Test 6 Review Sheet (Topics 14 - 17, 20f and Labs)
1/93
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering topics in cell division, meiosis, genetics, and immunology.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
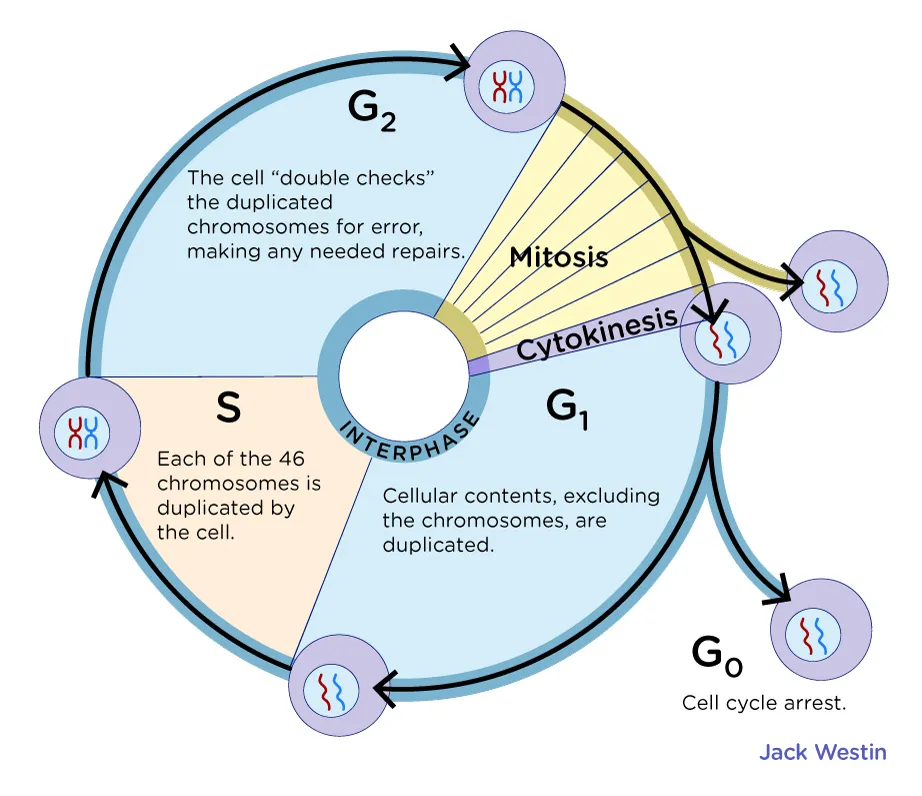
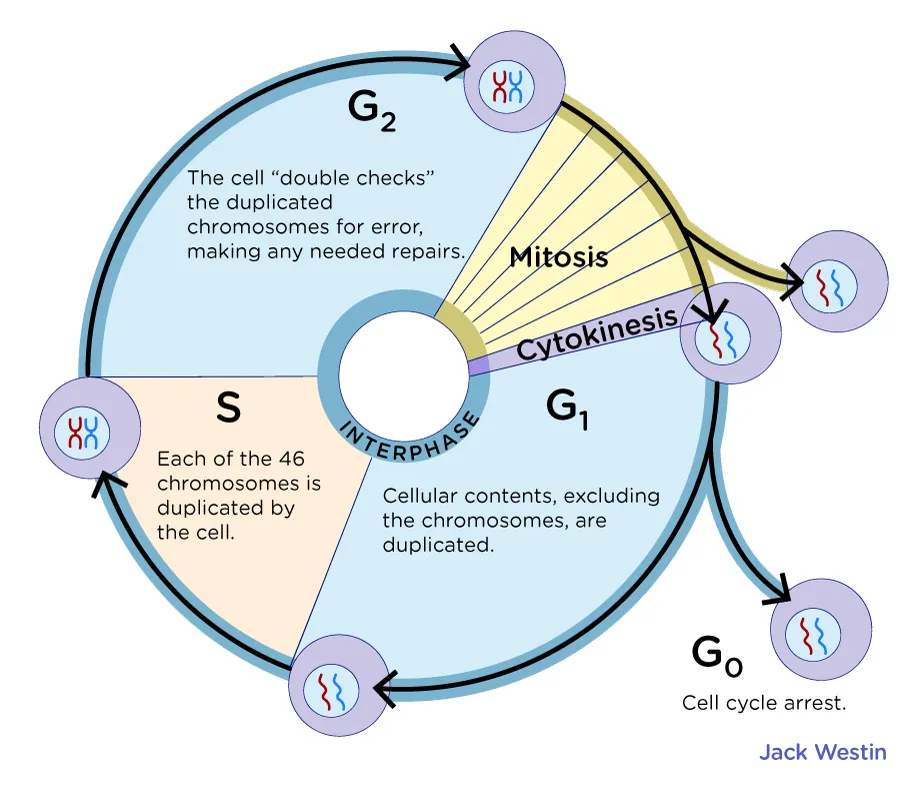
Cell Cycle
The series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication
Mitosis
A type of cell division that results in two daughter cells each having the same number and kind of chromosomes as the parent nucleus, typical of ordinary tissue growth.
Interphase
The period of the cell cycle during which the cell is not undergoing division.
G1 Phase
The first gap phase of the cell cycle, during which the cell grows and prepares for DNA replication.
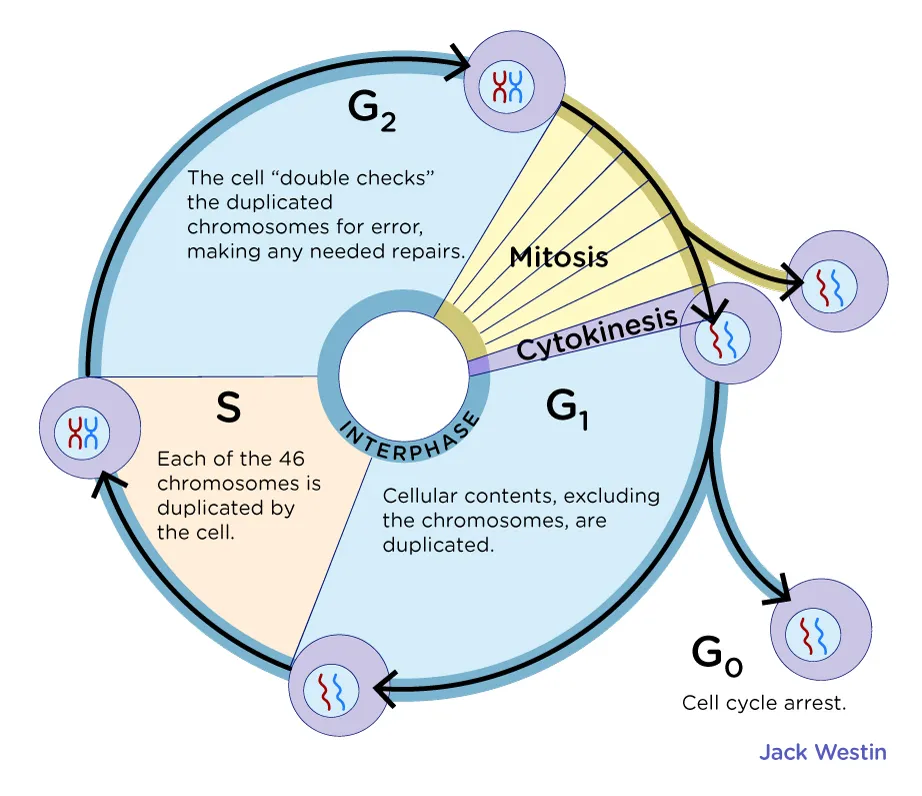
S Phase
The synthesis phase of the cell cycle, during which DNA replication occurs.
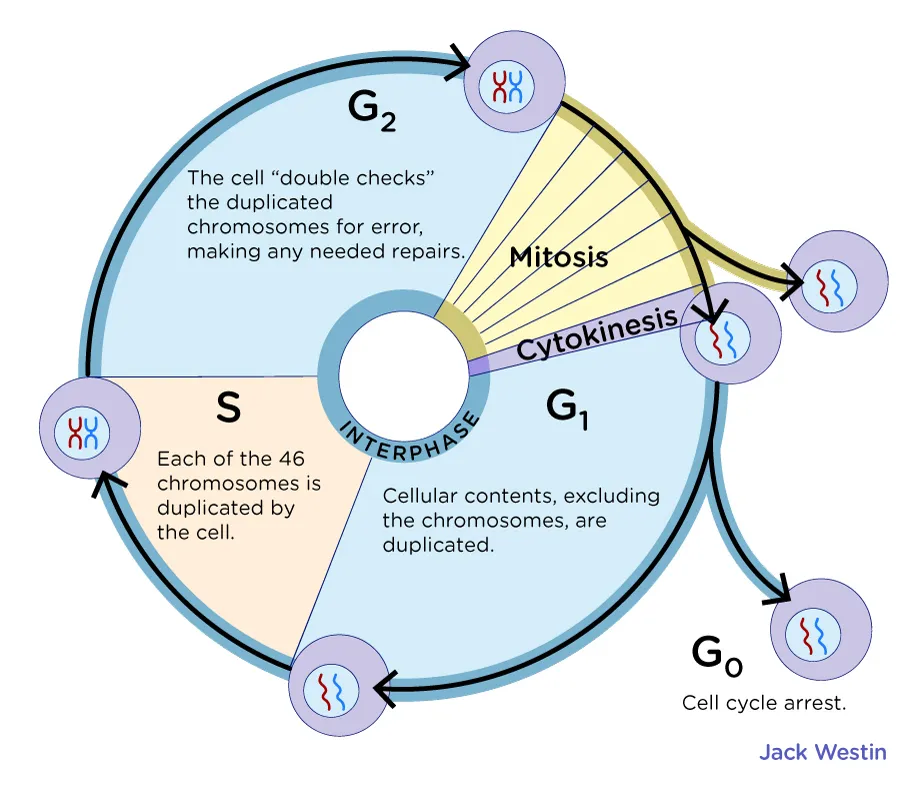
G2 Phase
The second gap phase of the cell cycle, during which the cell prepares for mitosis.
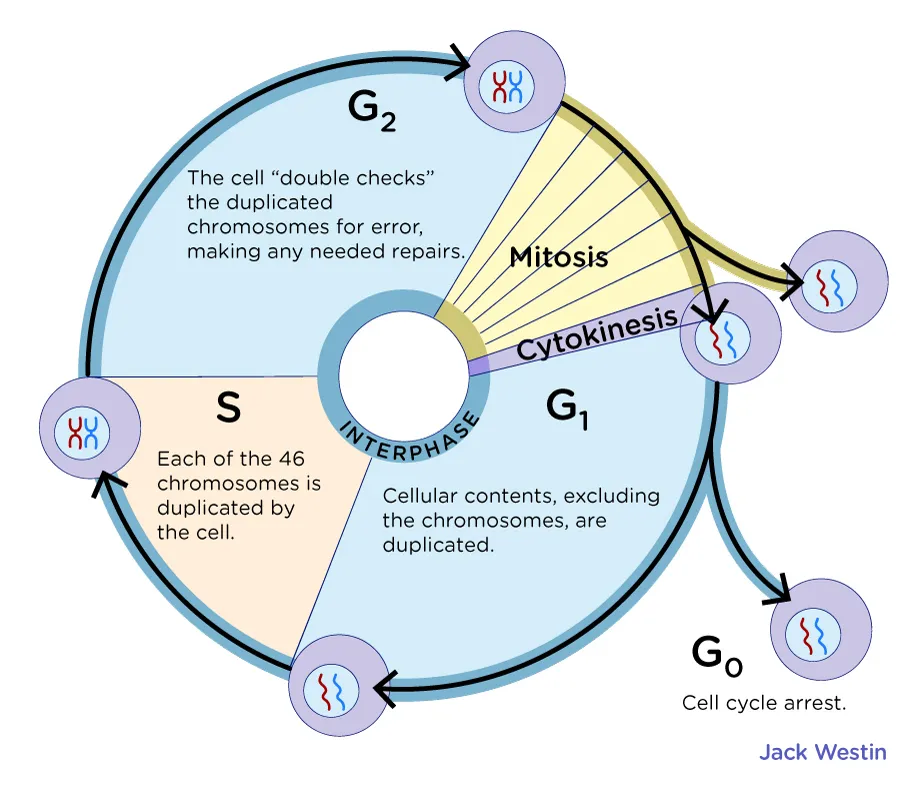
M Phase
The phase of the cell cycle that includes mitosis and cytokinesis.
Prokaryotic cells division
Favors binary fission, a simpler process than division in eukaryotic cells.
Cell Cycle Checkpoints
Control points in the cell cycle where progress is halted until certain conditions are met.
Chemical Clock
Chemicals inside a cell that control its progression through the cell cycle.
Alternate Phase of the Cell Cycle
The cell enters this phase if it does not pass through the G1 checkpoint and is not going to divide.
Linear DNA
DNA arranged in a linear, non-circular fashion
Genes
Units of heredity made up of DNA.
Chromosomes
Structures within cells that contain DNA.
Chromatin
The material of which chromosomes are made of other than DNA.
Genome
The complete set of genes or genetic material present in a cell or organism.
Duplicated Chromosome
A chromosome that has been copied and consists of two sister chromatids.
Sister Chromatids
Two identical copies of a single replicated chromosome that are connected by a centromere.
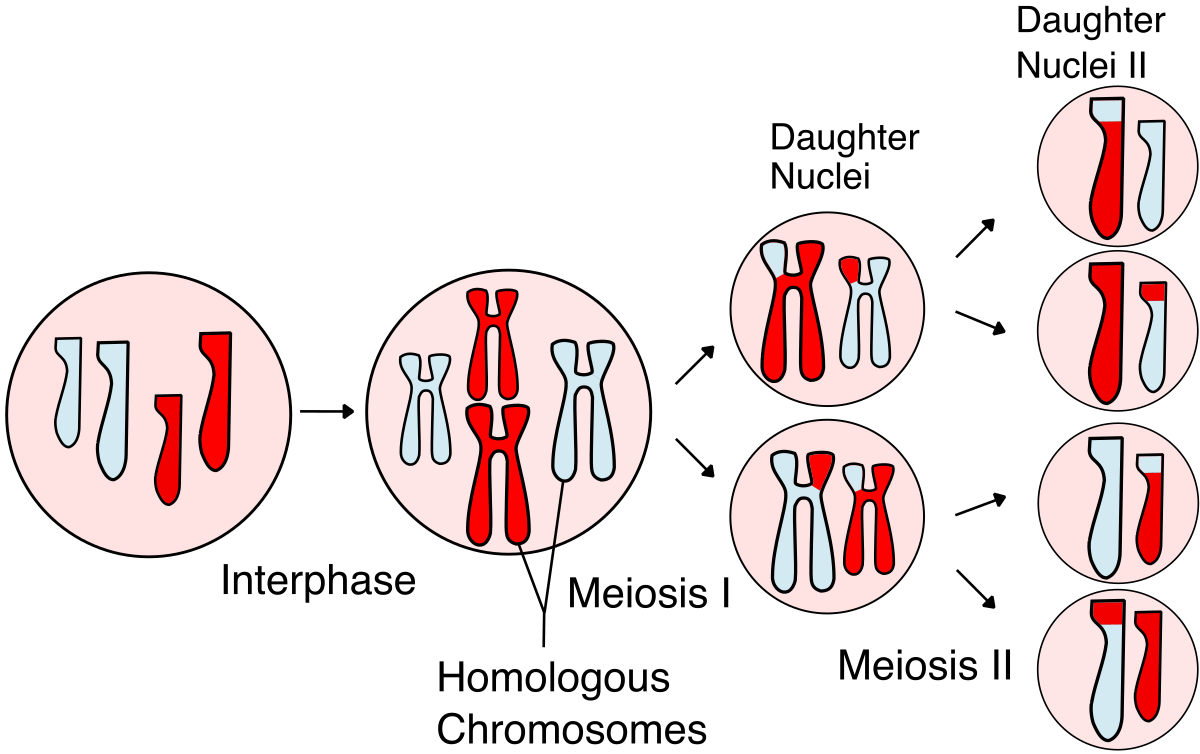
Homologous Pairs
A pair of chromosomes having the same genes but possibly different alleles.
Autosomes
Any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome.
Sex Chromosomes
Chromosomes involved in determining the sex of an organism.
Diploid
Containing two complete sets of chromosomes, one from each parent (2n).
Haploid
Having a single set of unpaired chromosomes (n).
Asexual Reproduction
A type of reproduction that does not involve the fusion of gametes or change in the number of chromosomes.
Mitosis
Cell division that results in two identical daughter cells.
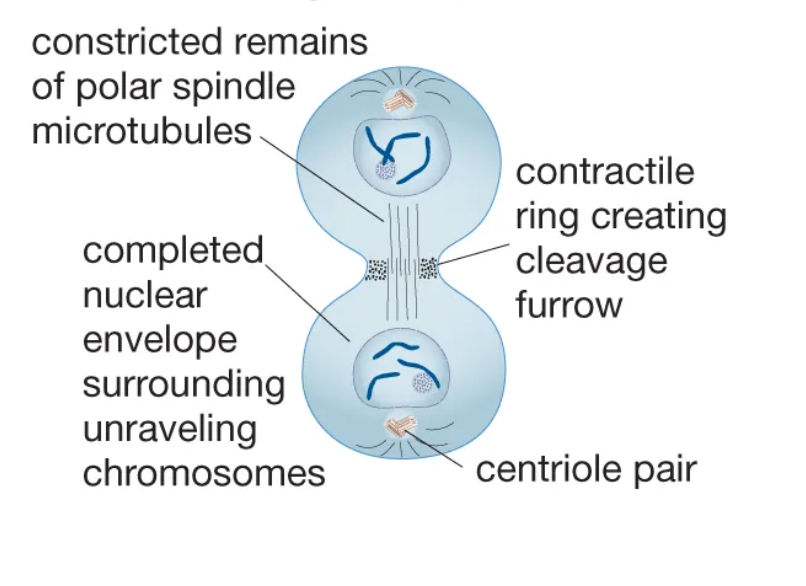
Cytokinesis
The physical process of cell division that divides the cytoplasm of a parental cell into two daughter cells.
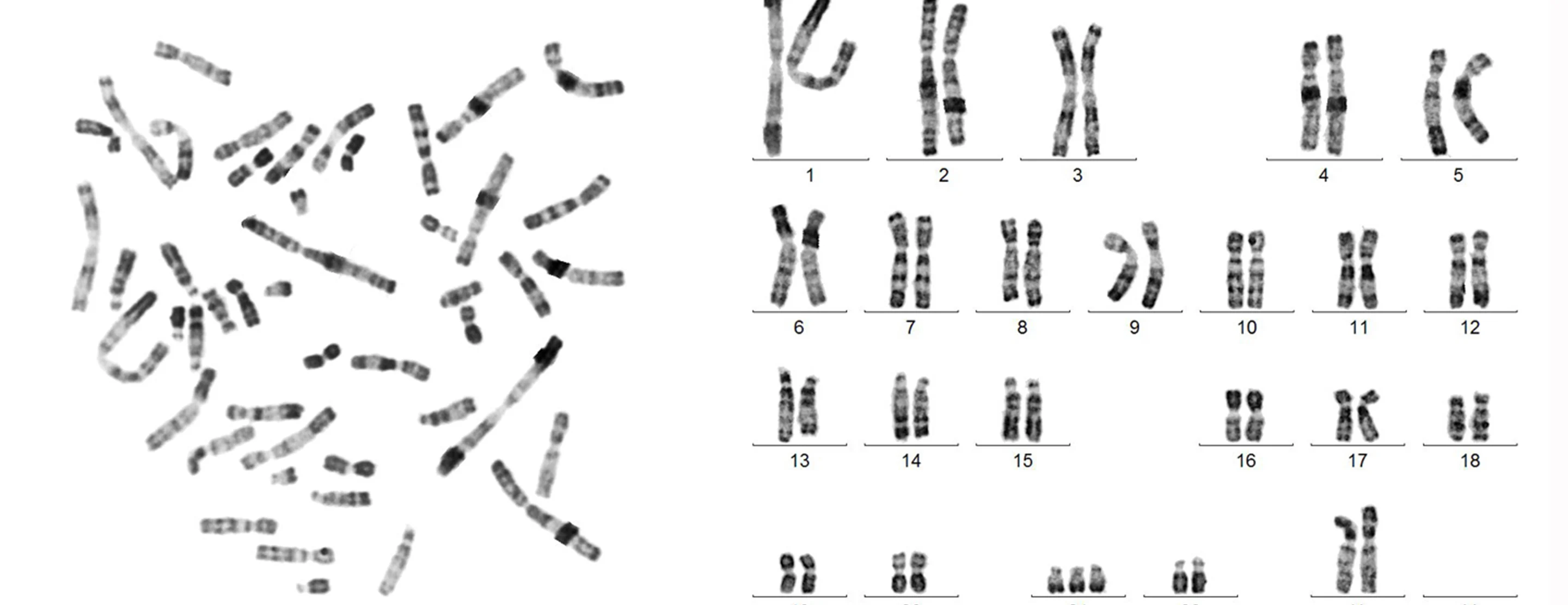
Karyotype
The number and visual appearance of the chromosomes in the cell nuclei of an organism or species.
Sexual Reproduction
A type of reproduction that involves the fusion of gametes.
Meiosis
A type of cell division that results in four daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
Crossing Over
The exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes during meiosis.
Independent Assortment
The random distribution of genes during meiosis.
Inheritance
The process by which genetic information is passed from parent to offspring.
Gregor Mendel
The 'father of modern genetics' observed that organisms inherit traits through genes.
Alleles
Different forms of a gene.
Homozygous
Having two identical alleles for a gene.
Heterozygous
Having two different alleles for a gene.
Dominant
An allele that masks the effect of another allele.
Recessive
An allele whose effect is masked by a dominant allele.
Genotype
The genetic makeup of an organism.
Phenotype
The observable characteristics of an organism.
Carrier
An individual who carries and is capable of passing on a genetic mutation associated with a disease and may or may not display disease symptoms.
Incomplete Dominance
A form of intermediate inheritance in which one allele for a specific trait is not completely expressed over its paired allele.
Codominance
A relationship between two versions of a gene.
Polygenic Inheritance
A trait controlled by two or more genes.
Pleiotropy
The production by a single gene of two or more apparently unrelated effects.
Linkage
The proximity of genes or other DNA markers to one another on a chromosome.
Sex Linkage
The phenotypic expression of an allele that is dependent on the sex of the individual and is directly tied to the sex chromosomes.
X-Chromosome Inactivation
A process by which one of the two X chromosomes present in female mammals is randomly inactivated, resulting in the inactivation of most of its genes.
Barr Bodies
The inactive X chromosome in a female somatic cell, rendered inactive in a process called lyonization, in those species in which sex is determined by the presence of the Y chromosome.
Nondisjunction
The failure of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids to separate properly during cell division.
Monosomy
The condition of having a diploid chromosome complement in which one chromosome lacks its homologous partner.
Trisomy
A genetic condition in which a person has three copies of a chromosome instead of the usual two.
Innate Immunity
The defense system with which you were born. It protects you against all antigens.
Antigens
Any substance that causes your immune system to produce antibodies against it.
Antibodies
A blood protein produced in response to and counteracting a specific antigen.
Vaccines
A substance used to stimulate the production of antibodies and provide immunity against one or several diseases.
COVID-19
A contagious disease caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2).
mRNA Vaccines
A type of vaccine that uses messenger RNA to instruct cells to produce viral proteins.
Rapid Antibody Test
A diagnostic test that detects the presence of antibodies against COVID-19 in a blood sample.
Interphase
The period of the cell cycle when the cell is not dividing.
Prophase
The first stage of mitosis, during which chromosomes become visible.
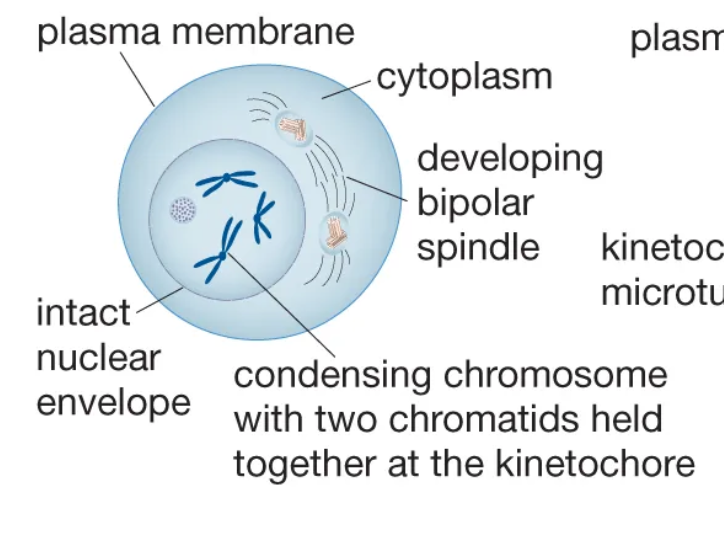
Metaphase
The stage of mitosis during which chromosomes align in the middle of the cell.
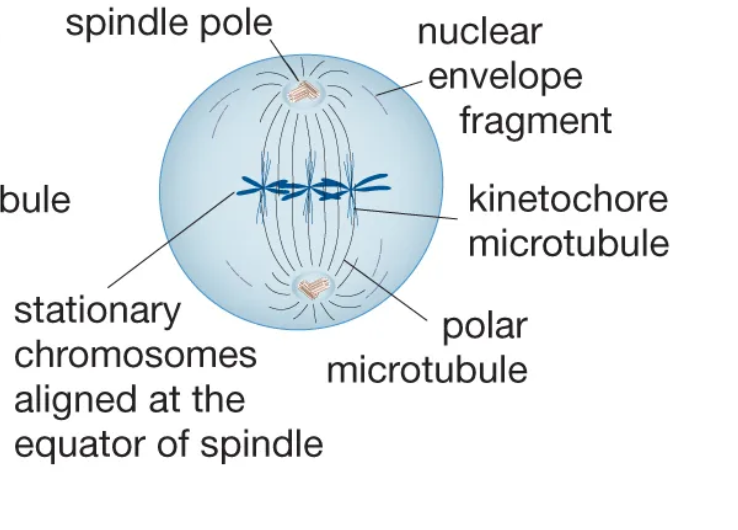
Anaphase
The stage of mitosis during which sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles.
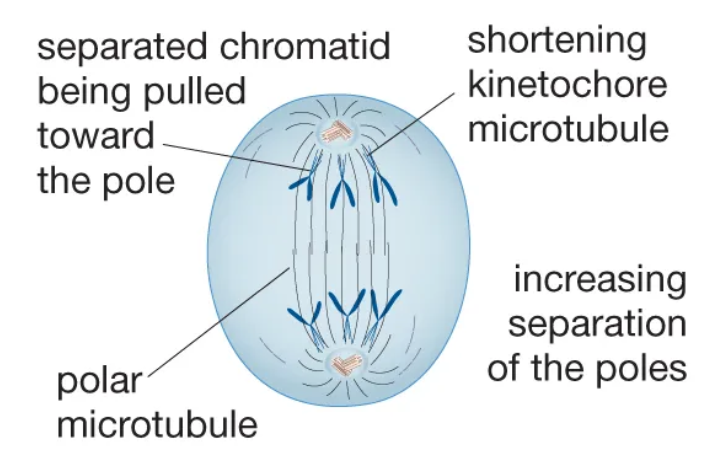
Telophase
The final stage of mitosis, during which two new nuclei form.
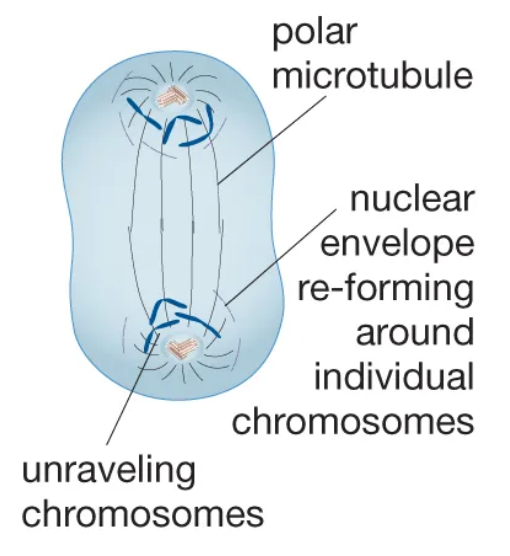
Cytokinesis
The division of the cytoplasm to form two separate daughter cells.
Law of Segregation
Each inherited trait is defined by a gene pair.
Law of Independent Assortment
Genes for different traits are sorted separately from one another so that the inheritance of one trait is not dependent on the inheritance of another.
Chi-Square Goodness of Fit Test
A statistical test used to determine how well a sample of data fits with a theoretical distribution.
P Value
The probability of obtaining test results at least as extreme as the results actually observed, assuming that the null hypothesis is correct.
Monohybrid Cross
A genetic cross between parents that differ in one trait.
Dihybrid Cross
A genetic cross between parents that differ in two traits.
Alleles
One of two or more versions of a gene.
Genotype
The genetic makeup of an organism.
Phenotype
A set of observable characteristics of an individual resulting from the interaction of its genotype with the environment.
Dominant
The allele that masks the presence of another allele for the same characteristic.
Recessive
An allele that causes a phenotype that is only visible in a homozygous genotype.
Linkage
Genes that are located close together on a chromosome will tend to be inherited together.
Sex-linked
A trait associated with a gene that is carried only by the male or female parent.
Nondisjunction
The failure of homologous chromosomes (meiosis I) or sister chromatids (meiosis II) to separate properly during cell division.
Trisomy
A genetic condition in which a person has three copies of a chromosome instead of the usual two.
Monosomy
The absence of one member of a pair of chromosomes.
Antibodies
A blood protein produced in response to and counteracting a specific antigen.
Vaccines
A substance used to stimulate the production of antibodies and provide immunity against one or several diseases.
COVID-19
A contagious disease caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2).
Primary Immune System
The body's first line of defense against pathogens.
Secondary Antibodies
Antibodies that bind to primary antibodies, amplifying the signal in a test.
Mitosis
Cell division that produces two identical daughter cells.
Meiosis
Cell division that produces four genetically different daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes.
P < 0.05
Statistically significant.
P > 0.05
Not statistically significant.
Progeria
A rare, progressive genetic disorder that causes children to age rapidly, starting in their first two years of life.
Polydactyly
A condition in which a person has more than five fingers per hand or toes per foot.
Albinism
A genetic condition that reduces the amount of melanin pigment formed in the skin, hair and/or eyes.
Achondroplasia
A form of human dwarfism caused by a single dominant allele; the homozygous condition is lethal