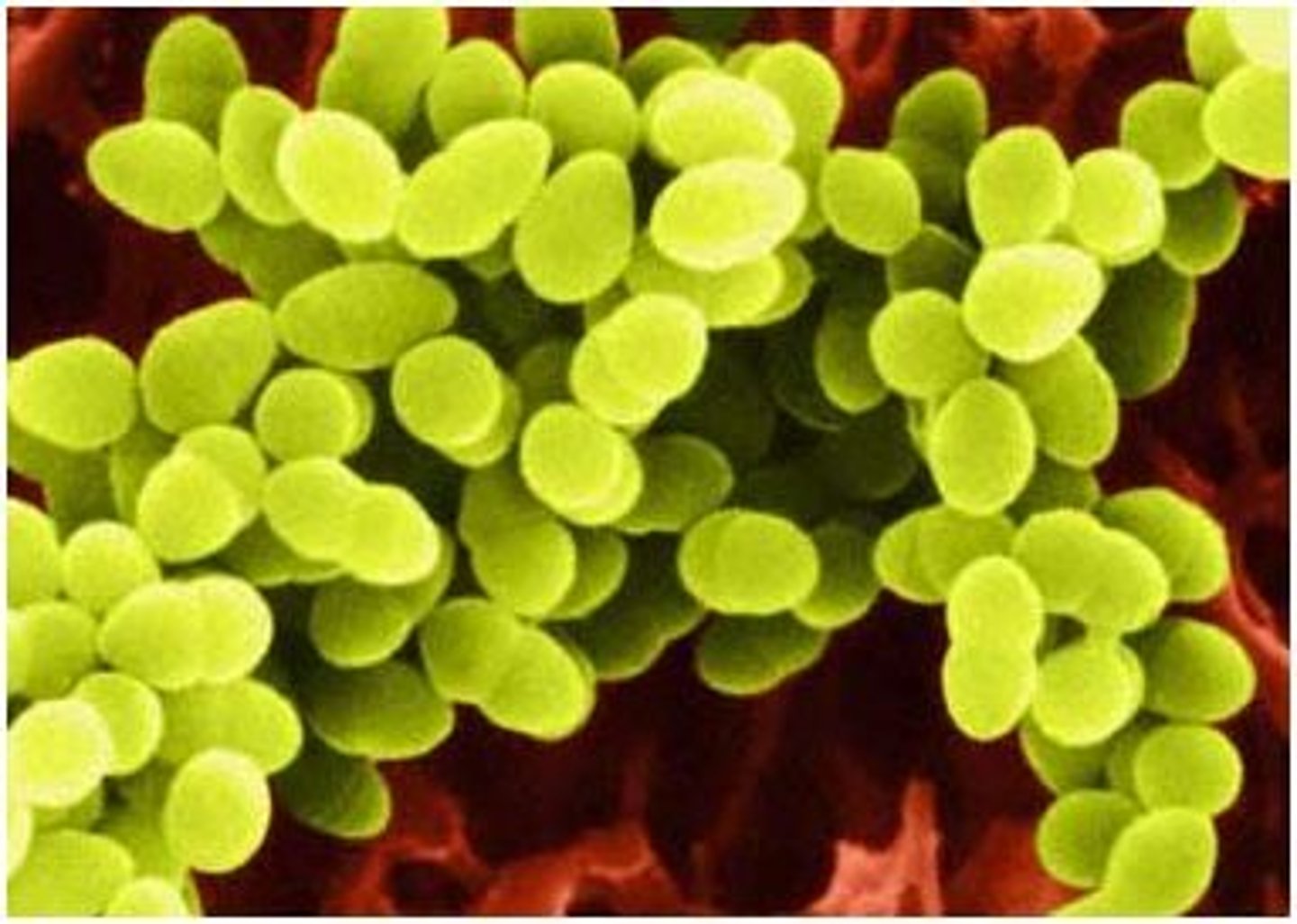
Cocci
What is this shape of bacteria?
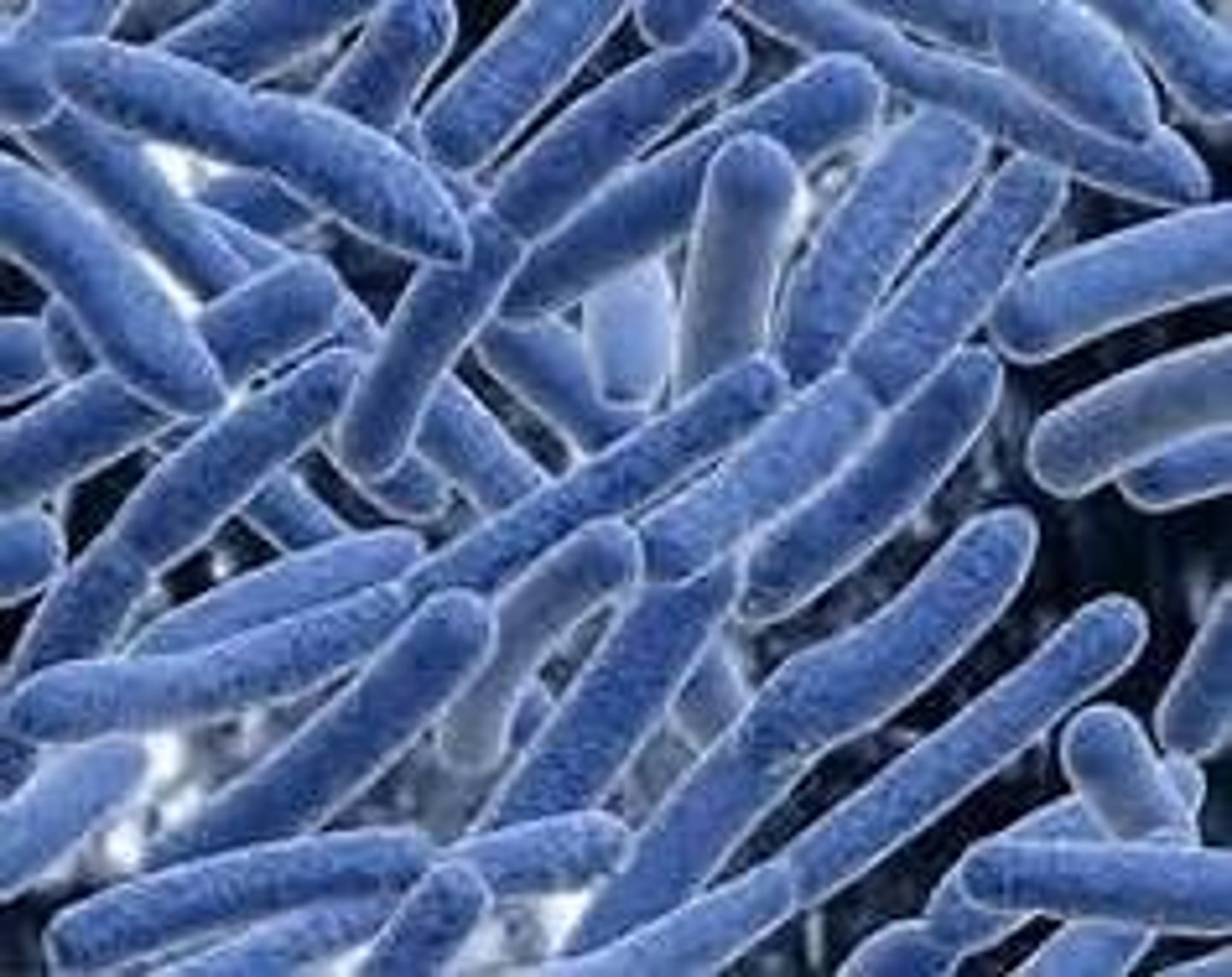
Rod
What is this shape of bacteria?
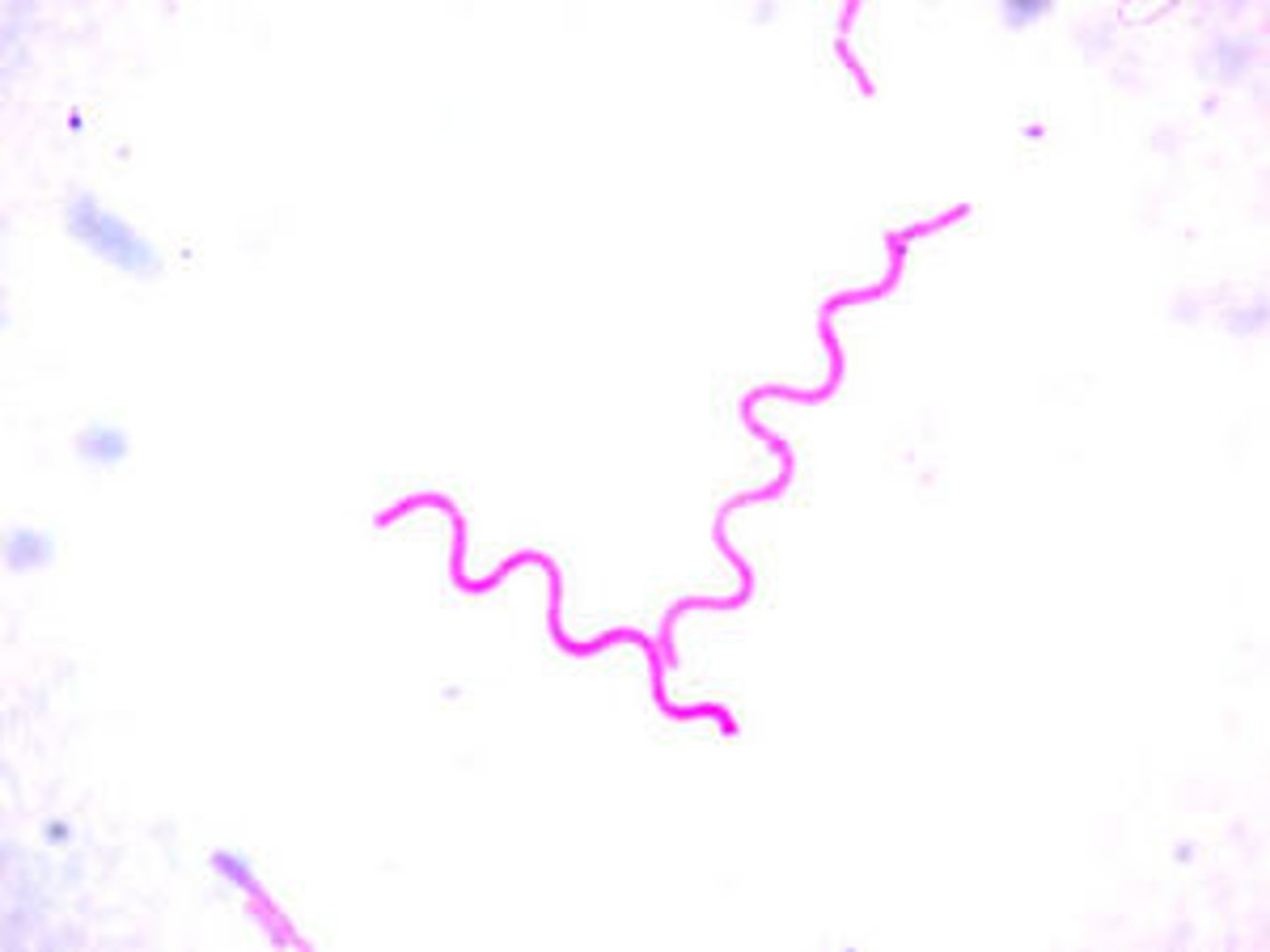
Helical
What is this shape of bacteria?
Intrinsic and Extrinsic factors
What are the factors that affect microbial growth in the food system?
Associated with the food itself
Examples: nutrients, water activity, and pH
Define Intrinsic factors
Associated with the storage environment
Examples: Storage temperature, relative humidity, and gaseous atmosphere
Define Extrinsic factors
This is known as the cafeteria bug, it is a vegetative cell that is destroyed by cooking. These spores live an eternity and they can grow in areas where there is little to no oxygen
What are Clostridium Perfringens?
In the microflora of sheep and cattle, it can survive extremely acidic conditions. (low infectious dose)
Where does E. coli generally live?
Stool of infected person (15-50 days), illness several weeks to several months
What is the "vehicle" for Hepatitis A?
Cooking temperature for ground meat?
160
Cooking temperature of ground poultry
165
145
Cooking temperature fresh meat
165
Cooking temperature of fresh poultry
145
Cooking temperature of pork and ham
everything
Make sure you clean...
40 or below
You chill meat to
raw from cooked meat
You separate
40-140
What is the danger zone
60 days
What is the withdraw time for Scour Bos 9?
60 days
What is the withdraw time for Vira Shield 5+VL5 Somnus?
8 days
What is the withdraw time for Panacur Cattle Dewormer?
None
What is the withdraw time for Saber Pour-On Insecticide?
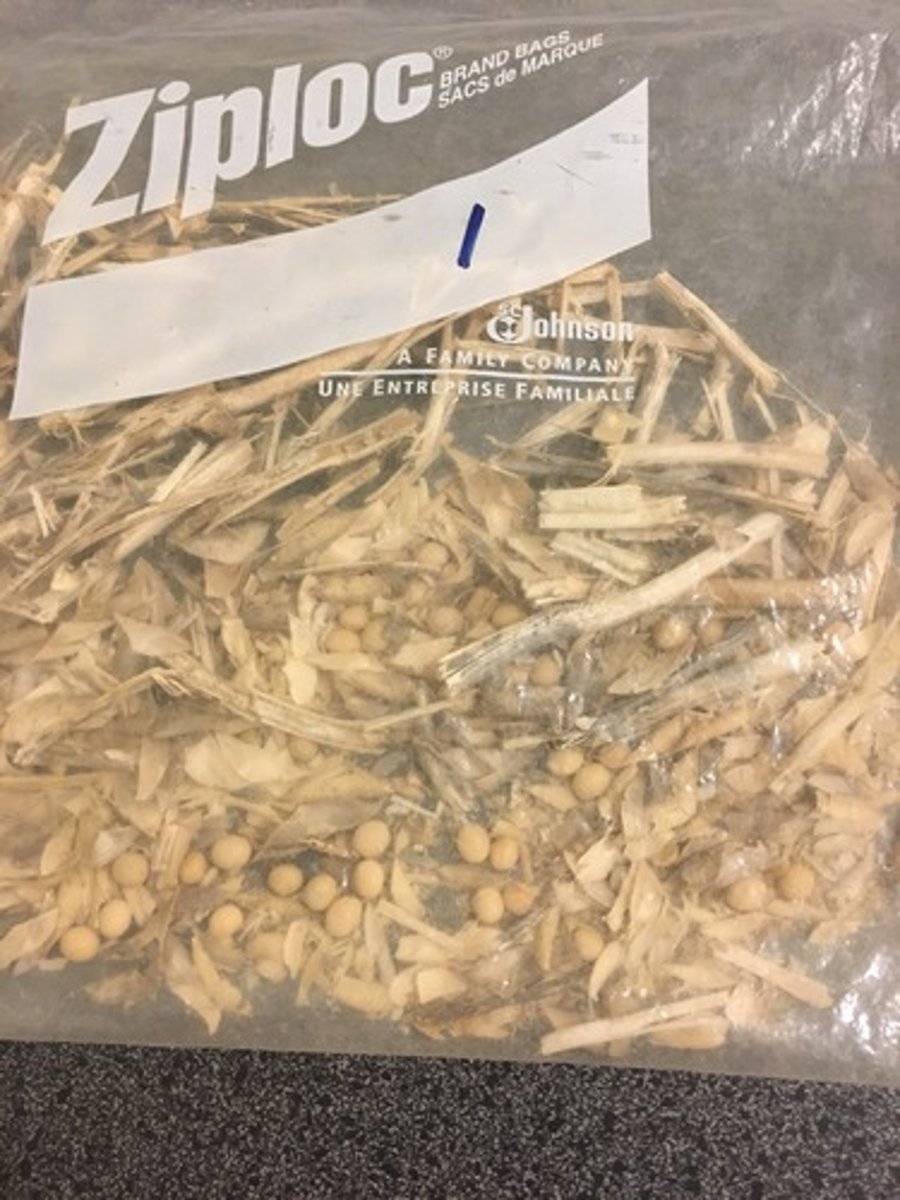
Soy Bean Stover

Corn Stover

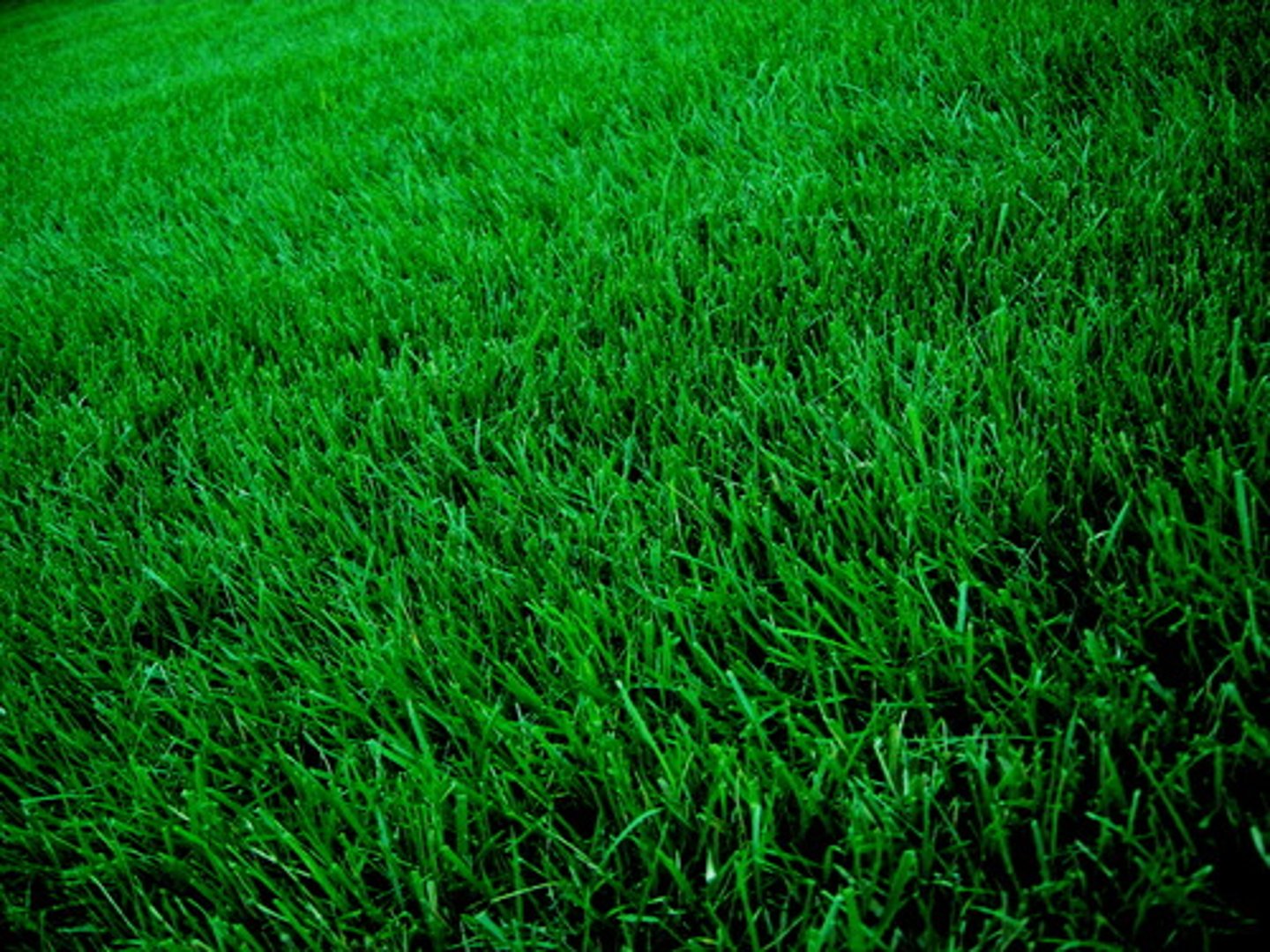
Grass Hay

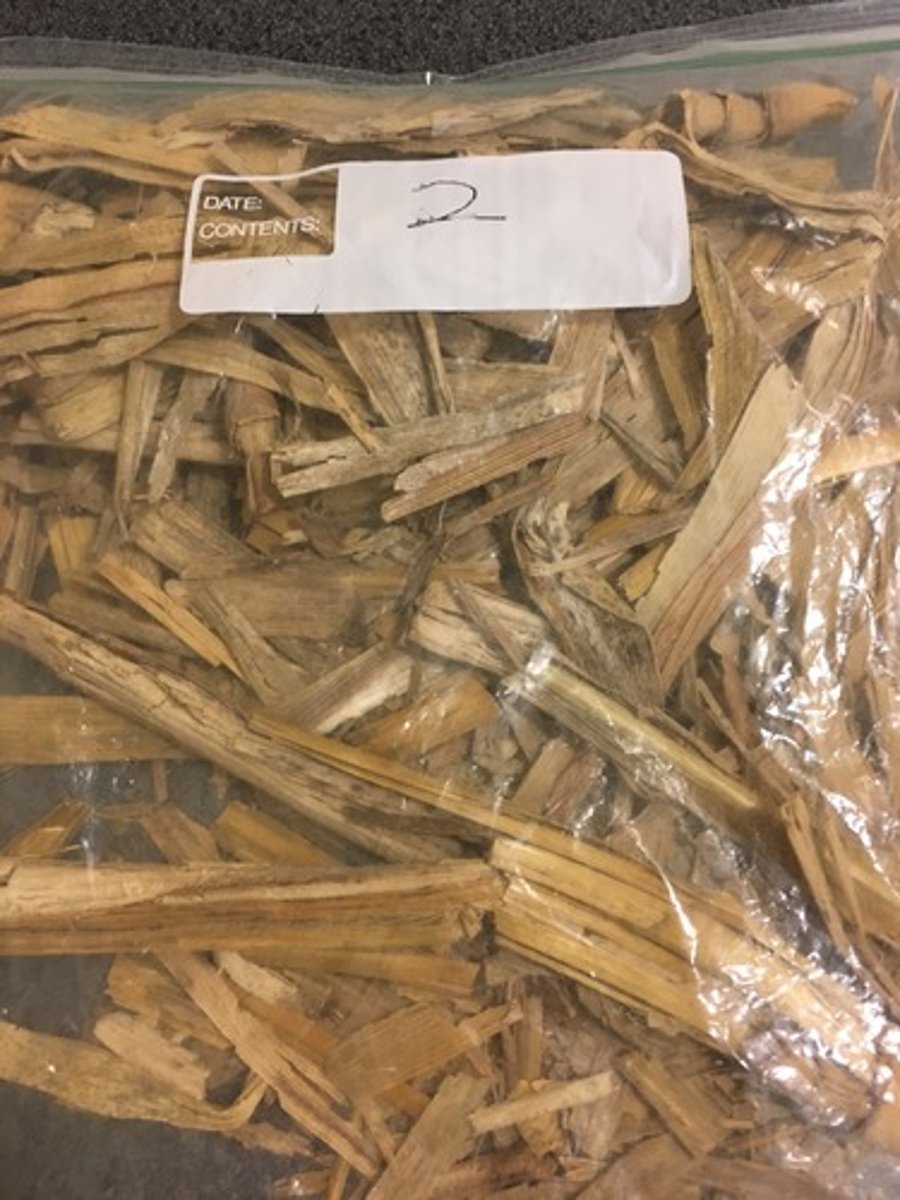
Straw

Beet pulp

Cottonseed Hulls

Alfalfa Hay

Corn silage

Alfalfa Haylage

Corn

Wheat

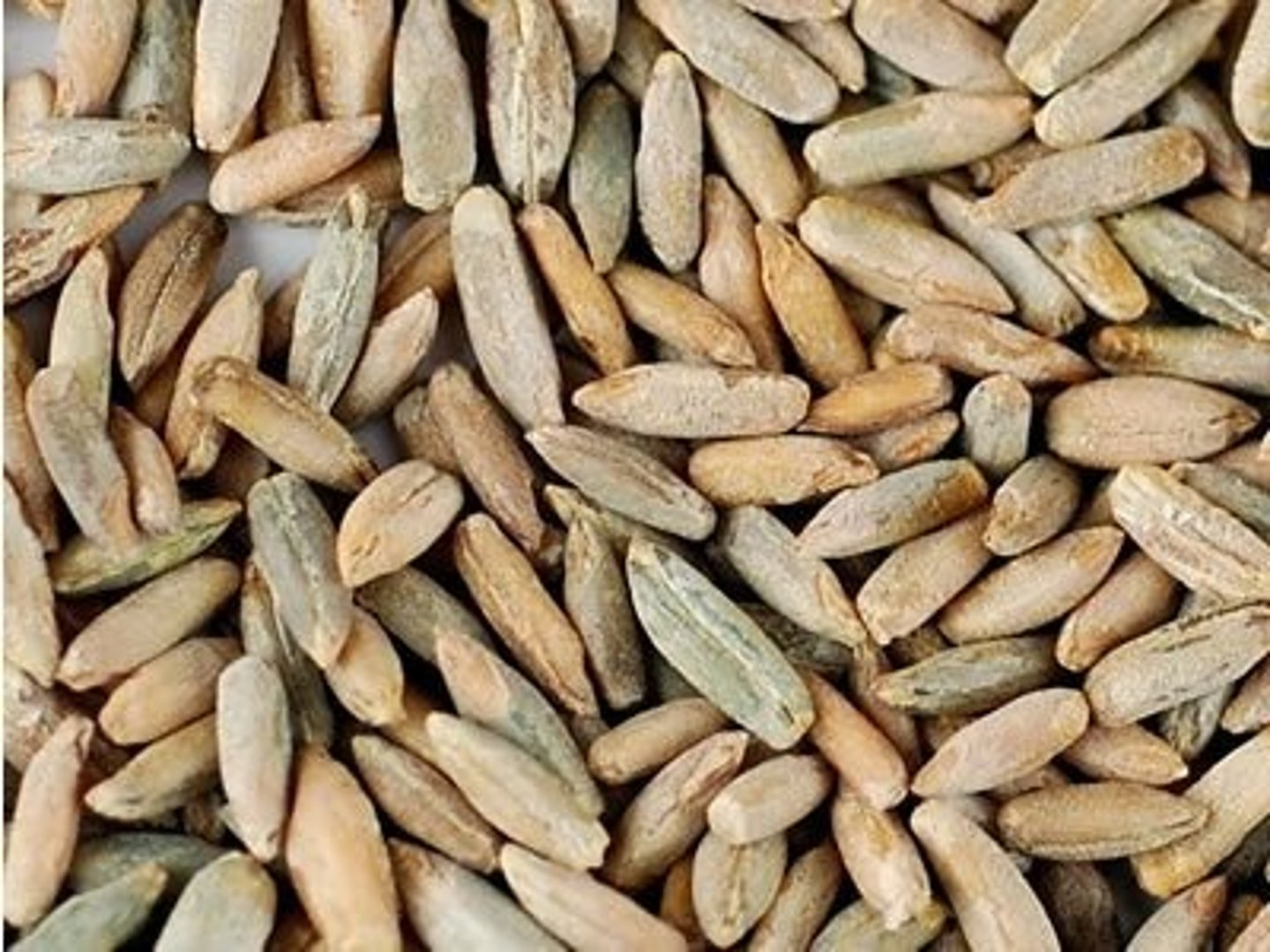
Rye
