Principles of Chemistry I - Final Exam Study Guide
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/210
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
211 Terms
1
New cards
C
Which is a heterogeneous mixture?
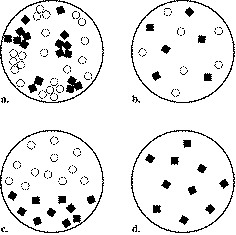
2
New cards
B
Which is a homogeneous mixture?
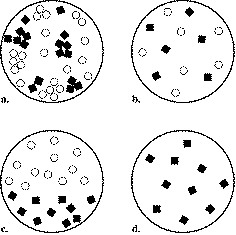
3
New cards
D
Which is a pure substance?
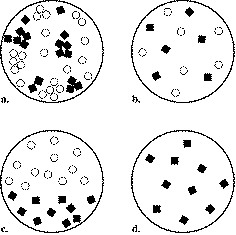
4
New cards
True
T or F: Every substance has at least 1 differentiating characteristic.
5
New cards
A, C
Which 2 of these are requirements for differentiating characteristics?
A) Are intensive
B) Are extensive
C) Are unique for each substance
D) Change depending on environment (temp, pressure, etc)
A) Are intensive
B) Are extensive
C) Are unique for each substance
D) Change depending on environment (temp, pressure, etc)
6
New cards
Boiling point, melting point, density, melting point
List some good differentiating characteristics
7
New cards
Mass, volume, concentration, temperature, pressure, solubility
List some bad differentiating characteristics
8
New cards
A
Is it intensive or extensive? -- Chemical reactions
A) Intensive
B) Extensive
A) Intensive
B) Extensive
9
New cards
A
Is it intensive or extensive? -- Temperature
A) Intensive
B) Extensive
A) Intensive
B) Extensive
10
New cards
A
Is it intensive or extensive? -- Density
A) Intensive
B) Extensive
A) Intensive
B) Extensive
11
New cards
B
Is it intensive or extensive? -- Volume
A) Intensive
B) Extensive
A) Intensive
B) Extensive
12
New cards
The water comes out of the gas phase and freezes, and the oxygen becomes a liquid, so the balloon shrinks
If you put a balloon in liquid nitrogen, what happens to the balloon?
13
New cards
C
During a phase change, energy is ____________ stored/released by the system.
A) Sometimes
B) Never
C) Always
A) Sometimes
B) Never
C) Always
14
New cards
D
The amount of energy exchanged per unit mass of a substance is a ______________.
A) Phase change
B) Triple point
C) Vaporization
D) Differentiating Characteristic
A) Phase change
B) Triple point
C) Vaporization
D) Differentiating Characteristic
15
New cards
D
Where are the phase changes occurring?
A) Between A&B, and D&E
B) Between A&B, and C&D
C) Between C&D, and E&F
D) Between B&C, and D&E
A) Between A&B, and D&E
B) Between A&B, and C&D
C) Between C&D, and E&F
D) Between B&C, and D&E
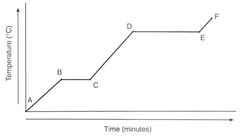
16
New cards
D
Where is PE increasing a lot?
A) Between A&B, and D&E
B) Between A&B, and C&D
C) Between C&D, and E&F
D) Between B&C, and D&E
A) Between A&B, and D&E
B) Between A&B, and C&D
C) Between C&D, and E&F
D) Between B&C, and D&E
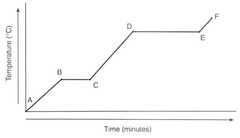
17
New cards
B
Where is KE increasing a lot?
A) Between A&B, and D&E
B) Between A&B, and C&D
C) Between C&D, and E&F
D) Between B&C, and D&E
A) Between A&B, and D&E
B) Between A&B, and C&D
C) Between C&D, and E&F
D) Between B&C, and D&E
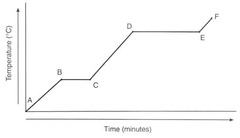
18
New cards
C
Phase stability relies on...
A) The number of molecules
B) Potential energy
C) Pressure & Temperature
D) Pressure only
A) The number of molecules
B) Potential energy
C) Pressure & Temperature
D) Pressure only
19
New cards
A glass of water sitting out for a week and "losing" water
What is an example of a liquid that evaporates (to a certain extent) at any temp?
20
New cards
Vapor pressure, atmospheric pressure
Boiling point occurs when ________ equals ________.
21
New cards
Liquid
On a vapor pressure graph, the left side of one of these lines represents what phase?
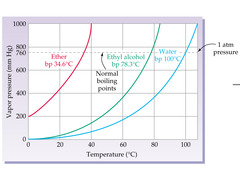
22
New cards
Ether
Which of these is most volatile?
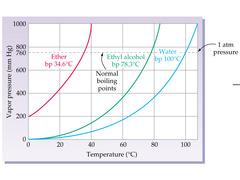
23
New cards
Filtration
A separating method based on the mechanical separation of substances in the solid-state from substances in a fluid phase (liquid or gas) by using a physical barrier which only the fluid can pass.
24
New cards
Distillation
This technique is used to separate substances in a liquid mixture taking advantage of differences in the boiling points of the various components. It involves a phase change from liquid to gas and the reconversion of the separated substances to the liquid phase.
25
New cards
Crystillation
A separation method that includes changing the temperature or the concentration of the components in a fluid (liquid or gas) mixture, or by adding other substances to include a solid-state.
26
New cards
Pressure
In the ideal gas law, changing mass changes speed, but does not change___________.
27
New cards
Speed
In the ideal gas law, changing temperature changes pressure and ________.
28
New cards
False
T or F: The movement of gas particles in the ideal gas law is uniform and predictable.
29
New cards
Area
Pressure = Force/?
30
New cards
Temperature
A measure of the average KE per particle.
31
New cards
8 J
What is the average KE for a 1kg particle moving at 4 m/s?
KE = (1/2) * m * v^2
KE = (1/2) * m * v^2
32
New cards
Mass
At the same temperature, the speed of different particles will depend on the __________.
33
New cards
Looking at the substance with the highest fraction of particles moving the slowest (least velocity)
In a "% of particles v velocity" graph, the substance with the HIGHEST mass can be found by....
34
New cards
Looking at the substance with the highest fraction of particles moving the fastest (highest velocity)
In a "% of particles v velocity" graph for molecules with different masses, the substance with the LOWEST mass can be found by....
35
New cards
Higher temperature
In a "% of particles v velocity" graph for molecules with different temperatures, the substance with the higher distribution of velocities (aka a "less steep" curve) might have a...
36
New cards
Looking at the substance with the highest fraction of particles moving the fastest (highest velocity).
In a "% of particles v velocity" graph for molecules with different temperatures, the substance with the HIGHEST temperature can be found by....
37
New cards
True
T or F: In a "% of particles v velocity" graph, you shouldn't look at the one with the highest mountain, you should look at the one that has the peak at the highest velocity (when looking for highest temperature or smallest mass)
38
New cards
True
T or F: Substances at the same temperature will have the same KE, regardless of mass.
39
New cards
Pressure, Temperature
What graph is this?
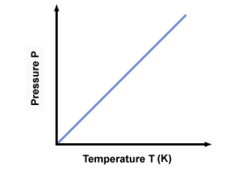
40
New cards
Pressure, Volume
What graph is this?
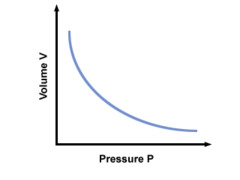
41
New cards
False
T or F: The average KE of a substance changes during a phase change.
42
New cards
True
T or F: Ionic compounds are not molecules.
43
New cards
Moles
For gases of equal temperature (𝑇),(T), pressure (𝑃),(P), and volume (𝑉),(V), the number of _________ of the gases is equal as well.
44
New cards
D
Gases that represent the ideal gas law are at a high ________ and low __________.
A) Temperature, Mass
B) Pressure, Temperature
C) Number of moles, Volume
D) Temperature, Pressure
A) Temperature, Mass
B) Pressure, Temperature
C) Number of moles, Volume
D) Temperature, Pressure
45
New cards
A
Use Kb when your amount of substance is given in...
A) Molecules
B) Moles
C) Neither
A) Molecules
B) Moles
C) Neither
46
New cards
B
Use R when your amount of substance is given in...
A) Molecules
B) Moles
C) Neither
A) Molecules
B) Moles
C) Neither
47
New cards
B
If you raise temperature and the strength of IMFs, what happens to the pressure?
A) No change
B) Increase
C) Decrease
A) No change
B) Increase
C) Decrease
48
New cards
Distance
The strength of intermolecular forces depends on the ____________ between particles.
49
New cards
A
At a single temperature, the substance with the _________ vapor pressure has the highest IMFs.
A) Highest
B) Lowest
C) Neither
A) Highest
B) Lowest
C) Neither
50
New cards
D
Phase changes depend on how _________ and ________ are distributed
A) pressure, temperature
B) mass, IMFs
C) volume, temperature
D) energy, matter
A) pressure, temperature
B) mass, IMFs
C) volume, temperature
D) energy, matter
51
New cards
Distance, strength
PE depends on the _________ and ___________ of interactions between particles.
52
New cards
Lower PE
For ATTRACTION, closer molecules means....
53
New cards
Higher PE
For REPULSION, closer molecules means....
54
New cards
C
During a phase change, all energy is invested or lost in the form of ___________.
A) Heat
B) KE
C) PE
D) None of the above
A) Heat
B) KE
C) PE
D) None of the above
55
New cards
True
T or F: The size of the particles matters when considering the PE needed to separate two atoms.
56
New cards
A
When turning a liquid into a gas, we must _________ PE in order to separate the two atoms.
A) Add
B) Subtract
C) Do nothing to
A) Add
B) Subtract
C) Do nothing to
57
New cards
PE & # Configurations
When a system can adopt different states, the one it picks depends on...
58
New cards
B
A system wants to be in a place with the _________ PE and _________ # of configurations
A) Highest, highest
B) Lowest, highest
C) Highest, Lowest
D) Lowest, Lowest
A) Highest, highest
B) Lowest, highest
C) Highest, Lowest
D) Lowest, Lowest
59
New cards
Energetic; configuration
In PEC diagrams, a substance is looking for __________ and _________ stability
60
New cards
Higher
Lower pressures favor states with a ___________ # of configurations.
61
New cards
The composition of the structure of the particles
What is the key differentiating characteristic between substances?
62
New cards
True
T or F: If T, V, and P is the same for 3 gases, the number of mols must be the same for all of them.
63
New cards
A
Higher temps prefer a ________ PE.
A) Higher
B) Lower
A) Higher
B) Lower
64
New cards
1000 L
1 m^3
65
New cards
False
T or F: Most space in the atom is taken up by the nucleus.
66
New cards
True
T or F: Most space in the atom is taken up by the electron cloud.
67
New cards
True
T or F: Most of the mass of the atom comes from the nucleus.
68
New cards
False
T or F: Most of the mass of the atom comes from the electron cloud.
69
New cards
Atomic #
This number refers to the number of protons in the nucleus, but also refers to the number of electrons of the atom if it's in a neutral state.
70
New cards
B
In a neutral atom, __________ = ___________.
A) Protons, neutrons
B) Protons, electrons
C) Neutrons, electrons
D) None of the above
A) Protons, neutrons
B) Protons, electrons
C) Neutrons, electrons
D) None of the above
71
New cards
A
The mass of an atom can be determined by adding the number of __________ and ___________.
A) Protons, neutrons
B) Protons, electrons
C) Neutrons, electrons
D) None of the above
A) Protons, neutrons
B) Protons, electrons
C) Neutrons, electrons
D) None of the above
72
New cards
True
T or F: Protons and neutrons have about the same mass.
73
New cards
True
T or F: Atoms that are isotopes have the same number of protons, but a different number of neutrons.
74
New cards
Top left: mass, Bottom left: atomic number, Center: symbol
How do you write the atomic symbol of an element?
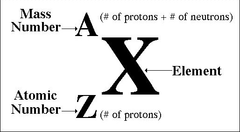
75
New cards
D
Average atomic mass (mass of an element on the PT) is equal to the...
A) Protons + neutrons of every isotope
B) Number of electrons
C) Percent abundance only
D) Mass times relative abundance
A) Protons + neutrons of every isotope
B) Number of electrons
C) Percent abundance only
D) Mass times relative abundance
76
New cards
A
In a mass spectrometry graph, all fragments are __________ charged.
A) Positively
B) Negatively
C) Neutral
A) Positively
B) Negatively
C) Neutral
77
New cards
Particle Composition
Type and number of atoms of each type per particle.
78
New cards
1. Set the percent abundance to grams (ex: 92% becomes 92 grams)
2. Divide each by molar mass
3. Divide the mols by the smallest mass
4. Multiply to whole number if needed
2. Divide each by molar mass
3. Divide the mols by the smallest mass
4. Multiply to whole number if needed
Steps for Finding the Empirical Formula
79
New cards
Divide the given mass of the substance by the mass of the empirical formula, and then multiply that number into the empirical formula
How do you convert the empirical formula to the molecular formula?
80
New cards
X4Y6
A substance is 50 amu. If the empirical formula of this substance is X2Y3, and the mass of X2Y3 is 25 amu, what is the molecular formula of this substance?
81
New cards
C
If you're trying to find the molecular formula of a mass spec, the mass of the substance is the peak on the farthest...
A) Left
B) Center
C) Right
D) None of the above
A) Left
B) Center
C) Right
D) None of the above
82
New cards
Electromagnetic radiation
Energy travelling through space as waves formed by oscillating electric and magnetic fields
83
New cards
A
The period of a wave, inverse to frequency, and denoted by ƛ
A) Wavelength
B) Frequency
C) Wavenumber
A) Wavelength
B) Frequency
C) Wavenumber
84
New cards
B
The number of waves per unit time, inverse to wavelength, and denoted by v
A) Wavelength
B) Frequency
C) Wavenumber
A) Wavelength
B) Frequency
C) Wavenumber
85
New cards
Wavelength x frequency
Speed of light = ________ x _____________
86
New cards
C
In absorption spectroscopy, the color that is released is the wavelength with the ___________ absorption.
A) Highest
B) Medium
C) Lowest
A) Highest
B) Medium
C) Lowest
87
New cards
C
Absorption is highest when transmittance is ___________.
A) Highest
B) Medium
C) Lowest
A) Highest
B) Medium
C) Lowest
88
New cards
A
In an emission spectrum, more lines of emission corresponds to a _____________ molar mass.
A) Higher
B) Medium
C) Lower
A) Higher
B) Medium
C) Lower
89
New cards
Excited State
Any state above ground state for an atom.
90
New cards
Ground state
The lowest energy state of an atom
91
New cards
A
Absorption occurs when the energy is __________.
A) Increasing
B) Decreasing
C) Remaining the same
A) Increasing
B) Decreasing
C) Remaining the same
92
New cards
B
Emmission occurs when the energy is __________.
A) Increasing
B) Decreasing
C) Remaining the same
A) Increasing
B) Decreasing
C) Remaining the same
93
New cards
A
Frequency is __________ as bond strength is increasing.
A) Increasing
B) Decreasing
C) Remaining the same
A) Increasing
B) Decreasing
C) Remaining the same
94
New cards
B
Frequency is __________ as mass is increasing.
A) Increasing
B) Decreasing
C) Remaining the same
A) Increasing
B) Decreasing
C) Remaining the same
95
New cards
B
Total energy is __________ during a bond formation.
A) Increasing
B) Decreasing
C) Remaining the same
A) Increasing
B) Decreasing
C) Remaining the same
96
New cards
Plank's constant x frequency
Energy = ________ * __________ (use v)
97
New cards
Plank's constant x (speed of light/wavelength)
Energy = ________ * __________ (use ƛ)
98
New cards
J/photon
The equation E = hc/ƛ gives you an answer with what unit?
99
New cards
Multiply by Avogadro's number
If you have energy in units of J/photon, how do you find the energy of 1 mol?
100
New cards
C
Microwaves are usually associated with a change in _________________.
A) excitation/bond breaking state
B) vibrational state
C) rotational state
A) excitation/bond breaking state
B) vibrational state
C) rotational state